Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
System Context for the Lawful Intercept Feature
Installing the Lawful Intercept Feature
Provisioning the Cisco PGW to Use the LI Feature
Provisioning (for the Service Provider)
Adding a Wiretap Entry (For the Mediation Device)
Provisioning the Cisco PGW 2200 Components (for Service Provider users)
Retrieving Signal Path Status and Parameters
Retrieving IP Link Status and Parameters
MML Provisioning to Add the LI Mediation Device
MML Provisioning to Configure a Wiretap Entry
Examples of Wiretapping Error Conditions
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
Lawful Intercept Feature
Revised September 28, 2009, OL-12889-04
Feature History
This document describes the LI feature on the Cisco PGW 2200 and LI Mediation devices.
The Lawful Intercept Feature (LI) is described in the following sections:
•
Installing the Lawful Intercept Feature
•
Provisioning the Cisco PGW to Use the LI Feature
•
Examples of Wiretapping Error Conditions
•
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
Feature Overview
The LI feature on the Cisco PGW 2200 allows personnel authorized by a Law Enforcement Agency (LEA) to intercept data from targeted calls and send the call data to an LI Mediation Device.
Lawful Intercept on Cisco PGW 2200 works within the architecture of the Cisco Service Independent Intercept (SII). This document describes the high-level architecture of Lawful Intercept in the Cisco PGW 2200 based on Packet Cable Electronic Surveillance Specification and Packet Cable Event Message Specification.
A unique login ID is used to set up a subscriber number for intercept or wiretap using MML. If your site is properly authorized, SSH can be used for provisioning the system.
When a call involving this number (called, calling or forwarding) is made, the Cisco PGW 2200 collects the call data pertaining to this number and sends it to the Mediation Device over a RADIUS interface. Part of this data also contains the address of the voice gateway (if available) that will be responsible for sending the call content to the Mediation Device. The Mediation Device is responsible for setting up interception on this gateway to get the call content. Interception of this number remains enabled in the Cisco PGW 2200 unless a request for cancellation is received.
Note
Only one Mediation Device is available for each Cisco PGW 2200 node.
The Cisco PGW 2200 provides a configuration to support two kinds of surveillance:
•
Call Data Type—Signaling information for incoming and outgoing calls.
•
Call Content Type—Signaling information and media stream report for incoming and outgoing calls.
The signaling or call data is sent to the Mediation Device for each type of surveillance. The types of signaling and call data include:
•
For completed calls originating/terminating from/to a surveillance subject under a Pen Register and Trap and Trace surveillance order (Call Data Type), three call-identifying messages are generated for delivery to a Mediation Device: Signaling_Start, Call_Answer, and Call_Disconnect.
•
For completed calls originating/terminating from/to a subject under a Communication Intercept order (Call Content Type), five call-identifying messages are generated for delivery to Mediation Device: Signaling_Start, Qos_Reserve, Call_Answer, Qos_Release, and Call_Disconnect.
•
For failed or abandoned call attempts when dialing information is presented to the Call Agent, a Signaling_Start message is generated for delivery to the Mediation Device.
•
The QoS_Commit or QoS_Change event messages are not currently supported by the Cisco PGW 2200. For call services including LNP and 800 number calls, Mid-Call Codec changes, or when SDP information is unavailable when sending messages to the Mediation Device, a Qos_Reserve and Qos_Release message are sent to update the Mediation Device with the new information.
•
For H.323 to H.323 calls, the Cisco PGW 2200 does not receive any SDP information. QOS messages are not generated for this call.
•
For H.323 Slow Start Originated calls, the upstream SDP is available after the call is answered. There might be a scenario where the call terminates or switches over before the Cisco PGW 2200 receives the SDP information. In this case, Call Content Type messages are not generated.
•
The Cisco PGW 2200 prioritizes calls based on the originating number. Calls between two target subscribers are not prioritized above calls from a target subscriber to a non-target number.
•
When a call is forwarded by an external entity such as SIP-UA to another subscriber on the Cisco PGW, two sets of packet cable event messages are sent to the Mediation Device. One set of messages is for the original call through the Cisco PGW and the second set is for the forwarded call through Cisco PGW.
•
The Cisco PGW 2200 Softswitch inserts the intercepted calling party number into the calling party field of a signaling start message. The Cisco PGW 2200 Softswitch also inserts the intercepted called party number into the called party field of the signaling start message.
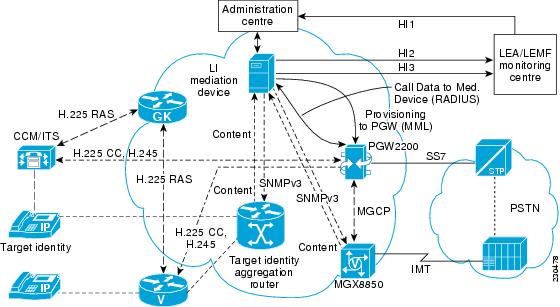
System Context for the Lawful Intercept Feature
The following figure illustrates how the Cisco PGW 2200 fits into the Cisco Service Independent Intercept (SII) architecture.
Figure 1 PGW 2200 in Cisco Service Independent Intercept (SII) Architecture
Cisco SII dissociates call content requests from the signaling architecture. This is done by having the LI Mediation Device make call content requests through the SNMPV3 from the voice gateway.
When a call is made on the Cisco PGW 2200 that matches a trunk group, full number, or partial number on the target list, the PGW sends the call data to the LI Mediation Device. The LI Mediation Device is triggered when it receives the call data from the PGW.
The external interfaces implemented for this feature are the ones between the PGW 2200 and the LI Mediation Device. There are two interfaces between these two entities—Provisioning Interface and RADIUS interface.
MML Interface
All commands to be used by the LI Mediation Device require using the user ID liusr. Anyone logged in with this user ID cannot operate any other MML commands. Any authorized person logging in to the Cisco PGW 2200 using the liusr user ID (via Mediation Device) can do so either through a regular Telnet session or, if available, through a session using SSH.
Supported Platforms
The hardware platforms supported for the Cisco MGC, BAMS, and HSI software are described in the Cisco MGC Software Release 9.7 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Note
Cisco PGW 2200 consists of platforms that run the Cisco Media Gateway Controller (MGC) software, Billing and Measurements Server (BAMS), and H.323 Signaling Interface (HSI).
The Cisco PGW 2200 also supports the following media gateways which can be used with call content LI:
•
Cisco AS5350XM, AS5400XM, and AS5850 Series Universal Gateways
•
Cisco MGX 8000 Voice Gateway (VISM-PR) and MGX 8880 Voice Gateway (Cisco VXSM),
•
Cisco 2651XM, 2691XM, 36xx, 37xx Series Routers
•
Cisco 1721 1751, 1751v, 1761, 1761v, and 2612 Routers (BRI backhaul)
•
Cisco 2691 Router (PRI/Q.931 backhaul for call agents)
For more information on supported Media Gateways, refer to the Release Notes for the Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9.7.
Feature Requirements
To implement this feature, your system must have the following:
•
Cisco MGC software release 9.7, Service Patch 5 or higher
CautionIf you install the LI feature on Service Patch 5 and choose to downgrade to an earlier Service Patch number, you must delete all subscriber, partial and trunk group wiretap entries using the wiretap-dlt:subscriber:"all" MML command.
•
Main Memory Database (MMDB)
•
MMDB replication enabled
Related Documents
This document contains information about the Cisco PGW 2200, BAMS, and HSI Security Enhancements feature. The following documents contain additional information about the Cisco PGW 2200, BAMS, and HSI:
•
Release notes for Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9.7
•
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Hardware Installation Guide
•
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Media Gateway Controller
•
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9.7 Installation and Configuration Guide
•
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Provisioning Guide
•
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Dial Plan Guide
•
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 MML Command Reference Guide
•
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Messages Reference Guide
•
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Billing Interface Guide
•
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 MIB Guide
•
Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Operations, Maintenance, and Troubleshooting Guide
•
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server (BAMS), Release 3.x
•
H.323 Signaling Interface Guide
Installing the Lawful Intercept Feature
To enable the Cisco PGW to process LI requests and commands, you must run the LI installation script on both the active and standby Cisco PGW systems. The LI installation script is located in the directory /opt/CiscoMGC/local/.create_liusr. This script performs the following:
•
Verifies that a liusr user ID has been created on the PGW.
•
If liusr user ID does not exist, then create it and set up directories for it under /opt/CiscoMGC/local/.liusr. The ".cshrc" file from /opt/CiscoMGC/local is copied to the liusr home directory to set up an environment appropriate for running MML. This user will be part of new LI user group called ligrp.
•
When you use the liusr user ID for the first time, the system prompts for a password.
•
Any time you log in successfully using the liusr user ID, you are either taken into an MML session if PGW is running or your login fails if PGW is not running. When the you exit the MML session, you are logged out.
Step 1
On the active Cisco MGC host log in as root.
Step 2
Go to the opt/CiscoMGC.
Step 3
Run the replication_status.sh script in /opt/CiscoMGC/local. This script indicates whether the Times Ten replication is turned on.
Note
Run the setup_replication.sh script in /opt/CiscoMGC/local if replication is not turned on.
Provisioning the Cisco PGW to Use the LI Feature
There are two different types of commands that you can use to interact with the Cisco PGW 2200 when implementing the LI features. The first set of commands are used by the service provider organization to provision the Cisco PGW to be able to handle lawful intercept or wiretap. These provisioning commands involve adding LI sigpaths and IP links.
The second set of commands is used by someone authorized by the LEA to add, modify, delete and retrieve wiretapped numbers.
Provisioning (for the Service Provider)
To provision the system from the service provider organization:
Step 1
Provision the Cisco PGW 2200 with the IP addresses of the Mediation Device(s) that it will contact for call interception.
Step 2
Edit the XECfgParm.dat file and set the LISupport variable to enable. The default value is *.LISupport=disable. For more information about how to update the XECfgParm.dat file, refer to the Cisco MGC Software Release 9.7 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Step 3
Provision the LI Mediation Device Communication Path.
Note
Provision a wiretap Channel Controller and associated IP Link before adding wiretap entries. Do not use the user ID meant for controlling wiretap entries (liusr).
Step 4
Use the prov-add command to add the LI Mediation Device as an external node.
To establish a provisioning session with the PGW, use the prov-sta command. After entering the command, use the prov-copy or prov-dply command to activate the new configuration. For further information, refer to the MML provisioning guide.
prov-add:EXTNODE:NAME="LI_node_name", TYPE="LIMD", DESC="description"Step 5
Type the following command to add the LI Mediation Device Signal Path:
prov-add:LIPATH:NAME="SigPath_Name", DESC="description", EXTNODE="LI_node_name"Step 6
Use the IPLNK command to add the LI Mediation Device IP Link and press Enter. This command defines an IP link to the LI Mediation Device and associates an LI SigPath to the IP link.
prov-add:IPLNK:NAME="link_name", DESC="description", SVC="SigPath_Name", IPADDR="local_IP_address", PORT="local_port_number", PEERADDR="LI_IP_address", PEERPORT="LI_port_number", PRI="1"The local_address and local_port are parameters in the existing Cisco PGW 2200 two-way communications IP link object. In this case, the LI Channel Controller does not use the local_port, thus the local port value is ignored.
Use the prov-dlt command to delete the above sigpaths and IP links.
Adding a Wiretap Entry (For the Mediation Device)
You must be an authorized LI user and logged in as liusr to add a wiretap entry. Type one of the following commands and press Enter to add a wiretap entry:
•
To add a wiretap for an individual number:
wiretap-add:subscriber:number="target_number", type="tap_type", cdc_ip="cdc_address", cdc_port="cdc_port", ccc_ip="ccc_address", ccc_port="ccc_port"•
To add a wiretap entry for a trunk group ID:
wiretap-add:trunkgroup:name="trunk_group_name", type="tap_type", cdc_ip="cdc_address", cdc_port="cdc_port", ccc_ip="ccc_address", ccc_port="ccc_port"•
To add a wiretap based on a partial number:
wiretap-add:partialnumber:number="partial_number", type="tap-type", cdc_ip="cdc_address", cdc_port="cdc_port", ccc_ip="ccc_address", ccc_port="ccc_port"Where:
•
cdc—call data channel
•
ccc—call content channel
•
type—can have one of two values: calldata or callcontent. callcontent includes both call data and call content. calldata results in only call data being sent to the mediation device.
•
target_number—The number to be wiretapped. The number cannot contain dashes, special characters or spaces (ex: "7034843000").
•
ccc_ip and cc_port—optional parameters that are ignored by the Cisco PGW 2200.
•
trunk_group_name—The group number of the trunk to be wiretapped. This must be a number between 1 and 9999.
•
partial_number—a partial number to be wiretapped. The number cannot contain dashes, special characters or spaces (ex: "7034843000"). The Cisco PGW 2200 Softswitch uses this partial number to match the beginning of the number. If there is a match, the call will be wiretapped.
Note
Only one mediation device per PGW is supported. Hence only type of wiretap can be edited from an existing entry in the data store.
Editing a Wiretap Entry
To edit an existing wiretap entry, type one of the following commands and press Enter:
•
To change wiretap trunk group id entry:
wiretap-ed:trunk_group_name=target_number, type=tap_type•
To change a wiretap target number:
wiretap-ed:subscriber:number=target_number, type=tap_type•
To change wiretap partial number entry:
wiretap-ed:partial_number=target_number, type=tap_typeRetrieving a Wiretap Entry
To retrieve an existing wiretap entry, type one of the following commands and press Enter:
•
To retrieve a single wiretap entry:
wiretap-rtrv:subscriber:number=target_number•
To retrieve all provisioned wiretap subscriber entries:
wiretap-rtrv:subscriber:"all"•
To retrieve a single wiretap entry trunk group id:
wiretap-rtrv:trunkgroup:name=target_number•
To retrieve all existing wiretap trunk group entries:
wiretap-rtrv:trunkgroup:"all"•
To retrieve an existing wiretap partial number entry:
wiretap-rtrv:partialnumber:number=target_number•
To retrieve all existing wiretap partial number entries:
wiretap-rtrv:partialnumber:"all"Removing a Wiretap Entry
To remove an existing wiretap entry, type one of the following commands and Enter:
•
To remove an existing wiretap subscriber entry:
wiretap-dlt:subscriber:number=target_number•
To remove all existing wiretap subscriber entries:
wiretap-dlt:subscriber:"all"•
To remove a single wiretap trunk group id:
wiretap-dlt:trunkgroup:name=target_number•
To remove all existing wiretap trunk group entries:
wiretap-dlt:trunkgroup:"all"•
To remove an existing wiretap partial number entry:
wiretap-dlt:partialnumber:number=target_number•
To remove all existing wiretap partial number entries:
wiretap-dlt:partialnumber:"all"Provisioning the Cisco PGW 2200 Components (for Service Provider users)
Retrieving Signal Path Status and Parameters
To show the status and parameters of one or all configured signal-paths, type one of the following commands and press Enter:
•
To show the status and parameters of a single signal path:
rtrv-dest:SigPath-name•
To show the status and parameters of all single paths:
rtrv-dest:"all"
Note
The signal path of the LI device will not be displayed in this list of destinations.
Note
This command is restricted to users logged in as mgcusr.
Retrieving IP Link Status and Parameters
To show the status and configured parameters of one or more IP links, type one of the following commands and press Enter:
•
To show the status and parameters of a single IP link:
rtrv-iplnk:link_name
•
To show the status and parameters of all configured IP links:
rtrv-iplnk:"all"
Note
LI IP links will not be displayed in this list of links.
RADIUS Interface
The RADIUS interface is used to send the required call data to the LI Mediation Device. As the name suggests, a RADIUS stack is used by the I/O Channel Controller to send this information. This interface implements a retry mechanism in case of failure to send data successfully to the Mediation Device. An alarm is raised if the retry mechanism fails.
Alarms
When the PGW fails to successfully send any call data over the RADIUS interface to the Mediation Device it will retry "retryCount" times. If none of these attempts succeed, the Cisco PGW 2200 raises an alarm to indicate failure.
Provisioning Examples
MML Provisioning to Add the LI Mediation Device
The following are the steps to provision the LI Mediation Device on the Cisco PGW 2200. This example shows how to provision a LI Mediation Device that utilizes IP address 10.82.80.30 and UDP port 2047. For further details, refer to the Cisco Media Gateway Controller Software Release 9 Provisioning Guide
Note
If the PGW and the LI Mediation Device are not in the same network, you must also provision an IPROUTE to the remote network.
Prov-add:EXTNODE:NAME="LI_node_name", TYPE="LIMD", DESC="LI Mediation Device"Prov-add:LIPATH:NAME="lipath", DESC="SigPath to the LI", EXTNODE="LI_node_name"Prov-add:IPLNK:NAME="lilink", DESC="IP link to the LI", SVC="lipath", IPADDR="IP_addr1", PORT="1813", PEERADDR="10.82.80.30", PEERPORT="1813"MML Provisioning to Configure a Wiretap Entry
Only one MML session per LI user is allowed at any time to log in to the Cisco PGW 2200.
The following steps show how to add, retrieve, then delete a wiretap entry. In this example, the wiretap Call Data is sent to the LI Mediation Device at IP address 10.82.80.30, and port number 2047 (which was configured as an IP Link to an External Node of type LI). The command wiretap-rtrv is used to retrieve one entry or all wiretap entries from the PGW 2200. These examples show successful completion of MML wiretap commands.
¢ wiretap-add:subscriber:number="7035551234", type="calldata", cdc_ip="10.82.80.30", cdc_port="1813"MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM COMPLD"SUBSCRIBER";¢ wiretap-rtrv:subscriber:"all"MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:27.872 ESTM RTRV"SUBSCRIBER"number=7035551234,type=calldata,cdc_ip=10.82.80.30,cdc_port=1813,ccc_ip=10.82.81.30,ccc_port=1814number=7035551235,type=calldata,cdc_ip=10.82.80.30,cdc_port=1813,ccc_ip=10.82.81.30,ccc_port=1814;¢ wiretap-rtrv:subscriber:number="7035551234"MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:27.872 ESTM RTRV"SUBSCRIBER"number=7035551234,type=calldata,cdc_ip=10.82.80.30,cdc_port=2047,ccc_ip=10.82.81.30,ccc_po rt=2048;¢ wiretap-dlt:subscriber:number="7035551234"MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:45.274 ESTM COMPLD"SUBSCRIBER";Examples of Wiretapping Error Conditions
The following are examples of error messages for wiretap commands in MML:
Adding a Wiretap
A wiretap for the number being added already exists:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIDNV"7035551234 already exists"/* Input, Data Not Valid */;The IP address being added is not yet provisioned on the Cisco PGW 2200:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIDNV"10.82.80.30"/* Input, Data Not Valid */;The Port number being added is not yet provisioned on the Cisco PGW 2200:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIDNV"1813"/* Input, Data Not Valid */;The wiretap type is not valid:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIDNV"CALLHOME"/* Input, Data Not Valid */;If a target other than SUBSCRIBER is used:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIITA /* Input, Invalid Target */;One of the required parameters is missing:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIPRM"TYPE"/* Input, Parameter Missing */;Incorrect syntax.MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIISP /* Input, Syntax Error */;Database error:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYSDBE /* Status, Internal Database Error */;Editing Wiretaps
The given number does not exist:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIDNV"7035551234 does not exist"/* Input, Data Not Valid */;The IP address being edited is not yet provisioned on the Cisco PGW 2200:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYSNSP"10.82.80.31"/* Status, Operation Not Supported By Component */;The value of the tap type is incorrect:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIDNV"CALLHOME"/* Input, Data Not Valid */;A target other than SUBSCRIBER is being used:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIITA /* Input, Invalid Target */;
One of the required parameters is missing:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIPRM"TYPE"/* Input, Parameter Missing */;Incorrect syntax:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIISP /* Input, Syntax Error */;Data store error:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYSDBE /* Status, Internal Database Error */;Removing Wiretap Errors
Number does not exist in PGW database:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIDNV"7035551234 does not exist"/* Input, Data Not Valid */;A target other than SUBSCRIBER is being used:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIITA /* Input, Invalid Target */;One of the required parameters is missing:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIPRM"TYPE"/* Input, Parameter Missing */;Incorrect syntax:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYIISP /* Input, Syntax Error */;Data store error:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM DENYSDBE /* Status, Internal Database Error */;Retrieving Wiretap Errors
The number does not exist in the PGW database:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM RTRVIDNV"7035551234 does not exist"/* Input, Data Not Valid */;A target other than SUBSCRIBER is being used:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM RTRVIITA /* Input, Invalid Target */;One of the required parameters is missing:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM RTRVIPRM"TYPE"/* Input, Parameter Missing */;Incorrect syntax:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM RTRVIISP /* Input, Syntax Error */;Database error:
MGC-01 - Media Gateway Controller 2003-02-12 15:44:25.874 ESTM RTRVSDBE /* Status, Internal Database Error */;Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
For information on obtaining documentation, obtaining support, providing documentation feedback, security guidelines, and also recommended aliases and general Cisco documents, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
CCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, the Cisco logo, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn and Cisco Store are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0807R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.