Table Of Contents
Release Notes for Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers and Lightweight Access Points for Release 7.3.112.0
Contents
Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Components
Controller Platforms Not Supported
What's New in This Release?
Hierarchical Mobility (New Mobility)
Configuring Hierarchical Mobility (GUI)
Configuring Hierarchical Mobility (CLI)
Compatibility Matrix
Compatibility Matrix with Mobility Network Elements
Compatibility Matrix with Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch
Compatibility Matrix without Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch
Software Release Support for Access Points
Upgrading to Controller Software Release 7.3.112.0
Guidelines and Limitations
Upgrading to Controller Software Release 7.3.112.0 (GUI)
Special Notes for Licensed Data Payload Encryption on
Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers
Downloading and Installing a DTLS License for an LDPE Controller
Upgrading from an LDPE to a Non-LDPE Controller
Interoperability With Other Clients in 7.3.112.0
Features Not Supported on Controller Platforms
Features Not Supported on Cisco 2500 Series Controllers
Features Not Supported on WiSM2 and Cisco 5500 Series Controllers
Features Not Supported on Cisco Flex 7500 Controllers
Features Not Supported on Cisco 8500 Controllers
Features Not Supported on Cisco Wireless Controller on Cisco Services-Ready Engine
Features Not Supported on Cisco Virtual Wireless LAN Controllers
Features Not Supported on Mesh Networks
Caveats
Open Caveats
Resolved Caveats
Installation Notes
Warnings
Safety Information
FCC Safety Compliance Statement
Safety Precautions
Installation Instructions
Service and Support
Information About Caveats
Troubleshooting
Related Documentation
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Release Notes for Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers and Lightweight Access Points for Release 7.3.112.0
First Published: January 2013
OL-26898-03
These release notes describe what is new in this release, instructions to upgrade to this release, and open and resolved caveats for this release.
Note  Unless otherwise noted, all of the Cisco Wireless LAN controllers are referred to as controllers, and all of the Cisco lightweight access points are referred to as access points.
Unless otherwise noted, all of the Cisco Wireless LAN controllers are referred to as controllers, and all of the Cisco lightweight access points are referred to as access points.
Contents
These release notes contain the following sections:
• Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Components
Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Components
• What's New in This Release?
What's New in This Release?
• Compatibility Matrix
Compatibility Matrix
• Software Release Support for Access Points
Software Release Support for Access Points
• Upgrading to Controller Software Release 7.3.112.0
Upgrading to Controller Software Release 7.3.112.0
• Special Notes for Licensed Data Payload Encryption on Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers
Special Notes for Licensed Data Payload Encryption on Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers
• Interoperability With Other Clients in 7.3.112.0
Interoperability With Other Clients in 7.3.112.0
• Features Not Supported on Controller Platforms
Features Not Supported on Controller Platforms
• Caveats
Caveats
• Installation Notes
Installation Notes
• Service and Support
Service and Support
• Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Components
The following components are part of the Cisco UWN Solution and are compatible in this release:
Note  For more information on the compatibility of wireless software components across releases, see the Cisco Wireless Solutions Software Compatibility Matrix.
For more information on the compatibility of wireless software components across releases, see the Cisco Wireless Solutions Software Compatibility Matrix.
Note  The 7.3.112.0 controller software release is not compatible with Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) 1.1.1.24. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 is required to support the controller features introduced in the 7.3.x controller software releases. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 is the subsequent version of Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) 1.1.1.24.
The 7.3.112.0 controller software release is not compatible with Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) 1.1.1.24. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 is required to support the controller features introduced in the 7.3.x controller software releases. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 is the subsequent version of Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) 1.1.1.24.
• Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) JA1.
Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) JA1.
• Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2.
Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2.
• Mobility Services Engine software release 7.3 and context-aware software
Mobility Services Engine software release 7.3 and context-aware software
Note  Client and tag licenses are required to get contextual (such as location) information within the context-aware software. For more information, see the Release Notes for Cisco 3350 Mobility Services Engine for Software Release 7.3.
Client and tag licenses are required to get contextual (such as location) information within the context-aware software. For more information, see the Release Notes for Cisco 3350 Mobility Services Engine for Software Release 7.3.
• Cisco 3350, 3310, 3355 Mobility Services Engine, Virtual Appliance
Cisco 3350, 3310, 3355 Mobility Services Engine, Virtual Appliance
• Cisco 2500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco 2500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
• Cisco 5500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco 5500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
• Cisco Flex 7500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco Flex 7500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
• Cisco 8500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco 8500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
• Cisco Virtual Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco Virtual Wireless LAN Controllers
• Cisco Wireless Controllers for high availability (HA controllers) for 5500 series, WiSM2, Flex 7500 series, and 8500 series controllers
Cisco Wireless Controllers for high availability (HA controllers) for 5500 series, WiSM2, Flex 7500 series, and 8500 series controllers
• Cisco Wireless Services Module 2 (WiSM2) for Catalyst 6500 Series switches
Cisco Wireless Services Module 2 (WiSM2) for Catalyst 6500 Series switches
• Cisco Wireless Controller on Cisco Services-Ready Engine (SRE) (WLCM2) running on ISM 300, SM 700, SM 710, SM 900, and SM 910
Cisco Wireless Controller on Cisco Services-Ready Engine (SRE) (WLCM2) running on ISM 300, SM 700, SM 710, SM 900, and SM 910
• Cisco Aironet 1550 (1552) Series outdoor 802.11n mesh access points; Cisco Aironet 1520 (1522, 1524) series outdoor mesh access points
Cisco Aironet 1550 (1552) Series outdoor 802.11n mesh access points; Cisco Aironet 1520 (1522, 1524) series outdoor mesh access points
• Cisco 1040, 1130, 1140, 1240, 1250, 1260, 2600, 3500, 3500p, 3600, Cisco 600 Series OfficeExtend Access Points, AP801, and AP802
Cisco 1040, 1130, 1140, 1240, 1250, 1260, 2600, 3500, 3500p, 3600, Cisco 600 Series OfficeExtend Access Points, AP801, and AP802
The AP801 and AP802 are integrated access points on the Cisco 800 Series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs). For more information about the stock-keeping units (SKUs) for the access points and the ISRs, see the following data sheets:
• AP860:
AP860:
– http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/data_sheet_c78_461543.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/data_sheet_c78_461543.html
• AP880:
AP880:
– http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/data_sheet_c78_459542_ps380_Products_Data_Sheet.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/data_sheet_c78_459542_ps380_Products_Data_Sheet.html
– http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/data_sheet_c78-613481.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/data_sheet_c78-613481.html
– http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/ps10082/data_sheet_c78_498096.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/ps10082/data_sheet_c78_498096.html
– http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/ps10082/data_sheet_c78-682548.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/ps10082/data_sheet_c78-682548.html
• AP890:
AP890:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/data_sheet_c78-519930.html
Note  The AP802 is an integrated access point on the Next Generation Cisco 880 Series ISRs.
The AP802 is an integrated access point on the Next Generation Cisco 880 Series ISRs.
Note  Before you use an AP802 series lightweight access point with controller software release 7.3.112.0, you must upgrade the software in the Next Generation Cisco 880 Series ISRs to Cisco IOS 151-4.M or later releases.
Before you use an AP802 series lightweight access point with controller software release 7.3.112.0, you must upgrade the software in the Next Generation Cisco 880 Series ISRs to Cisco IOS 151-4.M or later releases.
Controller Platforms Not Supported
The following controller platforms are not supported:
• Cisco 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controller
Cisco 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controller
• Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controller
Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controller
• Cisco Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller
Cisco Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller
• Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series/7600 Series Wireless Services Module (WiSM)
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series/7600 Series Wireless Services Module (WiSM)
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module (NM/NME)
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module (NM/NME)
What's New in This Release?
This section provides a brief description of what is new in this release. For more information about instructions on how to configure controller features, see the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide.
• Hierarchical Mobility (New Mobility)
Hierarchical Mobility (New Mobility)
Hierarchical Mobility (New Mobility)
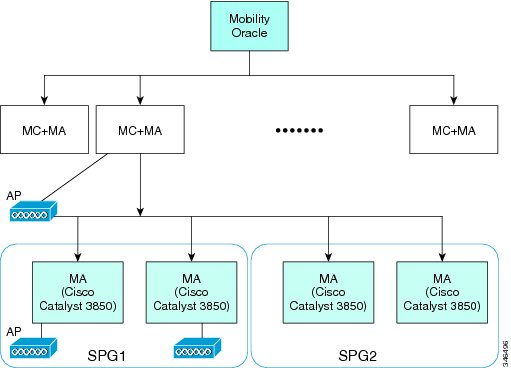
Hierarchical Mobility is referred to as New Mobility in the controller configuration. The release enables the controller to be compatible with Converged Access controllers with Wireless Control Module (WCM) like Cisco Catalyst 3850 switch and Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller.
The Cisco 5500 Series Wireless LAN Controller, Cisco WiSM2, or the Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller functions as a Mobility Controller (MC) with the Cisco Catalyst 3850 switch. The MC is part of a hierarchical architecture that consists of a Mobility Agent (MA), and a Mobility Oracle (MO).
A group of 3850 catalyst switch MAs can form a switch peer group (SPG). The internal MA of 5500, WISM2, and 5760 controllers form an independent SPG. The MC, MA, and MO can be in a single 5500, WISM2, or 5760 controller. Each MC forms a subdomain that can have multiple SPGs. Cisco 5500 Series Wireless LAN Controller, Cisco WiSM2, or the Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller are MA/MC, by default. However, Cisco Catalyst 3850 switch can function both as MA/MC or MA only. The keepalives between MC and MO are not DTLS encrypted. Figure 1 shows the architecture of hierarchical mobility (also known as New Mobility). For more information, see Compatibility Matrix with Mobility Network Elements. By default, hierarchical mobility is disabled. For seamless mobility, the controller should either use hierarchical mobility or old mobility (flat mobility). Interoperability between the two types of mobility is not supported. High availability for Mobility Oracle is not supported in this release.

Note  Hierarchical Mobility is supported only on Cisco 5500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers and Cisco WiSM2.
Hierarchical Mobility is supported only on Cisco 5500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers and Cisco WiSM2.
Figure 1 Architecture of Hierarchical Mobility
This section describes how to configure hierarchical mobility through either the GUI or the CLI:
• Configuring Hierarchical Mobility (GUI)
Configuring Hierarchical Mobility (GUI)
• Configuring Hierarchical Mobility (CLI)
Configuring Hierarchical Mobility (CLI)
Configuring Hierarchical Mobility (GUI)
Step 1  Choose CONTROLLER > Mobility Management > Mobility Configuration to enable and configure hierarchical mobility on the controller.
Choose CONTROLLER > Mobility Management > Mobility Configuration to enable and configure hierarchical mobility on the controller.
Step 2  Configure the following fields for hierarchical mobility:
Configure the following fields for hierarchical mobility:
Table 1 Mobility Configuration Parameters
Parameter
|
Description
|
General
|
Enable New Mobility
|
Check box that you can select to enable or disable hierarchical mobility.
Note  When you enable hierarchical mobility, you must save the config and reboot the controller. When you enable hierarchical mobility, you must save the config and reboot the controller.
|
Mobility Parameters
|
Mobility Oracle
|
Check box that you can select to enable the controller as a Mobility Oracle. The Mobility Oracle is optional, it maintains the client database under one complete mobility domain.
|
Multicast Mode
|
Check box that you can select to enable or disable multicast mode in a mobility group.
|
Multicast IP Address
|
Multicast IP address of the switch peer group.
|
Mobility Oracle IP Address
|
IP address of the Mobility Oracle. You cannot enter the value if you have checked the Mobility Oracle check box.
|
Mobility Controller Public IP Address
|
IP address of the controller, if there is no NAT. If the controller has NAT configured, the public IP address will be the NATed IP address.
|
Mobility Keep Alive Count
|
Number of times a ping request is sent to an peer controller before the peer is considered to be unreachable. The valid range is 3 to 20, and the default value is 3.
|
Mobility Keep Alive Interval
|
Amount of time (in seconds) between each ping request sent to an peer controller. The valid range is 1 to 30 seconds, and the default value is 10 seconds.
|
Mobility DSCP Value
|
DSCP value that you can set for the mobility controller. The valid range is 0 to 63, and the default value is 0.
|
Step 3  Click Apply.
Click Apply.
Step 4  Choose CONTROLLER > Mobility Management > Switch Peer Group to add or remove members to the switch peer group.
Choose CONTROLLER > Mobility Management > Switch Peer Group to add or remove members to the switch peer group.
This page lists all the switch peer groups and their details like bridge domain ID, multicast IP address, and status of the multicast mode. Click the name of the switch peer group to navigate to the Edit page and update the parameters, if required.
Step 5  Choose CONTROLLER > Mobility Management > Mobility Controller to view all the mobility controllers and their details like IP address, MAC address, client count, and link status.
Choose CONTROLLER > Mobility Management > Mobility Controller to view all the mobility controllers and their details like IP address, MAC address, client count, and link status.
Step 6  Choose CONTROLLER > Mobility Management > Mobility Clients to view all the mobility clients and their parameters.
Choose CONTROLLER > Mobility Management > Mobility Clients to view all the mobility clients and their parameters.
Table 2 Mobility Client Parameters
Parameter
|
Description
|
Client MAC Address
|
MAC address of the mobility client.
|
Client IP Address
|
IP address of the mobility client.
|
Anchor MC IP Address
|
IP address of the anchor Mobility Controller.
|
Anchor MC Public IP Address
|
Public IP address of the anchor Mobility Controller.
|
Foreign MC IP Address
|
IP address of the foreign Mobility Controller.
|
Foreign MC Public IP Address
|
Public IP address of the foreign Mobility Controller.
|
Client Association Time
|
Time when the mobility client associated with the Mobility Controller.
|
Client Entry Update Timestamp
|
Timestamp when the client entry is updated.
|
Configuring Hierarchical Mobility (CLI)
Step 1  Enable or disable hierarchical mobility on the controller by entering this command:
Enable or disable hierarchical mobility on the controller by entering this command:
config mobility new-architecture {enable | disable}
When you enable or disable hierarchical mobility, you must save the config and reboot the controller.
Step 2  Enable the Mobility Oracle (MO), or configure an external MO by entering this command:
Enable the Mobility Oracle (MO), or configure an external MO by entering this command:
config mobility oracle {enable | disable | ip ip_address}
ip_address is the IP address of the Mobility Oracle. The Mobility Oracle maintains the client database under one complete mobility domain. It consists of a station database, an interface to the Mobility Controller, and an NTP server. There can be only one MO in the entire mobility domain.
Step 3  Create, or delete switch peer groups (SPG) by entering this command:
Create, or delete switch peer groups (SPG) by entering this command:
config mobility switchPeerGroup {create | delete} peer-group-name
peer-group-name s the name of the switch peer group.
Step 4  Configure the MAC address of the member switch for compatibility between the flat and hierarchical (old and new) mobility by entering this command:
Configure the MAC address of the member switch for compatibility between the flat and hierarchical (old and new) mobility by entering this command:
config mobility group member add ip_address {[group-name] | mac-address | [public-ip-address]}
ip_address is the IP address of the member.
group-name is the member switch group name, if it is different from the default group name.
mac-address is the MAC address of the member switch.
Step 5  Add, remove members, configure bridge domain ID, and multicast address of the switch peer group by entering this command:
Add, remove members, configure bridge domain ID, and multicast address of the switch peer group by entering this command:
config mobility switchPeerGroup {bridge-domain-id peer-group-name bridge_domain_id | member {add | delete} ip_address peer-group-name [public_ip_address] | multicast-address peer-group-name multicast_IP_address}
peer-group-name is the name of the SPG. bridge_domain_id is the bridge domain ID of the SPG.
ip_address is the IP address of switch peer group member.
public_ip_address is the public IP address of the switch peer group member.
Step 6  View the details of the mobility controllers according to the Mobility Oracle by entering this command:
View the details of the mobility controllers according to the Mobility Oracle by entering this command:
show mobility oracle summary
Step 7  View the summary and details of the Mobility Oracle client database by entering this command:
View the summary and details of the Mobility Oracle client database by entering this command:
show mobility oracle client {summary | detail}
Step 8  Verify the mobility statistics by entering this command:
Verify the mobility statistics by entering this command:
show mobility statistics
Step 9  Verify the mobility configuration by entering this command:
Verify the mobility configuration by entering this command:
show mobility summary
Step 10  Save your changes by entering this command:
Save your changes by entering this command:
save config
Step 11  Enable or disable debugging of mobility packets by entering this command:
Enable or disable debugging of mobility packets by entering this command:
debug mobility packet {enable | disable}
Step 12  Enable or disable debugging of the Mobility Oracle events and errors by entering this command:
Enable or disable debugging of the Mobility Oracle events and errors by entering this command:
debug mobility oracle {events | errors} {enable | disable}
Compatibility Matrix
This section consists of the following compatibility matrix:
• Compatibility Matrix with Mobility Network Elements
Compatibility Matrix with Mobility Network Elements
• Compatibility Matrix with Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch
Compatibility Matrix with Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch
• Compatibility Matrix without Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch
Compatibility Matrix without Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch
Compatibility Matrix with Mobility Network Elements
Table 3 lists the compatibility matrix with Mobility Network Elements: Mobility Controller (MC), Mobility Agent (MA), and Mobility Oracle (MO).
Table 3 Compatibility Matrix with Mobility Network Elements
Controller/Switch
|
Mobility Network Elements
|
Limitation/Comment
|
| |
MC
|
MA
|
MO
|
|
Cisco 5500 Series Wireless LAN Controller
|
Yes
|
Yes (internal)
|
Yes
|
• By default, the controller is MA/MC. By default, the controller is MA/MC.
• MO + MC + MA can be in a single controller. MO + MC + MA can be in a single controller.
• 5760, WiSM2, and 5500 controllers are the only platforms that support MO. 5760, WiSM2, and 5500 controllers are the only platforms that support MO.
• Can have only one MO. Can have only one MO.
|
Cisco WiSM2 Controller
|
Yes
|
Yes (internal)
|
Yes
|
Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller
|
Yes
|
Yes (internal)
|
Yes
|
Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch
|
Yes
|
Yes1 (external)
|
No
|
• Can function both as MA/MC and MA only. Can function both as MA/MC and MA only.
• 5760, WiSM2, and 5500 controllers are the only platforms that support MO. 5760, WiSM2, and 5500 controllers are the only platforms that support MO.
• Can have only one MO. Can have only one MO.
|
Compatibility Matrix with Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch
For a seamless mobility between Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller or Cisco Catalyst 3850 switch, and Cisco 5508 Wireless LAN and WiSM2 controllers, following are the prerequisites:
• Upgrade 5508 and WiSM2 to 7.3.112.0.
Upgrade 5508 and WiSM2 to 7.3.112.0.
• Enable hierarchical mobility on 5508 and WiSM2. When you enable hierarchical mobility, the controller reboots.
Enable hierarchical mobility on 5508 and WiSM2. When you enable hierarchical mobility, the controller reboots.
Table 4 lists the software compatibility matrix with Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850 switch.
Table 4 Compatibility Matrix with Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850
5508 or WiSM2
|
5760 and 3850
|
PI
|
MSE
|
7.3.112.0
|
3.2.0SE
|
1.3.0.201
|
7.4.100.0
|
Compatibility Matrix without Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch
Table 5 lists the software compatibility matrix without Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850 switch.
Table 5 Compatibility Matrix without Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850
5508 or WiSM2
|
PI
|
MSE
|
7.3.112.0
|
PI 1.2
|
7.3
|
Software Release Support for Access Points
Table 6 lists the controller software releases that support specific Cisco access points. The First Support column lists the earliest controller software release that supports the access point. For access points that are not supported in ongoing releases, the Last Support column lists the last release that supports the access point.
Table 6 Software Support for Access Points
Access Points
|
First Support
|
Last Support
|
1000 Series
|
AIR-AP1010
|
3.0.100.0
|
4.2.209.0
|
| |
AIR-AP1020
|
3.0.100.0
|
4.2.209.0
|
AIR-AP1030
|
3.0.100.0
|
4.2.209.0
|
Airespace AS1200
|
—
|
4.0
|
AIR-LAP1041N
|
7.0.98.0
|
—
|
AIR-LAP1042N
|
7.0.98.0
|
—
|
1100 Series
|
AIR-LAP1121
|
4.0.155.0
|
7.0.x
|
1130 Series
|
AIR-LAP1131
|
3.1.59.24
|
—
|
1140 Series
|
AIR-LAP1141N
|
5.2.157.0
|
—
|
AIR-LAP1142N
|
5.2.157.0
|
—
|
1220 Series
|
AIR-AP1220A
|
3.1.59.24
|
7.0.x
|
AIR-AP1220B
|
3.1.59.24
|
7.0.x
|
1230 Series
|
AIR-AP1230A
|
3.1.59.24
|
7.0.x
|
AIR-AP1230B
|
3.1.59.24
|
7.0.x
|
AIR-LAP1231G
|
3.1.59.24
|
7.0.x
|
AIR-LAP1232AG
|
3.1.59.24
|
7.0.x
|
1240 Series
|
AIR-LAP1242G
|
3.1.59.24
|
—
|
AIR-LAP1242AG
|
3.1.59.24
|
—
|
1250 Series
|
AIR-LAP1250
|
4.2.61.0
|
—
|
AIR-LAP1252G
|
4.2.61.0
|
—
|
AIR-LAP1252AG
|
4.2.61.0
|
—
|
1260 Series
|
AIR-LAP1261N
|
7.0.116.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-LAP1262N
|
7.0.98.0
|
—
|
1300 Series
|
AIR-BR1310G
|
4.0.155.0
|
7.0.x
|
1400 Series
|
Standalone Only
|
—
|
—
|
AP801
|
|
5.1.151.0
|
|
AP802
|
|
7.0.98.0
|
|
AP802H
|
|
7.3.101.0
|
|
2600 Series
|
AIR-CAP2602I-x-K9
|
7.2.110.0
|
|
AIR-CAP2602I-xK910
|
7.2.110.0
|
|
AIR-SAP2602I-x-K9
|
7.2.110.0
|
|
AIR-SAP2602I-x-K95
|
7.2.110.0
|
|
AIR-CAP2602E-x-K9
|
7.2.110.0
|
|
AIR-CAP2602E-xK910
|
7.2.110.0
|
|
AIR-SAP2602E-x-K9
|
7.2.110.0
|
|
AIR-SAP2602E-x-K95
|
7.2.110.0
|
|
3500 Series
|
AIR-CAP3501E
|
7.0.98.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP3501I
|
7.0.98.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP3502E
|
7.0.98.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP3502I
|
7.0.98.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP3502P
|
7.0.116.0
|
—
|
3600 Series
|
AIR-CAP3602I-x-K9
|
7.1.91.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP3602I-xK910
|
7.1.91.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP3602E-x-K9
|
7.1.91.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP3602E-xK910
|
7.1.91.0
|
—
|
600 Series
|
AIR-OEAP602I
|
7.0.116.0
|
|
Note  The Cisco 3600 Access Point was introduced in 7.1.91.0. If your network deployment uses Cisco 3600 Access Points with release 7.1.91.0, we highly recommend that you upgrade to 7.2.103.0 or a later release. The Cisco 3600 Access Point was introduced in 7.1.91.0. If your network deployment uses Cisco 3600 Access Points with release 7.1.91.0, we highly recommend that you upgrade to 7.2.103.0 or a later release.
|
1500 Mesh Series
|
AIR-LAP-1505
|
3.1.59.24
|
4.2.207.54M
|
AIR-LAP-1510
|
3.1.59.24
|
4.2.207.54M
|
1520 Mesh Series
|
AIR-LAP1522AG
|
-A and N: 4.1.190.1 or 5.2 or later1
|
—
|
All other reg. domains: 4.1.191.24M or 5.2 or later1
|
—
|
AIR-LAP1522HZ
|
-A and N: 4.1.190.1 or 5.2 or later1
|
—
|
All other reg. domains: 4.1.191.24M or 5.2 or later1
|
—
|
AIR-LAP1522PC
|
-A and N: 4.1.190.1 or 5.2 or later1
|
—
|
All other reg. domains: 4.1.191.24M or 5.2 or later1
|
—
|
AIR-LAP1522CM
|
7.0.116.0 or later.
|
—
|
AIR-LAP1524SB
|
-A, C and N: 6.0 or later
|
—
|
All other reg. domains: 7.0.116.0 or later.
|
—
|
AIR-LAP1524PS
|
-A: 4.1.192.22M or 5.2 or later1
|
—
|
1550
|
AIR-CAP1552I-x-K9
|
7.0.116.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP1552E-x-K9
|
7.0.116.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP1552C-x-K9
|
7.0.116.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP1552H-x-K9
|
7.0.116.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP1552CU-x-K9
|
7.3.101.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP1552EU-x-K9
|
7.3.101.0
|
—
|
1552S
|
AIR-CAP1552SA-x-K9
|
7.0.220.0
|
—
|
| |
AIR-CAP1552SD-x-K9
|
7.0.220.0
|
—
|
Upgrading to Controller Software Release 7.3.112.0
Guidelines and Limitations
• The 7.3.112.0 controller software release is not compatible with Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) 1.1.1.24. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 is required to support the controller features introduced in the 7.3.x controller software release. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 is the subsequent version of Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) 1.1.1.24.
The 7.3.112.0 controller software release is not compatible with Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) 1.1.1.24. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 is required to support the controller features introduced in the 7.3.x controller software release. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 is the subsequent version of Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) 1.1.1.24.
• If you require a downgrade from one release to another, you might lose the configuration from your current release. The workaround is to reload the previous controller configuration files saved on the backup server or to reconfigure the controller.
If you require a downgrade from one release to another, you might lose the configuration from your current release. The workaround is to reload the previous controller configuration files saved on the backup server or to reconfigure the controller.
• It is not possible to directly upgrade to the 7.3.112.0 release from a release that is older than 7.0.98.0.
It is not possible to directly upgrade to the 7.3.112.0 release from a release that is older than 7.0.98.0.
• You can upgrade or downgrade the controller software only between certain releases. In some instances, you must first install an intermediate release prior to upgrading to software release 7.3.112.0. Table 7 shows the upgrade path that you must follow before downloading software release 7.3.112.0.
You can upgrade or downgrade the controller software only between certain releases. In some instances, you must first install an intermediate release prior to upgrading to software release 7.3.112.0. Table 7 shows the upgrade path that you must follow before downloading software release 7.3.112.0.
Table 7 Upgrade Path to Controller Software Release 7.3.112.0
Current Software Release
|
Upgrade Path to 7.3.112.0 Software
|
5.2 to 6.0.196.0
|
• Upgrade to 7.0.98.0. Upgrade to 7.0.98.0.
• From 7.0.98.0 you can upgrade directly to 7.3.112.0. From 7.0.98.0 you can upgrade directly to 7.3.112.0.
|
7.0.98.0 or later 7.0 releases
|
You can upgrade directly to 7.3.112.0
|
7.1.91.0
|
You can upgrade directly to 7.3.112.0
|
7.2. or later 7.2 releases
|
You can upgrade directly to 7.3.112.0
|
7.3.101.0
|
You can upgrade directly to 7.3.112.0
|
• When you downgrade the controller from 7.3.112.0 to a software release that does not support hierarchical mobility (new mobility) like 7.3.101.0, 7.2, 7.0, or earlier releases (all releases prior to 7.3.112.0), the controller automatically transits to flat mobility (old mobility). This is due to the difference in mobility architecture and noninteroperability between flat mobility (EOIP tunnels) and hierarchical mobility(CAPWAP tunnels).
When you downgrade the controller from 7.3.112.0 to a software release that does not support hierarchical mobility (new mobility) like 7.3.101.0, 7.2, 7.0, or earlier releases (all releases prior to 7.3.112.0), the controller automatically transits to flat mobility (old mobility). This is due to the difference in mobility architecture and noninteroperability between flat mobility (EOIP tunnels) and hierarchical mobility(CAPWAP tunnels).
• When you upgrade the controller to an intermediate software release, you must wait until all of the access points that are associated with the controller are upgraded to the intermediate release before you install the latest controller software. In large networks, it can take some time to download the software on each access point.
When you upgrade the controller to an intermediate software release, you must wait until all of the access points that are associated with the controller are upgraded to the intermediate release before you install the latest controller software. In large networks, it can take some time to download the software on each access point.
• If you upgrade to the controller software release 7.3.112.0 from an earlier release, you must also upgrade to Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 and MSE 7.3.
If you upgrade to the controller software release 7.3.112.0 from an earlier release, you must also upgrade to Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 and MSE 7.3.
• You can upgrade to a new release of the controller software or downgrade to an older release even if Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) is enabled.
You can upgrade to a new release of the controller software or downgrade to an older release even if Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) is enabled.
• When you upgrade to the latest software release, the software on the access points associated with the controller is also automatically upgraded. When an access point is loading software, each of its LEDs blinks in succession.
When you upgrade to the latest software release, the software on the access points associated with the controller is also automatically upgraded. When an access point is loading software, each of its LEDs blinks in succession.
• We recommend that you access the controller GUI using any of the following browsers:
We recommend that you access the controller GUI using any of the following browsers:
– Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 SP1 (or a later release)
Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 SP1 (or a later release)
– Mozilla Firefox 2.0.0.11 (or a later release)
Mozilla Firefox 2.0.0.11 (or a later release)
– Safari 5.1.5 (or a later release)
Safari 5.1.5 (or a later release)
– Chrome 24.0.1312.52 m (or a later release)
Chrome 24.0.1312.52 m (or a later release)
– Android 4.0.4 (or a later release) built-in browser
Android 4.0.4 (or a later release) built-in browser
• Cisco controllers support standard SNMP Management Information Base (MIB) files. MIBs can be downloaded from the Software Center on Cisco.com.
Cisco controllers support standard SNMP Management Information Base (MIB) files. MIBs can be downloaded from the Software Center on Cisco.com.
• The controller software is factory installed on your controller and automatically downloaded to the access points after a release upgrade and whenever an access point joins a controller. We recommend that you install the latest software version available for maximum operational benefit.
The controller software is factory installed on your controller and automatically downloaded to the access points after a release upgrade and whenever an access point joins a controller. We recommend that you install the latest software version available for maximum operational benefit.
• We recommend that you install Wireless LAN Controller Field Upgrade Software (FUS) for Release 1.7.0.0-FUS first, which is a special AES package that contains several system-related component upgrades. These include the bootloader, field recovery image, and FPGA/MCU firmware. Installing the FUS image requires special attention because it installs some critical firmware. The FUS image is independent of the runtime image. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/wireless/controller/release/notes/fus_rn_1_7_0_0.html. Upgrade the controller image after you upgrade the FUS, as the controller reboots during the upgrade.
We recommend that you install Wireless LAN Controller Field Upgrade Software (FUS) for Release 1.7.0.0-FUS first, which is a special AES package that contains several system-related component upgrades. These include the bootloader, field recovery image, and FPGA/MCU firmware. Installing the FUS image requires special attention because it installs some critical firmware. The FUS image is independent of the runtime image. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/wireless/controller/release/notes/fus_rn_1_7_0_0.html. Upgrade the controller image after you upgrade the FUS, as the controller reboots during the upgrade.
• Ensure that you have a TFTP or FTP server available for the software upgrade. Follow these guidelines when setting up a TFTP or FTP server:
Ensure that you have a TFTP or FTP server available for the software upgrade. Follow these guidelines when setting up a TFTP or FTP server:
– Ensure that your TFTP server supports files that are larger than the size of the controller software release 7.3.112.0. Some TFTP servers that support files of this size are tftpd32 and the TFTP server within the Prime Infrastructure. If you attempt to download the 7.3.112.0 controller software and your TFTP server does not support files of this size, the following error message appears: "TFTP failure while storing in flash."
Ensure that your TFTP server supports files that are larger than the size of the controller software release 7.3.112.0. Some TFTP servers that support files of this size are tftpd32 and the TFTP server within the Prime Infrastructure. If you attempt to download the 7.3.112.0 controller software and your TFTP server does not support files of this size, the following error message appears: "TFTP failure while storing in flash."
For large files, you can use a tftpd32 server. For more information, see http://tftpd32.jounin.net/tftpd32_download.html
– If you are upgrading through the distribution system network port, the TFTP or FTP server can be on the same or a different subnet because the distribution system port is routable.
If you are upgrading through the distribution system network port, the TFTP or FTP server can be on the same or a different subnet because the distribution system port is routable.
• When you plug a controller into an AC power source, the bootup script and power-on self-test run to initialize the system. During this time, you can press Esc to display the bootloader Boot Options Menu. The menu options for the 5500 differ from the menu options for the other controller platforms.
When you plug a controller into an AC power source, the bootup script and power-on self-test run to initialize the system. During this time, you can press Esc to display the bootloader Boot Options Menu. The menu options for the 5500 differ from the menu options for the other controller platforms.
Bootloader Menu for 5500 Series Controllers:
Please choose an option from below:
3. Change active boot image
6. Manually update images
Please enter your choice:
Bootloader Menu for Other Controller Platforms:
Please choose an option from below:
3. Manually update images
4. Change active boot image
Please enter your choice:
Enter 1 to run the current software, enter 2 to run the previous software, enter 4 (on a 5500 series controller), or enter 5 (on another controller platform) to run the current software and set the controller configuration to factory defaults. Do not choose the other options unless directed to do so.
Note  See the Installation Guide or the Quick Start Guide for your controller for more details on running the bootup script and power-on self-test.
See the Installation Guide or the Quick Start Guide for your controller for more details on running the bootup script and power-on self-test.
• The controller bootloader stores a copy of the active primary image and the backup image. If the primary image becomes corrupted, you can use the bootloader to boot with the backup image.
The controller bootloader stores a copy of the active primary image and the backup image. If the primary image becomes corrupted, you can use the bootloader to boot with the backup image.
With the backup image stored before rebooting, be sure to choose Option 2: Run Backup Image from the boot menu to boot from the backup image. Then, upgrade with a known working image and reboot the controller.
• Control which address(es) are sent in CAPWAP discovery responses when NAT is enabled on the Management Interface using the following command:
Control which address(es) are sent in CAPWAP discovery responses when NAT is enabled on the Management Interface using the following command:
config network ap-discovery nat-ip-only {enable | disable}
where:
– enable— Enables use of NAT IP only in a discovery response. This is the default. Use this command if all APs are outside of the NAT gateway.
enable— Enables use of NAT IP only in a discovery response. This is the default. Use this command if all APs are outside of the NAT gateway.
– disable—Enables use of both NAT IP and non-NAT IP in a discovery response. Use this command if APs are on the inside and outside of the NAT gateway; for example, Local Mode and OfficeExtend APs are on the same controller.
disable—Enables use of both NAT IP and non-NAT IP in a discovery response. Use this command if APs are on the inside and outside of the NAT gateway; for example, Local Mode and OfficeExtend APs are on the same controller.
Note  To avoid stranding APs, you must disable AP link latency (if enabled) before you use the disable option for the config network ap-discovery nat-ip-only command. To disable AP link latency, use the config ap link-latency disable all command.
To avoid stranding APs, you must disable AP link latency (if enabled) before you use the disable option for the config network ap-discovery nat-ip-only command. To disable AP link latency, use the config ap link-latency disable all command.
• You can configure 802.1p tagging by using the config qos dot1p-tag {bronze | silver | gold | platinum} tag. For the 7.2.103.0 and later releases, if you tag 802.1p packets, the tagging has impact only on wired packets. Wireless packets are impacted only by the maximum priority level set for QoS.
You can configure 802.1p tagging by using the config qos dot1p-tag {bronze | silver | gold | platinum} tag. For the 7.2.103.0 and later releases, if you tag 802.1p packets, the tagging has impact only on wired packets. Wireless packets are impacted only by the maximum priority level set for QoS.
• You can reduce the network downtime using the following options:
You can reduce the network downtime using the following options:
– You can predownload the AP image.
You can predownload the AP image.
– For FlexConnect access points, use the FlexConnect AP upgrade feature to reduce traffic between the controller and the AP (main site and the branch). For more information about the FlexConnect AP upgrade feature, see the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide.
For FlexConnect access points, use the FlexConnect AP upgrade feature to reduce traffic between the controller and the AP (main site and the branch). For more information about the FlexConnect AP upgrade feature, see the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide.
Note  Predownloading a 7.3.112.0 version on a Cisco Aironet 1240 access point is not supported when upgrading from a previous controller release. If predownloading is attempted to a Cisco Aironet 1240 access point, an AP disconnect will occur momentarily.
Predownloading a 7.3.112.0 version on a Cisco Aironet 1240 access point is not supported when upgrading from a previous controller release. If predownloading is attempted to a Cisco Aironet 1240 access point, an AP disconnect will occur momentarily.
• Do not power down the controller or any access point during the upgrade process; otherwise, you might corrupt the software image. Upgrading a controller with a large number of access points can take as long as 30 minutes, depending on the size of your network. However, with the increased number of concurrent access point upgrades supported, the upgrade time should be significantly reduced. The access points must remain powered, and the controller must not be reset during this time.
Do not power down the controller or any access point during the upgrade process; otherwise, you might corrupt the software image. Upgrading a controller with a large number of access points can take as long as 30 minutes, depending on the size of your network. However, with the increased number of concurrent access point upgrades supported, the upgrade time should be significantly reduced. The access points must remain powered, and the controller must not be reset during this time.
• If you want to downgrade from the 7.3.112.0 release to a 6.0 or an older release, do either of the following:
If you want to downgrade from the 7.3.112.0 release to a 6.0 or an older release, do either of the following:
– Delete all WLANs that are mapped to interface groups and create new ones.
Delete all WLANs that are mapped to interface groups and create new ones.
– Ensure that all WLANs are mapped to interfaces rather than interface groups.
Ensure that all WLANs are mapped to interfaces rather than interface groups.
• After you perform these functions on the controller, you must reboot the controller for the changes to take effect:
After you perform these functions on the controller, you must reboot the controller for the changes to take effect:
– Enable or disable link aggregation (LAG)
Enable or disable link aggregation (LAG)
– Enable a feature that is dependent on certificates (such as HTTPS and web authentication)
Enable a feature that is dependent on certificates (such as HTTPS and web authentication)
– Add a new license or modify an existing license
Add a new license or modify an existing license
– Increase the priority for a license
Increase the priority for a license
– Enable the HA
Enable the HA
– Install SSL certificate
Install SSL certificate
– Configure the database size
Configure the database size
– Install vendor device certificate
Install vendor device certificate
– Download CA certificate
Download CA certificate
– Upload configuration file
Upload configuration file
– Install Web Authentication certificate
Install Web Authentication certificate
– Changes to management or virtual interface
Changes to management or virtual interface
– TCP MSS
TCP MSS
• Ensure that you apply the calibration fix for AP1260 and AP3500 models (see the resolved caveat CSCty68030). This addresses a manufacturing calibration issue on the AP1260 and AP3500 models (VID V01). For more information, see https://supportforums.cisco.com/docs/DOC-25460.
Ensure that you apply the calibration fix for AP1260 and AP3500 models (see the resolved caveat CSCty68030). This addresses a manufacturing calibration issue on the AP1260 and AP3500 models (VID V01). For more information, see https://supportforums.cisco.com/docs/DOC-25460.
Upgrading to Controller Software Release 7.3.112.0 (GUI)
Step 1  Upload your controller configuration files to a server to back them up.
Upload your controller configuration files to a server to back them up.
Note  We highly recommend that you back up your controller's configuration files prior to upgrading the controller software.
We highly recommend that you back up your controller's configuration files prior to upgrading the controller software.
Step 2  Follow these steps to obtain the 7.3.112.0 controller software:
Follow these steps to obtain the 7.3.112.0 controller software:
a.  Click this URL to go to the Software Center:
Click this URL to go to the Software Center:
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/software/navigator.html
b.  Choose Wireless from the center selection window.
Choose Wireless from the center selection window.
c.  Click Wireless LAN Controllers.
Click Wireless LAN Controllers.
The following options are available:
– Integrated Controllers and Controller Modules
Integrated Controllers and Controller Modules
– Standalone Controllers
Standalone Controllers
d.  Depending on your controller platform, click one of the above options.
Depending on your controller platform, click one of the above options.
e.  Click the controller model number or name. The Download Software page is displayed.
Click the controller model number or name. The Download Software page is displayed.
f.  Click a controller software release. The software releases are labeled as follows to help you determine which release to download:
Click a controller software release. The software releases are labeled as follows to help you determine which release to download:
• Early Deployment (ED)—These software releases provide new features and new hardware platform support as well as bug fixes.
Early Deployment (ED)—These software releases provide new features and new hardware platform support as well as bug fixes.
• Maintenance Deployment (MD)—These software releases provide bug fixes and ongoing software maintenance.
Maintenance Deployment (MD)—These software releases provide bug fixes and ongoing software maintenance.
• Deferred (DF)—These software releases have been deferred. We recommend that you migrate to an upgraded release.
Deferred (DF)—These software releases have been deferred. We recommend that you migrate to an upgraded release.
g.  Click a software release number.
Click a software release number.
h.  Click the filename (filename.aes).
Click the filename (filename.aes).
i.  Click Download.
Click Download.
j.  Read Cisco's End User Software License Agreement and then click Agree.
Read Cisco's End User Software License Agreement and then click Agree.
k.  Save the file to your hard drive.
Save the file to your hard drive.
l.  Repeat steps a. through k. to download the remaining file.
Repeat steps a. through k. to download the remaining file.
Step 3  Copy the controller software file (filename.aes) to the default directory on your TFTP or FTP server.
Copy the controller software file (filename.aes) to the default directory on your TFTP or FTP server.
Step 4  (Optional) Disable the controller 802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n networks.
(Optional) Disable the controller 802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n networks.
Note  For busy networks, controllers on high utilization, or small controller platforms, we recommend that you disable the 802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n networks as a precautionary measure.
For busy networks, controllers on high utilization, or small controller platforms, we recommend that you disable the 802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n networks as a precautionary measure.
Step 5  Disable any WLANs on the controller.
Disable any WLANs on the controller.
Step 6  Choose Commands > Download File to open the Download File to Controller page.
Choose Commands > Download File to open the Download File to Controller page.
Step 7  From the File Type drop-down list, choose Code.
From the File Type drop-down list, choose Code.
Step 8  From the Transfer Mode drop-down list, choose TFTP or FTP.
From the Transfer Mode drop-down list, choose TFTP or FTP.
Step 9  In the IP Address text box, enter the IP address of the TFTP or FTP server.
In the IP Address text box, enter the IP address of the TFTP or FTP server.
Step 10  If you are using a TFTP server, the default values of 10 retries for the Maximum Retries text field, and 6 seconds for the Timeout text field should work correctly without any adjustment. However, you can change these values if desired. To do so, enter the maximum number of times that the TFTP server attempts to download the software in the Maximum Retries text box and the amount of time (in seconds) that the TFTP server attempts to download the software in the Timeout text box.
If you are using a TFTP server, the default values of 10 retries for the Maximum Retries text field, and 6 seconds for the Timeout text field should work correctly without any adjustment. However, you can change these values if desired. To do so, enter the maximum number of times that the TFTP server attempts to download the software in the Maximum Retries text box and the amount of time (in seconds) that the TFTP server attempts to download the software in the Timeout text box.
Step 11  In the File Path text box, enter the directory path of the software.
In the File Path text box, enter the directory path of the software.
Step 12  In the File Name text box, enter the name of the software file (filename.aes).
In the File Name text box, enter the name of the software file (filename.aes).
Step 13  If you are using an FTP server, follow these steps:
If you are using an FTP server, follow these steps:
a.  In the Server Login Username text box, enter the username to log on to the FTP server.
In the Server Login Username text box, enter the username to log on to the FTP server.
b.  In the Server Login Password text box, enter the password to log on to the FTP server.
In the Server Login Password text box, enter the password to log on to the FTP server.
c.  In the Server Port Number text box, enter the port number on the FTP server through which the download occurs. The default value is 21.
In the Server Port Number text box, enter the port number on the FTP server through which the download occurs. The default value is 21.
Step 14  Click Download to download the software to the controller. A message appears indicating the status of the download.
Click Download to download the software to the controller. A message appears indicating the status of the download.
Step 15  After the download is complete, click Reboot.
After the download is complete, click Reboot.
Step 16  If prompted to save your changes, click Save and Reboot.
If prompted to save your changes, click Save and Reboot.
Step 17  Click OK to confirm your decision to reboot the controller.
Click OK to confirm your decision to reboot the controller.
Step 18  After the controller reboots, repeat Step 6 to Step 17 to install the remaining file.
After the controller reboots, repeat Step 6 to Step 17 to install the remaining file.
Step 19  Reenable the WLANs.
Reenable the WLANs.
Step 20  For Cisco WiSM2 on the Catalyst switch, check the port channel and reenable the port channel if necessary.
For Cisco WiSM2 on the Catalyst switch, check the port channel and reenable the port channel if necessary.
Step 21  If you have disabled the 802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n networks in Step 4, reenable them.
If you have disabled the 802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n networks in Step 4, reenable them.
Step 22  To verify that the 7.3.112.0 controller software is installed on your controller, click Monitor on the controller GUI and look at the Software Version field under Controller Summary.
To verify that the 7.3.112.0 controller software is installed on your controller, click Monitor on the controller GUI and look at the Software Version field under Controller Summary.
Special Notes for Licensed Data Payload Encryption on
Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers
Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) is required for all Cisco 600 Series OfficeExtend Access Point deployments to encrypt data plane traffic between the APs and the controller. You can purchase Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers with either DTLS that is enabled (non-LDPE) or disabled (LDPE). If DTLS is disabled, you must install a DTLS license to enable DTLS encryption. The DTLS license is available for download on Cisco.com.
Important Note for Customers in Russia
If you plan to install a Cisco Wireless LAN Controller in Russia, you must get a Paper PAK, and not download the license from Cisco.com. The DTLS Paper PAK license is for customers who purchase a controller with DTLS that is disabled due to import restrictions but have authorization from local regulators to add DTLS support after the initial purchase. Consult your local government regulations to ensure that DTLS encryption is permitted.
Note  Paper PAKs and electronic licenses available are outlined in the respective controller datasheets.
Paper PAKs and electronic licenses available are outlined in the respective controller datasheets.
Downloading and Installing a DTLS License for an LDPE Controller
Step 1  Download the Cisco DTLS license.
Download the Cisco DTLS license.
a.  Go to the Cisco Software Center at this URL:
Go to the Cisco Software Center at this URL:
https://tools.cisco.com/SWIFT/LicensingUI/Home
b.  On the Product License Registration page, choose Get New > IPS, Crypto, Other Licenses.
On the Product License Registration page, choose Get New > IPS, Crypto, Other Licenses.
c.  Under Wireless, choose Cisco Wireless Controllers (2500/5500/7500/8500/WiSM2) DTLS License.
Under Wireless, choose Cisco Wireless Controllers (2500/5500/7500/8500/WiSM2) DTLS License.
d.  Complete the remaining steps to generate the license file. The license file information will be sent to you in an e-mail.
Complete the remaining steps to generate the license file. The license file information will be sent to you in an e-mail.
Step 2  Copy the license file to your TFTP server.
Copy the license file to your TFTP server.
Step 3  Install the DTLS license. You can install the license either by using the controller web GUI interface or the CLI:
Install the DTLS license. You can install the license either by using the controller web GUI interface or the CLI:
• To install the license using the web GUI, choose:
To install the license using the web GUI, choose:
Management > Software Activation > Commands > Action: Install License
• To install the license using the CLI, enter this command:
To install the license using the CLI, enter this command:
license install tftp://ipaddress /path /extracted-file
After the installation of the DTLS license, reboot the system. Ensure that the DTLS license that is installed is active.
Upgrading from an LDPE to a Non-LDPE Controller
Step 1  Download the non-LDPE software release:
Download the non-LDPE software release:
a.  Go to the Cisco Software Center at this URL:
Go to the Cisco Software Center at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/software/navigator.html?mdfid=282585015&i=rm
b.  Choose the controller model from the right selection box.
Choose the controller model from the right selection box.
c.  Click Wireless LAN Controller Software.
Click Wireless LAN Controller Software.
d.  From the left navigation pane, click the software release number for which you want to install the non-LDPE software.
From the left navigation pane, click the software release number for which you want to install the non-LDPE software.
e.  Choose the non-LDPE software release: AIR-X-K9-X-X.X.aes
Choose the non-LDPE software release: AIR-X-K9-X-X.X.aes
f.  Click Download.
Click Download.
g.  Read Cisco's End User Software License Agreement and then click Agree.
Read Cisco's End User Software License Agreement and then click Agree.
h.  Save the file to your hard drive.
Save the file to your hard drive.
Step 2  Copy the controller software file (filename.aes) to the default directory on your TFTP or FTP server.
Copy the controller software file (filename.aes) to the default directory on your TFTP or FTP server.
Step 3  Upgrade the controller with this version by following the instructions from Step 3 through Step 22 detailed in the "Upgrading to Controller Software Release 7.3.112.0" section.
Upgrade the controller with this version by following the instructions from Step 3 through Step 22 detailed in the "Upgrading to Controller Software Release 7.3.112.0" section.
Interoperability With Other Clients in 7.3.112.0
This section describes the interoperability of the version of controller software with other client devices.
Table 8 describes the configuration used for testing the clients.
Table 8 Test Bed Configuration for Interoperability
Hardware/Software Parameter
|
Hardware/Software Configuration Type
|
Release
|
7.3.112.0
|
Controller
|
Cisco 5500 Series Controller
|
Access points
|
1131, 1142, 1242, 1252, 3500e, 3500i, and 3600
|
Radio
|
802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11n2, 802.11n5
|
Security
|
Open, WEP, PSK (WPA and WPA2), 802.1X (WPA-TKIP and WPA2-AES) (LEAP, PEAP, EAP-FAST, EAP-TLS)
|
RADIUS
|
ACS 4.2, ACS 5.2
|
Types of tests
|
Connectivity, traffic, and roaming between two access points
|
Table 9 lists the client types on which the tests were conducted. The clients included laptops, handheld devices, phones, and printers.
Table 9 Client Types
Client Type and Name
|
Version
|
Laptop
|
Intel 3945/4965
|
11.5.1.15 or 12.4.4.5, v13.4
|
Intel 5100/5300/6200/6300
|
v14.3.0.6
|
Intel 1000/1030/6205
|
v14.3.0.6
|
Dell 1395/1397/Broadcom 4312HMG(L)
|
XP/Vista: 5.60.18.8 Win7: 5.30.21.0
|
Dell 1501 (Broadcom BCM4313)
|
v5.60.48.35/v5.60.350.11
|
Dell 1505/1510/Broadcom 4321MCAG/4322HM
|
5.60.18.8
|
Dell 1515(Atheros)
|
8.0.0.239
|
Dell 1520/Broadcom 43224HMS
|
5.60.48.18
|
Dell 1530 (Broadcom BCM4359)
|
v5.100.235.12
|
Cisco CB21
|
v1.3.0.532
|
Atheros HB92/HB97
|
8.0.0.320
|
Atheros HB95
|
7.7.0.358
|
MacBook Pro (Broadcom)
|
5.10.91.26
|
Handheld Devices
|
Apple iPad
|
iOS 5.0.1
|
Apple iPad2
|
iOS 5.0.1
|
Apple iPad3
|
iOS 5.1.1
|
Asus Slider
|
Android 3.2.1
|
Asus Transformer
|
Android 4.0.3
|
Sony Tablet S
|
Android 3.2.1
|
Toshiba Thrive
|
Android 3.2.1
|
Samsung Galaxy Tab
|
Android 3.2
|
Motorola Xoom
|
Android 3.1
|
Intermec CK70
|
Windows Mobile 6.5 / 2.01.06.0355
|
Intermec CN50
|
Windows Mobile 6.1 / 2.01.06.0333
|
Symbol MC5590
|
Windows Mobile 6.5 / 3.00.0.0.051R
|
Symbol MC75
|
Windows Mobile 6.5 / 3.00.2.0.006R
|
Phones and Printers
|
Cisco 7921G
|
1.4.2.LOADS
|
Cisco 7925G
|
1.4.2.LOADS
|
Ascom i75
|
1.8.0
|
Spectralink 8030
|
119.081/131.030/132.030
|
Vocera B1000A
|
4.1.0.2817
|
Vocera B2000
|
4.0.0.345
|
Apple iPhone 4
|
iOS 5.0.1
|
Apple iPhone 4S
|
iOS 5.1.1
|
Ascom i62
|
2.5.7
|
HTC Legend
|
Android 2.2
|
HTC Sensation
|
Android 2.3.3
|
LG Optimus 2X
|
Android 2.2.2
|
Motorola Milestone
|
Android 2.2.1
|
RIM Blackberry Pearl 9100
|
WLAN version 4.0
|
RIM Blackberry Bold 9700
|
WLAN version 2.7
|
Samsung Galaxy S II
|
Android 2.3.3
|
SpectraLink 8450
|
3.0.2.6098/5.0.0.8774
|
Samsung Galaxy Nexus
|
Android 4.0.2
|
Motorola Razr
|
Android 2.3.6
|
Features Not Supported on Controller Platforms
This section lists the features that are not supported in the following platforms:
• Features Not Supported on Cisco 2500 Series Controllers
Features Not Supported on Cisco 2500 Series Controllers
• Features Not Supported on WiSM2 and Cisco 5500 Series Controllers
Features Not Supported on WiSM2 and Cisco 5500 Series Controllers
• Features Not Supported on Cisco Flex 7500 Controllers
Features Not Supported on Cisco Flex 7500 Controllers
• Features Not Supported on Cisco 8500 Controllers
Features Not Supported on Cisco 8500 Controllers
• Features Not Supported on Cisco Wireless Controller on Cisco Services-Ready Engine
Features Not Supported on Cisco Wireless Controller on Cisco Services-Ready Engine
• Features Not Supported on Cisco Virtual Wireless LAN Controllers
Features Not Supported on Cisco Virtual Wireless LAN Controllers
• Features Not Supported on Mesh Networks
Features Not Supported on Mesh Networks
Features Not Supported on Cisco 2500 Series Controllers
• Wired guest access
Wired guest access
• Cisco 2500 Series Controller cannot be configured as a guest anchor controller. However, it can be configured as a foreign controller to tunnel guest traffic to a guest anchor controller in a DMZ.
Cisco 2500 Series Controller cannot be configured as a guest anchor controller. However, it can be configured as a foreign controller to tunnel guest traffic to a guest anchor controller in a DMZ.
• Bandwidth contract
Bandwidth contract
• Service port
Service port
• AppleTalk Bridging
AppleTalk Bridging
• LAG
LAG
• Right to Use licensing
Right to Use licensing
• Multicast-to-unicast
Multicast-to-unicast
• High Availability
High Availability
• PMIPv6
PMIPv6
• Hierarchical Mobility
Hierarchical Mobility
Note  The features that are not supported on Cisco WiSM2 and Cisco 5500 Series Controllers are also not supported on Cisco 2500 Series Controllers.
The features that are not supported on Cisco WiSM2 and Cisco 5500 Series Controllers are also not supported on Cisco 2500 Series Controllers.
Note  Directly connected APs are supported only in Local mode.
Directly connected APs are supported only in Local mode.
Features Not Supported on WiSM2 and Cisco 5500 Series Controllers
• Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
• Port mirroring
Port mirroring
• Layer 2 access control list (ACL) support
Layer 2 access control list (ACL) support
• VPN termination (such as IPsec and L2TP)
VPN termination (such as IPsec and L2TP)
• VPN passthrough option
VPN passthrough option
Note  You can replicate this functionality on a 5500 series controller by creating an open WLAN using an ACL.
You can replicate this functionality on a 5500 series controller by creating an open WLAN using an ACL.
• Configuration of 802.3 bridging, AppleTalk, and Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Configuration of 802.3 bridging, AppleTalk, and Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE)
• Fragmented pings on any interface
Fragmented pings on any interface
• Right to Use licensing
Right to Use licensing
• High availability for Mobility Oracle.
High availability for Mobility Oracle.
Features Not Supported on Cisco Flex 7500 Controllers
• Static AP-manager interface
Static AP-manager interface
Note  For Cisco 7500 Series controllers, it is not necessary to configure an AP-manager interface. The management interface acts like an AP-manager interface by default, and the access points can join on this interface.
For Cisco 7500 Series controllers, it is not necessary to configure an AP-manager interface. The management interface acts like an AP-manager interface by default, and the access points can join on this interface.
• L3 Roaming
L3 Roaming
• VideoStream
VideoStream
• TrustSec SXP
TrustSec SXP
• IPv6/Dual Stack client visibility
IPv6/Dual Stack client visibility
Note  IPv6 client bridging and Router Advertisement Guard are supported.
IPv6 client bridging and Router Advertisement Guard are supported.
• Internal DHCP server
Internal DHCP server
• Access points in local mode
Access points in local mode
Note  An AP associated with the controller in local mode should be converted to FlexConnect mode or Monitor mode, either manually or by enabling the autoconvert feature. On the Flex 7500 controller CLI, enable the autoconvert feature by entering the config ap autoconvert enable command.
An AP associated with the controller in local mode should be converted to FlexConnect mode or Monitor mode, either manually or by enabling the autoconvert feature. On the Flex 7500 controller CLI, enable the autoconvert feature by entering the config ap autoconvert enable command.
• Mesh
Mesh
• LAG
LAG
• Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
• Cisco Flex 7500 Series Controller cannot be configured as a guest anchor controller. However, it can be configured as a foreign controller to tunnel guest traffic to a guest anchor controller in a DMZ.
Cisco Flex 7500 Series Controller cannot be configured as a guest anchor controller. However, it can be configured as a foreign controller to tunnel guest traffic to a guest anchor controller in a DMZ.
• Multicast
Multicast
• PMIPv6
PMIPv6
• Hierarchical Mobility
Hierarchical Mobility
Features Not Supported on Cisco 8500 Controllers
• LAG
LAG
• Cisco 8500 Series Controller cannot be configured as a guest anchor controller. However, it can be configured as a foreign controller to tunnel guest traffic to a guest anchor controller in a DMZ.
Cisco 8500 Series Controller cannot be configured as a guest anchor controller. However, it can be configured as a foreign controller to tunnel guest traffic to a guest anchor controller in a DMZ.
• TrustSec SXP
TrustSec SXP
• Local authentication (controller acting as authentication server)
Local authentication (controller acting as authentication server)
• Internal DHCP server
Internal DHCP server
• Wired guest access
Wired guest access
• Data DTLS for locally switched clients
Data DTLS for locally switched clients
• Hierarchical Mobility
Hierarchical Mobility
Features Not Supported on Cisco Wireless Controller on Cisco Services-Ready Engine
• Wired guest access
Wired guest access
• Cisco Wireless Controller on Cisco Services-Ready Engine (SRE) cannot be configured as a guest anchor controller. However, it can be configured as a foreign controller to tunnel guest traffic to a guest anchor controller in a DMZ.
Cisco Wireless Controller on Cisco Services-Ready Engine (SRE) cannot be configured as a guest anchor controller. However, it can be configured as a foreign controller to tunnel guest traffic to a guest anchor controller in a DMZ.
• Bandwidth contract
Bandwidth contract
• Access points in direct connect mode
Access points in direct connect mode
• Service port support
Service port support
• AppleTalk Bridging
AppleTalk Bridging
• LAG
LAG
• Hierarchical Mobility
Hierarchical Mobility
Features Not Supported on Cisco Virtual Wireless LAN Controllers
• Data DTLS
Data DTLS
• Cisco 600 Series OfficeExtend Access Points
Cisco 600 Series OfficeExtend Access Points
• Wireless rate limiting (bandwidth contract)
Wireless rate limiting (bandwidth contract)
• Internal DHCP server
Internal DHCP server
• TrustSec SXP
TrustSec SXP
• Access points in local mode
Access points in local mode
• Mobility/guest anchor
Mobility/guest anchor
• Multicast-unicast mode
Multicast-unicast mode
• IPv6
IPv6
• PMIPv6
PMIPv6
• WGB
WGB
• VideoStream
VideoStream
• High Availability
High Availability
• Outdoor mesh access points
Outdoor mesh access points
Note  Outdoor APs such as AP1552 are supported in FlexConnect mode are supported if the APs are not used in a mesh deployment.
Outdoor APs such as AP1552 are supported in FlexConnect mode are supported if the APs are not used in a mesh deployment.
• Hierarchical Mobility
Hierarchical Mobility
Features Not Supported on Mesh Networks
• Multicountry support
Multicountry support
• Load-based CAC (mesh networks support only bandwidth-based CAC or static CAC)
Load-based CAC (mesh networks support only bandwidth-based CAC or static CAC)
• High availability (fast heartbeat and primary discovery join timer)
High availability (fast heartbeat and primary discovery join timer)
• AP acting as supplicant with EAP-FASTv1 and 802.1X authentication
AP acting as supplicant with EAP-FASTv1 and 802.1X authentication
• Access point join priority (mesh access points have a fixed priority)
Access point join priority (mesh access points have a fixed priority)
• Location-based services
Location-based services
Caveats
The following sections lists Open Caveats and Resolved Caveats for Cisco controllers and lightweight access points for version 7.3.112.0. For your convenience in locating caveats in Cisco's Bug Toolkit, the caveat titles listed in this section are drawn directly from the Bug Toolkit database. These caveat titles are not intended to be read as complete sentences because the title field length is limited. In the caveat titles, some truncation of wording or punctuation might be necessary to provide the most complete and concise description. The only modifications made to these titles are as follows:
• Commands are in boldface type.
Commands are in boldface type.
• Product names and acronyms might be standardized.
Product names and acronyms might be standardized.
• Spelling errors and typos might be corrected.
Spelling errors and typos might be corrected.
Note  If you are a registered cisco.com user, view Bug Toolkit on cisco.com at the following website:
If you are a registered cisco.com user, view Bug Toolkit on cisco.com at the following website:
http://tools.cisco.com/Support/BugToolKit/
To become a registered cisco.com user, go to the following website:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Open Caveats
Table 10 lists the open caveats in the 7.3.112.0 controller software release.
Table 10 Open Caveats
ID
|
Description
|
CSCuc97529
|
Symptom: Guest anchor mobility fails when a client roams from a guest anchor controller to an export foreign controller.
Conditions: Client mobility breaks when it roams from a guest anchor controller to an export foreign controller. Web authentication is configured on both controllers.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud21357
|
Symptom: AIR-LAP1252AG-E-K9 AP crashes with 7.3.50.13 on 5508 controller.
Conditions: Crash occurs when there is high user traffic.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud77105
|
Symptom: New mobility peer configurations are missing in the uploaded config file.
Conditions: Enable hierarchical mobility on the controller, add multiple mobility peers and save the config.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud83697
|
Symptom: XML errors occur on the controller.
Conditions: When you reboot the controller after creating an ACL.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud90934
|
Symptom: Clients stay in foreign state in the MA even they are deauthenticated on the MC.
Conditions: Client roams from one switch peer group (SPG) to another. and fails 801.X authentication on the MC.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc27273
|
Symptom: WiSM2 Mobility Oracle client output shows a client with 00:00:00:00:00:00 MAC address. The client does have a valid MAC address.
Conditions: WiSM2 reloads during roaming.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud34204
|
Symptom: Hierarchical mobility DTLS database does not get updated when the 5508 MC management IP changes.
Conditions: When the 5508 MC management IP changes.
Workaround: Reboot the controller after you change the management IP address.
|
CSCud54520
|
Symptom: Local mode APs do not work with ACL on the WLAN if local switching is enabled.
Conditions: If an ACL on a WLAN with a FlexConnect ACL is used and if local switching-enabled local APs ACL fail, the FlexConnect AP works, if local switching is disabled, the local APs ACL work as expected.
Workaround: Create two separate WLANs: one for local mode specific APs and another for FlexConnect APs.
|
CSCuc72073
|
Symptom: The controller reboots with memory errors.
Conditions: Controller is an MC in a NAT environment.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCsv54436
|
Symptom: While doing SSH to controller, it is sometimes denied with "Sorry, telnet is not allowed on this port."
If the same controller retries immediately, the SSH connection is accepted. No changes are seen in between.
Conditions: SSH connection is done from a different Layer 3 network, issue found both in 4400 and 2106.
This is breaking monitoring tools through SSH.
Workaround: Retry SSH connection.
|
CSCsy66246
|
Symptom: An 802.11n AP does not downshift rates for retries when Low Latency MAC is enabled. It sends three retransmissions, but the data rate for the retransmissions is the same data rate at which the initial packet was sent.
Conditions: Using an 802.11n AP with Low Latency MAC enabled.
Workaround: Do not enable Low Latency MAC.
More information: The Low Latency MAC feature has been removed for 802.11n APs (see CSCtc73527).
|
CSCtc16222
|
Symptom: The following messages are displayed on Cisco WiSM2:
Message from ******* at Sep 20 08:38:46 ...
wism2 wism2-ms9: *spamApTask7: Sep 20 08:38:42.434:
#OSAPI-0-INVALID_TIMER_HANDLE: timerlib_mempool.c:241 Task is using
invalid timer handle 15069/46996
Message from ******* at Sep 20 08:38:46 ...
wism2 wism2: -Traceback: 0x113b0060 0x10a26264 0x105c9810 0x105c2760
0x105c2b90 0x105c3094 0x105a19e0 0x10348180 0x103d88ec 0x103e4ac4
0x10e4c86c 0x10a22318 0x11d316a0 0x11d8ffcc
Conditions: Cisco WiSM2 using 7.3.101.0 controller software release.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCtf30526
|
Symptom: The "advanced 802.11a/b channel" settings are not in backup configuration.
You can reproduce this issue by following these steps:
1.  Enter the clear config command. Enter the clear config command.
2.  Restart the controller. Restart the controller.
3.  Initialize setup, then restart the controller. Initialize setup, then restart the controller.
4.  Upload backup-01.cfg file to TFTP server. Upload backup-01.cfg file to TFTP server.
5.  Download the backup file and restart the controller. Download the backup file and restart the controller.
6.  Upload backup-02.cfg file to TFTP server. Upload backup-02.cfg file to TFTP server.
7.  Compared backup-01.cfg with backup-02.cfg. The following lines are not in backup-01. Compared backup-01.cfg with backup-02.cfg. The following lines are not in backup-01.
config advanced 802.11a channel device disable
config advanced 802.11a channel load disable
config advanced 802.11a channel noise enable
config advanced 802.11a channel foreign enable
config advanced 802.11b channel device disable e
config advanced 802.11b channel load disable
config advanced 802.11b channel noise enable
config advanced 802.11b channel foreign enable
These configurations are default, so does not cause any issue, but it decreases maintainability.
Condition: 6.0.196.0, 7.0.230.0, and 7.2.103.0 controller software releases.
Workaround: Use the backup-02.cfg file as backup.
|
CSCtj06944
|
Symptom: A Cisco 5508 Controller or Cisco WiSM2 might stop working with messages similar to the following displayed on the console log:
Kernel panic - not syncing: Failed to allocate skb for hardware pool 0
LKCD: Dumping from interrupt handler!
swapper: page allocation failure. order:0, mode:0x20
[<ffffffff81126b28>] dump_stack+0x8/0x48
[<ffffffff81196de4>] __alloc_pages+0x32c/0x3c0
[<ffffffff811b56a8>] cache_alloc_refill+0x398/0x6e8
[<ffffffff811b5b50>] __kmalloc+0x158/0x168
[<c0000000003f758c>] ssh_kernel_alloc+0x5c/0x1b0 [sshquicksec]
[<c0000000003faaec>] ssh_interceptor_packet_alloc_header+0x64c/0x708
[sshquicksec]
[<c0000000004947e0>] ssh_interceptor_packet_in+0xe8/0x750 [sshquicksec]
Conditions: The service port on the controller is plugged into a VLAN that is also present on one of the controller's uplink interfaces. This occurs when the controller receives a high-broadcast traffic rate over the service port.
Workaround: Unplug the service port, or connect it to a VLAN, which is not switched to the controller's uplink interfaces.
Further Problem Description: The service port, if connected to the switched network, must be put into a VLAN, which is not connected to the controller's distribution ports. It is not a valid configuration to have the service port in a VLAN, which is in use by the controller's management, AP Manager or dynamic interfaces.
|
CSCtn58181
|
Symptom: When multicast is disabled on the controller, traplogs for multicast/broadcast queue are seen to be full.
Conditions: Might occur when multicast is globally disabled.
Workaround: Enable multicast globally.
|
CSCts86091
|
Symptom: Radio resets every few minutes followed by Radio Down/AP Reboot, possibly during EAPoL negotiation.
Conditions: Unknown.
Workaround: Unknown.
|
CSCty78495
|
Symptom: Multicast message delivery may be affected.
Conditions: During 802.11r testing with intercontroller roaming at a rate of 350 roams per second, BCastQ on foreign controller gets full.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCtz80256
|
Symptom: When a controller is configured for local EAP with LDAP and the server is permanently returning a referral/user failure for all authentications, the controller might leak file descriptors leading to a crash on the controller console and the following message is displayed:
unable to open /proc/net/snmp! unable to open /proc/net/snmp! unable to
open /proc/net/snmp!
After 30 minutes, msglogs show the following message:
*osapiReaper: May 09 10:23:53.653: %OSAPI-3-TASK_GETTIME_FAILED:
osapi_task.c:3430 Failed to retrieve statistics (/proc/<pid>/stats) for
task 'spamApTask2'
Conditions: LDAP server returning always a referral answer.
|
CSCtz91549
|
Symptom: AP3500 stops working with traceback 0x6055B8 0x6078B0.
Conditions: Aggregation scheduler stops working.
Workaround: Disable aggregation scheduler by entering this command:
config 802.11{a|b} 11nSupport a-mpdu tx scheduler disable
|
CSCua04683
|
Symptom: Protocol is showing as "unknown" for wired clients on the client detail page.
Conditions: Unknown.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCua14756
|
Symptom: CAPWAP VLAN tagging is not supported on outdoor APs, however, the system does not currently prevent this configuration. If an outdoor AP in local mode is accidentally configured with CAPWAP VLAN tagging, the AP reboots and tries to get an IP, but will keep printing the following message:
*Mar 1 00:02:23.967: %CAPWAP-3-DHCP_RENEW: Could not discover controller
using DHCP IP. Renewing DHCP IP. *Mar 1 00:02:33.967: %CAPWAP-3-ERRORLOG:
Not sending discovery request AP does not have an Ip !! *Mar 1
00:02:43.967: %CAPWAP-3-ERRORLOG: Not sending discovery request AP does
not have an Ip !!
Conditions: When configuring CAPWAP VLAN tagging on the 1550 outdoor Local mode AP, which should not be allowed.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCua53765
|
Symptom: When an AP operates in FlexConnect mode, link test and pings to the client fail. When the AP is changed to Local mode, pings and link test pass as expected.
Conditions:: AP operates in FlexConnect mode.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCub24389
|
Symptom: Using LSC on a 5508 controller crashes Multiple APs (AP3500 and AP1131 models).
Conditions:
Stack Trace [0x001A1A60] crashdump(0x1a18dc) 0x184 [0x001A19B0]
crashdump(0x1a18dc) 0xd4 [0x001CB2F8] get_block(0x1cb130) 0x1c8
[0x001BA118] malloc(0x1b9e9c) 0x27c [0x005AAA08]
spamProcessCertPayload(0x5aa9e8) 0x20 [0x00585BAC]
lwapp_client_process_q(0x5859c0) 0x1ec [0x00586BB4]
lwapp_client_process(0x58679c) 0x418 [0x001A5AF0]
process_execute(0x1a5964) 0x18c
Workaround: Disable LSC on the controller.
|
CSCub26654
|
Symptom: AP3600 DFS false detect.
Conditions: AP3600 sees false radar events from the 7925 phone.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCub28914
|
Symptom: Static client can ping BVI 18.
Conditions: It should be a central DHCP or a local split tunnel client.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCub36414
|
Symptom: The change (enable/disable) in admin mode of ports on 7500 and 8500 controllers is not updated on upstream switch.
Conditions: Disable/enable admin mode of port on 7500 and 8500 controllers.
Workaround: Instead of enabling/disabling port admin from the controller, make it shut/no shut from upstream switch.
|
CSCub65739
|
Symptom: When an AP with DTLS is enabled and the AP is administratively enabled or disabled within a few seconds, this process can cause it to drop from the controller for a few seconds.
Conditions: This occurs when DTLS is enabled and the AP is administratively enabled/disabled within a few seconds. The AP will re-join the controller within a short period of time such as a few seconds.
Workaround: This issue can be avoided by disabling DTLS or avoiding administratively cycling the AP quickly.
|
CSCub88183
|
Symptom: WiSM2 controller crash at Task Name emWeb under instruction ewaFormSubmit_login_callback.
Model: WS-SVC-WISM2-K9, Version: 7.2.110.0 Timestamp: Wed Aug 29 10:10:52
2012 SystemUpTime: 0 days 5 hrs 28 mins 49 secs signal: 11 pid: 1144 TID:
1582011216 Task Name: emWeb Reason: System Crash si_signo: 11 si_errno: 0
si_code: 1 si_addr: 0x41 timer tcb: 0x5615 timer cb: 0x104552a0
('mmMipTimeout 216') timer arg1: 0x2c47e7fc timer arg2: 0x0 Long time
taken timer call back inforamtion: Time Stamp: Wed Aug 29 10:10:52 2012
timer cb : 0x104552a0 ('mmMipTimeout 216') Duration : 164624 usecs,
cbCount= 18
Analysis of Failure: Software failed on instruction at: pc = 0x108e3090 (ewaFormSubmit_login_callback 96), ra = 0x108e3080 (ewaFormSubmit_login_callback 96)
Conditions: Not applicable at this time, however, this is a large campus deployment and it is possible that it may be related to a large influx of clients (2000 to 3000) connecting to the wireless controller(s).
Workaround: None.
|
CSCub89883
|
Symptom: Crash in different tasks after enabling guest LAN.
Conditions: Guest LAN on a 5500 series controller using 7.2 or later software releases with IPv6 traffic from clients.
Workaround: Disable guest LAN or disable IPv6.
|
CSCub96053
|
Symptom: AP3500 gets DFS events due to radar on a DFS channel associated with an 7925 phone. The frequency of DFS events is higher on weekdays and business hours.
Conditions: 7.2.103.0 controller software release.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCub98230
|
Symptom: Client associated to WLAN ID 1 is unable to pass traffic to local site, with VLAN tagging enabled for AP, and local-split enabled for the WLAN at the AP.
Conditions: If there is no local-switching WLAN, and local-split is enabled for WLAN ID 1, for AP with VLAN tagging enabled, client associated is unable to pass traffic to local site.
Workaround: Do not enable local-split for WLAN ID 1, with VLAN tagging enabled AP, or create another local-switching WLAN. Issue is not seen when another local-switching WLAN is created.
Further Problem Description: VLAN tagging enabled for AP. Local-split applied for WLAN ID 1. Client associated to this WLAN is unable to pass traffic to local site, when traffic is permitted in local-split ACL. If another local-switching WLAN is created, issue is not seen.
|
CSCuc02149
|
Symptom: AP3600 in either autonomous IOS or FlexConnect local switching mode drops IP6to4 TCP SYN ACK packets that are received from its LAN port. A wired sniff at the AP port shows, when the wireless client attempts to establish a TCP connection over IPv6 in IPv4, that the AP transmits the TCP SYN (in IPv6 in IPv4) to the switch, and receives the SYN ACK from the switch, but fails to forward the SYN ACK packet to the wireless client. The first time that the AP, after a reload, drops the SYN ACK packet, the following message will be seen on the AP console, or in its log file:
WARNING - Received pak from RXTX port - Check log for detailed
information
At the same time, the wireless client can successfully ping the IPv6 address of its 6to4 gateway.
Conditions: AP3600 or AP2600 in autonomous or FlexConnect local switching mode. Wireless client is attempting to establish TCP connections over IPv6 in IPv4, that is IPv4 protocol type 41.
Workaround:
1.  Use AP1040, AP1140, AP1260, or AP3500 Use AP1040, AP1140, AP1260, or AP3500
2.  Disable IPv6 support on the application server. Disable IPv6 support on the application server.
3.  Instead of using lightweight mode, use a centrally switched WLAN rather than a locally switched one. Instead of using lightweight mode, use a centrally switched WLAN rather than a locally switched one.
|
CSCuc19950
|
Symptom: Anchored SSIDs on the 7.3.101.0 controller software release incorrectly show recently configured peer controllers in its anchor list after reboot.
Conditions: 7.3.101.0 software release with existing anchored SSIDs.
Workaround: Go to the anchored SSID and manually remove the recently added peer controllers from its anchor list.
|
CSCuc22875
|
Symptom: Post SSO, controller fails to make a connection with IDS.
Conditions: In an HA pair, controller establishes a successful connection with IDS and clients are shunned accordingly. Only after SSO is activated, controller deletes the entry for IDS and fails to establish a connection with IDS resulting in the illegitimate clients being not shunned and having access to the network.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc28983
|
Symptom: Ascom i62 phones do not respond to packets and do not send packets when associated with AP3502 on a 5508 controller using the 7.2.110.0 software release after going to power-save mode with WMM enabled on the WLAN, using the 2.4-GHz radios.
Conditions: Ascom i62 phones with newest firmware, AP3502i, 5508 controller, 7.2.110.0 software release, voice WLAN with WMM enabled.
Workaround: Disable WMM.
|
CSCuc31715
|
Symptom: The clear ap config ap-name command is to return the AP to factory default completely. The AP should boot up in Local mode. However, an AP which was running in Bridge mode boot up in Bridge mode even after the clear ap config ap-name command was entered.
Conditions: Bridge mode.
Workaround: Return to local mode manually after associating with a controller.
|
CSCuc32120
|
Symptom: AP crashes and reboots. The following tracebacks are getting dumped continuously, before the crash:
Oct 1 11:38:14.111: %SYS-2-INTSCHED: 'idle' at level 0 , all interrupts disabled \
-Process= "CAPWAP CLIENT", ipl= 0, pid= 118
-Traceback= 2190904z 22F83FCz 22A0C78z 285F350z 2313760z 22F8838z
Conditions: When no primary controller was configured for the access point.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc49667
|
Symptom: SNMP configuration looks for a negative value for the RSSI level while the CLI is defined to be a positive number and used in a negative sense.
Conditions: Under all conditions.
Workaround: Enter positive number for the SNMP.
|
CSCuc50906
|
Symptom: Client gets excluded.
Conditions: WLAN local-switching (interface or VLAN-X) and ip-src-guard, DAI disabled. Also had AP-group (VLAN-Y). AP is in VLAN-X. VLAN mapping on the AP is VLAN-Y. Client gets IP address in VLAN-Y. Change the IP of the client to the gateway of the AP. AP updates the ARP for the gateway and loses the connectivity from controller (the AP joined the other controller. The AP port was shut on the switch and then was opened to avoid image downgrade). When the AP comes back, the client is unable to reassociate. The WLAN was deleted and re-created with a different name. changed the AP was changed to AP3500 (previously it was AP1040). This did not have any impact. The Controller and AP do not show AP's entry.
Workaround: Corner case and normally in real time client IP address and the controller do not share the same VLAN in local switching.
|
CSCuc52952
|
Symptom: Error messages indicating duplicate IP addresses of the service port for WiSM2 in an HA setup.
Conditions: WiSM-SW1-5-DUP_SRVC_IP Service IP 10.6.1.4 of Controller 35/1 is same as Controller 19/1 WiSM-SW1-5-DUP_SRVC_IP Service IP 10.6.1.4 of Controller 35/1 is same as Controller 19/1.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc56857
|
Symptom: Access points disconnect when code you upgrade the code and flash write takes time. The access point disassociate and reassociate when the Association Up Time is reset.
Conditions: Controllers with image 7.0.220.0 to 7.3.101.0.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc60927
|
Symptom: 5508 controller fails to boot. SYS LED - Blinking Amber and ALM LED = OFF.
Conditions: Console logging is set to debugging and high rate of console logs are generated while you reboot the controller.
Workaround: Do not set console logging to debugging and reboot the controller at the same time, or send the debug output to an SSH/Telnet session (which also has a lower impact on CPU).
|
CSCuc68995
|
Symptom: A wireless WebAuth client might be unable to authenticate to the network. When the client opens a browser window, the window is blank. With "debug web-auth redirect" in effect, messages similar to the following might appear:
*webauthRedirect: Oct 15 18:43:19.470: #EMWEB-6-REQUEST_IS_NOT_GET_ERROR:
webauth_redirect.c:1055 Invalid request not GET on client socket 72 or
*webauthRedirect: Oct 10 16:36:30.715: %EMWEB-3-PARSE_ERROR: parse error
after reading. bytes parsed = 0 and bytes read = 189
Conditions: The HTTP GET from the client arrives at the controller in multiple TCP segments.
Workaround: Reconfigure your network and/or the client's TCP/IP stack to ensure that the HTTP GET arrives in a single segment.
|
CSCuc69522
|
Symptom: Client sends TCP SYN to a Multicast MAC for its gateway results in the controller not sending a TCP SYN ACK. TCP Handshake does not complete, so client never generates HTTP traffic and is never redirected. Traffic can be seen arriving at foreign and sending to anchor. Anchor appears to ignore/drop the TCP SYN.
Conditions: Controller Foreign/Anchor doing CWA. Client which has Multicast MAC address for gateway has this issue. This is usually the result of having a load-balance/clustered node for gateway of client.
Workaround: Do not use Multicast MAC.
|
CSCuc73832
|
Symptom: The AP will crash on the process "CAPWAP CLIENT" with a stack trace of "disc_tx_11n_aggr_timer_send".
Conditions: This is a rare occurrence and happens during heavy traffic loading from various types of client traffic and client power save modes.
Workaround: None. The AP will crash and reboot so no action is needed from the user to recover the AP.
|
CSCuc73900
|
Symptom: Inspection of the logs shows that the radios reset because the radio firmware image (8001.img) was not found in AP flash write a radio core dump.
Conditions: During image download from the controller.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc78713
|
Symptom: Wireless client cannot receive broadcast packets after broadcast key rotation.
Conditions: Dynamic WEP; 7.0.235.0, 7.2.110.0, and 7.3.101.0 controller software releases.
Workaround:
• Execute the config advanced eap bcast-key-interval 86400 in the middle of the night Execute the config advanced eap bcast-key-interval 86400 in the middle of the night
• Change security setting to WPA2, and so on. Change security setting to WPA2, and so on.
|
CSCuc81022
|
Symptom: The 1520 outdoor mesh APs may get false DFS triggers when an in-band/off-channel (ch 124) weather RADAR signals are present and received above -20 dBm causing network instability. A similar behavior is observed with off-band maritime radars operating in the 3.05-GHz band, but this can be addressed with band-pass filters installed at the antenna port.
Conditions: AIR-LAP152x outdoor mesh AP installed nearby a weather RADAR installation.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc81911
|
Symptom: CAPWAP 3600 APs are stuck in the boot mode when there is a power outage requiring manual boot.
Conditions: When there is a power outage, there is a possibility of AP being stuck in boot mode.
Workaround: Enter the following commands on the AP console to get the AP working again:
|
CSCuc84281
|
Symptom: Several AES-CCMP TSC replay messages are displayed on the AP console similar to the one shown below:
........ *Oct 23 08:54:16.431: %DOT11-4-CCMP_REPLAY: Client
001f.2774.c400 had 3 AES-CCMP TSC replays
*Oct 23 09:22:22.406: %DOT11-4-CCMP_REPLAY: Client 0817.35c7.8c2f had 60
AES-CCMP TSC replays
*Oct 23 09:23:13.426: %DOT11-4-CCMP_REPLAY: Client 0817.35c7.8c2f had 60
AES-CCMP TSC replays
*Oct 23 09:24:10.440: %DOT11-4-CCMP_REPLAY: Client 0817.35c7.8c2f had 1
AES-CCMP TSC replays
The number associated with AES-CCMP TSC replays (for example 60 in `60 AES-CCMP TSC replays') is the number of dropped packets due to not being acknowledged.
Conditions: These AES-CCMP TSC replay messages appear most often when the traffic is heavy but could appear under normal traffic condition. They are seen more often on the 3502 and 1522 mesh APs.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc86938
|
Symptom: On a Flex 7500 series controller with two WLANs, say WLAN 1 and WLAN 2, it is not possible to switch from WLAN 1 to WLAN 2 if FlexConnect local authentication is not enabled on WLAN 2. This is with fast SSID change enabled and the security simply being WPA2/AES with a pre-shared key on both WLANs. Issue is not prevalent if FlexConnect local authentication is enabled on both WLANs.
Conditions: FlexConnect APs on a Flex 7500 series controller using the 7.3.101.0 controller software release.
Workaround: Enable FlexConnect local authentication on both WLANs.
|
CSCuc88522
|
Symptom: When LAPs lose connectivity with the controller, the controller generates the "Reason for association `Dot11g Mode Change'" trap.
Conditions: This can be triggered by network congestion problems. There is no issue with any of the radio interfaces for the controller to log this message.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc90457
|
Symptom: When Cisco 600 series OEAP channel width is configured to 40 manually, after an AP reboot, the width changes to 20.
Conditions: This is seen only when the controller DCA is kept at a channel bandwidth of 20 and configured manually to a channel bandwidth of 40.
Workaround: Configure controller to assigned channel bandwidth of 40 automatically.
|
CSCuc91441
|
Symptom: Some clients were not removed from the database of the controller after user idle timer expired.
When 100 clients expire their user idle timeout simultaneously, only 64 or 65 deauthentications are sent and 36 or 37 clients were not removed from the controller database.
Workaround: Manually remove the stale clients or reboot the AP that had these clients or reboot the controller.
|
CSCuc93152
|
Symptom: The license capacity changes on the secondary unit (High Availability) if the adder license is added.
Conditions: This behavior is seen if the AP base count license is modified on the secondary unit (when Active). This is seen when the license is modified only on the controller GUI.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc93635
|
Symptom: IP address of the default gateway appears reversed in the show client detail command output.
Conditions: Associate a client to diagchannel.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc94504
|
Symptom: Related to PMF configuration on WLAN.
Conditions: This relates to the configuration when PMF is set as required on WLAN. Tried to enable PSK or 802.1X. This was allowed. Only PFM-PSK or PFM-802.1X should be allowed with PFM in required state.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc94860
|
Symptom: If you configure Security > AAA > MAC Filtering > RADIUS Compatibility Mode or config macfilter radius-compat as Cisco ACS or Free RADIUS, the controller sends Access-Request packet with all bit zero Message Authenticator attribute.
Conditions: Configuring MAC Filtering RADIUS compatibility mode as Cisco ACS or Free RADIUS.
Workaround: Choose Other (default value) if possible.
|
CSCuc96679
|
Symptom: When running chariot based QoS test, VoIP throughput drops by about 3 MB.
Conditions: VoIP throughput drops when BE traffic is introduced to the test; 30 seconds of traffic, 10 Mb VoIP QoS stream, unlimited BE Stream with 10-second start delay.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc97834
|
Symptom: The "wrong index passed" error message appears when configuring 802.11u Auth detail parameters using SRE GUI.
Conditions: This issue is seen only on Cisco SRE. Not seen on the SRE CLI.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc98518
|
Symptom: Guest LAN interface loses its guest LAN check box due to which the guest LAN WLAN is disabled.
Conditions: Guest LAN interface loses its guest LAN check box.
Workaround: Re-enable the guest LAN check box on the guest LAN interface. Enable the guest WLAN and set the correct ingress interface.
|
CSCuc99037
|
Symptom: RRM queues on the 7.3 controller software release are running full for both bands. The controller message logs are filled up with continuous flow of errors related to RRM queuing errors.
Conditions: Following errors are seen in the message log:
#RRM-3-MSGTAG021: rrmClient.c:1237 Airewave Director: Unable to queue
enhanced coverage data from AP C8:F9:F9:34:21:60(1) on 802.11a
#RRM-3-RRM_LOGMSG: rrmClient.c:1843 RRM LOG: Airewave Director: Unable to
queue load data from AP D0:C2:82:F0:A2:A0(1) on 802.11a
#RRM-3-RRM_LOGMSG: rrmClient.c:1727 RRM LOG: Airewave Director: Unable to
queue interference data from AP 00:23:EB:E6:31:10(1) on 802.11a
#RRM-3-RRM_LOGMSG: rrmClient.c:715 RRM LOG: Airewave Director: Unable to
queue noise data from AP 00:23:EB:E6:31:10(1) on 802.11a
#RRM-3-RRM_LOGMSG: rrmClient.c:1727 RRM LOG: Airewave Director: Unable to
queue interference data from AP 00:23:EB:E6:31:10(1) on 802.11a
#RRM-3-MSGTAG022: rrmClient.c:1070 Airewave Director: Unable to queue
aggregated neighbor packet from AP 00:1E:F7:EB:0D:70(1) on 802.11a
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc99637
|
Symptom: MFP anomalies detected on the 7.3 controller software release.
Conditions: Unknown.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCuc99675
|
Symptom: AP802 fails to change to FlexConnect mode.
Conditions: AP802 is in Local mode.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud00104
|
Symptom: CPU ACL is not stored while downloading configuration from the TFTP server.
Conditions: Unknown.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud00277
|
Symptom: Locally switched 802.11 frames incorrectly passed to AP BVI1.
A frame received on a locally-switched 802.11 subinterface should only be bridged to the BVI1 interface if the subinterface belongs to the AP native bridge group.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud04901
|
Symptom: The LAP1550 series outdoor mesh APs may get false DFS triggers when an in-band/off-channel (ch 124) weather RADAR signals are present and received above -20 dBm causing network instability.
Conditions: AIR-LAP155x outdoor mesh AP installed nearby a weather RADAR installation.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud06844
|
Symptom: Unable to change WLAN from MAC-filtering to 802.1X with RADIUS NAC enabled.
Conditions: Unable to change WLAN from MAC-filtering with RADIUS NAC to 802.1X (WPA2/WPA/802.1x) RADIUS NAC combination. When attempted to change it, an error message is displayed in both CLI and GUI and WLAN cannot be edited.
Workaround: Delete WLAN and create a new one with a valid combination.
|
CSCud07983
|
Symptom: The local AAA sever of the controller shows the outer username of wireless users who authenticate using local EAP.
Conditions: When using local EAP on the controller.
Workaround: Disable identity protection on the wireless client to use the same username for the inner and outer EAP username.
|
CSCud09056
|
Symptom: AP3500 stops responding during rate shift operation.
Conditions: Aggregation scheduler is disabled.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud09998
|
Symptom: WiSM2 stops responding triggered by DP keepalive lost.
Conditions: WiSM2 on the 7.2.111.3 controller software release.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud10200
|
Symptom: CAP1552 outdoor AP used in local mode exhibits incorrect behavior upon a DFS event.
Conditions: CAP1552 in local mode; 7.2 and 7.4 controller software releases.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud10479
|
Symptom: APs not displayed as "Monitor/wIPS" on the Wireless tab of the controller GUI.
Conditions: Some APs configured to be in Monitor mode with wIPS submode.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud10563
|
Symptom: When you use the config ap logging syslog facility command with the all keyword, the controller configures only the access points that are currently associated with the it and not the new access points that will associate later.
Conditions: Configure access point syslog commands using controllers.
Workaround: Reapply the command when new access points join the controller.
|
CSCud10632
|
Symptom: MIC error reports from clients on a Clients on Counter Mode with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol (CCMP) only SSID are sent to the controller and all clients are deauthenticated.
Conditions: MIC error reports from clients in a CCMP-only SSID.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud11249
|
Symptom: Incorrect client username appears during Layer 2 roaming.
Conditions: Clients in a WLAN configured with 802.1X and WebAuth authentication.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud12109
|
Symptom: When you restore the controller configuration from a backup file, some rogue rule conditions such as No Encryption, Client Count, and Managed SSID do not get updated.
Conditions: Restore controller configuration from a backup file.
Workaround: Reconfigure the rogue rule conditions again.
|
CSCud12373
|
Symptom: Many access points display the following message on the console:
Received packet with invalid sequence number.
Conditions: WGB is associated to the access point.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud12437
|
Symptom: Clients receive DHCPv6 traffic from clients on access points associated to the same controller.
Conditions: IPv6 is enabled and multicast is disabled.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud12518
|
Symptom: Multicast traffic does not flow when you set the multicast mode in Cisco WiSM2.
Conditions: Multicast mode is set to multicast.
Workaround: Set the multicast mode to unicast.
|
CSCud12582
|
Symptom: Processing AAA Error Out of Memory error appears and client authentication fails.
Conditions: Large scale deployments with multiple clients. RADIUS queues are full when the authentication or accounting server fails.
Workaround: Lower request timeouts.
|
CSCud14147
|
Symptom: Controller calculates an incorrect message authenticator value for RFC3576 CoA requests from some RADIUS servers such as PacketFence NAC.
Conditions: Controller with 7.3 and 7.4 releases.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud16495
|
Symptom: Cisco 7510 controller crashes when it is part of an HA pair. After the crash, the controller reloads and becomes online.
Conditions: Controller is part of an HA pair.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud16984
|
Symptom: Access points are assigned to channels with lower maximum powers.
Conditions: Varying power levels in different channels of the new access points. The controller detects more neighbors with high RSSIs on channels with higher power.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud17506
|
Symptom: Prime Infrastructure detects a false switchover trap when you reboot a redundancy enabled controller.
Conditions: Redundancy is enabled on the primary controller, but it is not paired with the secondary controller.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud17856
|
Symptom: Deleted native VLAN appears in the trunk VLAN. When you add trunk VLANs on the controller and change the native VLAN, the previously configured native VLAN is added to the trunk VLAN.
Conditions: Add trunk VLANs on the controller and change the native VLAN.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud19187
|
Symptom: Cisco 3500 series access points with crash during the process execute function.
Conditions: Cisco IOS image is 15.2(2)JA.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud22456
|
Symptom: When you filter clients in the controller GUI using the WLAN ID, clients of all WLANs with similar names appear in the Monitor > Client page.
Conditions: Starting characters of the WLAN ID are same. For example, Test and Test1.
Workaround: Use names with different starting characters for WLAN IDs.
|
CSCud23567
|
Symptom: When you apply the Lightweight AP template in NCS for VLAN support and WLAN-VLAN mapping, the administrative state changes from enabled to disabled and the VLAN ID is not applied.
Conditions: Controller with 7.0.235.0 image.
Workaround: Reconfigure the controller.
|
CSCud23648
|
Symptom: Controller crashes and encounters a fatal condition at broffu_fp_dapi_cmd.c:3679.
Conditions: Task Name is osapiReaper.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud26632
|
Symptom: The following SNMP trap appears on the controller when you change the channel width number to 40-MHz:
RF failure notification ErrorType: 32 Reason :Error: Config Sync failed on Standby for the usmdb:HA_send_usmDbSpamSetRadSlotAntennaType.
Conditions: Controller is in an HA pair. Join the 802.11n access point to the controller and change the channel width to 40-MHz and channel number to 157.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud26706
|
Symptom: After a High Availability (HA) failover of the Cisco 8500 controller, the show redundancy peer-route summary command does not show any service port routes.
Conditions: None.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud33095
|
Symptom: Cisco 5508 controllers with LAG mode disabled send ARP requests with incorrect source MAC address.
Conditions: No LAG and several ports are connected with multiple dynamic interfaces.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud33394
|
Symptom: After a switchover, audit mismatch of 802.11u access point venue parameters occurs in a redundancy paired controller.
Conditions: On a redundancy paired controller, set the AP venue parameters such as Venue group, Venue Type, Venue Name, and Language. Switchover to standby and switchover back to primary.
Workaround: Restore the configuration from Prime Infrastructure.
|
CSCud33577
|
Symptom: FlexConnect access point are stuck in a loop.
Conditions: FlexConnect access point cannot renew the DHCP lease when the bvi1 interface goes down.
Workaround: Reboot the access point or increase the lease time to a high value. Use static IP addresses on the access point. This problem does not occur if the native VLAN of the FlexConnect access point is 1.
|
CSCud33759
|
Symptom: Communication from the Backbone Router (BBR) gateway to the wired network fails on AP 1552S.
Conditions: 7.3 and later builds.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud34693
|
Symptom: LDAP authentication occurs on a globally defined LDAP server not configured for the WLAN.
Conditions: Timeout of the LDAP authentication on the configured WLAN LDAP server.
Workaround: Use one LDAP sever or an Organizational Unit (OU) for all users or use RADIUS authentication.
|
CSCud34744
|
Symptom: Controller crashes randomly and recovers on its own after reboot.
Conditions: show ap join info summary causes the crash.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud35479
|
Symptom: Debug logs for power changes are not synchronized with the RF group member controller.
Conditions: When the controller forms an RF group and the Transmit Power Control (TPC) is TPCv2.
Workaround: Use TPCv1.
|
CSCud37012
|
Symptom: Controller does not have a command to configure the HTTP or HTTPS timeout.
Conditions: None.
Workaround: Use the controller GUI to configure the HTTP or HTTPS timeout.
|
CSCud37324
|
Symptom: Clients experience poor performance, and erratic roaming due to the beacon loss of a WLAN.
Conditions: Beacon loss occurs for a WLAN. The problem occurs for 30 to 60 seconds, and then beacons transmit normally.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud37443
|
Symptom: Clients are able to connect to the 802.11b/g band even when the WLAN radio policy is 802.11a only.
Conditions: Create a WLAN with the radio policy as 802.11a only and configure the clients in 802.11b/g mode.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud38734
|
Symptom: WebAuth clients are not deleted by the anchor controller after an L3 roaming. The clients are serviced continuously.
Conditions: WLAN session timeout is used instead of AAA override.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud40334
|
Symptom: You cannot configure some Mesh features using Prime Infrastructure.
Conditions: The following Mesh features cannot be configured from using Prime Infrastructure as there is no SNMP support:
• VLAN Transparent VLAN Transparent
• Force External Authentication Force External Authentication
• External MAC Filter Authorization External MAC Filter Authorization
Workaround: Configure these features directly on the controller.
|
CSCud41334
|
Symptom: Ethernet bridged clients of Mesh APs (MAPs) do not work.
Conditions: When an Ethernet bridged client is plugged to the Ethernet port of a MAP before the MAP joins the controller, then the client will not work. This caveat occurs for Cisco 1140, 3500, and 3600 (all indoor mesh APs), and not on Cisco 1552 (outdoor mesh AP).
Workaround: Ensure that the bridged client is not plugged into the Ethernet port of the MAP and reload the MAP. The MAP must join the controller before the client plugs into the MAP Ethernet port.
|
CSCud43410
|
Symptom: If the available channels for an access point are exhausted, the access point drops off from the controller and does not join the controller until the channels are available.
Conditions: Channel list is limited to less number of channels.
Workaround: If the channels are not available, you must add additional channels to the DCA list.
|
CSCud43646
|
Symptom: Cisco WiSM crashes with a deadlock during the RRM group calculation. Reaper crashes because timer task hogs the CPU.
Conditions: Controllers with 7.0.116 and 7.0.235.0 image.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud44269
|
Symptom: Access point sends ARP responses to clients in DHCP required state.
Conditions: This problem occurs for FlexConnect access points connected to a 7.3.101.0 controller.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud46376
|
Symptom: MAC filter interface mapping does not work.
Conditions: Interface mapped to VLAN A is changed to VLAN B.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud48620
|
Symptom: In the steady state mode, the DCA is unable to change channels in spite of high channel utilization and high interference.
Conditions: In steady state, DCA influences AP towards its RF neighborhood.
Workaround: Put DCA back to aggressive mode.
|
CSCud48146
|
Symptom: When you limit the maximum concurrent logins for a user name, the max-login-ignore-identity-response gets enabled.
Conditions: max-login-ignore-identity-response does not work and the global maximum concurrent logins for a user name takes precedence.
Workaround: Increase the global maximum concurrent logins for a user name to the desired number.
|
CSCud50980
|
Symptom: Coredump file is not uploaded properly and cannot be unzipped.
Conditions: Size of the file is more than 32 MB.
Workaround: Use FTP to transfer and upload the coredump file.
|
CSCud47733
|
Symptom: When the 5-GHz channel is configured as static and not DCA, the 5-GHz channel sometimes reverts back as a static channel at unexpected intervals after a Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) event.
Conditions: Controller with 7.2.103.0 image.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud57163
|
Symptom: AP1142 crashes during upgrade.
Conditions: Upgrade controller from 7.3.101.0 to 7.4.1.55 image.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud56936
|
Symptom: Radio is reset when the transmitter shuts down.
Conditions: The following log appears on the access point: %DOT11-2-RESET_RADIO: Restarting Radio interface Dot11Radio
Workaround: Reboot the access point.
|
CSCud57083
|
Symptom: Access point crashes with an invalid stack trace for the SOAP LED process.
Conditions: None.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud05385
|
Symptom: In a controller with 7.2 image, the radio statistics are not updated.
Conditions: When you use the show ap stats <ap_name> command.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCtf30535
|
Symptom: config wlan apgroup add default-group setting does not appear in the backup configuration.
Conditions:
1.  Clear the configuration. Clear the configuration.
2.  Restart the controller with the 6.0.196.0 image. Restart the controller with the 6.0.196.0 image.
3.  After the initial setup, restart the controller. After the initial setup, restart the controller.
4.  Upload the backup-01.cfg file to a TFTP server. Upload the backup-01.cfg file to a TFTP server.
5.  Download the backup file. Download the backup file.
6.  Restart controller. Restart controller.
7.  Upload backup-02.cfg file to TFTP server. Upload backup-02.cfg file to TFTP server.
8.  Compare the backup-01.cfg and backup-02.cfg files. The following line is not in backup-01.cfg file: Compare the backup-01.cfg and backup-02.cfg files. The following line is not in backup-01.cfg file:
config wlan apgroup add default-group
Workaround: Use the backup-02.cfg file for backup.
|
CSCtf30550
|
Symptom: config wlan security wpa wpa2 enable setting does not appear in the backup configuration.
Conditions:
1.  Clear the configuration. Clear the configuration.
2.  Restart the controller with the 6.0.196.0 image. Restart the controller with the 6.0.196.0 image.
3.  After the initial setup, restart the controller. After the initial setup, restart the controller.
4.  Upload the backup-01.cfg file to a TFTP server. Upload the backup-01.cfg file to a TFTP server.
5.  Download the backup file. Download the backup file.
6.  Restart controller. Restart controller.
7.  Upload backup-02.cfg file to TFTP server. Upload backup-02.cfg file to TFTP server.
8.  Compare the backup-01.cfg and backup-02.cfg files. The following line is not in backup-01.cfg file: Compare the backup-01.cfg and backup-02.cfg files. The following line is not in backup-01.cfg file:
config wlan security wpa wpa2 enable
Workaround: Use the backup-02.cfg file for backup.
|
CSCts70063
|
Symptom: When a Cisco 5500 Series controller boots, the following error appears:
Error (2048) found in fsck check - attempt to repair.
The error number varies.
Conditions: When you boot a controller 5508 controller manufactured between June and October 2011 (range of the serial number is FCW1511xxxx through FCW1540xxxx) with a 6.0 image.
Workaround: You can ignore the message as it is a minor error and has no effect on the operation of the controller. If you upgrade to a 7.0 release of software, the message will no longer appear.
|
CSCtx87530
|
Symptom: Ping operation to the controller's management interface fails due to the ICMP checksum.
Conditions: Packet size is 17 bytes or less, or, nonzero padding is used.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCud56753
|
Symptom: In a VMware ESX cluster, when you migrate a virtual controller from one host to another using VMotion, the controller management becomes unreachable for 15 to 30 seconds. This scenario causes the access points to temporarily transition to the standalone mode and prevents communicating within the centrally switched WLANs.
Conditions: Management interface of the virtual controller is configured with a dot1q VLAN tag and communicates through a virtual switch network configured with VLAN (4095 ALL) in a promiscuous network.
Workaround: WLAN communication is established as soon as the virtual controller generates or egresses traffic through the new host after a VMotion event.
|
CSCud52785
|
Symptom: Unable to create SNMP community strings for Virtual controllers from Prime Infrastructure.
Conditions: Virtual controller with 7.4 image.
Workaround: Create the SNMP community strings for the Virtual controller from the controller GUI.
|
CSCuc87875
|
Symptom: AP1250 crashes when a client associates with it, and the controller has the 7.4 image.
Conditions: When clients associate alone.
Workaround: None.
|
CSCua23018
|
WCP status never comes to oper-up even after reconfiguring the service IP.
Symptom: Static/DHCP service-vlan IP is lost after HA configuration.
Conditions: Even after reconfiguration of service port IP, WCP status shows keep alive and never comes to oper-up state.
Workaround: Enter no wism service-vlan vlan command in catalyst 6K device and add the configuration again.
|
CSCui77735
|
Symptom: Cisco 8510 WLC using Release 7.3.112.0 stopped working on taskname SNMPTask.
Conditions: claPriorityOrder is set to 0 in SNMP set on 7510/8510/vWLC.
snmpset -v2c -c private 83.83.83.22 .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.598.1.1.1.1.2.1 u 0
snmpset -v2c -c private 83.83.83.22 .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.598.1.1.1.1.2.2 u 0
snmpset -v2c -c private 83.83.83.22 .1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.598.1.1.1.1.2.3 u 0
0 = None - where crash is happening.
1,2 = Either first or second
Management authentication server order:
1............................................ local
2............................................ radius
On Cisco 5508 WLC, value of 0 will be taken. The box does not stop working.
Workaround: Do not set claPriorityOrder to 0 when using this MIB.
|
Resolved Caveats
Table 11 lists the caveats that are resolved in the 7.3.112.0 controller software release.
Table 11 Resolved Caveats
ID
|
Title
|
CSCtz35999
|
Cisco IOS Software Protocol Translation Vulnerability.
|
CSCud65237
|
Encryption key corruption on BA acknowledged with wrong ID.
|
CSCto02968
|
Memory leak sshpm on line 252 of sshencode.
|
CSCuc34199
|
5508 controller running 7.3.101.0 crashes without a crash file.
|
CSCtx03556
|
TACACS user login failed on 5508 series controllers with 7.0.116.0 image.
|
CSCua08980
|
Controller inconsistently performed the association accept for Local mode, HREAP with central authentication, and HREAP with local authentication.
|
CSCua58554
|
AAA override dynamic RADIUS VLAN HREAP FlexConnect broken on the 7.2.110.0 controller software release.
|
CSCub27807
|
Controller sent incorrect NMSP measurement notification for rogue access points.
|
CSCub07050
|
Port configuration of interfaces was deleted when the controller was downgraded to an image that did not support LAG.
|
CSCub47822
|
When client changed the WLAN and fast SSID change was enabled, the controller sent wrong VLAN accounting stop for the client.
|
CSCub50981
|
GTK key update broke for clients on FlexConnect AP using local authentication.
|
CSCub58507
|
WebAuth failed for IPv6 only clients using global config and custom web.
|
CSCub65575
|
Controller forwarded ARP broadcast requests to centrally switched clients.
|
CSCub67462
|
Ethernet bridged clients on AP3600 models are unable get IP.
|
CSCub77220
|
Controller crashed while deleting FlexConnect ACL.
|
CSCub78700
|
WiSM2 crashed from wcpTask every few hours.
|
CSCuc15636
|
Controller stops working on WebAuth redirect processing.
|
CSCuc16850
|
Radio stopped transmitting when the transmit queues were full.
|
CSCuc47106
|
Mobility failed when there was an error in sending broadcast traffic.
|
CSCuc56697
|
8500 series controller with 6K access points coredump after selecting the AP group from GUI .
|
CSCuc62460
|
AP HTTP profiler stopped working on multiple codenomicon tests.
|
CSCuc74677
|
High Availability controller rebooted and lost its AP count license.
|
CSCuc74769
|
WiSM1 controllers stopped working randomly on the 7.0.235.0 software release.
|
CSCuc74835
|
Fragmented packets arriving at controller from AP, which contain EAP response from supplicant, are not processed.
|
CSCuc95993
|
Access points send ARP requests to IP addresses in different subnets.
|
CSCud07497
|
The 7500 and 8500 series controller send wrong PMK cache timer for 802.1111r client to mobility peers.
|
CSCud90030
|
SNMP walk on cLMobilityExtSpgTable had inconsistent cLMobilityExtSpgMulticastAddressType and cLMobilityExtSpgMulticastAddress values.
|
CSCuc10258
|
AP 3600 reloads in standalone mode and invalid ACL messages appear on console.
|
CSCub67978
|
Missing SSIDs on AP radios when SSIDs were enabled.
|
CSCub88183
|
WiSM2 controller crash at Task Name emWeb under instruction ewaFormSubmit_login_callback.
|
CSCud90670
|
When you add a new wired client to a WGB, which roams from anchor to foreign, the wired clients fails to estabilish a foriegn or anchor state.
|
CSCud00484
|
When you switch from a primary to a secondary controller, with HA AP SSO enabled, and back from primary to secondary, the clients they stay in 8021X_REQD state when they reauthenticate.
|
Installation Notes
This section contains important information to keep in mind when installing controllers and access points:
• Warnings
Warnings
• Safety Information
Safety Information
• Installation Instructions
Installation Instructions
Warnings
 |
Warning  This warning means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. Use the statement number provided at the end of each warning to locate its translation in the translated safety warnings that accompanied this device. Statement 1071 This warning means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. Use the statement number provided at the end of each warning to locate its translation in the translated safety warnings that accompanied this device. Statement 1071
|
 |
Warning  Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030 Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030
|
 |
Warning  Do not locate the antenna near overhead power lines or other electric light or power circuits, or where it can come into contact with such circuits. When installing the antenna, take extreme care not to come into contact with such circuits, as they may cause serious injury or death. For proper installation and grounding of the antenna, please refer to national and local codes (e.g. U.S.: NFPA 70, National Electrical Code, Article 810, Canada: Canadian Electrical Code, Section 54). Statement 280 Do not locate the antenna near overhead power lines or other electric light or power circuits, or where it can come into contact with such circuits. When installing the antenna, take extreme care not to come into contact with such circuits, as they may cause serious injury or death. For proper installation and grounding of the antenna, please refer to national and local codes (e.g. U.S.: NFPA 70, National Electrical Code, Article 810, Canada: Canadian Electrical Code, Section 54). Statement 280
|
 |
Warning  This product relies on the building's installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that a fuse or circuit breaker no larger than 120 VAC, 15A U.S. (240 VAC, 10A international) is used on the phase conductors (all current-carrying conductors). Statement 13 This product relies on the building's installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that a fuse or circuit breaker no larger than 120 VAC, 15A U.S. (240 VAC, 10A international) is used on the phase conductors (all current-carrying conductors). Statement 13
|
 |
Warning  This equipment must be grounded. Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the equipment in the absence of a suitably installed ground connector. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you are uncertain that suitable grounding is available. Statement 1024 This equipment must be grounded. Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the equipment in the absence of a suitably installed ground connector. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you are uncertain that suitable grounding is available. Statement 1024
|
 |
Warning  Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source. Statement 10 Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source. Statement 10
|
 |
Warning  Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect any cables (Ethernet, cable, or power) during periods of lightning activity. The possibility of serious physical injury exists if lightning should strike and travel through those cables. In addition, the equipment could be damaged by the higher levels of static electricity present in the atmosphere. Statement 276 Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect any cables (Ethernet, cable, or power) during periods of lightning activity. The possibility of serious physical injury exists if lightning should strike and travel through those cables. In addition, the equipment could be damaged by the higher levels of static electricity present in the atmosphere. Statement 276
|
 |
Warning  Do not operate the unit near unshielded blasting caps or in an explosive environment unless the device has been modified to be especially qualified for such use. Statement 364 Do not operate the unit near unshielded blasting caps or in an explosive environment unless the device has been modified to be especially qualified for such use. Statement 364
|
 |
Warning  In order to comply with radio frequency (RF) exposure limits, the antennas for this product should be positioned no less than 6.56 ft. (2 m) from your body or nearby persons. Statement 339 In order to comply with radio frequency (RF) exposure limits, the antennas for this product should be positioned no less than 6.56 ft. (2 m) from your body or nearby persons. Statement 339
|
 |
Warning  This unit is intended for installation in restricted access areas. A restricted access area can be accessed only through the use of a special tool, lock and key, or other means of security. Statement 1017 This unit is intended for installation in restricted access areas. A restricted access area can be accessed only through the use of a special tool, lock and key, or other means of security. Statement 1017
|
Safety Information
Follow the guidelines in this section to ensure proper operation and safe use of the controllers and access points.
FCC Safety Compliance Statement
FCC Compliance with its action in ET Docket 96-8, has adopted a safety standard for human exposure to RF electromagnetic energy emitted by FCC-certified equipment. When used with approved Cisco Aironet antennas, Cisco Aironet products meet the uncontrolled environmental limits found in OET-65 and ANSI C95.1, 1991. Proper operation of this radio device according to the instructions in this publication results in user exposure substantially below the FCC recommended limits.
Safety Precautions
For your safety, and to help you achieve a good installation, read and follow these safety precautions. They might save your life!
1.  If you are installing an antenna for the first time, for your own safety as well as others, seek professional assistance. Your Cisco sales representative can explain which mounting method to use for the size and type of antenna you are about to install.
If you are installing an antenna for the first time, for your own safety as well as others, seek professional assistance. Your Cisco sales representative can explain which mounting method to use for the size and type of antenna you are about to install.
2.  Select your installation site with safety as well as performance in mind. Electric power lines and phone lines look alike. For your safety, assume that any overhead line can kill you.
Select your installation site with safety as well as performance in mind. Electric power lines and phone lines look alike. For your safety, assume that any overhead line can kill you.
3.  Call your electric power company. Tell them your plans and ask them to come look at your proposed installation. This is a small inconvenience considering your life is at stake.
Call your electric power company. Tell them your plans and ask them to come look at your proposed installation. This is a small inconvenience considering your life is at stake.
4.  Plan your installation carefully and completely before you begin. Successfully raising a mast or tower is largely a matter of coordination. Each person should be assigned to a specific task and should know what to do and when to do it. One person should be in charge of the operation to issue instructions and watch for signs of trouble.
Plan your installation carefully and completely before you begin. Successfully raising a mast or tower is largely a matter of coordination. Each person should be assigned to a specific task and should know what to do and when to do it. One person should be in charge of the operation to issue instructions and watch for signs of trouble.
5.  When installing an antenna, remember:
When installing an antenna, remember:
a.  Do not use a metal ladder.
Do not use a metal ladder.
b.  Do not work on a wet or windy day.
Do not work on a wet or windy day.
c.  Do dress properly—shoes with rubber soles and heels, rubber gloves, long-sleeved shirt or jacket.
Do dress properly—shoes with rubber soles and heels, rubber gloves, long-sleeved shirt or jacket.
6.  If the assembly starts to drop, get away from it and let it fall. Remember that the antenna, mast, cable, and metal guy wires are all excellent conductors of electrical current. Even the slightest touch of any of these parts to a power line completes an electrical path through the antenna and the installer: you!
If the assembly starts to drop, get away from it and let it fall. Remember that the antenna, mast, cable, and metal guy wires are all excellent conductors of electrical current. Even the slightest touch of any of these parts to a power line completes an electrical path through the antenna and the installer: you!
7.  If any part of an antenna system should come in contact with a power line, do not touch it or try to remove it yourself. Call your local power company. They will remove it safely.
If any part of an antenna system should come in contact with a power line, do not touch it or try to remove it yourself. Call your local power company. They will remove it safely.
8.  If an accident should occur with the power lines, call for qualified emergency help immediately.
If an accident should occur with the power lines, call for qualified emergency help immediately.
Installation Instructions
See the appropriate quick start guide or hardware installation guide for instructions on installing controllers and access points.
Note  To meet regulatory restrictions, all external antenna configurations must be installed by experts.
To meet regulatory restrictions, all external antenna configurations must be installed by experts.
Personnel installing the controllers and access points must understand wireless techniques and grounding methods. Access points with internal antennas can be installed by an experienced IT professional.
The controller must be installed by a network administrator or qualified IT professional, and the proper country code must be selected. Following installation, access to the controller should be password protected by the installer to maintain compliance with regulatory requirements and ensure proper unit functionality.
Service and Support
Information About Caveats
If you need information about a specific caveat that does not appear in these release notes, you can use the Cisco Bug Toolkit to find caveats of any severity. Click this URL to browse to the Bug Toolkit:
http://tools.cisco.com/Support/BugToolKit/
(If you request a defect that cannot be displayed, the defect number might not exist, the defect might not yet have a customer-visible description, or the defect might be marked Cisco Confidential.)
Troubleshooting
For the most up-to-date, detailed troubleshooting information, see the Cisco TAC website at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/support/index.html
Click Product Support > Wireless. Then choose your product and Troubleshooting to find information on the problem you are experiencing.
Related Documentation
For additional information about the Cisco controllers and lightweight access points, see these documents:
• The quick start guide or installation guide for your particular controller or access point
The quick start guide or installation guide for your particular controller or access point
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guides
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guides
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Command References
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Command References
• Cisco Wireless LAN Controller System Message Guide
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller System Message Guide
You can access these documents at this URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/wireless/index.html.
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What's New in Cisco Product Documentation as an RSS feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service. Cisco currently supports RSS Version 2.0.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2013 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Feedback
Feedback
Unless otherwise noted, all of the Cisco Wireless LAN controllers are referred to as controllers, and all of the Cisco lightweight access points are referred to as access points.
Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution Components
Software Release Support for Access Points
Upgrading to Controller Software Release 7.3.112.0
Special Notes for Licensed Data Payload Encryption on Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers
Interoperability With Other Clients in 7.3.112.0
Features Not Supported on Controller Platforms
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For more information on the compatibility of wireless software components across releases, see the Cisco Wireless Solutions Software Compatibility Matrix.
The 7.3.112.0 controller software release is not compatible with Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) 1.1.1.24. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 is required to support the controller features introduced in the 7.3.x controller software releases. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 is the subsequent version of Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) 1.1.1.24.
Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) JA1.
Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2.
Mobility Services Engine software release 7.3 and context-aware software
Client and tag licenses are required to get contextual (such as location) information within the context-aware software. For more information, see the Release Notes for Cisco 3350 Mobility Services Engine for Software Release 7.3.
Cisco 3350, 3310, 3355 Mobility Services Engine, Virtual Appliance
Cisco 2500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco 5500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco Flex 7500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco 8500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco Virtual Wireless LAN Controllers
Cisco Wireless Controllers for high availability (HA controllers) for 5500 series, WiSM2, Flex 7500 series, and 8500 series controllers
Cisco Wireless Services Module 2 (WiSM2) for Catalyst 6500 Series switches
Cisco Wireless Controller on Cisco Services-Ready Engine (SRE) (WLCM2) running on ISM 300, SM 700, SM 710, SM 900, and SM 910
Cisco Aironet 1550 (1552) Series outdoor 802.11n mesh access points; Cisco Aironet 1520 (1522, 1524) series outdoor mesh access points
Cisco 1040, 1130, 1140, 1240, 1250, 1260, 2600, 3500, 3500p, 3600, Cisco 600 Series OfficeExtend Access Points, AP801, and AP802
AP860:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/data_sheet_c78_461543.html
AP880:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/data_sheet_c78_459542_ps380_Products_Data_Sheet.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/data_sheet_c78-613481.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/ps10082/data_sheet_c78_498096.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/routers/ps380/ps10082/data_sheet_c78-682548.html
AP890:
The AP802 is an integrated access point on the Next Generation Cisco 880 Series ISRs.
Before you use an AP802 series lightweight access point with controller software release 7.3.112.0, you must upgrade the software in the Next Generation Cisco 880 Series ISRs to Cisco IOS 151-4.M or later releases.
Cisco 4400 Series Wireless LAN Controller
Cisco 2100 Series Wireless LAN Controller
Cisco Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller
Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series/7600 Series Wireless Services Module (WiSM)
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Module (NM/NME)
Hierarchical Mobility (New Mobility)
Hierarchical Mobility is supported only on Cisco 5500 Series Wireless LAN Controllers and Cisco WiSM2.
Configuring Hierarchical Mobility (GUI)
Configuring Hierarchical Mobility (CLI)
Choose CONTROLLER > Mobility Management > Mobility Configuration to enable and configure hierarchical mobility on the controller.
Configure the following fields for hierarchical mobility:
Click Apply.
Choose CONTROLLER > Mobility Management > Switch Peer Group to add or remove members to the switch peer group.
Choose CONTROLLER > Mobility Management > Mobility Controller to view all the mobility controllers and their details like IP address, MAC address, client count, and link status.
Choose CONTROLLER > Mobility Management > Mobility Clients to view all the mobility clients and their parameters.
Enable or disable hierarchical mobility on the controller by entering this command:
Enable the Mobility Oracle (MO), or configure an external MO by entering this command:
Create, or delete switch peer groups (SPG) by entering this command:
Configure the MAC address of the member switch for compatibility between the flat and hierarchical (old and new) mobility by entering this command:
Add, remove members, configure bridge domain ID, and multicast address of the switch peer group by entering this command:
View the details of the mobility controllers according to the Mobility Oracle by entering this command:
View the summary and details of the Mobility Oracle client database by entering this command:
Verify the mobility statistics by entering this command:
Verify the mobility configuration by entering this command:
Save your changes by entering this command:
Enable or disable debugging of mobility packets by entering this command:
Enable or disable debugging of the Mobility Oracle events and errors by entering this command:
Compatibility Matrix with Mobility Network Elements
Compatibility Matrix with Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch
Compatibility Matrix without Cisco 5760 Wireless LAN Controller and Cisco Catalyst 3850 Switch
By default, the controller is MA/MC.
MO + MC + MA can be in a single controller.
5760, WiSM2, and 5500 controllers are the only platforms that support MO.
Can have only one MO.
Can function both as MA/MC and MA only.
5760, WiSM2, and 5500 controllers are the only platforms that support MO.
Can have only one MO.
Upgrade 5508 and WiSM2 to 7.3.112.0.
Enable hierarchical mobility on 5508 and WiSM2. When you enable hierarchical mobility, the controller reboots.
The Cisco 3600 Access Point was introduced in 7.1.91.0. If your network deployment uses Cisco 3600 Access Points with release 7.1.91.0, we highly recommend that you upgrade to 7.2.103.0 or a later release.
The 7.3.112.0 controller software release is not compatible with Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) 1.1.1.24. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 is required to support the controller features introduced in the 7.3.x controller software release. Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 is the subsequent version of Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) 1.1.1.24.
If you require a downgrade from one release to another, you might lose the configuration from your current release. The workaround is to reload the previous controller configuration files saved on the backup server or to reconfigure the controller.
It is not possible to directly upgrade to the 7.3.112.0 release from a release that is older than 7.0.98.0.
You can upgrade or downgrade the controller software only between certain releases. In some instances, you must first install an intermediate release prior to upgrading to software release 7.3.112.0. Table 7 shows the upgrade path that you must follow before downloading software release 7.3.112.0.
When you downgrade the controller from 7.3.112.0 to a software release that does not support hierarchical mobility (new mobility) like 7.3.101.0, 7.2, 7.0, or earlier releases (all releases prior to 7.3.112.0), the controller automatically transits to flat mobility (old mobility). This is due to the difference in mobility architecture and noninteroperability between flat mobility (EOIP tunnels) and hierarchical mobility(CAPWAP tunnels).
When you upgrade the controller to an intermediate software release, you must wait until all of the access points that are associated with the controller are upgraded to the intermediate release before you install the latest controller software. In large networks, it can take some time to download the software on each access point.
If you upgrade to the controller software release 7.3.112.0 from an earlier release, you must also upgrade to Cisco Prime Infrastructure 1.2 and MSE 7.3.
You can upgrade to a new release of the controller software or downgrade to an older release even if Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) is enabled.
When you upgrade to the latest software release, the software on the access points associated with the controller is also automatically upgraded. When an access point is loading software, each of its LEDs blinks in succession.
We recommend that you access the controller GUI using any of the following browsers:
Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 SP1 (or a later release)
Mozilla Firefox 2.0.0.11 (or a later release)
Safari 5.1.5 (or a later release)
Chrome 24.0.1312.52 m (or a later release)
Android 4.0.4 (or a later release) built-in browser
Cisco controllers support standard SNMP Management Information Base (MIB) files. MIBs can be downloaded from the Software Center on Cisco.com.
The controller software is factory installed on your controller and automatically downloaded to the access points after a release upgrade and whenever an access point joins a controller. We recommend that you install the latest software version available for maximum operational benefit.
We recommend that you install Wireless LAN Controller Field Upgrade Software (FUS) for Release 1.7.0.0-FUS first, which is a special AES package that contains several system-related component upgrades. These include the bootloader, field recovery image, and FPGA/MCU firmware. Installing the FUS image requires special attention because it installs some critical firmware. The FUS image is independent of the runtime image. For more information, see http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/wireless/controller/release/notes/fus_rn_1_7_0_0.html. Upgrade the controller image after you upgrade the FUS, as the controller reboots during the upgrade.
Ensure that you have a TFTP or FTP server available for the software upgrade. Follow these guidelines when setting up a TFTP or FTP server:
Ensure that your TFTP server supports files that are larger than the size of the controller software release 7.3.112.0. Some TFTP servers that support files of this size are tftpd32 and the TFTP server within the Prime Infrastructure. If you attempt to download the 7.3.112.0 controller software and your TFTP server does not support files of this size, the following error message appears: "TFTP failure while storing in flash."
If you are upgrading through the distribution system network port, the TFTP or FTP server can be on the same or a different subnet because the distribution system port is routable.
When you plug a controller into an AC power source, the bootup script and power-on self-test run to initialize the system. During this time, you can press Esc to display the bootloader Boot Options Menu. The menu options for the 5500 differ from the menu options for the other controller platforms.
See the Installation Guide or the Quick Start Guide for your controller for more details on running the bootup script and power-on self-test.
The controller bootloader stores a copy of the active primary image and the backup image. If the primary image becomes corrupted, you can use the bootloader to boot with the backup image.
Control which address(es) are sent in CAPWAP discovery responses when NAT is enabled on the Management Interface using the following command:
enable— Enables use of NAT IP only in a discovery response. This is the default. Use this command if all APs are outside of the NAT gateway.
disable—Enables use of both NAT IP and non-NAT IP in a discovery response. Use this command if APs are on the inside and outside of the NAT gateway; for example, Local Mode and OfficeExtend APs are on the same controller.
To avoid stranding APs, you must disable AP link latency (if enabled) before you use the disable option for the config network ap-discovery nat-ip-only command. To disable AP link latency, use the config ap link-latency disable all command.
You can configure 802.1p tagging by using the config qos dot1p-tag {bronze | silver | gold | platinum} tag. For the 7.2.103.0 and later releases, if you tag 802.1p packets, the tagging has impact only on wired packets. Wireless packets are impacted only by the maximum priority level set for QoS.
You can reduce the network downtime using the following options:
You can predownload the AP image.
For FlexConnect access points, use the FlexConnect AP upgrade feature to reduce traffic between the controller and the AP (main site and the branch). For more information about the FlexConnect AP upgrade feature, see the Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guide.
Predownloading a 7.3.112.0 version on a Cisco Aironet 1240 access point is not supported when upgrading from a previous controller release. If predownloading is attempted to a Cisco Aironet 1240 access point, an AP disconnect will occur momentarily.
Do not power down the controller or any access point during the upgrade process; otherwise, you might corrupt the software image. Upgrading a controller with a large number of access points can take as long as 30 minutes, depending on the size of your network. However, with the increased number of concurrent access point upgrades supported, the upgrade time should be significantly reduced. The access points must remain powered, and the controller must not be reset during this time.
If you want to downgrade from the 7.3.112.0 release to a 6.0 or an older release, do either of the following:
Delete all WLANs that are mapped to interface groups and create new ones.
Ensure that all WLANs are mapped to interfaces rather than interface groups.
After you perform these functions on the controller, you must reboot the controller for the changes to take effect:
Enable or disable link aggregation (LAG)
Enable a feature that is dependent on certificates (such as HTTPS and web authentication)
Add a new license or modify an existing license
Increase the priority for a license
Enable the HA
Install SSL certificate
Configure the database size
Install vendor device certificate
Download CA certificate
Upload configuration file
Install Web Authentication certificate
Changes to management or virtual interface
TCP MSS
Ensure that you apply the calibration fix for AP1260 and AP3500 models (see the resolved caveat CSCty68030). This addresses a manufacturing calibration issue on the AP1260 and AP3500 models (VID V01). For more information, see https://supportforums.cisco.com/docs/DOC-25460.
Upload your controller configuration files to a server to back them up.
We highly recommend that you back up your controller's configuration files prior to upgrading the controller software.
Follow these steps to obtain the 7.3.112.0 controller software:
Click this URL to go to the Software Center:
Choose Wireless from the center selection window.
Click Wireless LAN Controllers.
Integrated Controllers and Controller Modules
Standalone Controllers
Depending on your controller platform, click one of the above options.
Click the controller model number or name. The Download Software page is displayed.
Click a controller software release. The software releases are labeled as follows to help you determine which release to download:
Early Deployment (ED)—These software releases provide new features and new hardware platform support as well as bug fixes.
Maintenance Deployment (MD)—These software releases provide bug fixes and ongoing software maintenance.
Deferred (DF)—These software releases have been deferred. We recommend that you migrate to an upgraded release.
Click a software release number.
Click the filename (filename.aes).
Click Download.
Read Cisco's End User Software License Agreement and then click Agree.
Save the file to your hard drive.
Repeat steps a. through k. to download the remaining file.
Copy the controller software file (filename.aes) to the default directory on your TFTP or FTP server.
(Optional) Disable the controller 802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n networks.
For busy networks, controllers on high utilization, or small controller platforms, we recommend that you disable the 802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n networks as a precautionary measure.
Disable any WLANs on the controller.
Choose Commands > Download File to open the Download File to Controller page.
From the File Type drop-down list, choose Code.
From the Transfer Mode drop-down list, choose TFTP or FTP.
In the IP Address text box, enter the IP address of the TFTP or FTP server.
If you are using a TFTP server, the default values of 10 retries for the Maximum Retries text field, and 6 seconds for the Timeout text field should work correctly without any adjustment. However, you can change these values if desired. To do so, enter the maximum number of times that the TFTP server attempts to download the software in the Maximum Retries text box and the amount of time (in seconds) that the TFTP server attempts to download the software in the Timeout text box.
In the File Path text box, enter the directory path of the software.
In the File Name text box, enter the name of the software file (filename.aes).
If you are using an FTP server, follow these steps:
In the Server Login Username text box, enter the username to log on to the FTP server.
In the Server Login Password text box, enter the password to log on to the FTP server.
In the Server Port Number text box, enter the port number on the FTP server through which the download occurs. The default value is 21.
Click Download to download the software to the controller. A message appears indicating the status of the download.
After the download is complete, click Reboot.
If prompted to save your changes, click Save and Reboot.
Click OK to confirm your decision to reboot the controller.
After the controller reboots, repeat Step 6 to Step 17 to install the remaining file.
Reenable the WLANs.
For Cisco WiSM2 on the Catalyst switch, check the port channel and reenable the port channel if necessary.
If you have disabled the 802.11a/n and 802.11b/g/n networks in Step 4, reenable them.
To verify that the 7.3.112.0 controller software is installed on your controller, click Monitor on the controller GUI and look at the Software Version field under Controller Summary.
Paper PAKs and electronic licenses available are outlined in the respective controller datasheets.
Download the Cisco DTLS license.
Go to the Cisco Software Center at this URL:
On the Product License Registration page, choose Get New > IPS, Crypto, Other Licenses.
Under Wireless, choose Cisco Wireless Controllers (2500/5500/7500/8500/WiSM2) DTLS License.
Complete the remaining steps to generate the license file. The license file information will be sent to you in an e-mail.
Copy the license file to your TFTP server.
Install the DTLS license. You can install the license either by using the controller web GUI interface or the CLI:
To install the license using the web GUI, choose:
To install the license using the CLI, enter this command:
Download the non-LDPE software release:
Go to the Cisco Software Center at this URL:
Choose the controller model from the right selection box.
Click Wireless LAN Controller Software.
From the left navigation pane, click the software release number for which you want to install the non-LDPE software.
Choose the non-LDPE software release: AIR-X-K9-X-X.X.aes
Click Download.
Read Cisco's End User Software License Agreement and then click Agree.
Save the file to your hard drive.
Copy the controller software file (filename.aes) to the default directory on your TFTP or FTP server.
Upgrade the controller with this version by following the instructions from Step 3 through Step 22 detailed in the "Upgrading to Controller Software Release 7.3.112.0" section.
Features Not Supported on Cisco 2500 Series Controllers
Features Not Supported on WiSM2 and Cisco 5500 Series Controllers
Features Not Supported on Cisco Flex 7500 Controllers
Features Not Supported on Cisco 8500 Controllers
Features Not Supported on Cisco Wireless Controller on Cisco Services-Ready Engine
Features Not Supported on Cisco Virtual Wireless LAN Controllers
Features Not Supported on Mesh Networks
Wired guest access
Cisco 2500 Series Controller cannot be configured as a guest anchor controller. However, it can be configured as a foreign controller to tunnel guest traffic to a guest anchor controller in a DMZ.
Bandwidth contract
Service port
AppleTalk Bridging
LAG
Right to Use licensing
Multicast-to-unicast
High Availability
PMIPv6
Hierarchical Mobility
The features that are not supported on Cisco WiSM2 and Cisco 5500 Series Controllers are also not supported on Cisco 2500 Series Controllers.
Directly connected APs are supported only in Local mode.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
Port mirroring
Layer 2 access control list (ACL) support
VPN termination (such as IPsec and L2TP)
VPN passthrough option
You can replicate this functionality on a 5500 series controller by creating an open WLAN using an ACL.
Configuration of 802.3 bridging, AppleTalk, and Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Fragmented pings on any interface
Right to Use licensing
High availability for Mobility Oracle.
Static AP-manager interface
For Cisco 7500 Series controllers, it is not necessary to configure an AP-manager interface. The management interface acts like an AP-manager interface by default, and the access points can join on this interface.
L3 Roaming
VideoStream
TrustSec SXP
IPv6/Dual Stack client visibility
IPv6 client bridging and Router Advertisement Guard are supported.
Internal DHCP server
Access points in local mode
An AP associated with the controller in local mode should be converted to FlexConnect mode or Monitor mode, either manually or by enabling the autoconvert feature. On the Flex 7500 controller CLI, enable the autoconvert feature by entering the config ap autoconvert enable command.
Mesh
LAG
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
Cisco Flex 7500 Series Controller cannot be configured as a guest anchor controller. However, it can be configured as a foreign controller to tunnel guest traffic to a guest anchor controller in a DMZ.
Multicast
PMIPv6
Hierarchical Mobility
LAG
Cisco 8500 Series Controller cannot be configured as a guest anchor controller. However, it can be configured as a foreign controller to tunnel guest traffic to a guest anchor controller in a DMZ.
TrustSec SXP
Local authentication (controller acting as authentication server)
Internal DHCP server
Wired guest access
Data DTLS for locally switched clients
Hierarchical Mobility
Wired guest access
Cisco Wireless Controller on Cisco Services-Ready Engine (SRE) cannot be configured as a guest anchor controller. However, it can be configured as a foreign controller to tunnel guest traffic to a guest anchor controller in a DMZ.
Bandwidth contract
Access points in direct connect mode
Service port support
AppleTalk Bridging
LAG
Hierarchical Mobility
Data DTLS
Cisco 600 Series OfficeExtend Access Points
Wireless rate limiting (bandwidth contract)
Internal DHCP server
TrustSec SXP
Access points in local mode
Mobility/guest anchor
Multicast-unicast mode
IPv6
PMIPv6
WGB
VideoStream
High Availability
Outdoor mesh access points
Outdoor APs such as AP1552 are supported in FlexConnect mode are supported if the APs are not used in a mesh deployment.
Hierarchical Mobility
Multicountry support
Load-based CAC (mesh networks support only bandwidth-based CAC or static CAC)
High availability (fast heartbeat and primary discovery join timer)
AP acting as supplicant with EAP-FASTv1 and 802.1X authentication
Access point join priority (mesh access points have a fixed priority)
Location-based services
Commands are in boldface type.
Product names and acronyms might be standardized.
Spelling errors and typos might be corrected.
If you are a registered cisco.com user, view Bug Toolkit on cisco.com at the following website:
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030
Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source. Statement 10
Do not operate the unit near unshielded blasting caps or in an explosive environment unless the device has been modified to be especially qualified for such use. Statement 364
In order to comply with radio frequency (RF) exposure limits, the antennas for this product should be positioned no less than 6.56 ft. (2 m) from your body or nearby persons. Statement 339
If you are installing an antenna for the first time, for your own safety as well as others, seek professional assistance. Your Cisco sales representative can explain which mounting method to use for the size and type of antenna you are about to install.
Select your installation site with safety as well as performance in mind. Electric power lines and phone lines look alike. For your safety, assume that any overhead line can kill you.
Call your electric power company. Tell them your plans and ask them to come look at your proposed installation. This is a small inconvenience considering your life is at stake.
Plan your installation carefully and completely before you begin. Successfully raising a mast or tower is largely a matter of coordination. Each person should be assigned to a specific task and should know what to do and when to do it. One person should be in charge of the operation to issue instructions and watch for signs of trouble.
When installing an antenna, remember:
Do not use a metal ladder.
Do not work on a wet or windy day.
Do dress properly—shoes with rubber soles and heels, rubber gloves, long-sleeved shirt or jacket.
If the assembly starts to drop, get away from it and let it fall. Remember that the antenna, mast, cable, and metal guy wires are all excellent conductors of electrical current. Even the slightest touch of any of these parts to a power line completes an electrical path through the antenna and the installer: you!
If any part of an antenna system should come in contact with a power line, do not touch it or try to remove it yourself. Call your local power company. They will remove it safely.
If an accident should occur with the power lines, call for qualified emergency help immediately.
To meet regulatory restrictions, all external antenna configurations must be installed by experts.
The quick start guide or installation guide for your particular controller or access point
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Configuration Guides
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Command References
Cisco Wireless LAN Controller System Message Guide