-
Cisco Unified CallManager System Guide, Release 5.0(4)
-
Index
-
Preface
-
Introduction
-
Cisco Unified Communications Overview
-
System Configuration Overview
-
Roles and User Groups
-
System-Level Configuration Settings
-
Clustering (Revised 12/05/2006)
-
Redundancy
-
Call Admission Control
-
Resource Reservation Protocol
-
Cisco TFTP (Revised 12/11/06)
-
Device Support
-
Autoregistration
-
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
-
Licensing
-
Partitions and Calling Search Spaces
-
Time-of-Day Routing
-
Understanding Route Plans (Revised 09/13/2006)
-
Understanding Directory Numbers
-
Dial Rules Overview
-
Understanding the Directory
-
Application Users and End Users
-
Media Resource Management
-
Annunciator
-
Conference Bridges (Revised 01/29/2007)
-
Transcoders
-
Music On Hold
-
Media Termination Points (Revised 08/29/2006)
-
Cisco DSP Resources for Transcoding, Conferencing, and MTP
-
Voice Mail Connectivity to Cisco Unified CallManager
-
SMDI Voice Mail Integration (Revised 12/11/2006)
-
Cisco Unity Messaging Integration
-
Cisco DPA Integration
-
Call Park
-
Call Pickup Group
-
Cisco Unified IP Phone Services
-
Cisco Extension Mobility and Phone Login Features
-
Cisco Unified CallManager Attendant Console
-
Cisco Unified CallManager Assistant
-
Understanding Cisco Unified CallManager Voice Gateways (Revised 09/19/06)
-
Understanding IP Telephony Protocols
-
Understanding Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) (Revised 09/22/2006)
-
Understanding Cisco Unified CallManager Trunk Types
-
Cisco Unified IP Phones
-
Understanding Video Telephony
-
Computer Telephony Integration
-
Cisco ATA 186
-
Administrative Tools Overview
-
Table Of Contents
Cisco Unity Messaging Integration
Cisco Unified CallManager SIP Trunk Integration
Cisco Unity Cisco Unified CallManager Integrated Mailbox Configuration
Cisco Unity Configuration Checklist
Where to Find More Information
Cisco Unity Messaging Integration
Cisco Unity comprises a communications solution that delivers voice messaging and unified messaging in a unified environment.
Unified messaging means that users can manage all message types from the same Inbox. Cisco Unity works in concert with an Exchange server or (for Cisco Unity 4.0 and later) a Domino server to collect and store all messages—both voice and e-mail—in one message facility. Users can then access voice and e-mail messages on a computer, through a touchtone phone, or over the Internet.
For complete, step-by-step instructions on how to integrate Cisco Unified CallManager with the Cisco Unity messaging system, refer to the Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity.
Note
For information on how to integrate Cisco Unified CallManager with the Cisco Unity Connection messaging system, refer to the Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 SCCP Integration Guide for Cisco Unity Connection 1.1 or the Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 SIP Trunk Integration Guide for Cisco Unity Connection 1.1.
This section covers the following topics:
•
Cisco Unity Cisco Unified CallManager Integrated Mailbox Configuration
•
Cisco Unity Configuration Checklist
•
Where to Find More Information
System Requirements
The following lists provide requirements for your phone system and the Cisco Unity server. For specific version information, refer to the Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity.
Phone System
•
A Cisco Unified Communications applications server that consists of Cisco Unified CallManager software that is running on a Cisco Media Convergence Server (MCS) or customer-provided server that meets approved Cisco configuration standards
•
Cisco licenses for all phone lines, IP phones, and other H.323-compliant devices or software (such as Cisco Virtual Phone and Microsoft NetMeeting clients) that will be connected to the network, as well as one license for each Cisco Unity port
•
IP phones for the Cisco Unified CallManager extensions
•
A LAN connection in each location where you will plug an IP phone into the network
•
For multiple Cisco Unified CallManager clusters, subscribers can dial an extension on another Cisco Unified CallManager cluster without having to dial a trunk access code or prefix.
Cisco Unity Server
•
Cisco Unity system that was installed and made ready for the integration as described in the Cisco Unity Installation Guide.
•
The applicable Cisco Unity-CM TSP installed. For more information on compatible versions of the TSP, refer to the Compatibility Matrix: Cisco Unity Connection, the Cisco Unity-CM TSP, and the Cisco Unified CallManager Express documentation.
•
A license that enables the appropriate number of voice-messaging ports.
Integration Description
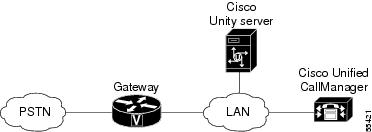
The integration uses the LAN to connect Cisco Unity and Cisco Unified CallManager. The gateway provides connections to the PSTN. Figure 31-1 shows the connections.
Figure 31-1 Connections Between the Phone System and Cisco Unity
Note
The following example applies only if the caller goes through the Cisco Unity Auto Attendant. Most other calls are routed directly to the correct voice mailbox. For example, callers who call a subscriber and get forwarded to voice mail go directly to the voice mailbox and can record a voice message. Subscribers who call in to check their voice messages from their own phones, go directly to their voice mailbox and can listen to voice messages.
1.
When an external call arrives, the Cisco gateway sends the call over the LAN to the machine on which Cisco Unified CallManager is installed.
2.
For Cisco Unified CallManager lines that are configured to route calls to Cisco Unity, Cisco Unified CallManager routes the call to an available Cisco Unity extension.
3.
Cisco Unity answers the call and plays the opening greeting.
4.
During the opening greeting, the caller enters either the name of a subscriber or an extension; for example, 1234.
5.
Cisco Unity notifies Cisco Unified CallManager that it has a call for extension 1234.
6.
At this point, the path of the call depends on whether Cisco Unity is set up to perform supervised transfers or release transfers. Refer to the Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity 4.0 for more information.
Cisco Unified CallManager SIP Trunk Integration
Cisco Unity Connection 1.1 supports a SIP trunk integration with the Cisco Unified CallManager phone system when the Cisco Unified CallManager phone system has only SIP phones. Refer to the Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 SIP Trunk Integration Guide for Cisco Unity Connection for more detailed information. The following list describes a few tips that should be performed from the Cisco Unified CallManager Administration side when integrating the Cisco Unified CallManager phone system with Cisco Unity Connection by a SIP trunk:
•
Create a SIP trunk that points to Cisco Unity 4.2 and ensure that "Redirecting Number IE Delivery - Outbound" is checked. This instructs Cisco Unified CallManager to send the Diversion Header to Cisco Unity, so you access the correct voice mailbox. Refer to "Trunk Configuration" in the Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide.
Note
Cisco Unified CallManager SIP trunk integration applies to MWI. When you configure the SIP trunk security profile for the SIP voice-messaging trunk, check "Accept Unsolicited Notification." This ensures that MWI will operate properly. You must enable "Accept Header Replacement" if you want to support transfers. This allows "REFER w/replaces" to be passed, which is used for Cisco Unity-initiated, supervised transfers.
•
Assure that your phones support DTMF Relay as per RFC-2833. Cisco Unity will support both OOB and RFC-2833. For more information on compatible versions of the TSP, refer to the Compatibility Matrix: Cisco Unity Connection, the Cisco Unity-CM TSP, and the Cisco Unified CallManager Express documentation.
•
Define a route pattern (for example, 7555) and point that route pattern to the SIP trunk to Cisco Unity. Refer to "Route Pattern Configuration" in the Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide.
•
Define a voice mail pilot (for example, 7555). Refer to "Cisco Voice-Mail Pilot Configuration" in the Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide.
•
Define a voice mail profile (for example, VM Profile 1) with the voice mail pilot that you defined in the previous step. Refer to "Voice-Mail Profile Configuration" in the Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide.
Note
Make the voice mail profile that you defined in the last step the system default.
Cisco Unity Cisco Unified CallManager Integrated Mailbox Configuration
When Cisco Unified CallManager release 5.0 integrates with Cisco Unity version 4.0(4) (or later) with Microsoft Exchange, Cisco Unified CallManager administrators can create Cisco Unity subscriber voice mailboxes, one at a time, from the Directory Number Configuration or End User Configuration windows.
Note
For information on Cisco Unified CallManager integration with Cisco Unity Connection, refer to the Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 SCCP Integration Guide for Cisco Unity Connection 1.1 or the Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 SIP Trunk Integration Guide for Cisco Unity Connection 1.1.
Requirements
•
Cisco Unified CallManager release 5.0(x)
•
Cisco Unity release 4.0(4) or later with Microsoft Exchange
•
Cisco Unified CallManager Integrated Voice Mailbox asp page (installed on the Cisco Unified CallManager server from the Cisco Unity server)
•
RIS Data Collector service that is activated on Cisco Unified CallManager server
Restrictions
•
After a mailbox is created, no automatic synchronization of mailbox data happens between Cisco Unity and Cisco Unified CallManager. All changes get synchronized manually on both systems.
•
The system does not support creation of Internet, VPIM, AMIS, Bridge, or Domino subscriber mailboxes from Cisco Unified CallManager Administration.
•
The system does not support bulk or batch import of Cisco Unity mailboxes by using the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT).
•
Creation of Cisco Unity mailbox creates a Cisco Unity subscriber account directly in SQL, so new subscribers can be viewed and updated on the Cisco Unity Administrator when the create mailbox transaction completes.
•
A log file records Cisco Unity mailbox transactions that are made by using Cisco Unified CallManager Administration on the Cisco Unity server.
•
The system writes associated diagnostic logs to a log file.
•
Audit log and diagnostic files do not record the transmission of credentials across the network.
Securing the Voice-Mail Port
When you configure security for Cisco Unified CallManager voice mail ports and Cisco Unity SCCP devices, a TLS connection (handshake) opens for authenticated devices after each device accepts the certificate of the other device; likewise, the system sends SRTP streams between devices; that is, if you configure the devices for encryption.
When the device security mode equals authenticated or encrypted, the Cisco Unity-Unified CMTSP connects to Cisco Unified CallManager through the Cisco Unified CallManager TLS port. When the security mode equals non-secure, the Cisco Unity TSP connects to Cisco Unified CallManager through the Cisco Unified CallManager port.
For interactions, restrictions, and procedures on how to configure security, refer to the Cisco Unified CallManager Security Guide.
Cisco Unity Configuration Checklist
Table 31-1 provides steps to configure the Cisco Unity voice-messaging system.
Table 31-1 Cisco Unity Configuration Checklist
Step 1
Ensure that you have met the system requirements for Cisco Unified CallManager and Cisco Unity.
Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity
Step 2
Add voice-mail ports (directory numbers) for each port that you are connecting to Cisco Unity.
Cisco Voice-Mail Port Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity
Step 3
Add a voice-mail pilot number for the voice-mail ports.
Cisco Voice-Mail Pilot Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity
Step 4
Specify MWI and voice-mail extensions.
Service Parameters Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
Message Waiting Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity
Step 5
Add the Voice Mail Port DNs to a line group.
Configuring a Line Group, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration
Step 6
Add the line group that contains the Voice Mail Port DNs to a hunt list.
Adding a Route List, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration
Step 7
Associate the hunt list that contains the line group with a hunt pilot.
Note
The hunt pilot must match the voice-mail pilot that is configured and used by the voice-mail profiles.
Configuring a Route Pattern, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
Step 8
Set up the voice-mail pilot number.
Cisco Voice-Mail Pilot Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
Step 9
Set up the voice-mail profile.
Voice-Mail Profile Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
Cisco Unified CallManager Integration Guide for Cisco Unity
Step 10
Set up the voice-mail service parameters.
Service Parameters Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide.
Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity
Step 11
Enable the DTMF relay feature in the gateways.
Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity
Step 12
Install, configure, and test the TAPI service provider [for Cisco Unity 3.1(x) and earlier].
Step 13
Configure Cisco Unity for the integration [for Cisco Unity 3.1(x) and earlier].
For multiple clusters of Cisco Unified CallManager, set up MWI ports.
Create a new integration between Cisco Unity and Cisco Unified CallManager.
Message Waiting Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
Step 14
Set up Cisco Unified CallManager authentication and encryption (Cisco Unity 4.0(5) and later).
Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity
Cisco Unified CallManager Security Guide
Step 15
Test the integration.
Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity
Cisco Unity Troubleshooting Guide
Refer to the installation guide for the phone system.
Step 16
Integrate the secondary server for Cisco Unity failover (use when Cisco Unity failover is installed).
Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity
Cisco Unity Failover Guide
Step 17
Configure an application user.
Note
You must use the same user name and password that you defined in Cisco Unity Administrator.
Application User Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
Cisco Unified CallManager Installation Guide for Cisco Unity
Step 18
Choose the auto-generated Cisco Unity server in the Application Server Configuration window in Cisco Unified CallManager Administration.
Note
For application user, choose the application user you created in Step 17.
Application Server Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
Step 19
If using Cisco Unified CallManager Administration to configure voice mail subscribers, perform the following steps [requires Cisco Unity 4.0(4) or later]:
•
Copy the voicemailbox.asp file to the Cisco Unified CallManager server.
•
Set up the Cisco Unity Cisco Unified CallManager Integrated Mailbox Configuration administrator account. (You must perform this step for the failover server if subscribers will be created on the failover server.)
•
Create a Cisco Unity voice mailbox.
Note
You must configure both Cisco Unity and Cisco Unified CallManager Administration (for example, set up Cisco Unity voice mailbox templates, Cisco Unified CallManager dial plans) to create voice mailboxes.
Cisco Unified CallManager Installation Guide for Cisco Unity
Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity
Directory Number Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
End User Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
Where to Find More Information
Additional Cisco Documentation
•
Cisco Voice-Mail Port Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
•
Service Parameters Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
•
Directory Number Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
•
End User Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
•
Application User Configuration, Cisco Unified CallManager Administration Guide
•
Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 Integration Guide for Cisco Unity
•
Cisco Unified CallManager 5.0 SIP Trunk Integration Guide for Cisco Unity Connection
•
Cisco Unity Installation Guide
•
Cisco Unity Troubleshooting Guide

 Feedback
Feedback