Table Of Contents
RAID Controller Considerations
Supported RAID Controllers and Required Cables
Mixing Drive Types in RAID Groups
Factory-Default Option ROM Settings
Notes on Supported Embedded MegaRAID Levels
Installing a SCU Upgrade ROM Module For Embedded RAID SAS Support
Installing a Software RAID Key Module for Embedded RAID 5 Support
Enabling the Embedded RAID Controller in the BIOS
Disabling the Embedded RAID Controller in the BIOS
Launching the LSI Embedded RAID Configuration Utility
Installing LSI MegaSR Drivers For Windows and Linux
Downloading the LSI MegaSR Drivers
Microsoft Windows Driver Installation
Backplane and Expander Options
Restoring RAID Configuration After Replacing a RAID Controller
RAID Controller Considerations
This appendix contains the following sections:
•
Supported RAID Controllers and Required Cables
•
Factory-Default Option ROM Settings
•
Mixing Drive Types in RAID Groups
•
Restoring RAID Configuration After Replacing a RAID Controller
Supported RAID Controllers and Required Cables
This server supports the RAID controller options and cable requirements shown in Table C-1 for small form factor drives and Table C-2 for large form factor drives.
CautionDo not mix controller types in the server. Do not use the embedded MegaRAID controller and a hardware RAID controller card at the same time. This is not supported and could result in data loss.
Table C-1 Cisco UCS C220 M3 Small Form Factor Drives RAID Options
Onboard
4 SATA or
8 SAS
internal3No
0, 1, 54 , 10
4 drives:
1 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE15 )
8 drives:
2 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
PID UCSC-RAID-MZ-C220
Mezzanine
8 internal
No
0, 1, 1E, 10
4 drives:
1 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
8 drives:
2 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
PID UCSC-RAID-11-C220
(Includes RAID 5 & 50)
Mezzanine
8 internal
No
0, 1, 1E, 5, 10, 50
4 drives:
1 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
8 drives:
2 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
PCIe
8 internal
SCPM
0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60
4 drives:
1 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
8 drives:
2 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
9271-8iPCIe
8 internal
No
0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60
4 drives:
1 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
8 drives:
2 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
9271CV-8iPCIe
8 internal
SCPM
0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60
4 drives:
1 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
8 drives:
2 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
PCIe
8 external
SCPM
0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60
Not sold by Cisco
9286CV-8ePCIe
8 external
SCPM
0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60
Not sold by Cisco
1 SCPM = SuperCap power module (RAID backup unit). See RAID Backup Units.
2 Migrations from a RAID card to the embedded controller are not supported after-factory. See RAID Controller Migration.
3 Support for eight SAS drives requires an optional SCU upgrade ROM module on the motherboard.
4 Support for RAID 5 requires an optional RAID 5 software key module on the motherboard.
5 UCSC-CABLE1 is a kit of two mini-SAS cables. This pair of cables is shipped with every new system.
Table C-2 Cisco UCS C220 M3 Large Form Factor Drives RAID Options
Onboard
4 SATA or
4 SAS3
internalNo
0, 1, 54 , 10
4 drives:
1 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE3)
PID UCSC-RAID-MZ-C220
Mezzanine
4 internal
No
0, 1, 1E, 10
4 drives:
1 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE3)
PID UCSC-RAID-11-C220
(Includes RAID 5 & 50)
Mezzanine
4 internal
No
0, 1, 1E, 5, 10, 50
4 drives:
1 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE3)
The cache memory of this controller is ECC-protected.
PCIe
4 internal
SCPM
0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60
4 drives:
1 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE3)
9271-8iThe cache memory of this controller is ECC-protected.
PCIe
8 internal
No
0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60
4 drives:
1 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
8 drives:
2 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
9271CV-8iThe cache memory of this controller is ECC-protected.
PCIe
8 internal
SCPM
0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60
4 drives:
1 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
8 drives:
2 mini-SAS (UCSC-CABLE1)
PCIe
8 external
SCPM
0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60
Not sold by Cisco
9286CV-8ePCIe
8 external
SCPM
0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60
Not sold by Cisco
1 SCPM = SuperCap power module (RAID backup unit). See RAID Backup Units.
2 Migrations from a RAID card to the embedded controller are not supported after-factory. See RAID Controller Migration.
3 Support for four SAS drives requires an optional SCU upgrade ROM module on the motherboard.
4 Support for RAID 5 requires an optional RAID 5 software key module on the motherboard.
Mixing Drive Types in RAID Groups
Table C-3 lists the technical capabilities for mixing hard disk drive (HDD) and solid state drive (SSD) types in a RAID group. However, see the best practices recommendations that follow for the best performance.
Table C-3 Drive Type Mixing in RAID Groups
in RAID GroupSAS HDD + SATA HDD
Yes
SAS SSD + SATA SSD
Yes
HDD + SSD
No
Best Practices For Mixing Drive Types in RAID Groups
For the best performance, follow these guidelines:
•
Use either all SAS or all SATA drives in a RAID group.
•
Use the same capacity for each drive in the RAID group.
•
Never mix HDDs and SSDs in the same RAID group.
RAID Backup Units
This server supports installation of one SuperCap Power Module (SCPM). The unit mounts to a holder on the left-side air baffle (see Figure 3-24).
Note
The iBBU09 battery backup unit (BBU) has been phased out by Cisco and replaced with the SuperCap power module (SCPM). If you are replacing a BBU, order the SCPM for the replacement (UCS-RAID-CV-SC=). Cards that used the BBU are compatible with the SCPM.
•
The optional SCPM provides approximately 3 years of backup for the disk write-back cache DRAM in the case of sudden power loss by offloading the cache to the NAND flash.
Factory-Default Option ROM Settings
Table C-4 describes the option ROM (OPROM) settings for card slots that are made at the factory for various configurations. The version of the server and the number of CPUs affect the OPROM settings.
Note
If an option is listed as "not allowed" in Table C-4, that is because it is not supported in the particular configuration described in that table row. See the footnotes below the table for more information.
For additional information about RAID controller support, see Supported RAID Controllers and Required Cables.
Table C-4 Cisco UCS C220 Factory-Default Option ROM Settings
C220 SFF 8 HDD/ C220 LFF 4 HDD
1
Enabled
Not allowed1
Not allowed
Not allowed
Always enabled
All other OPROM is disabled.
C220 SFF 8 HDD/ C220 LFF 4 HDD
1
Not allowed
Not allowed2
Installed:
PCIe slot 1 enabled3Not allowed
Always enabled
All other OPROM is disabled.
C220 SFF 8 HDD/ C220 LFF 4 HDD
2
Enabled
Not allowed
Not allowed
Not allowed
Always enabled
All other OPROM is disabled.
C220 SFF 8 HDD/ C220 LFF 4 HDD
2
Not allowed
Installed:
connector enabledNot allowed4
Not allowed
Always enabled
All other OPROM is disabled.
C220 SFF 8 HDD/ C220 LFF 4 HDD
2
Not allowed
Not allowed5
Installed:
PCIe slot 2 enabledNot allowed
Always enabled
All other OPROM is disabled.
1 You cannot use the embedded SW RAID and HW RAID (mezzanine or PCIe card) at the same time.
2 In single-CPU configurations, the mezzanine card slot is not supported.
3 In single-CPU configurations, PCIe slot 2 is not available.
4 You cannot mix controller types in a server. A PCIe-style controller cannot be used when a mezzanine-style controller is used.
5 You cannot mix controller types in a server. A mezzanine-style controller cannot be used when a PCIe-style controller is used.
RAID Controller Migration
This server supports hardware RAID (mezzanine and PCIe controller cards) and embedded software RAID. See Table C-5 for which migrations are allowed and a summary of migration steps.
Embedded MegaRAID Controller
Note
VMware ESX/ESXi or any other virtualized environments are not supported for use with the embedded MegaRAID controller. Hypervisors such as Hyper-V, Xen, or KVM are also not supported for use with the embedded MegaRAID controller.
This server includes the option for an embedded MegaRAID controller with two mini-SAS connectors on the motherboard.
•
The default setting for this embedded controller is SAS RAID 0, 1, and 10 support for up to four SATA drives.
•
You can upgrade this to support to SAS RAID 0, 1, and 10 support for up to eight SAS drives by installing a Storage Controller Unit (SCU) upgrade ROM chip on the motherboard. See Installing a SCU Upgrade ROM Module For Embedded RAID SAS Support.
•
You can further upgrade this support by adding SAS RAID 5 support with an optional software key. See Installing a Software RAID Key Module for Embedded RAID 5 Support.
•
When you order the server with this controller, the controller is enabled in the BIOS. Instructions for enabling the controller are included for the case in which a server is reset to defaults (Disabled). See Enabling the Embedded RAID Controller in the BIOS.
Note
You cannot downgrade from using a RAID controller card to using the embedded controller (see RAID Controller Migration). Instructions for installing upgrade modules and enabling the embedded controller in the BIOS are included here for those upgrading a server with no RAID controller or drives.
CautionData migration from SW RAID (embedded RAID) to HW RAID (a controller card) is not supported and could result in data loss. Migrations from SW RAID to HW RAID are supported only before there is data on the drives, or the case in which there are no drives in the server (see RAID Controller Migration).
•
You can migrate from using the embedded controller to using a RAID card only before there is data on the drives. In this case, you must disable the embedded controller. See Disabling the Embedded RAID Controller in the BIOS.
•
The required drivers for this controller are already installed and ready to use with the LSI SWRAID Configuration Utility. However, if you will use this controller with Windows or Linux, you must download and install additional drivers for those operating systems. See Installing LSI MegaSR Drivers For Windows and Linux.
This section contains the following topics:
•
Notes on Supported Embedded MegaRAID Levels
•
Installing a SCU Upgrade ROM Module For Embedded RAID SAS Support
•
Installing a Software RAID Key Module for Embedded RAID 5 Support
•
Enabling the Embedded RAID Controller in the BIOS
•
Disabling the Embedded RAID Controller in the BIOS
•
Launching the LSI Embedded RAID Configuration Utility
•
Installing LSI MegaSR Drivers For Windows and Linux
Notes on Supported Embedded MegaRAID Levels
The following RAID levels are supported by the embedded MegaRAID controller.
•
RAID 0—You can configure a RAID 0 virtual drive (VD) using one or more physical drives (PDs). This level supports up to eight VDs and PDs.
•
RAID 1—A RAID 1 VD is configured from only two PDs. This level supports up to eight PDs (four RAID arrays) and eight VDs.
•
RAID 5—You can configure a RAID 5 VD using three or more PDs. This level supports up to eight PDs and eight VDs.
•
RAID 10—This is a spanned VD; that is, RAID 0 is implemented on two or more RAID 1 VDs. This level supports up to eight PDs (two to four RAID 1 volumes spanned) and one VD.
Note
None of these RAID levels require drives of the same size. The smallest drive in the array determines the size of the VD.
Note
An array can be divided into multiple VDs of the same RAID level, except when using RAID 10. Mixed arrays are not permitted. For example, you cannot configure a three-drive array into RAID 0 and RAID 5 VDs. Unlike RAID 0, 1, and 5, you cannot create multiple RAID 10 VDs from the same array. A single RAID 10 VD uses up the entire array.
Installing a SCU Upgrade ROM Module For Embedded RAID SAS Support
The SCU Upgrade ROM module contains a chip on a small circuit board. This module attaches to a motherboard header. This chip upgrades the standard four-drive SATA support to add SAS support for up to eight SAS or SATA drives.
Note
The Cisco PID UCSC-RAID-ROM5= includes the SCU upgrade ROM module.
The Cisco PID UCSC-RAID-ROM55= includes the SCU upgrade ROM module and the RAID 5 key.
To install a SCU upgrade ROM module, follow these steps:
Step 1
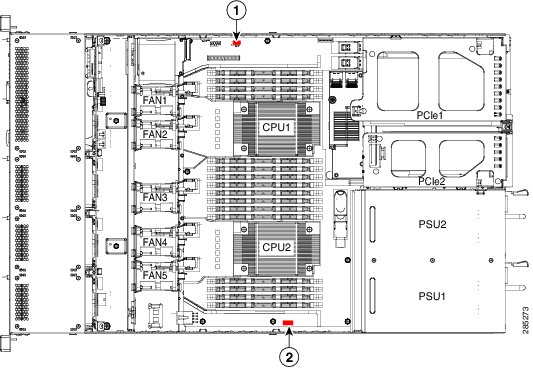
Locate the header labelled "PBG DYNAMIC SKU" under any cables that are routed along the chassis wall (see Figure C-1).
Step 2
Align the connector on the SCU upgrade ROM module with the pins on the header, then gently push the connector onto the pins.
Step 3
Replace the top cover.
Step 4
Replace the server in the rack, replace cables, and then power on the server by pressing the Power button.
Step 5
Continue with either Installing a Software RAID Key Module for Embedded RAID 5 Support or Enabling the Embedded RAID Controller in the BIOS.
Figure C-1 SCU Upgrade ROM and RAID 5 Key Header Locations on Motherboard
SCU upgrade ROM header
PBG DYNAMIC SKU
(adds SAS drive support)Software RAID 5 key header
SW RAID KEY
(adds RAID 5 support)
Installing a Software RAID Key Module for Embedded RAID 5 Support
The software RAID key module contains a chip on a small circuit board. This module attaches to a motherboard header. This chip upgrades SAS support to add RAID 5 support (RAID 0, 1, 5, and 10 for up to eight SAS or SATA drives).
Note
You must have the SCU upgrade ROM module installed before you can use this module.
To install a RAID 5 software key module, follow these steps:
Step 1
Locate the header that is labeled "SW RAID KEY" (see Figure C-1).
Step 2
Install the RAID 5 software key module onto the pins of the header.
Step 3
Replace the top cover.
Step 4
Replace the server in the rack, replace cables, and then power on the server by pressing the Power button.
Step 5
Continue with Enabling the Embedded RAID Controller in the BIOS.
Enabling the Embedded RAID Controller in the BIOS
When you order the server with this controller, the controller is enabled in the BIOS at the factory.
Note
The default setting in the BIOS for the embedded controller is Disabled. When you order the server with the embedded controller, the BIOS setting is Enabled at the factory. However, if a server is reset to defaults, this BIOS setting is reverted to Disabled. Use the procedure below to re-enable the embedded controller.
Use the following procedure to enable the LSI MegaSR drivers.
Step 1
Boot the server and press F2 when prompted to enter the BIOS Setup utility.
Step 2
Select the Advanced tab, then South Bridge.
Step 3
Set Onboard SCU Storage Support to Enabled.
Step 4
Press F10 to save your changes and exit the utility.
Disabling the Embedded RAID Controller in the BIOS
CautionData migration from SW RAID to HW RAID is not supported and could result in data loss. Migrations from SW RAID to HW RAID are supported only before there is data on the drives, or the case in which there are no drives in the server.
If you migrate from using this embedded controller to a RAID controller card, you must disable the embedded controller in the BIOS (see caution above).
Use the following procedure to disable the LSI MegaSR drivers.
Step 1
Boot the server and press F2 when prompted to enter the BIOS Setup utility.
Step 2
Select the Advanced tab, then South Bridge.
Step 3
Set Onboard SCU Storage Support to Disabled.
Step 4
Press F10 to save your changes and exit the utility.
Launching the LSI Embedded RAID Configuration Utility
Launch the utility by pressing Ctrl+M when you see the prompt during system boot.
For more information about using the Embedded MegaRAID software to configure your disk arrays, see the LSI Embedded MegaRAID Software User Guide.
Installing LSI MegaSR Drivers For Windows and Linux
Note
The required drivers for this controller are already installed and ready to use with the LSI SWRAID Configuration Utility. However, if you will use this controller with Windows or Linux, you must download and install additional drivers for those operating systems.
This section explains how to install the LSI MegaSR drivers for the following supported operating systems:
•
Microsoft Windows Server
•
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
•
SuSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES)
For the specific supported OS versions, see the Hardware and Software Interoperability Matrix for your server release.
This section contains the following topics:
•
Downloading the LSI MegaSR Drivers
•
Microsoft Windows Driver Installation
Downloading the LSI MegaSR Drivers
The MegaSR drivers are included in the C-series driver ISO for your server and OS. Download the drivers from Cisco.com:
Step 1
Find the drivers ISO file download for your server online and download it to a temporary location on your workstation:
a.
See the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/cisco/software/navigator.html
b.
Click Unified Computing and Servers in the middle column.
c.
Click Cisco UCS C-Series Rack-Mount Standalone Server Software in the right-hand column.
d.
Click your model of server in the right-hand column.
e.
Click Unified Computing System (UCS) Drivers.
f.
Click the release number that you are downloading.
g.
Click Download to download the drivers ISO file.
h.
Verify the information on the next page, then click Proceed With Download.
i.
Continue through the subsequent screens to accept the license agreement and then browse to a location where you want to save the drivers ISO file.
Microsoft Windows Driver Installation
This section explains the steps to install the LSI MegaSR driver in a Windows installation.
This section contains the following topics:
•
Windows Server 2008R2 Driver Installation
Windows Server 2008R2 Driver Installation
Perform the following steps to install the LSI MegaSR device driver in a new Windows Server 2008R2 operating system. The Windows operating system automatically adds the driver to the registry and copies the driver to the appropriate directory.
Step 1
Create a RAID drive group using the LSI SWRAID Configuration utility before you install this driver for Windows. Launch this utility by pressing Ctrl+M when LSI SWRAID is shown during BIOS post.
Step 2
Download the Cisco UCS C-Series drivers ISO, as described in Downloading the LSI MegaSR Drivers.
Step 3
Prepare the drivers on a USB thumb drive:
a.
Burn the ISO image to a disc.
b.
Browse the contents of the drivers folders to the location of the embedded MegaRAID drivers:
/<OS>/Storage/Intel/C600/
c.
Expand the Zip file, which contains the folder with the MegaSR driver files.
d.
Copy the expanded folder to a USB thumb drive.
Step 4
Start the Windows driver installation using one of the following methods:
•
To install from local media: Connect an external USB DVD drive to the server and then insert the first Windows install disc into the drive. Skip to Step 6.
•
To install from remote ISO: Log in to the server's CIMC interface and continue with the next step.
Step 5
Launch a Virtual KVM console window and select the Virtual Media tab.
a.
Click Add Image and browse to select your remote Windows installation ISO file.
b.
Select the check box in the Mapped column for the media that you just added, then wait for mapping to complete.
Step 6
Power cycle the server.
Step 7
Press F6 when you see the F6 prompt during bootup. The Boot Menu window opens.
Step 8
On the Boot Manager window, select the physical disc or virtual DVD and press Enter. The Windows installation begins when the image is booted.
Step 9
Press Enter when you see the prompt, "Press any key to boot from CD."
Step 10
Observe the Windows installation process and respond to prompts in the wizard as required for your preferences and company standards.
Step 11
When Windows prompts you with "Where do you want to install Windows," install the drivers for embedded MegaRAID:
a.
Click Load Driver. You are prompted by a Load Driver dialog to select the driver to be installed.
b.
Connect the USB thumb drive that you prepared in Step 3 to the target server.
c.
On the Windows Load Driver dialog that you opened in Step a, click Browse.
d.
Use the dialog to browse to the location of the drivers folder on the USB thumb drive, and click OK.
Windows loads the drivers from the folder and when finished, the driver is listed under the prompt, "Select the driver to be installed."
e.
Click Next to install the drivers.
Updating the Windows Driver
Perform the following steps to update the LSI MegaSR driver for Windows or to install this driver on an existing system booted from a standard IDE drive.
Step 1
Click Start, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
Step 2
Double-click System, click the Hardware tab, and then click Device Manager. Device Manager starts.
Step 3
In Device Manager, double-click SCSI and RAID Controllers, right-click the device for which you are installing the driver, and then click Properties.
Step 4
On the Driver tab, click Update Driver to open the Update Device Driver wizard, and then follow the wizard instructions to update the driver.
Linux Driver Installation
This section explains the steps to install the embedded MegaRAID device driver in a Red Hat Enterprise Linux installation or a SuSE Linux Enterprise Server installation.
This section contains the following topics:
•
Obtaining the Driver Image File
•
Preparing Physical Installation Diskettes For Linux
•
Installing the Red Hat Linux Driver
•
Installing the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server Driver
Obtaining the Driver Image File
See Downloading the LSI MegaSR Drivers for instructions on obtaining the drivers. The Linux driver is offered in the form of dud-[driver version].img, which is the boot image for the embedded MegaRAID stack.
Note
The LSI MegaSR drivers that Cisco provides for Red Hat Linux and SUSE Linux are for the original GA versions of those distributions. The drivers do not support updates to those OS kernels.
Preparing Physical Installation Diskettes For Linux
This section describes how to prepare physical Linux installation diskettes from the driver image files, using either the Windows operating system or the Linux operating system.
Note
Alternatively, you can mount the dud.img file as a virtual floppy disk, as described in the installation procedures.
Preparing Physical Installation Diskettes With the Windows Operating System:
Under Windows, you can use the RaWrite floppy image-writer utility to create disk images from image files. Perform the following steps to build installation diskettes.
Step 1
Download the Cisco UCS C-Series drivers ISO, as described in Downloading the LSI MegaSR Drivers and save it to your Windows system that has a diskette drive.
Step 2
Extract the dud.img file:
a.
Burn the ISO image to a disc.
b.
Browse the contents of the drivers folders to the location of the embedded MegaRAID drivers:
/<OS>/Storage/Intel/C600/
c.
Expand the Zip file, which contains the folder with the driver files.
Step 3
Copy the driver update disk image dud-[driver version].img and your file raw write.exe to a directory.
Note
RaWrite is not included in the driver package.
Step 4
If necessary, use this command to change the file name of the driver update disk to a name with fewer than eight characters: copy dud-[driver version].img dud.img
Step 5
Open the DOS Command Prompt and navigate to the directory where raw write.exe is located.
Step 6
Type the following command to create the installation diskette: raw write
Step 7
Press Enter.
You are prompted to enter the name of the boot image file.
Step 8
Type the following: dud.img
Step 9
Press Enter.
You are prompted for the target diskette.
Step 10
Insert a floppy diskette into the floppy drive and type: A:
Step 11
Press Enter.
Step 12
Press Enter again to start copying the file to the diskette.
Step 13
After the command prompt returns and the floppy disk drive LED goes out, remove the diskette.
Step 14
Label the diskette with the image name.
Preparing Installation Disks With a Linux Operating System:
Under Red Hat Linux and SuSE Linux, you can use a driver diskette utility to create disk images from image files. Perform the following steps to create the driver update disk:
Step 1
Download the Cisco UCS C-Series drivers ISO, as described in Downloading the LSI MegaSR Drivers and save it to your Linux system that has a diskette drive.
Step 2
Extract the dud.img file:
a.
Burn the ISO image to a disc.
b.
Browse the contents of the drivers folders to the location of the embedded MegaRAID drivers:
/<OS>/Storage/Intel/C600/
c.
Expand the Zip file, which contains the folder with the driver files.
Step 3
Copy the driver update disk image dud-[driver version].img to your Linux system.
Step 4
Insert a blank floppy diskette into the floppy drive.
Step 5
Confirm that the files are in the selected directory.
Step 6
Create the driver update diskette using the following command:
dd if=dud-[driver version].img of=/dev/fd0
Step 7
After the command prompt returns and the floppy disk drive LED goes out, remove the diskette.
Step 8
Label the diskette with the image name.
Installing the Red Hat Linux Driver
For the specific supported OS versions, see the Hardware and Software Interoperability Matrix for your server release.
This section describes the fresh installation of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux device driver on systems with the embedded MegaRAID stack.
Step 1
Create a RAID drive group using the LSI SWRAID Configuration utility before you install this driver for the OS. Launch this utility by pressing Ctrl+M when LSI SWRAID is shown during BIOS post.
Step 2
Prepare the dud.img file using one of the following methods:
•
To install from a physical diskette: Use one of the procedures in Preparing Physical Installation Diskettes For Linux.
Then return to Step 4 of this procedure.•
To install from a virtual floppy disk: Download and save the Cisco UCS C-Series drivers ISO, as described in Downloading the LSI MegaSR Drivers.
Then continue with the next step.Step 3
Extract the dud.img file:
a.
Burn the ISO image to a disc.
b.
Browse the contents of the drivers folders to the location of the embedded MegaRAID drivers:
/<OS>/Storage/Intel/C600/
c.
Copy the dud-<driver version>.img file to a temporary location on your workstation.
Step 4
Start the Linux driver installation using one of the following methods:
•
To install from local media: Connect an external USB DVD drive to the server and then insert the first RHEL install disc into the drive.
Then continue with Step 6.•
To install from remote ISO: Log in to the server's CIMC interface. Then continue with the next step.
Step 5
Launch a Virtual KVM console window and select the Virtual Media tab.
a.
Click Add Image and browse to select your remote RHEL installation ISO file.
b.
Click Add Image again and browse to select your dud.img file.
c.
Select the check boxes in the Mapped column for the media that you just added, then wait for mapping to complete.
Step 6
Power cycle the server.
Step 7
Press F6 when you see the F6 prompt during bootup. The Boot Menu window opens.
Step 8
On the Boot Manager window, select the physical disc or virtual DVD and press Enter.
The RHEL installation begins when the image is booted.
Step 9
Type one of the following commands at the boot prompt:
•
For RHEL 5.x (32- and 64-bit), type:
Linux dd blacklist=isci blacklist=ahci noprobe=<atadrive number>•
For RHEL 6.x (32- and 64-bit), type:
Linux dd blacklist=isci blacklist=ahci nodmraid noprobe=<atadrive number>
Note
The noprobe values depend on the number of drives. For example, to install RHEL 5.7 on a RAID 5 configuration with three drives, enter:
Linux dd blacklist=isci blacklist=ahci noprobe=ata1 noprobe=ata2 noprobe=ata3Step 10
Press Enter.
The prompt asks whether you have a driver disk.
Step 11
Use the arrow key to select Yes, and then press Enter.
Step 12
Select fd0 to indicate that you have a floppy diskette with the driver on it.
Step 13
Do one of the following actions:
•
If you prepared the IMG file on a physical diskette in Step 2: Connect an external USB diskette drive to the target server and then insert the diskette in the A:/ drive and press Enter.
•
If you mapped the IMG file as a virtual floppy in Step 5: Select the location of the virtual floppy.
The installer locates and loads the driver for your device. The following message appears:
Loading megasr driver...
Step 14
Follow the Red Hat Linux installation procedure to complete the installation.
Step 15
Reboot the system.
Installing the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server Driver
For the specific supported OS versions, see the Hardware and Software Interoperability Matrix for your server release.
This section describes the installation of the SuSE Linux Enterprise Server driver on a system with the embedded MegaRAID stack.
Us e the following procedure to install the SLES drivers.
Step 1
Create a RAID drive group using the LSI SWRAID Configuration utility before you install this driver for the OS. Launch this utility by pressing Ctrl+M when LSI SWRAID is shown during BIOS post.
Step 2
Prepare the dud.img file using one of the following methods:
•
To install from a physical diskette: Use one of the procedures in Preparing Physical Installation Diskettes For Linux.
Then return to Step 4 of this procedure.•
To install from a virtual floppy disk: Download and save the Cisco UCS C-Series drivers ISO, as described in Downloading the LSI MegaSR Drivers.
Then continue with the next step.Step 3
Extract the dud.img file:
a.
Burn the ISO image to a disc.
b.
Browse the contents of the drivers folders to the location of the embedded MegaRAID drivers:
/<OS>/Storage/Intel/C600/
c.
Copy the dud-<driver version>.img file to a temporary location on your workstation.
Step 4
Start the Linux driver installation using one of the following methods:
•
To install from local media: Connect an external USB DVD drive to the server and then insert the first RHEL install disc into the drive. Skip to Step 6.
•
To install from remote ISO: Log in to the server's CIMC interface and continue with the next step.
Step 5
Launch a Virtual KVM console window and select the Virtual Media tab.
a.
Click Add Image and browse to select your remote RHEL installation ISO file.
b.
Click Add Image again and browse to select your dud.img file.
c.
Select the check box in the Mapped column for the media that you just added, then wait for mapping to complete.
Step 6
Power cycle the server.
Step 7
Press F6 when you see the F6 prompt during bootup. The Boot Menu window opens.
Step 8
On the Boot Manager window, select the physical disc or virtual DVD and press Enter. The SLES installation begins when the image is booted.
Step 9
When the first SLES screen appears, select Installation on the menu.
Step 10
Type one of the following in the Boot Options field:
•
For SLES 11 and SLES 11 SP1 (32- and 64-bit), type: brokenmodules=ahci
•
For SLES 11 SP2 (32-and 64-bit), type: brokenmodules=ahci brokenmodules=isci
Step 11
Press F6 for the driver and select Yes.
Step 12
Do one of the following actions:
•
If you prepared the IMG file on a physical diskette in Step 2: Connect an external USB diskette drive to the target server and then insert the diskette in the A:/ drive and press Enter.
•
If you mapped the IMG file as a virtual floppy in Step 5: Select the location of the virtual floppy.
"Yes" appears under the F6 Driver heading.
Step 13
Press Enter to select Installation.
Step 14
Press OK.
The following message appears: LSI Soft RAID Driver Updates added.
Step 15
At the menu, select the driver update medium and press the Back button.
Step 16
Continue and complete the installation process by following the prompts.
RAID Controller Cabling
This section includes the following topics:
•
Cisco UCS C220 Server Cabling
Cable Routing
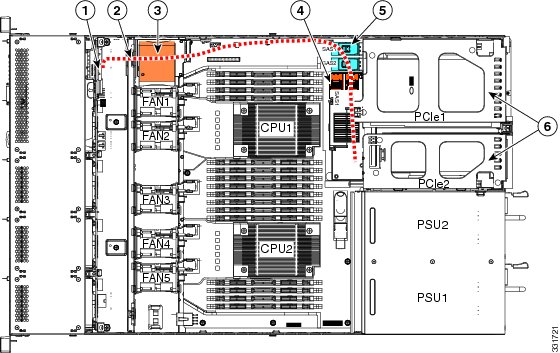
The RAID controller connectors in this server are shown in Figure C-2. The red line indicates the recommended cable routing path from the backplane to the possible controller locations. An opening in the chassis divider has been provided for cable routing to the backplane.
Figure C-2 RAID Controller Connectors
Cisco UCS C220 Server Cabling
This section contains the following topics:
•
Backplane and Expander Options
•
SFF 8-Drive Backplane Cabling
•
LFF 4-Drive Backplane Cabling
Backplane and Expander Options
The server is orderable in two different versions, each with one of two different front panel/backplane configurations:
•
Cisco UCS C220 (small form-factor (SFF) drives, with 8-drive backplane.
Holds up to eight 2.5-inch hard drives or solid state drives.•
Cisco UCS C220 (large form factor (LFF) drives, with 4-drive backplane).
Holds up to four 3.5-inch hard drives.SFF 8-Drive Backplane Cabling
The cable connections required for each type of controller are as follows:
Embedded RAID
This option can control up to eight drives.
The required UCSC-CABLE1 cable kit has two mini-SAS cables. Cable 1 controls drives 1-4 and cable 2 controls drives 5-8.
Step 1
Connect mini-SAS cable 1 from the motherboard connector SAS1 to the drives 1-4 connectors on the backplane.
Step 2
Connect the cable 1 SGPIO connector labeled, "S1" to backplane connector S1.
Step 3
Connect mini-SAS cable 2 from the motherboard connector SAS2 to the drives 5-8 connectors on the backplane.
Step 4
Connect the cable 2 SGPIO connector labeled, "S2" to backplane connector S2.
Mezzanine-Style Card
This option can control up to eight drives.
The required UCSC-CABLE1 cable kit has two mini-SAS cables. Cable 1 controls drives 1-4 and cable 2 controls drives 5-8.
Step 1
Connect mini-SAS cable 1 from connector SAS1 on the card to the drives 1-4 connectors on the backplane.
Step 2
Connect the mini-SAS cable 1 SGPIO connector S1 to backplane connector S1.
Step 3
Connect mini-SAS cable 2 from connector SAS2 on the card to the drives 5-8 connectors on the backplane.
Step 4
Connect the mini-SAS cable 2 SGPIO connector S2 to backplane connector S2.
PCIe-Style Card
This option can control up to eight drives.
The required UCSC-CABLE1 cable kit has two mini-SAS cables. Cable 1 controls drives 1-4 and cable 2 controls drives 5-8.
Step 1
Connect mini-SAS cable 1 from connector SAS1 on the card to the drives 1-4 connectors on the backplane.
Step 2
Connect the mini-SAS cable 1 SGPIO connector S1 to backplane connector S1.
Step 3
Connect mini-SAS cable 2 from connector SAS2 on the card to the drives 5-8 connectors on the backplane.
Step 4
Connect the mini-SAS cable 2 SGPIO connector S2 to backplane connector S2.
LFF 4-Drive Backplane Cabling
The cable connections required for each type of controller are as follows:
Embedded RAID
This option can control up to four drives.
The required UCSC-CABLE3 cable kit has two mini-SAS cables. Cable 1 controls drives 1-4.
Step 1
Connect mini-SAS cable 1 from the motherboard connector SAS1 to the drives 1-4 connectors on the backplane.
Step 2
Connect the cable 1 SGPIO connector labeled, "S1" to backplane connector S1.
Mezzanine-Style Card
This option can control up to four drives.
The required UCSC-CABLE3 cable kit has two mini-SAS cables. Cable 1 controls drives 1-4.
Step 1
Connect mini-SAS cable 1 from connector SAS1 on the card to the drives 1-4 connectors on the backplane.
Step 2
Connect the mini-SAS cable 1 SGPIO connector S1 to backplane connector S1.
PCIe-Style Card
This option can control up to four drives.
The required UCSC-CABLE3 cable kit has two mini-SAS cables. Cable 1 controls drives 1-4.
Step 1
Connect mini-SAS cable 1 from connector SAS1 on the card to the drives 1-4 connectors on the backplane.
Step 2
Connect the mini-SAS cable 1 SGPIO connector S1 to backplane connector S1.
Restoring RAID Configuration After Replacing a RAID Controller
When you replace a RAID controller, the RAID configuration that is stored in the controller is lost. Use the following procedure to restore your RAID configuration to your new RAID controller.
Step 1
Replace your RAID controller. See Replacing a PCIe Card.
Step 2
If this was a full chassis swap, replace all drives into the drive bays, in the same order that they were installed in the old chassis.
Step 3
Reboot the server and watch for the prompt to press F.
Note
For newer RAID controllers, you are not prompted to press F. Instead, the RAID configuration is imported automatically. In this case, skip to Step 6.
Step 4
Press F when you see the following on-screen prompt:
Foreign configuration(s) found on adapter.Press any key to continue or `C' load the configuration utility,or `F' to import foreign configuration(s) and continue.Step 5
Press any key (other than C) to continue when you see the following on-screen prompt:
All of the disks from your previous configuration are gone. If this isan unexpected message, then please power of your system and check your cablesto ensure all disks are present.Press any key to continue, or `C' to load the configuration utility.Step 6
Watch the subsequent screens for confirmation that your RAID configuration was imported correctly.
•
If you see the following message, your configuration was successfully imported. The LSI virtual drive is also listed among the storage devices.
N Virtual Drive(s) found on host adapter.•
If you see the following message, your configuration was not imported. This can happen if you do not press F quickly enough when prompted. In this case, reboot the server and try the import operation again wen you are prompted to press F.
0 Virtual Drive(s) found on host adapter.
For More Information
The LSI utilities have help documentation for more information about using the utilities.
For basic information about RAID and for using the utilities for the RAID controller cards that are supported in Cisco servers, see the Cisco UCS Servers RAID Guide.
For more information about using the Embedded MegaRAID software to configure your disk arrays, see the LSI Embedded MegaRAID Software User Guide.
Full LSI documentation is also available:
•
LSI MegaRAID SAS Software User's Guide (for LSI MegaRAID)
•
LSI SAS2 Integrated RAID Solution User Guide (for LSI SAS 2008)

 Feedback
Feedback