Table Of Contents
About Cisco Validated Design (CVD) Program
VMware vSphere 5.1 on FlexPod Data ONTAP Operating in 7-Mode Deployment Guide
FlexPod Cabling on Data ONTAP Operating in 7-Mode
Complete the Configuration Worksheet
Assign Controller Disk Ownership and initialize storage
64-Bit Aggregates in Data ONTAP 7-Mode
Active-Active Controller Configuration
Install Remaining Required Licenses and Enable MultiStore
Perform Initial Setup of Cisco UCS 6248 Fabric Interconnect for FlexPod Environments
FlexPod Cisco UCS FCoE vSphere on Data ONTAP 7-Mode
Upgrade Cisco UCS Manager Software to Version 2.1(1b)
Add Block of IP Addresses for KVM Access
Enable Server and Uplink Ports
Acknowledge Cisco UCS Chassis and FEX
Create Uplink Port Channels to Cisco Nexus 5548 Switches
Create VSANs and FCoE Port Channels
Set Jumbo Frames in Cisco UCS Fabric
Create Local Disk Configuration Policy (Optional)
Create Network Control Policy for Cisco Discovery Protocol
Create Server Pool Qualification Policy (Optional)
Create vNIC/vHBA Placement Policy for Virtual Machine Infrastructure Hosts
Update default Maintenance Policy
Create vHBA Templates for Fabric A and Fabric B
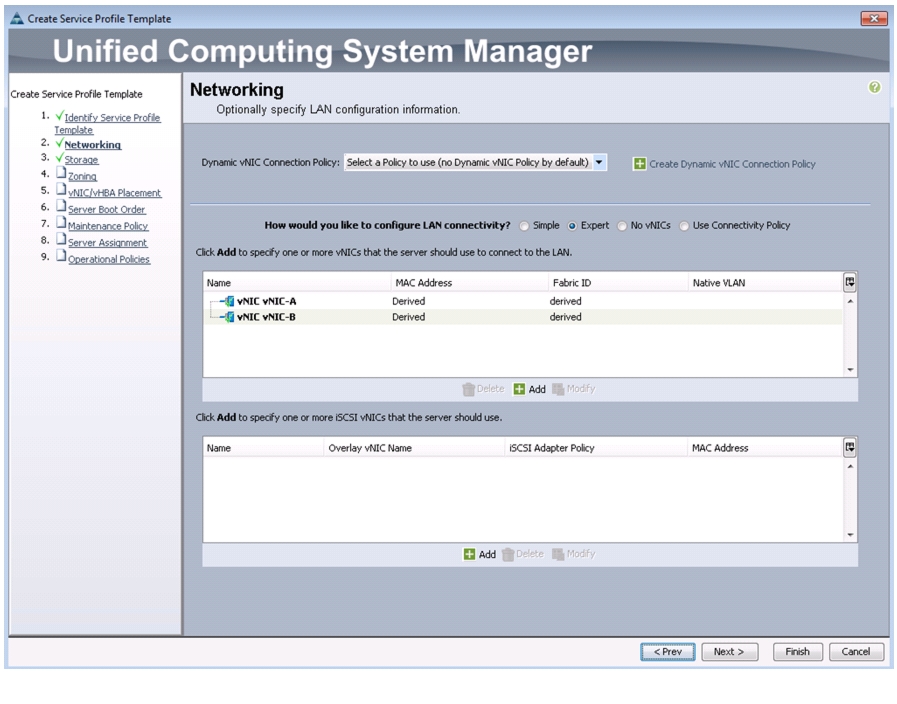
Create Service Profile Templates
Add More Servers to FlexPod Unit
FlexPod Cisco Nexus FCoE Storage vSphere on Data ONTAP 7-Mode
Add Individual Port Descriptions for Troubleshooting
Configure Virtual Port Channels
Configure Ports for Cisco Nexus 1110-X Virtual Appliances
Uplink into Existing Network Infrastructure
Create VSANs, Assign and Enable Virtual Fibre Channel Ports
Data ONTAP 7-Mode SAN Boot Storage Setup
FlexPod VMware ESXi 5.1 FCoE 7-Mode
Log in to Cisco UCS 6200 Fabric Interconnect
Set Up VMware ESXi Installation
Set Up Management Networking for ESXi Hosts
Download VMware vSphere Client and vSphere Remote CLI
Log in to VMware ESXi Hosts by Using VMware vSphere Client
Download Updated Cisco VIC enic and fnic Drivers
Load Updated Cisco VIC enic and fnic Drivers
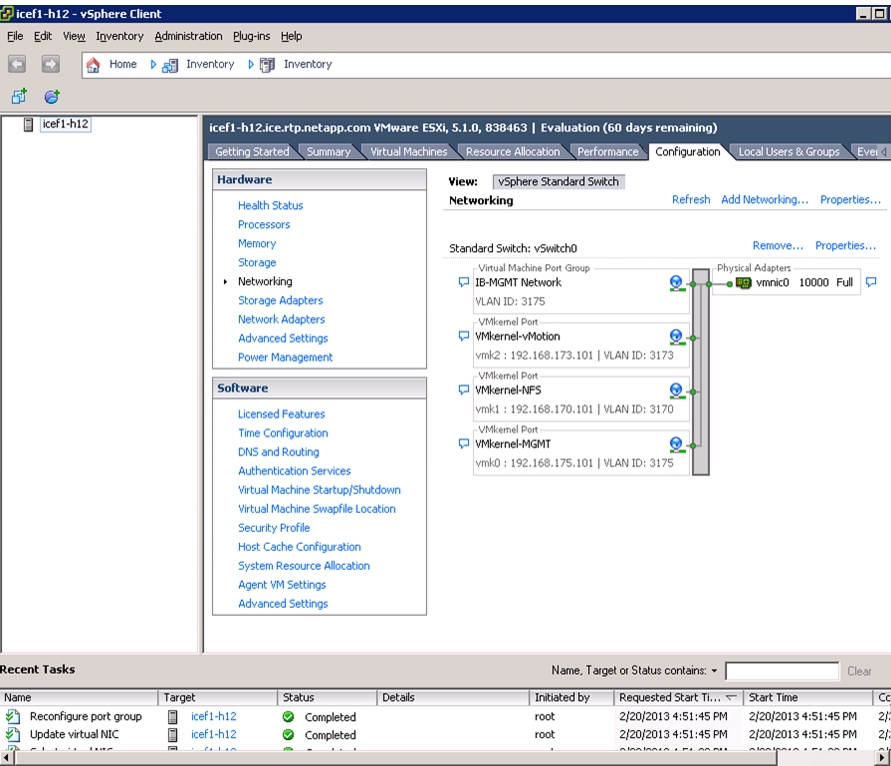
Set Up VMkernel Ports and Virtual Switch
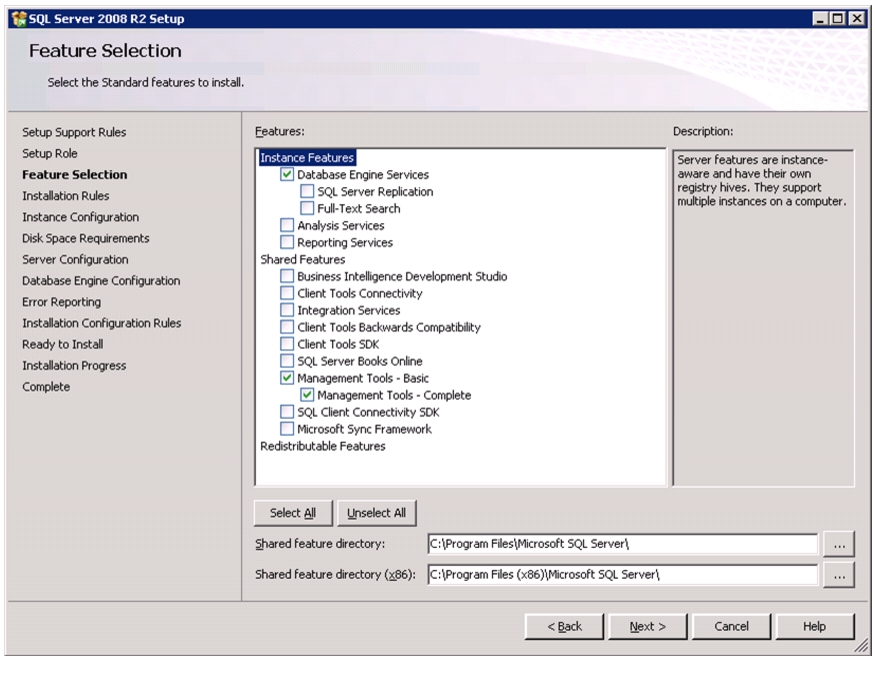
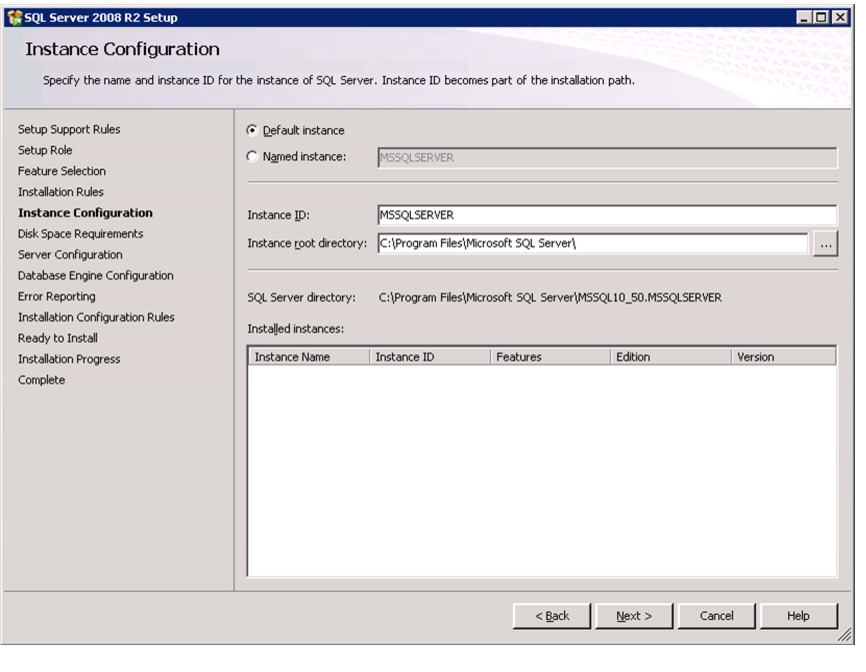
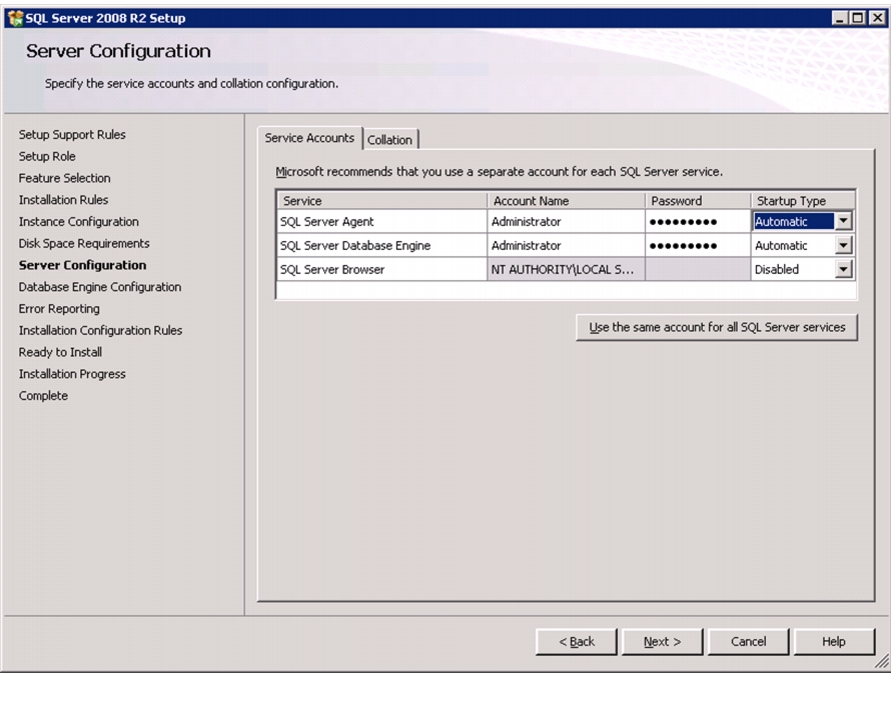
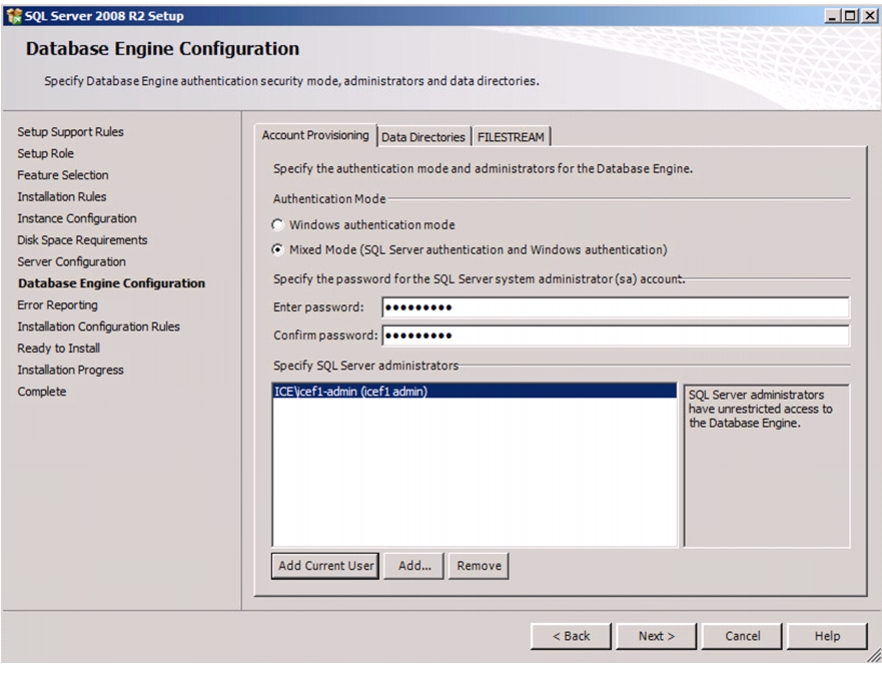
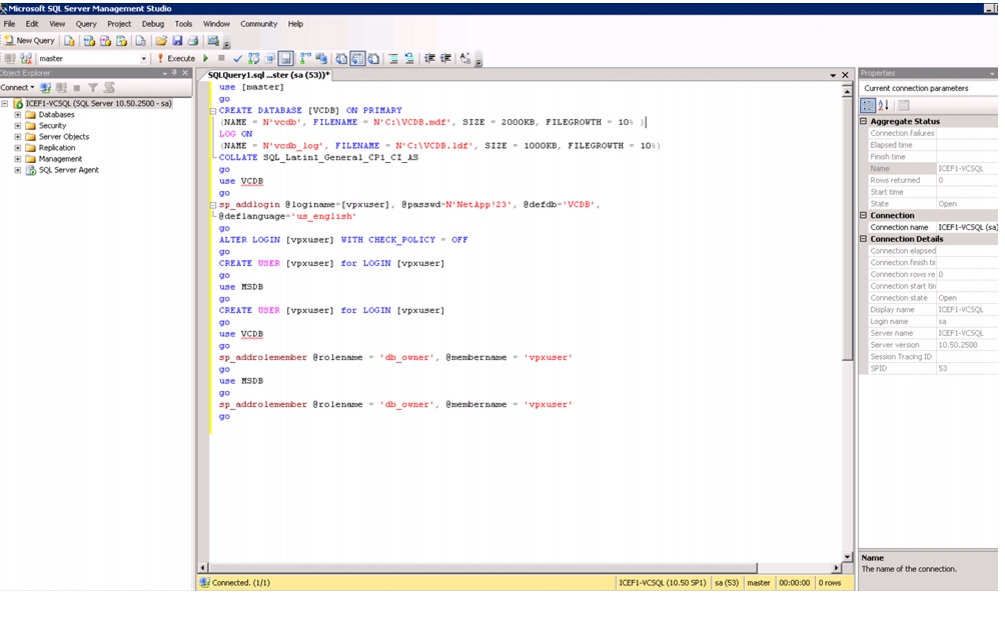
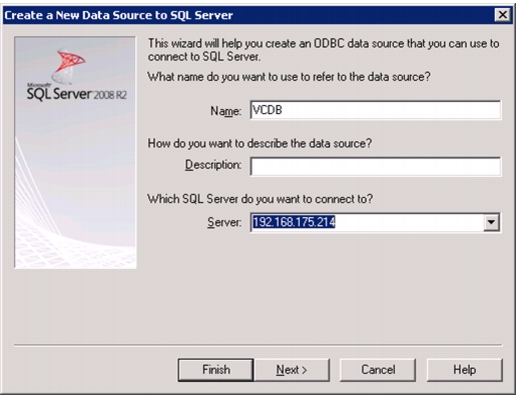
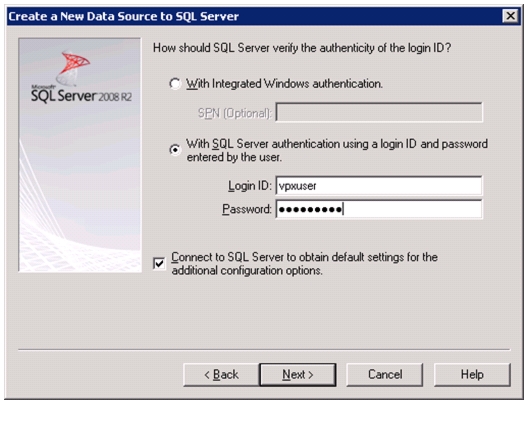
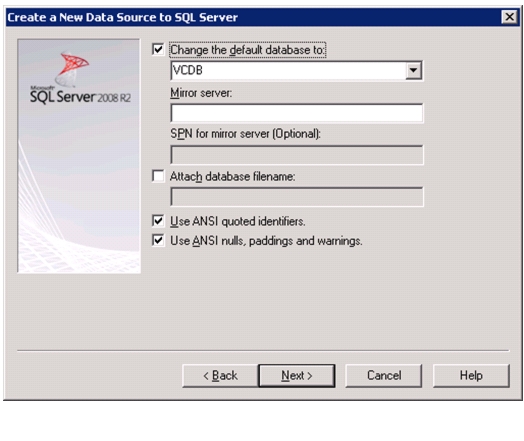
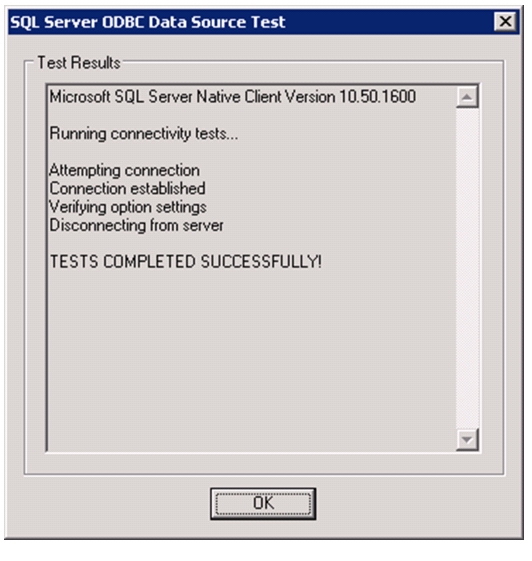
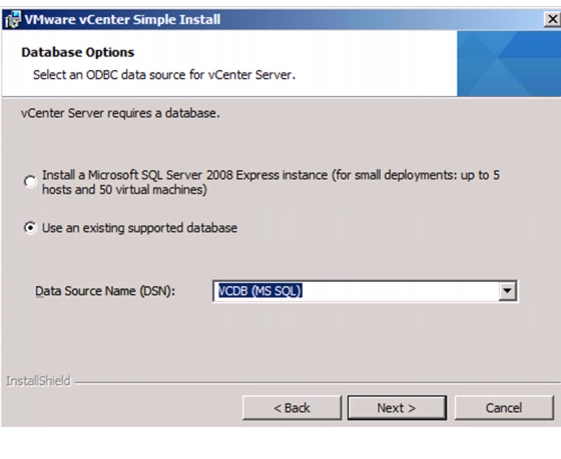
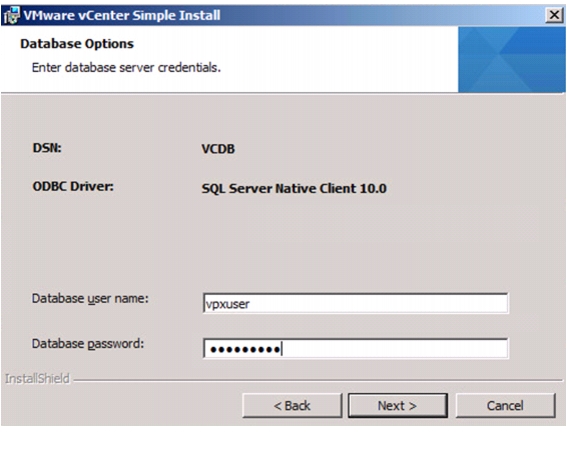
Install Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2
Build and Set Up VMware vCenter VM
FlexPod Cisco Nexus 1110-X and 1000V vSphere
Configure CIMC Interface on Both Cisco Nexus 1110-Xs
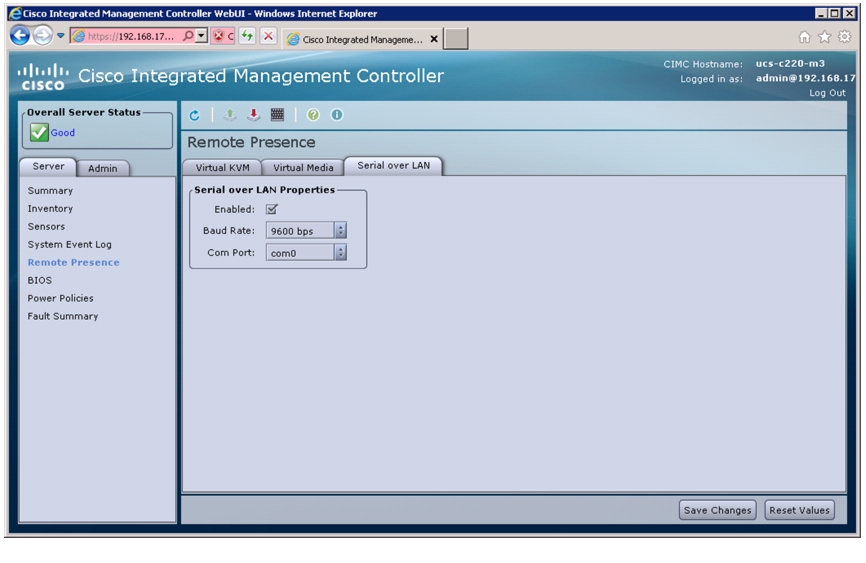
Configure Serial over LAN for Both Cisco Nexus 1110-Xs
Configure Cisco Nexus 1110-X Virtual Appliances
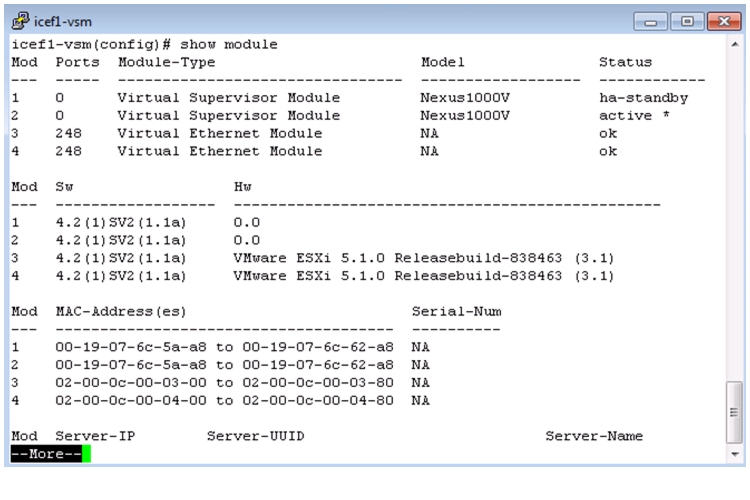
Set Up the Primary Cisco Nexus 1000V VSM
Set Up the Secondary Cisco Nexus 1000V VSM
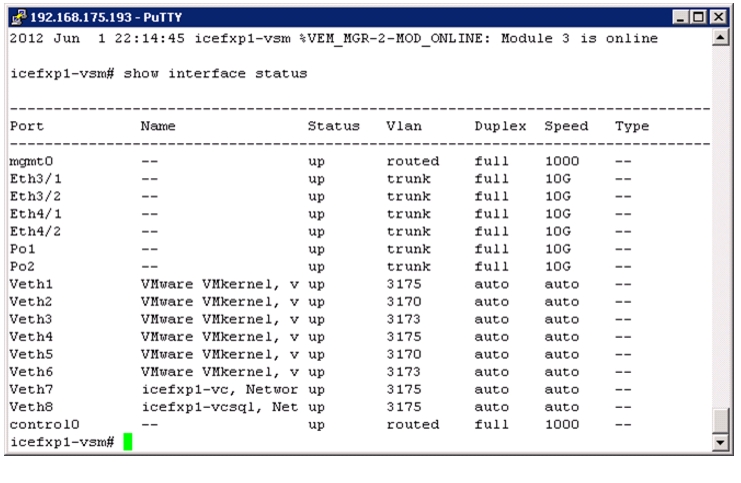
Install Virtual Ethernet Module on Each ESXi Host
Register Cisco Nexus 1000V as a vCenter Plug-in
Perform Base Configuration of the Primary VSM
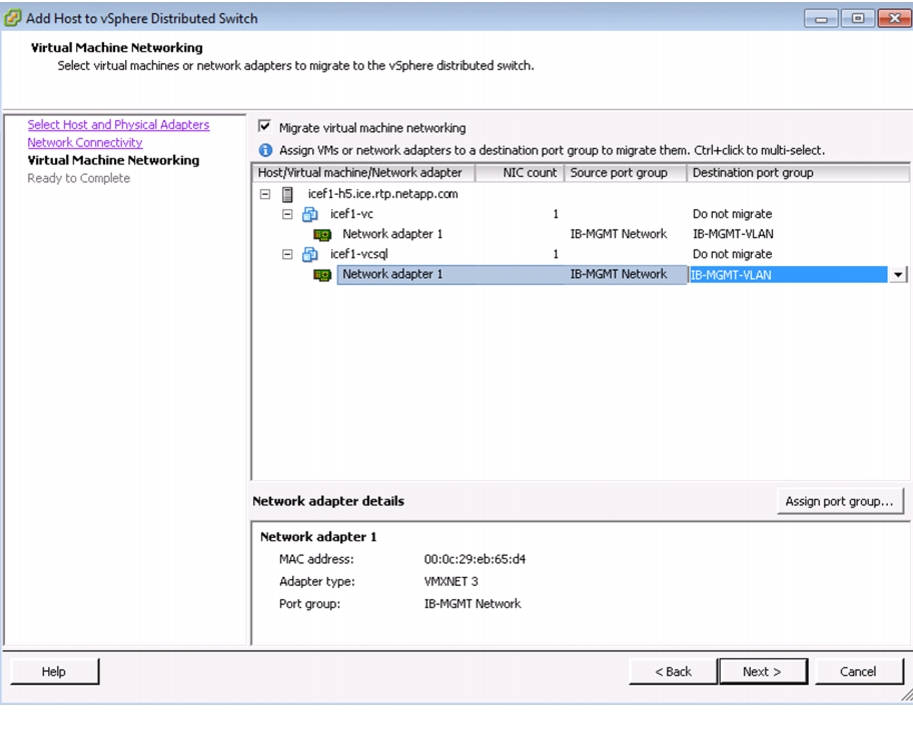
Migrate Networking Components for ESXi Hosts to Cisco Nexus 1000V
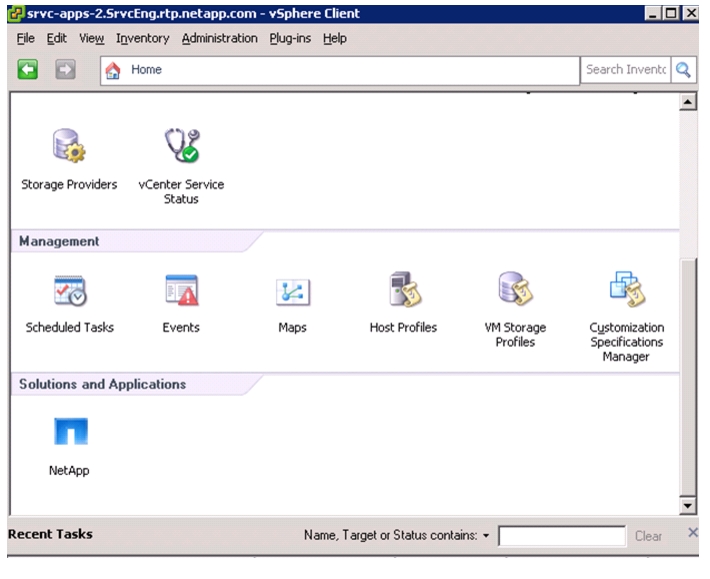
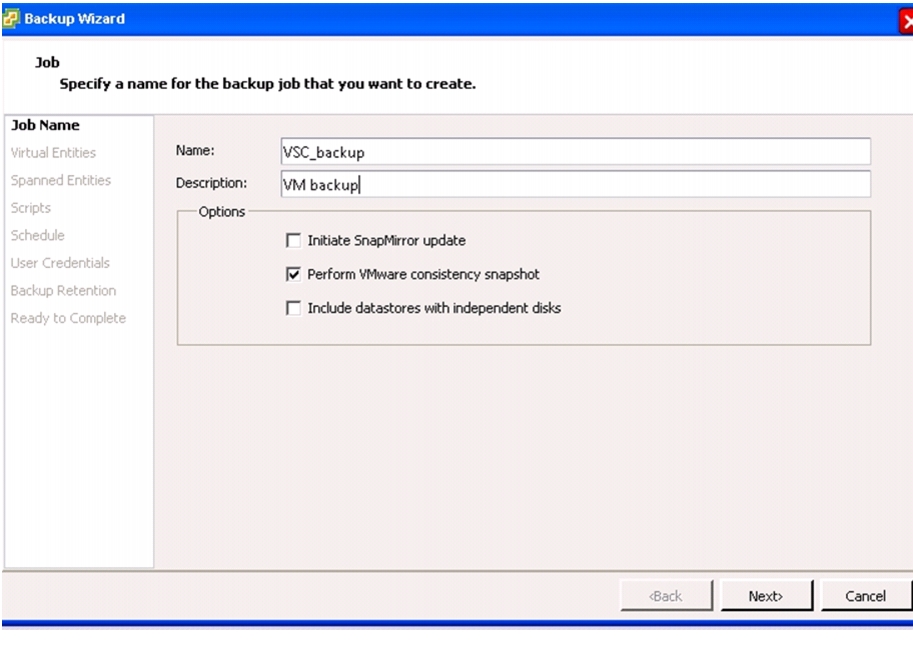
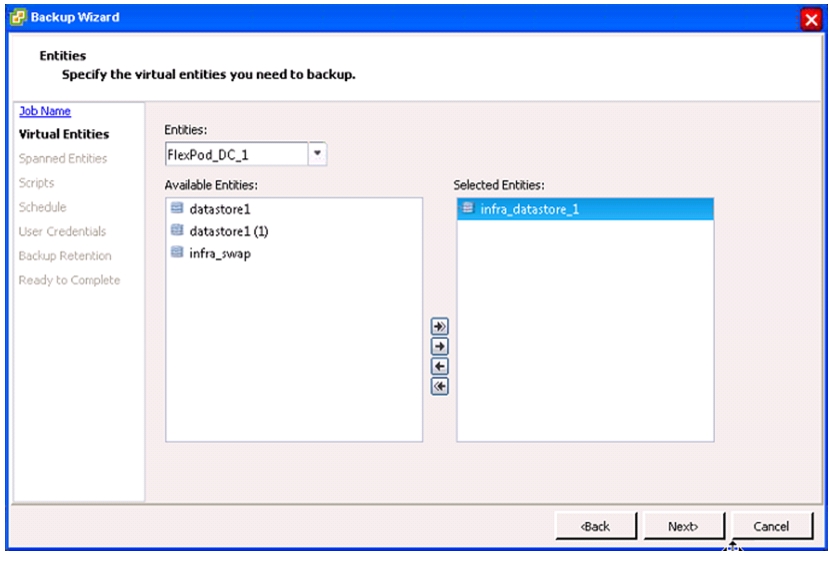
NetApp Virtual Storage Console (VSC) 4.1 Deployment Procedure
VSC 4.1 Preinstallation Considerations
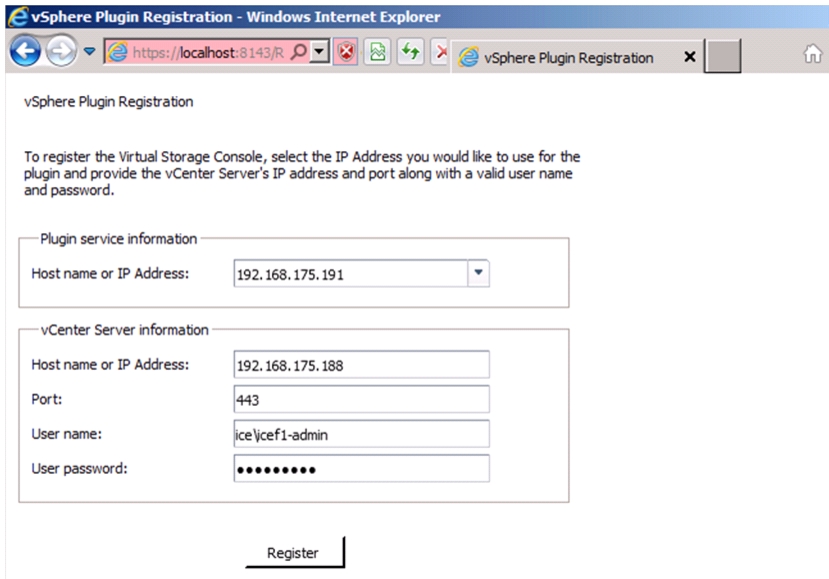
Register VSC with vCenter Server
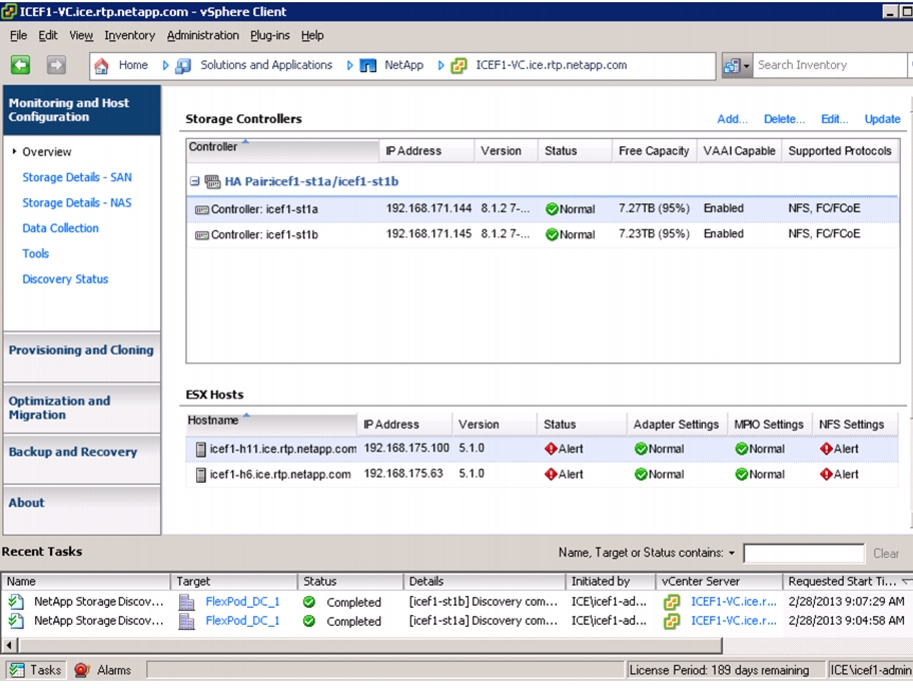
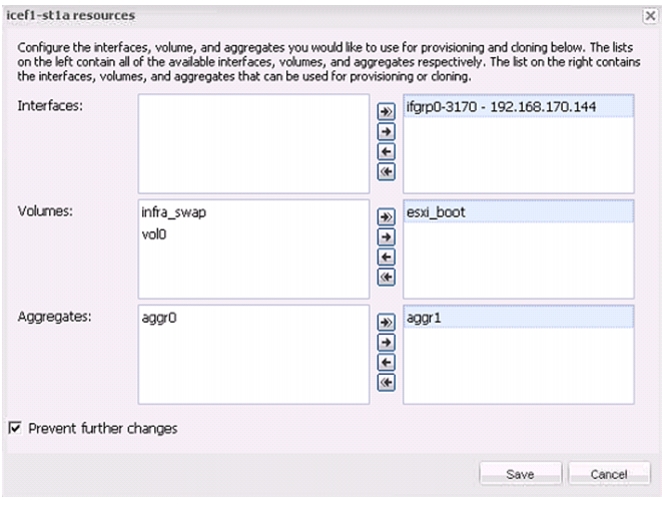
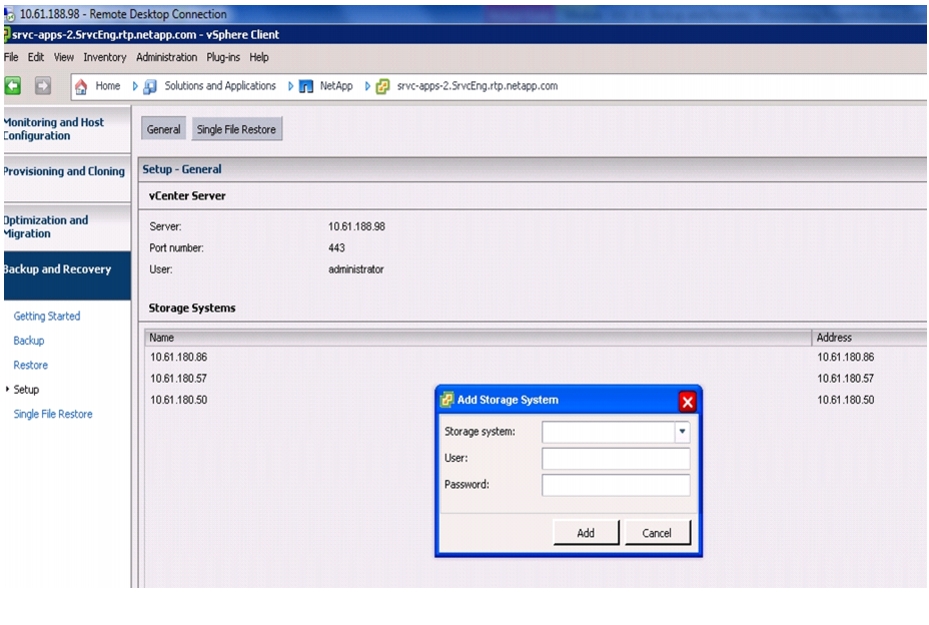
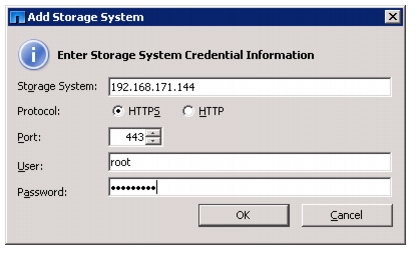
Discover and Add Storage Resources
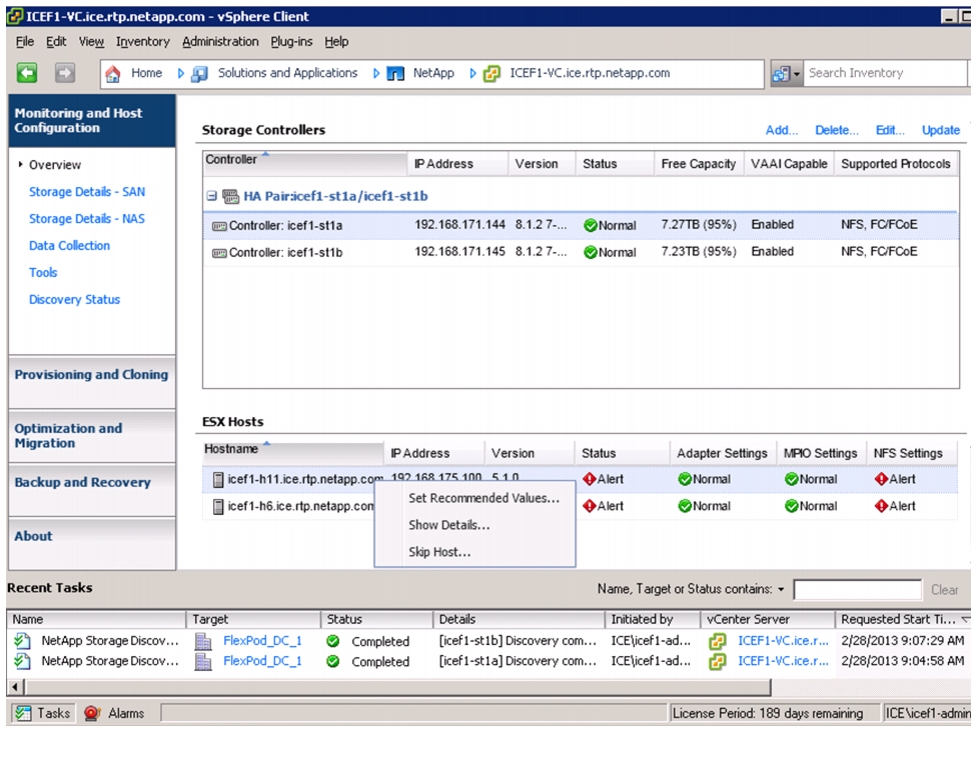
Optimal Storage Settings for ESXi Hosts
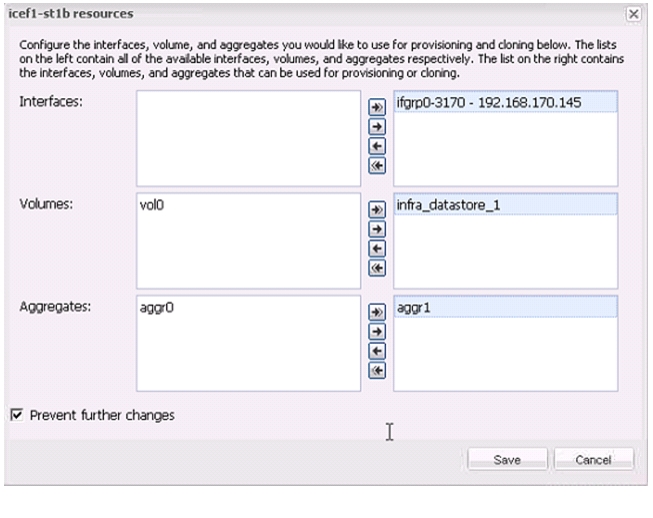
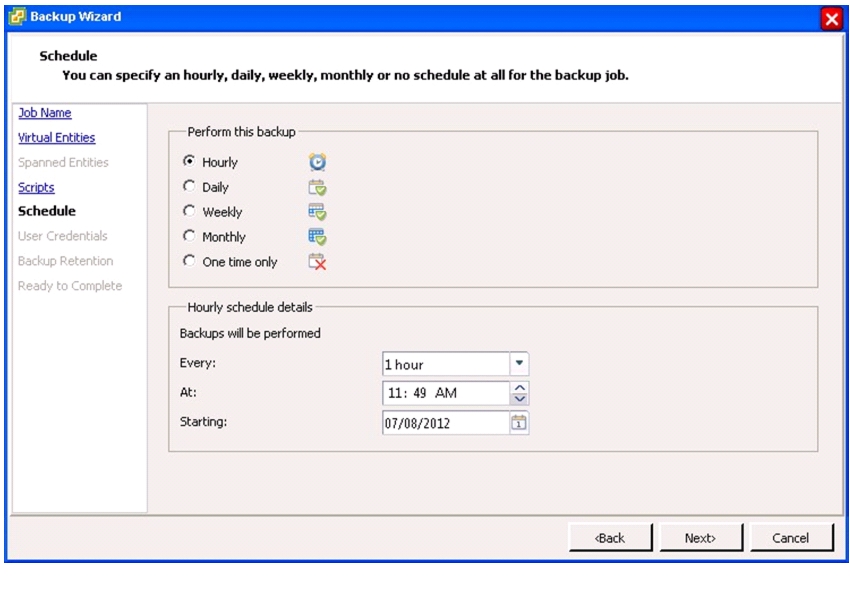
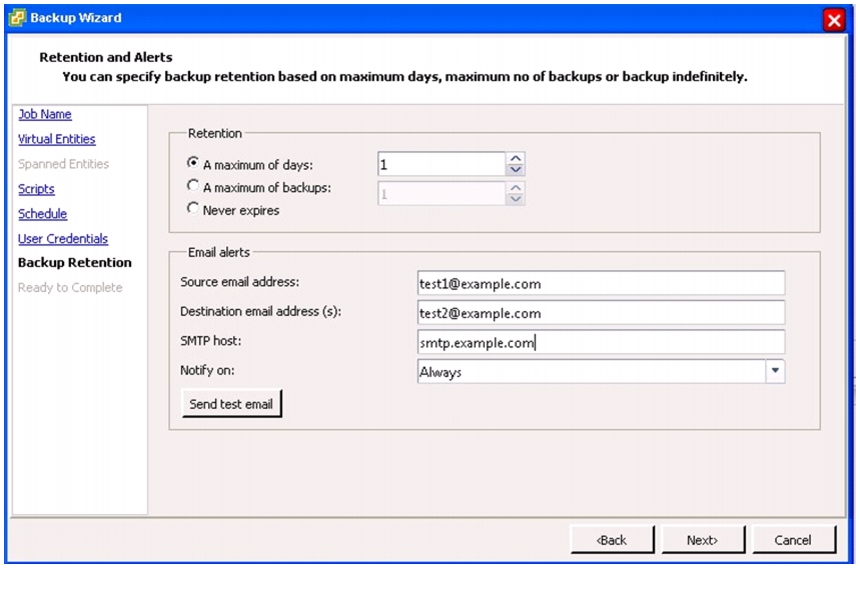
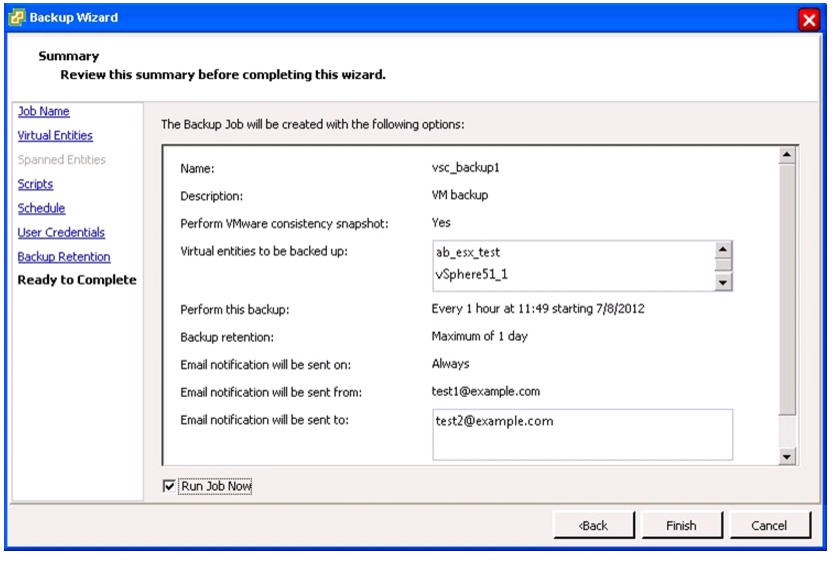
VSC 4.1 Provisioning and Cloning Setup
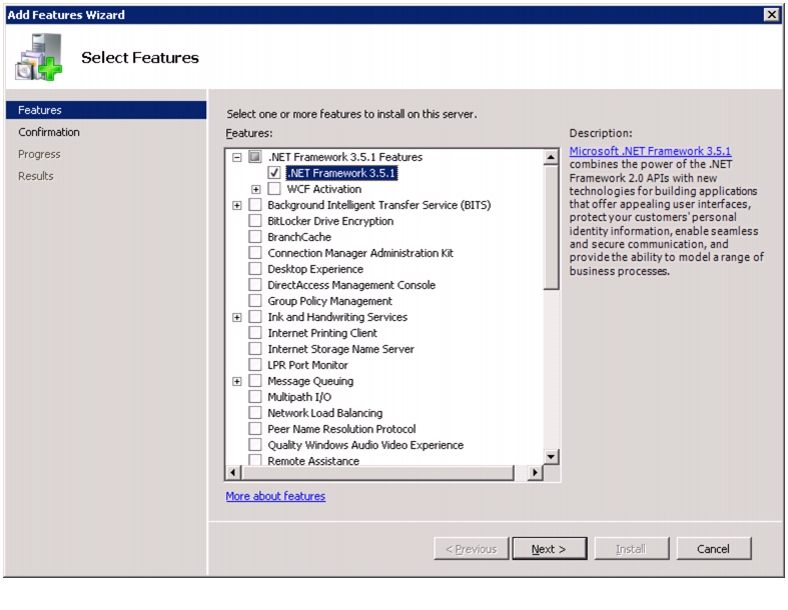
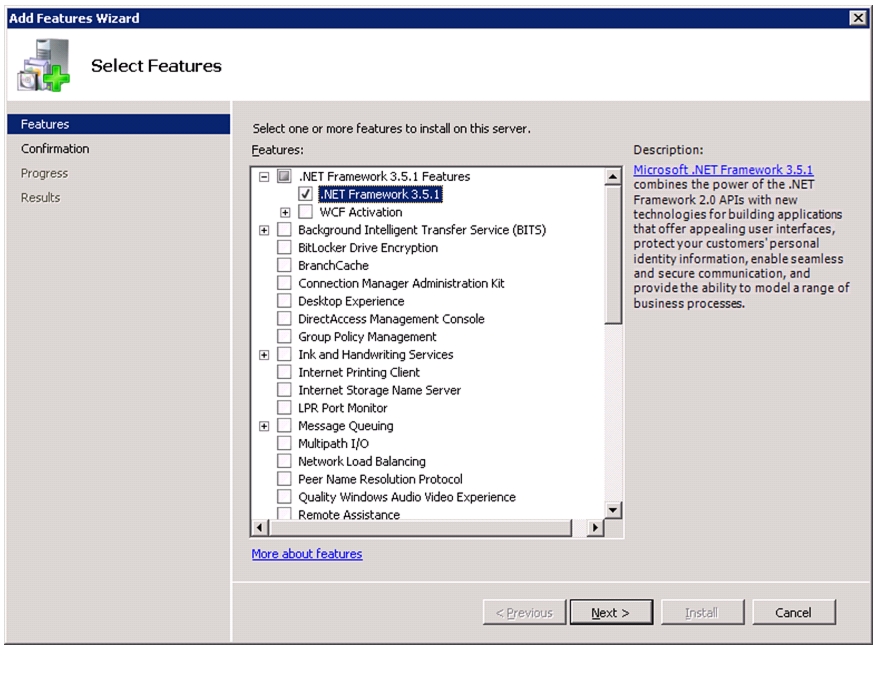
Install .NET Framework 3.5.1 Feature
Install NetApp OnCommand Core Package
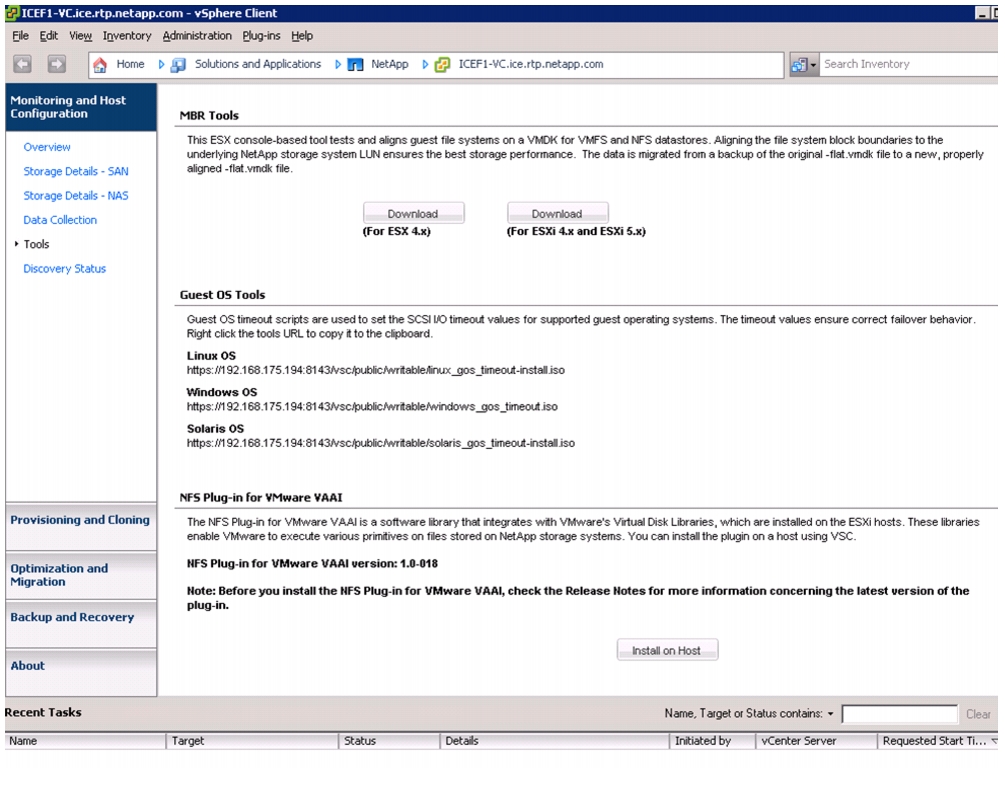
NetApp NFS Plug-In 1.0 for VMware VAAI
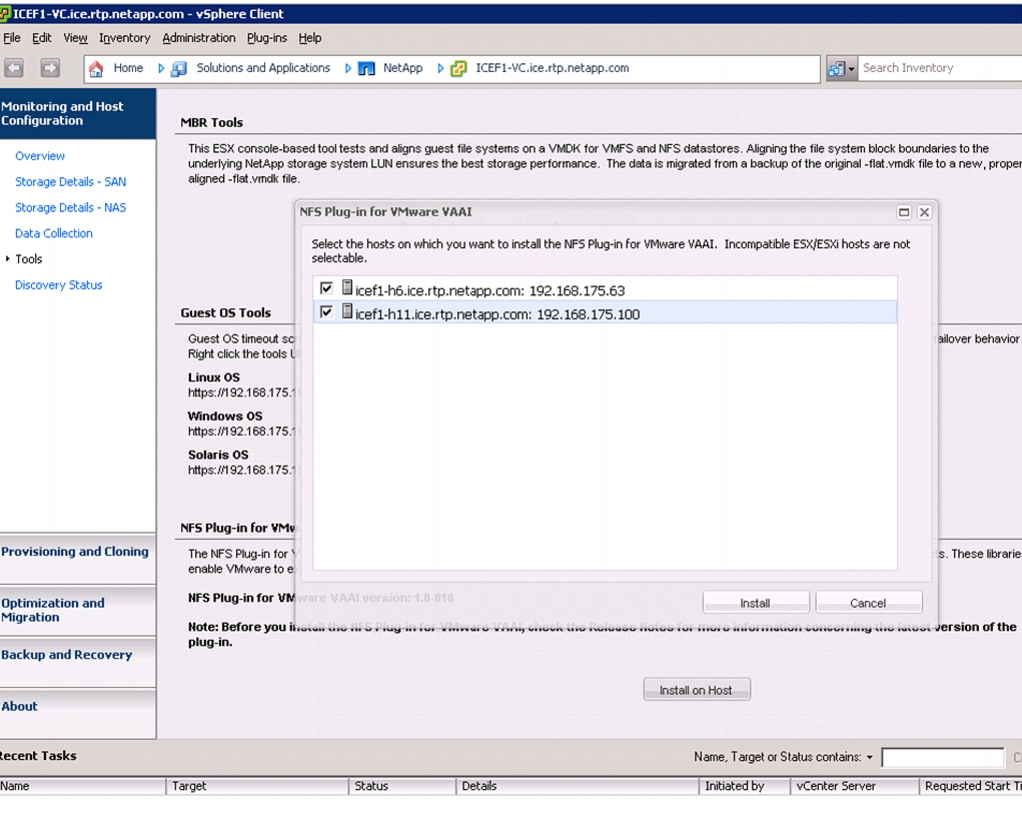
Install NetApp NFS Plug-In for VMware VAAI
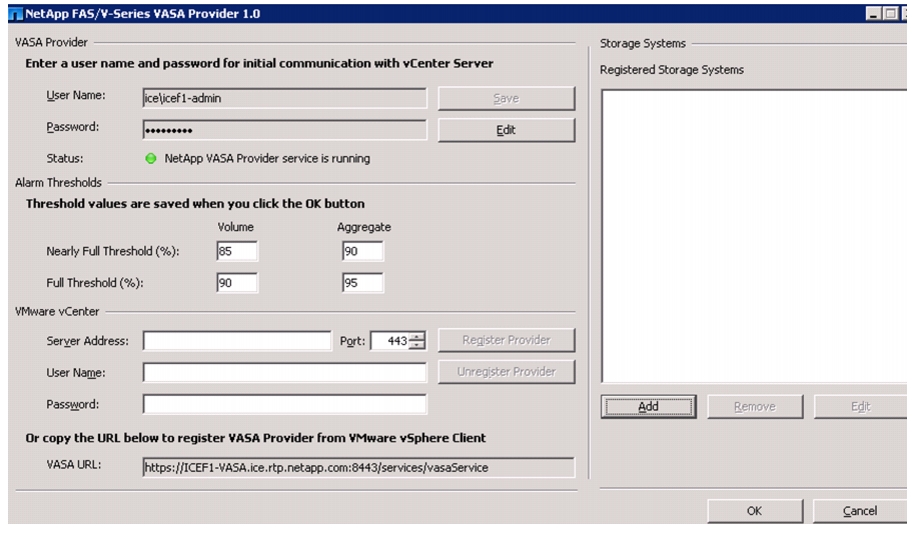
Configure NetApp VASA Provider
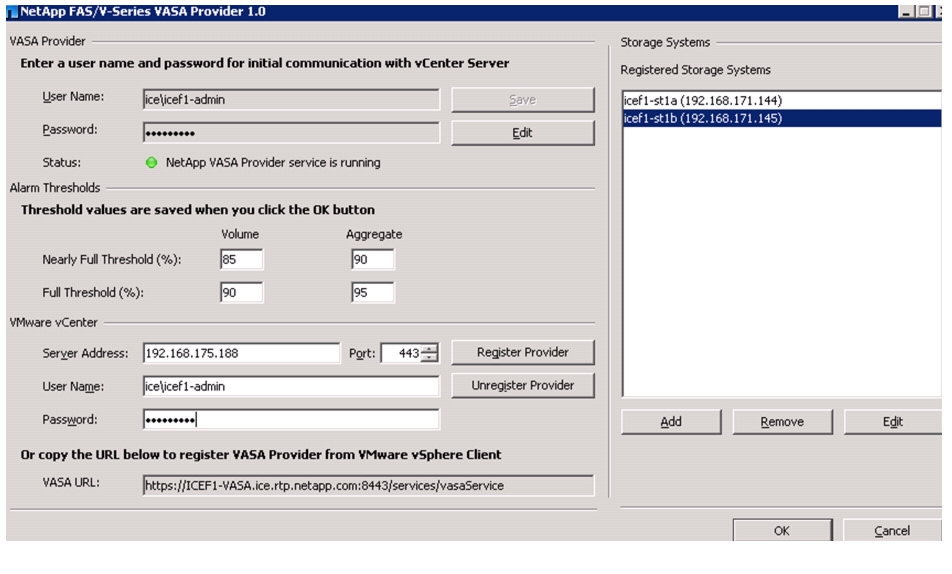
Register NetApp VASA Provider with vCenter Server
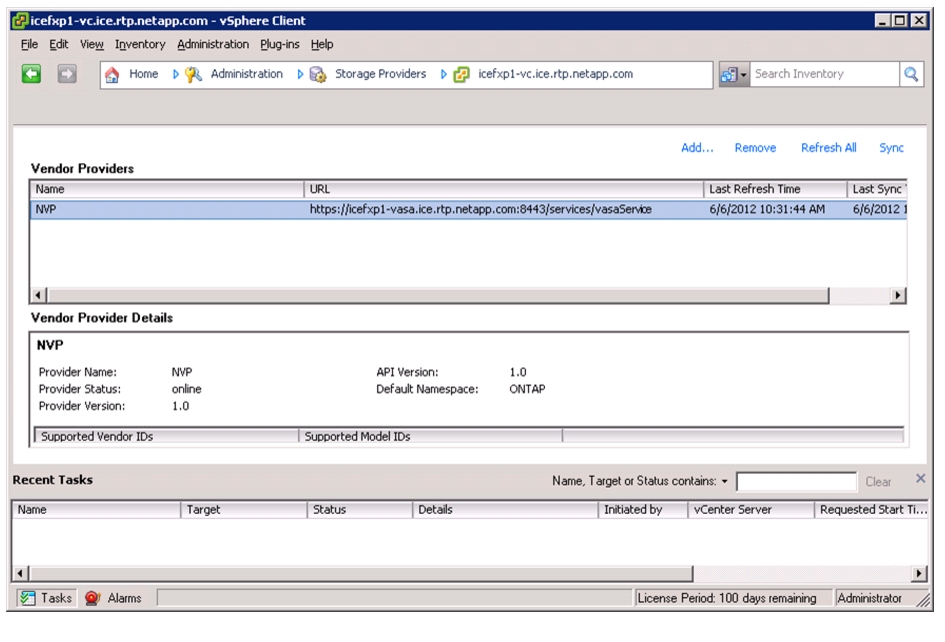
Verify VASA Provider in vCenter
Build Windows Active Directory Server VM(s)
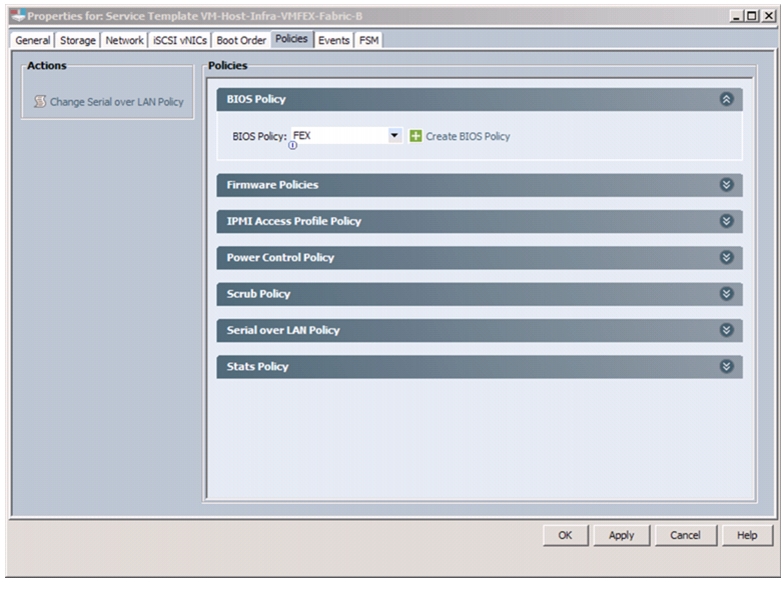
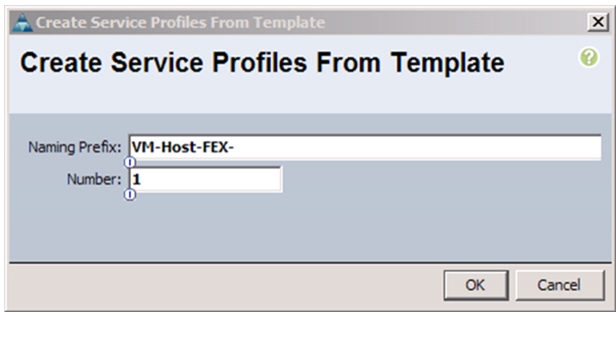
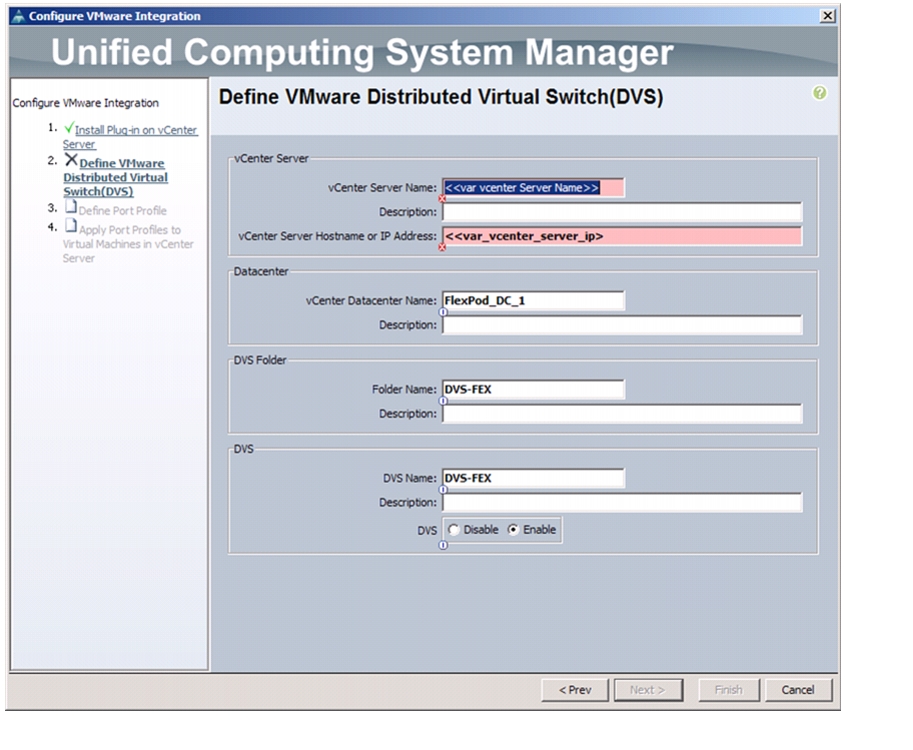
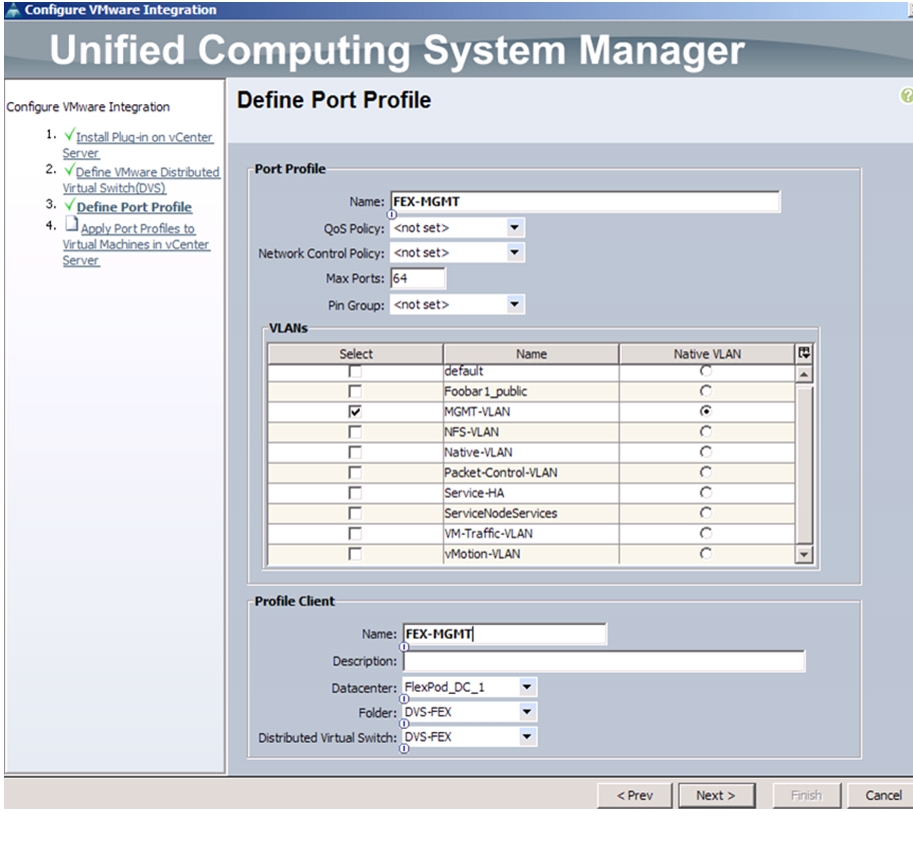
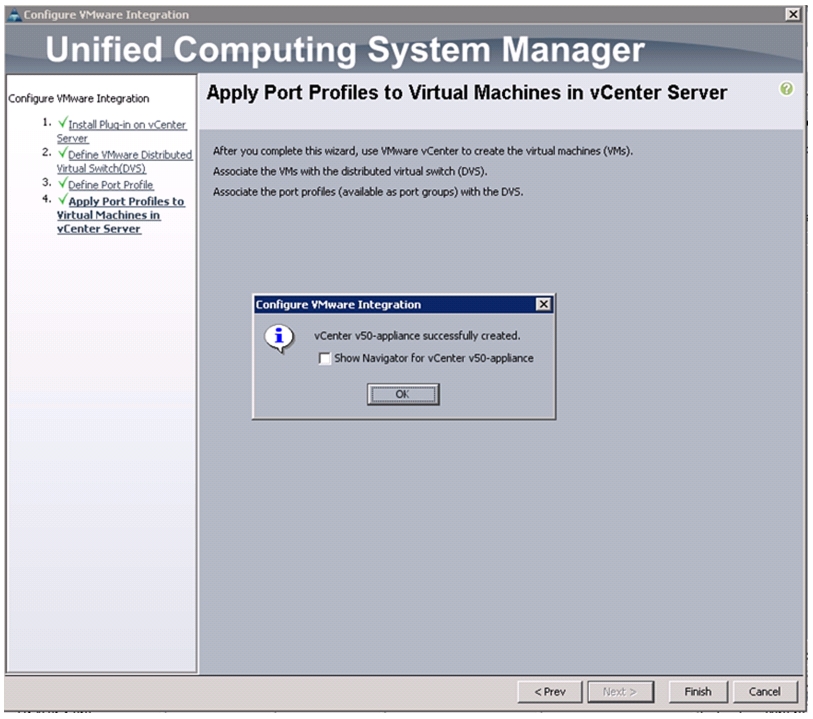
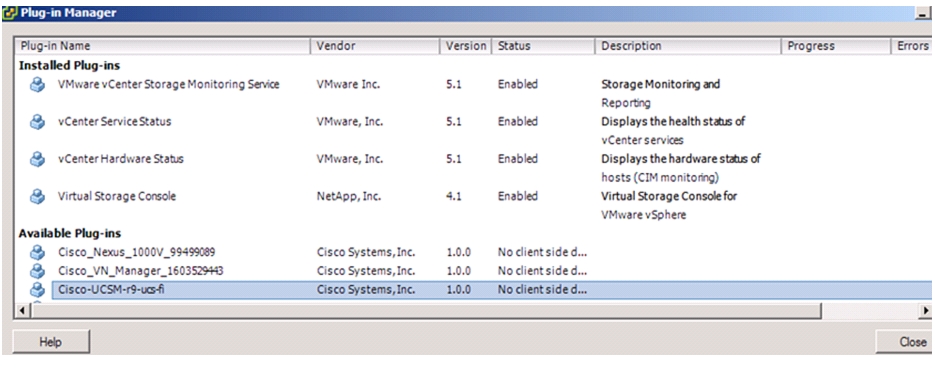
Configuring Cisco VM-FEX with the UCS Manager
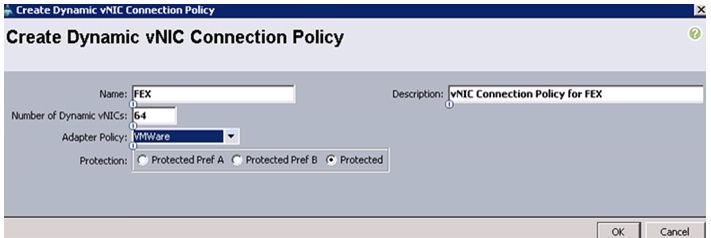
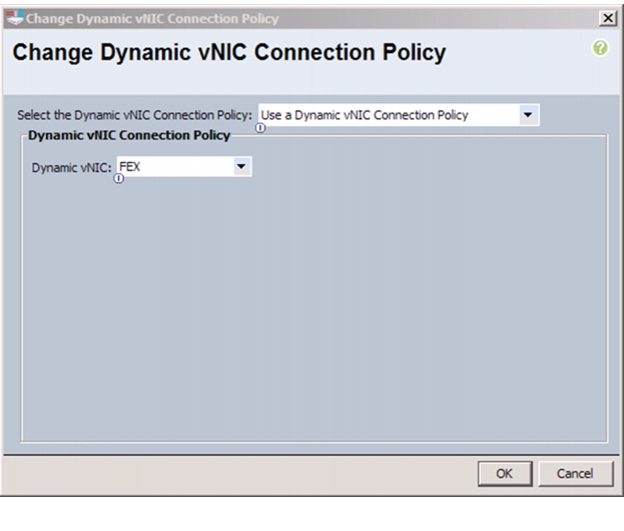
Create a Dynamic vNIC Connection Policy
Create a VM-FEX Enabled Service Profile Template
Install and Set Up VMware ESXi
Download Cisco VEM Software Bundle
Install the FEX Virtual Ethernet Module on Each ESXi Host
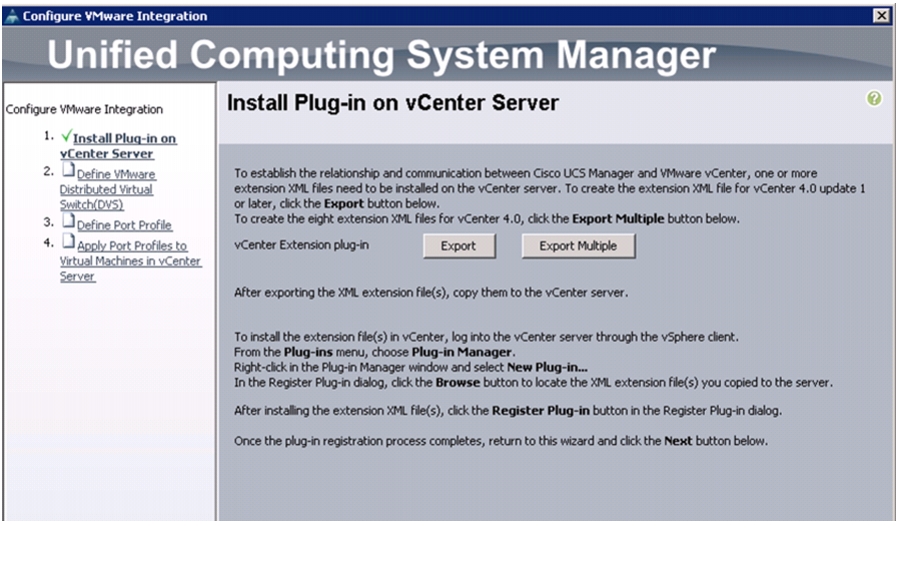
Integrate Cisco UCS with vCenter
Validate Setting in VMware vCenter
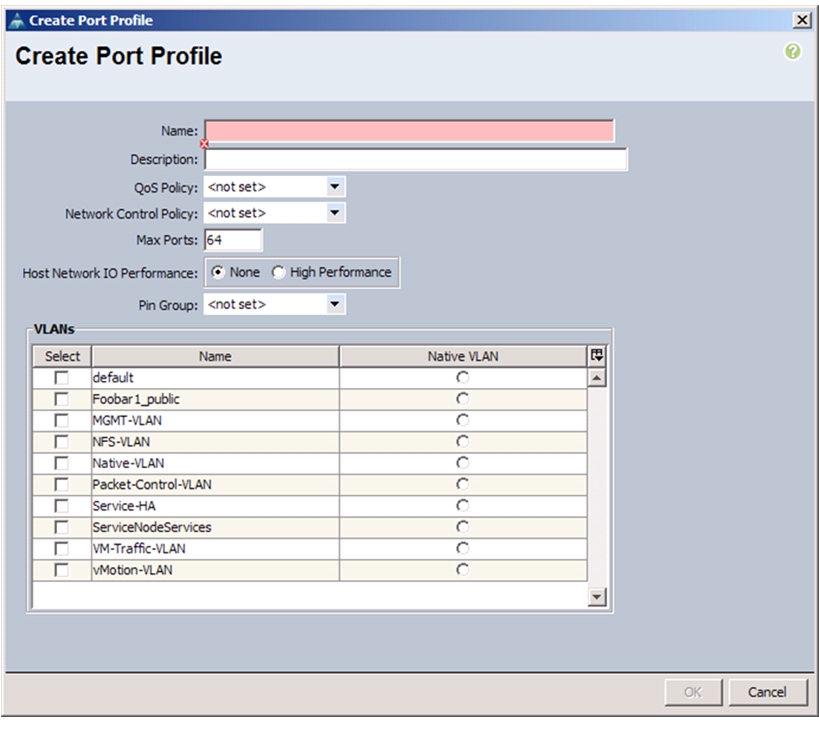
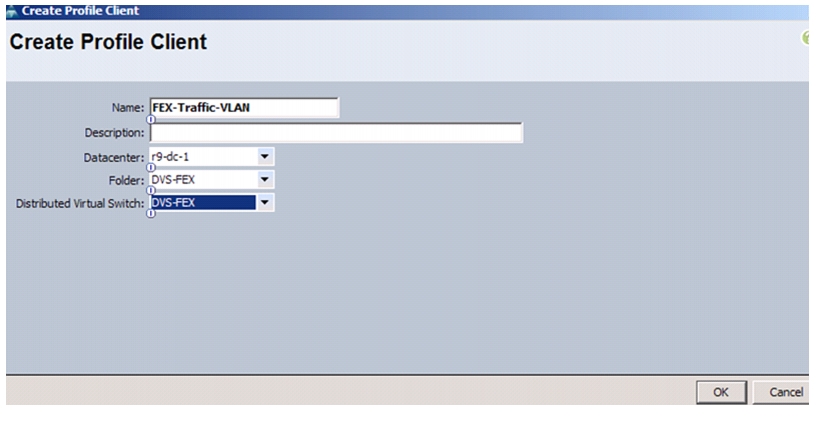
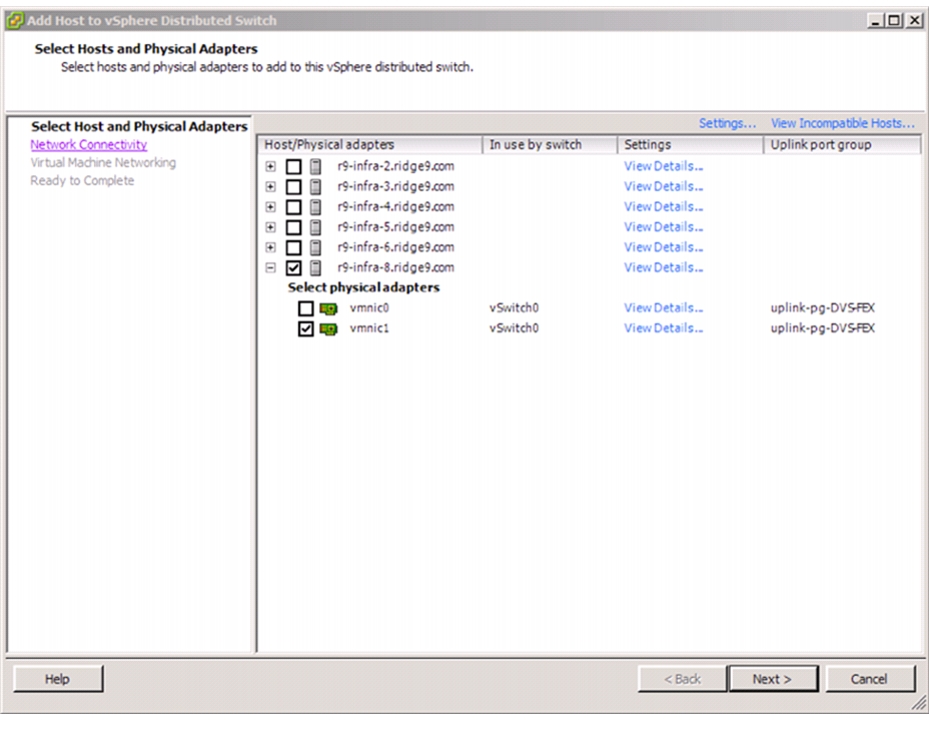
Add Distributed Port Group to the VDS (vSphere Distributed Switch)
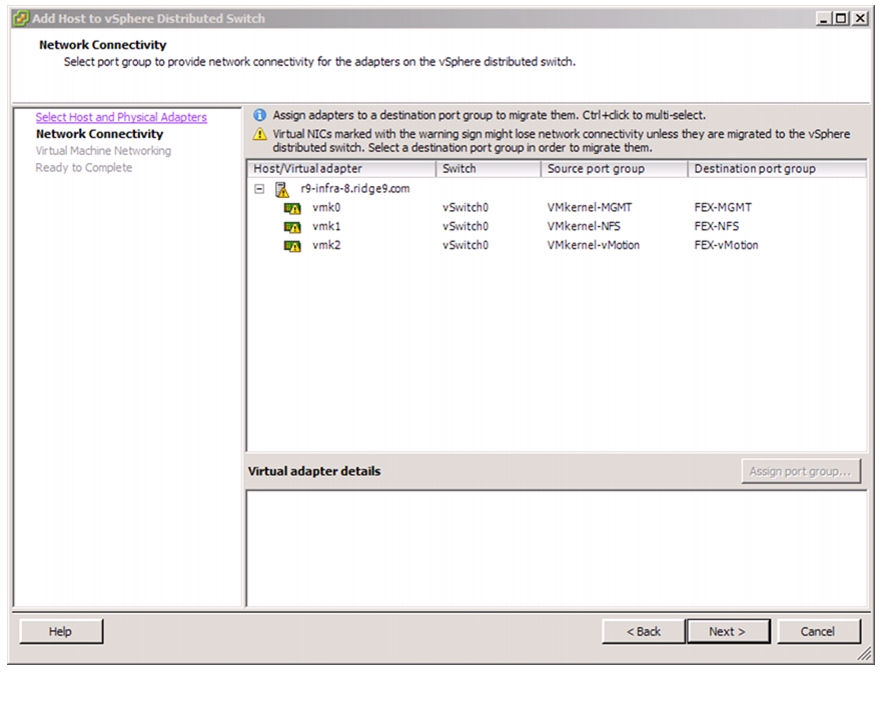
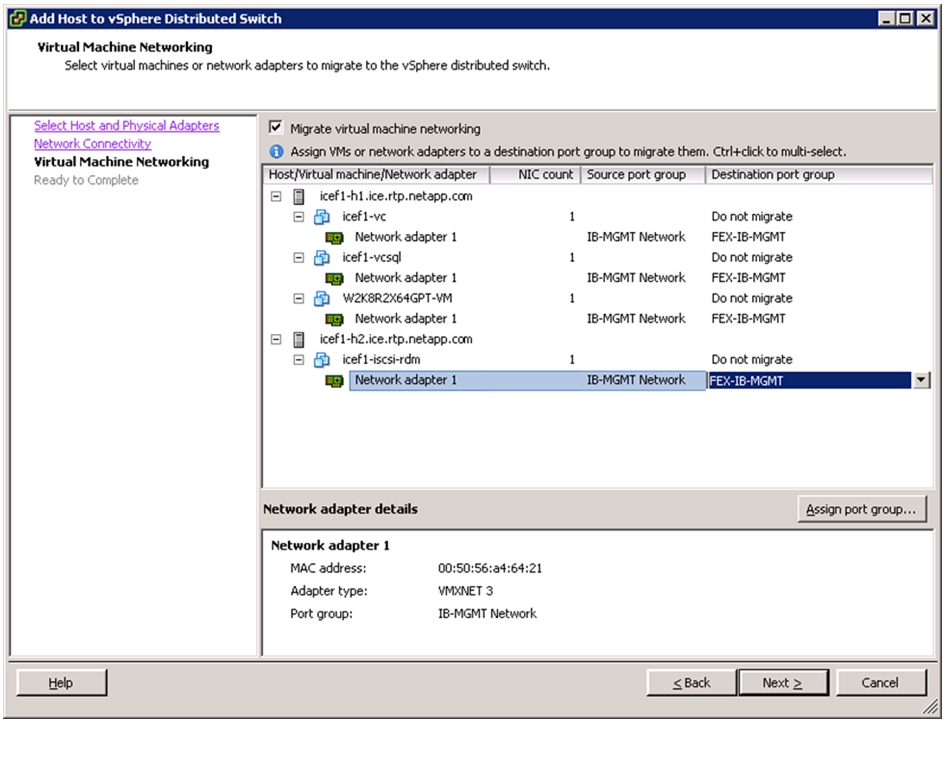
Migrate Networking Components for ESXi Hosts to Cisco DVS-FEX
Cisco Nexus 5548 Example Configurations
FlexPod Data Center with VMware vSphere 5.1 and Cisco Nexus 7000 with 7-ModeDeployment Guide for FlexPod with VMware vSphere 5.1 and Cisco Nexus 7000 with Data ONTAP 8.1.2 Operating in 7-ModeLast Updated: November 23, 2013
Building Architectures to Solve Business Problems
About the Authors
Lindsey Street, Systems Architect, Infrastructure and Cloud Engineering, NetApp SystemsLindsey Street is a systems architect in the NetApp Infrastructure and Cloud Engineering team. She focuses on the architecture, implementation, compatibility, and security of innovative vendor technologies to develop competitive and high-performance end-to-end cloud solutions for customers. Lindsey started her career in 2006 at Nortel as an interoperability test engineer, testing customer equipment interoperability for certification. Lindsey has her Bachelors of Science degree in Computer Networking and her Master's of Science in Information Security from East Carolina University.
John George, Reference Architect, Infrastructure and Cloud Engineering, NetApp SystemsJohn George is a Reference Architect in the NetApp Infrastructure and Cloud Engineering team and is focused on developing, validating, and supporting cloud infrastructure solutions that include NetApp products. Before his current role, he supported and administered Nortel's worldwide training network and VPN infrastructure. John holds a Master's degree in computer engineering from Clemson University.
Chris O'Brien, Technical Marketing Manager, Server Access Virtualization Business Unit, Cisco SystemsChris O'Brien is currently focused on developing infrastructure best practices and solutions that are designed, tested, and documented to facilitate and improve customer deployments. Previously, O'Brien was an application developer and has worked in the IT industry for more than 15 years.
Chris Reno, Reference Architect, Infrastructure and Cloud Engineering, NetApp SystemsChris Reno is a reference architect in the NetApp Infrastructure and Cloud Enablement group and is focused on creating, validating, supporting, and evangelizing solutions based on NetApp products. Before being employed in his current role, he worked with NetApp product engineers designing and developing innovative ways to perform Q and A for NetApp products, including enablement of a large grid infrastructure using physical and virtualized compute resources. In these roles, Chris gained expertise in stateless computing, netboot architectures, and virtualization.
About Cisco Validated Design (CVD) Program
The CVD program consists of systems and solutions designed, tested, and documented to facilitate faster, more reliable, and more predictable customer deployments. For more information visit:
http://www.cisco.com/go/designzone
ALL DESIGNS, SPECIFICATIONS, STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS (COLLECTIVELY, "DESIGNS") IN THIS MANUAL ARE PRESENTED "AS IS," WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND ITS SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE. IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE DESIGNS, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
THE DESIGNS ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. USERS ARE SOLELY RESPONSIBLE FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF THE DESIGNS. THE DESIGNS DO NOT CONSTITUTE THE TECHNICAL OR OTHER PROFESSIONAL ADVICE OF CISCO, ITS SUPPLIERS OR PARTNERS. USERS SHOULD CONSULT THEIR OWN TECHNICAL ADVISORS BEFORE IMPLEMENTING THE DESIGNS. RESULTS MAY VARY DEPENDING ON FACTORS NOT TESTED BY CISCO.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB's public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at http://www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2013 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
VMware vSphere 5.1 on FlexPod Data ONTAP Operating in 7-Mode Deployment Guide
Overview
Industry trends indicate a vast data center transformation toward shared infrastructures. By using virtualization, enterprise customers have embarked on the journey to the cloud by moving away from application silos and toward shared infrastructure, thereby increasing agility and reducing costs. Cisco and NetApp have partnered to deliver FlexPod, which serves as the foundation for a variety of workloads and enables efficient architectural designs that are based on customer requirements.
Audience
This document describes the architecture and deployment procedures of an infrastructure composed of Cisco®, NetApp®, and VMware® virtualization that uses FCoE-based storage serving NAS and SAN protocols. The intended audience for this document includes, but is not limited to, sales engineers, field consultants, professional services, IT managers, partner engineering, and customers who want to deploy the core FlexPod architecture with NetApp Data ONTAP® operating in 7-mode.
Architecture
The FlexPod architecture is highly modular or "podlike." Although each customer's FlexPod unit varies in its exact configuration, after a FlexPod unit is built, it can easily be scaled as requirements and demand change. The unit can be scaled both up (adding resources to a FlexPod unit) and out (adding more FlexPod units).
Specifically, FlexPod is a defined set of hardware and software that serves as an integrated foundation for both virtualized and nonvirtualized solutions. VMware vSphere® built on FlexPod includes NetApp storage, NetApp Data ONTAP, Cisco networking, the Cisco Unified Computing System™ (Cisco UCS®), and VMware vSphere software in a single package. The design is flexible enough that the networking, computing, and storage can fit in one data center rack or be deployed according to a customer's data center design. Port density enables the networking components to accommodate multiple configurations of this kind.
One benefit of the FlexPod architecture is the ability to customize or "flex" the environment to suit a customer's requirements. This is why the reference architecture detailed in this document highlights the resiliency, cost benefit, and ease of deployment of an FCoE-based storage solution. A storage system capable of serving multiple protocols across a single interface allows for customer choice and investment protection because it truly is a wire-once architecture.
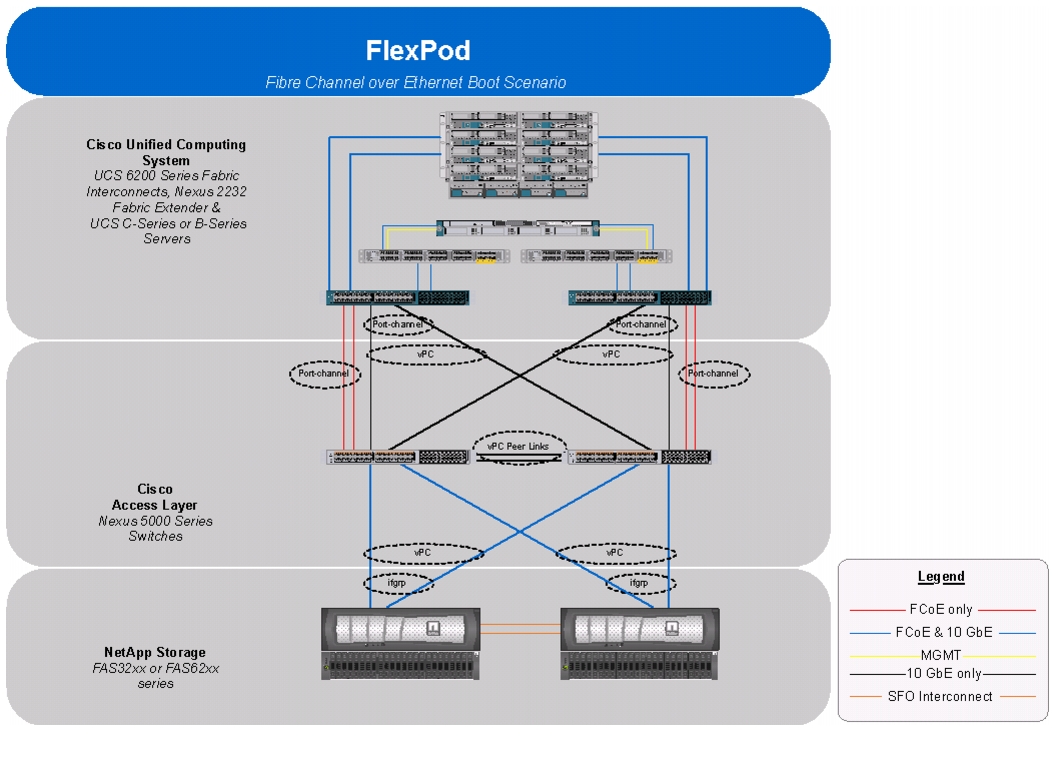
Figure 1 shows the VMware vSphere built on FlexPod components and the network connections for a configuration with FCoE-based storage. This design uses the Cisco Nexus® 5548UP, Cisco Nexus 2232PP FEX, and Cisco UCS C-Series and B-Series with the Cisco UCS virtual interface card (VIC) and the NetApp FAS family of storage controllers connected in a highly available design using Cisco Virtual PortChannels (vPCs). This infrastructure is deployed to provide FCoE-booted hosts with file- and block-level access to shared storage datastores. The reference architecture reinforces the "wire-once" strategy, because as additional storage is added to the architecture; be it FC, FCoE, or 10 Gigabit Ethernet, no recabling is required from the hosts to the Cisco UCS fabric interconnect.
Figure 1 VMware vSpahere Built on Flexpod Components
The reference configuration includes:
•
Two Cisco Nexus 5548UP switches
•
Two Cisco Nexus 2232PP fabric extenders
•
Two Cisco UCS 6248UP fabric interconnects
•
Support for 16 Cisco UCS C-Series servers without any additional networking components
•
Support for 8 Cisco UCS B-Series servers without any additional blade server chassis
•
Support for hundreds of Cisco UCS C-Series and B-Series servers by way of additional fabric extenders and blade server chassis
•
One NetApp FAS3250-A (HA pair) operating in 7-mode
Storage is provided by a NetApp FAS3250-AE (HA configuration in two chassis) operating 7-Mode. All system and network links feature redundancy, providing end-to-end high availability (HA). For server virtualization, the deployment includes VMware vSphere. Although this is the base design, each of the components can be scaled flexibly to support specific business requirements. For example, more (or different) servers or even blade chassis can be deployed to increase compute capacity, additional disk shelves can be deployed to improve I/O capacity and throughput, and special hardware or software features can be added to introduce new capabilities.
This document guides you through the low-level steps for deploying the base architecture, as shown in Figure 1. These procedures cover everything from physical cabling to compute and storage configuration to configuring virtualization with VMware vSphere.
Software Revisions
It is important to note the software versions used in this document. Table 1 details the software revisions used throughout this document.
Configuration Guidelines
This document provides details for configuring a fully redundant, highly available configuration for a FlexPod unit with IP-based storage. Therefore, reference is made to which component is being configured with each step, either A or B. For example, controller A and controller B are used to identify the two NetApp storage controllers that are provisioned with this document, and Nexus A and Nexus B identify the pair of Cisco Nexus switches that are configured. The Cisco UCS fabric interconnects are similarly configured. Additionally, this document details steps for provisioning multiple Cisco UCS hosts, and these are identified sequentially: VM-Host-Infra-01, VM-Host-Infra-02, and so on. Finally, to indicate that you should include information pertinent to your environment in a given step, <text> appears as part of the command structure. See the following example for the vlan create command:
controller A> vlan createUsage:vlan create [-g {on|off}] <ifname> <vlanid_list>vlan add <ifname> <vlanid_list>vlan delete -q <ifname> [<vlanid_list>]vlan modify -g {on|off} <ifname>vlan stat <ifname> [<vlanid_list>]Example:controller A> vlan create vif0 <management VLAN ID>This document is intended to enable you to fully configure the customer environment. In this process, various steps require you to insert customer-specific naming conventions, IP addresses, and VLAN schemes, as well as to record appropriate MAC addresses. Table 2 describes the VLANs necessary for deployment as outlined in this guide. The VM-Mgmt VLAN is used for management interfaces of the VMware vSphere hosts. Table 3 lists the VSANs necessary for deployment as outlined in this guide. Table 4 lists the configuration variables that are used throughout this document. Table 4 can be completed based on the specific site variables and used in implementing the document configuration procedures.
If you use separate in-band and out-of-band management VLANs, you must create a Layer 3 route between these VLANs. For this validation, a common management VLAN was used.
Physical Infrastructure
FlexPod Cabling on Data ONTAP Operating in 7-Mode
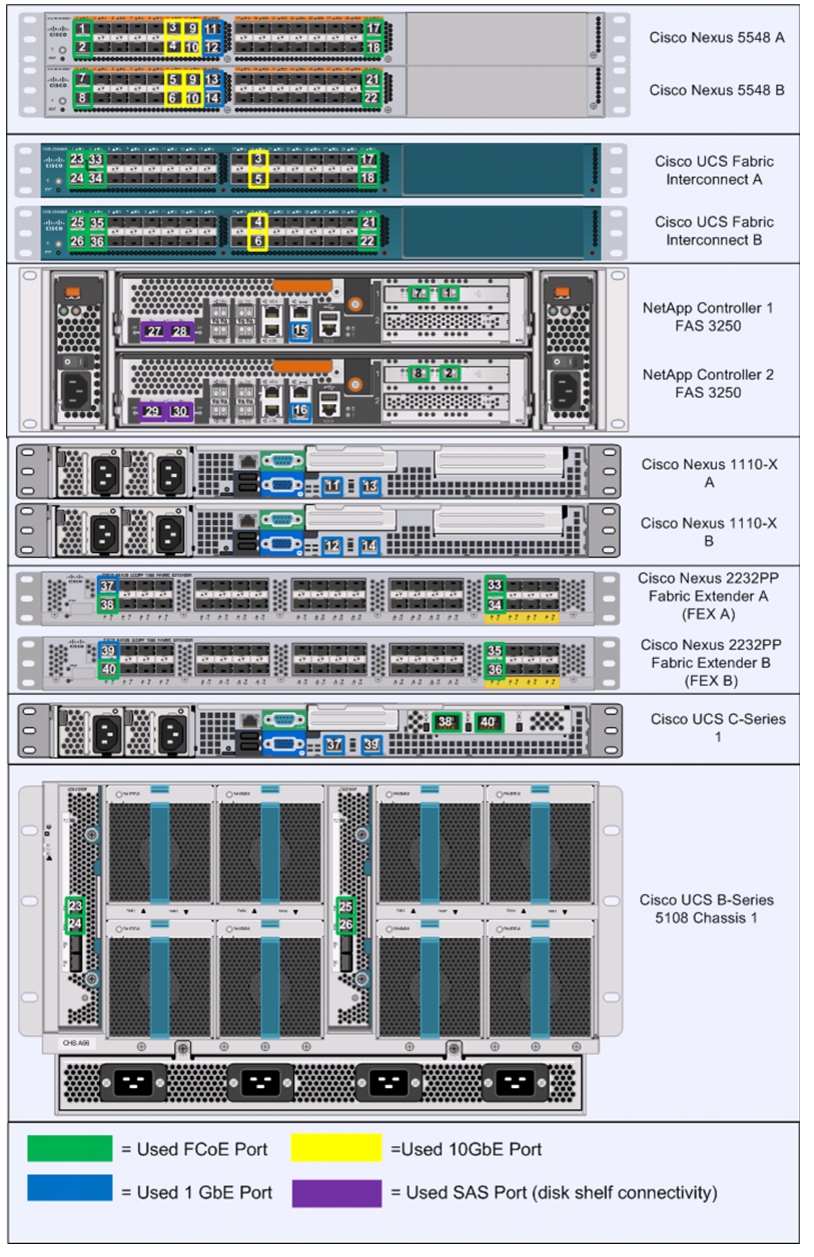
Figure 2 shows the cabling diagram for a FlexPod configuration using Data ONTAP operating on 7-mode.
Figure 2 Flexpod Cabling Diagram in Data ONTAP 7-Mode
The information provided in Table 6 through Table 17 corresponds to each connection shown in Figure 2.
Note
For devices requiring GbE connectivity, use the GbE Copper SFP+s (GLC-T=).
Note
For devices requiring GbE connectivity, use the GbE Copper SFP+s (GLC-T=).
Storage Configuration
Controller FAS32xx Series
Table 18 Controller FAS32XX Series Prerequisites
Physical site where storage system needs to be installed must be ready
Site Reference Guide:
http://support.netapp.com/NOW/public/knowledge/docs/hardware/NetApp/site/pdf/site.pdf
Refer to the "Site Preparation" section
Storage system connectivity requirements
Site Reference Guide:
http://support.netapp.com/NOW/public/knowledge/docs/hardware/NetApp/site/pdf/site.pdf
Refer to the "System Connectivity Requirements" section
Storage system general power requirements
Site Reference Guide:
http://support.netapp.com/NOW/public/knowledge/docs/hardware/NetApp/site/pdf/site.pdf
Refer to the "Circuit Breaker, Power Outlet Balancing, System Cabinet Power Cord Plugs, and Console Pinout Requirements" section
Storage system model-specific requirements
Site Reference Guide:
http://support.netapp.com/NOW/public/knowledge/docs/hardware/NetApp/site/pdf/site.pdf
Refer to the "FAS32xx/V32xx Series Systems" section
System Configuration Guides
System configuration guides provide supported hardware and software components for the specific Data ONTAP version. These online guides provide configuration information for all NetApp storage appliances currently supported by the Data ONTAP software. They also provide a table of component compatibilities.
1.
Make sure that the hardware and software components are supported with the version of Data ONTAP that you plan to install by checking the System Configuration Guides at:
https://now.netapp.com/NOW/knowledge/docs/hardware/NetApp/syscfg/
2.
Click the appropriate NetApp storage appliance and then click the component you want to view. Alternatively, to compare components by storage appliance, click a component and then click the NetApp storage appliance you want to view.
Controllers
Follow the physical installation procedures for the controllers in the FAS32xx documentation in NetApp Support site at:
https://now.netapp.com/NOW/knowledge/docs/hardware/filer/210-05224+A0.pdf
Disk Shelves DS2246 Series
DS2246 Disk Shelves
To install a disk shelf for a new storage system, see:
https://now.netapp.com/NOW/knowledge/docs/hardware/filer/210-04881+A0.pdf
For information on cabling with the controller model, see SAS Disk Shelves Universal SAS and ACP Cabling Guide at:
https://now.netapp.com/NOW/knowledge/docs/hardware/filer/215-05500_A0.pdf
The following information applies to DS2246 disk shelves:
•
SAS disk drives use software-based disk ownership. Ownership of a disk drive is assigned to a specific storage system by writing software ownership information on the disk drive rather than by using the topography of the storage system's physical connections.
•
Connectivity terms used: shelf-to-shelf (daisy-chain), controller-to-shelf (top connections), and shelf-to controller (bottom connections).
•
Unique disk shelf IDs must be set per storage system (a number from 0 through 98).
•
Disk shelf power must be turned on to change the digital display shelf ID. The digital display is on the front of the disk shelf.
•
Disk shelves must be power-cycled after the shelf ID is changed for it to take effect.
•
Changing the shelf ID on a disk shelf that is part of an existing storage system running Data ONTAP requires that you wait at least 30 seconds before turning the power back on so that Data ONTAP can properly delete the old disk shelf address and update the copy of the new disk shelf address.
•
Changing the shelf ID on a disk shelf that is part of a new storage system installation (the disk shelf is not yet running Data ONTAP) requires no wait; you can immediately power-cycle the disk shelf.
Data ONTAP 8.1.2
Complete the Configuration Worksheet
Before running the setup script, complete the configuration worksheet from the product manual.
For more information on Configuration Worksheet, see:
https://library.netapp.com/ecm/ecm_get_file/ECMM1249829
Note
To access Configuration Worksheet, you need to have access to NetApp Support site: http://now.netapp.com/
Assign Controller Disk Ownership and initialize storage
This section provides details for assigning disk ownership and disk initialization and verification.
Typical best practices should be followed when determining the number of disks to assign to each controller head. You may choose to assign a disproportionate number of disks to a given storage controller in an HA pair, depending on the intended workload.
In this reference architecture, half the total number of disks in the environment is assigned to one controller and the remainder to its partner.
Controller1
1.
Connect to the storage system console port. You should see a Loader-A prompt. However, if the storage system is in a reboot loop, Press Ctrl-C to exit the Autoboot loop when you see this message:
Starting AUTOBOOT press Ctrl-C to abort...2.
If the system is at the LOADER prompt, enter the following command to boot Data ONTAP:
autoboot3.
During system boot, press Ctrl-C when prompted for the Boot Menu:
Press Ctrl-C for Boot Menu...
Note
If 8.1.2 is not the version of software being booted, follow the steps to install new software. If 8.1.2 is the version being booted, then proceed with step 14, maintenance mode boot.
4.
To install new software first select option 7.
75.
Answer yes for performing a nondisruptive upgrade.
y6.
Select e0M for the network port you want to use for the download.
e0M7.
Select yes to reboot now.
y8.
Enter the IP address, netmask, and default gateway for e0M in their respective places.
<<var_controller1_e0m_ip>><<var_controller1_mask>><<var_controller1_mgmt_gateway>>9.
Enter the URL where the software can be found.
Note
This Web server must be pingable.
<<var_url_boot_software>>10.
Press Enter for the username, indicating no user name.
Enter11.
Enter yes to set the newly installed software as the default to be used for subsequent reboots.
y12.
Enter yes to reboot the node.
y13.
When you see "Press Ctrl-C for Boot Menu":
Ctrl-C14.
To enter Maintenance mode boot, select option 5.
515.
When you see the question "Continue to Boot?" type yes.
y16.
To verify the HA status of your environment, enter:
ha-config show
Note
If either component is not in HA mode, use the ha-config modify command to put the components in HA mode.
17.
To see how many disks are unowned, enter:
disk show -a
Note
No disks should be owned in this list.
18.
Assign disks.
disk assign -n <<var_#_of_disks>>
Note
This reference architecture allocates half the disks to each controller. However, workload design could dictate different percentages.
19.
Reboot the controller.
halt20.
At the LOADER-A prompt, enter:
autoboot21.
Press Ctrl-C for Boot Menu when prompted.
Ctrl-C22.
Select option 4 for Clean configuration and initialize all disks.
423.
Answer yes to zero disks, reset config and install a new file system.
y24.
Enter yes to erase all the data on the disks.
y
Note
The initialization and creation of the root volume can take 75 minutes or more to complete, depending on the number of disks attached. When initialization is complete, the storage system reboots. You can continue to controller 2 configuration while the disks for controller 1 are zeroing.
Controller 2
1.
Connect to the storage system console port. You should see a Loader-A prompt. However if the storage system is in a reboot loop, Press Ctrl-C to exit the Autoboot loop when you see this message:
Starting AUTOBOOT press Ctrl-C to abort...2.
If the system is at the LOADER prompt, enter the following command to boot Data ONTAP:
autoboot3.
During system boot, press Ctrl-C when prompted for the Boot Menu:
Press Ctrl-C for Boot Menu...
Note
If 8.1.2 is not the version of software being booted, follow the steps to install new software. If 8.1.2 is the version being booted, then proceed with step 14, maintenance mode boot
4.
To install new software first select option 7.
75.
Enter yes for performing a nondisruptive upgrade.
y6.
Select e0M for the network port you want to use for the download.
e0M7.
Enter yes to reboot now.
y8.
Enter the IP address, netmask and default gateway for e0M in their respective places.
<<var_controller2_e0m_ip>><<var_controller2_mask>><<var_controller2_mgmt_gateway>>9.
Enter the URL where the software can be found.
Note
This Web server must be pingable.
<<var_url_boot_software>>10.
Press Enter for the username, indicating no user name.
Enter11.
Enter yes to set the newly installed software as the default to be used for subsequent reboots.
y12.
Enter yes to reboot the node.
y13.
When you see "Press Ctrl-C for Boot Menu":
Ctrl-C14.
To enter Maintenance mode boot, select option 5:
515.
If you see the question "Continue to Boot?" type yes.
y16.
To verify the HA status of your environment, enter:
ha-config show
Note
If either component is not in HA mode, use the ha-config modify command to put the components in HA mode.
17.
To see how many disks are unowned, enter:
disk show -a
Note
The remaining disks should be shown.
18.
Assign disks by entering:
disk assign -n <<var_#_of_disks>>
Note
This reference architecture allocates half the disks to each controller. However, workload design could dictate different percentages.
19.
Reboot the controller.
halt20.
At the LOADER prompt, enter:
autoboot21.
Press Ctrl-C for Boot Menu when prompted.
Ctrl-C22.
Select option 4 for a Clean configuration and initialize all disks.
423.
Answer yes to zero disks, reset config and install a new file system.
y24.
Enter yes to erase all the data on the disks.
y
Note
The initialization and creation of the root volume can take 75 minutes or more to complete, depending on the number of disks attached. When initialization is complete, the storage system reboots.
Run Setup Process
When Data ONTAP is installed on a new storage system, the following files are not populated:
•
/etc/rc
•
/etc/exports
•
/etc/hosts
•
/etc/hosts.equiv
Controller 1
1.
Enter the configuration values the first time you power on the new system. The configuration values populate these files and configure the installed functionality of the system.
2.
Enter the following information:
Please enter the new hostname []:<<var_controller1>>Do you want to enable IPv6? [n]: EnterDo you want to configure interface groups? [n]: EnterPlease enter the IP address for Network Interface e0a []: Enter
Note
Press Enter to accept the blank IP address.
Should interface e0a take over a partner IP address during failover? [n]: EnterPlease enter the IP address for the Network Interface e0b []:EnterShould interface e0b take over a partner IP address during failover? [n]: EnterPlease enter the IP address for the Network Interface e1a []:EnterShould interface e1a take over a partner IP address during failover? [n]: EnterPlease enter the IP address for the Network Interface e1b []:EnterShould interface e1b take over a partner IP address during failover? [n]: EnterPlease enter the IP address for Network Interface e0M []: <<var_controller1_e0m_ip>>Please enter the netmaskfor the Network Interface e0M [255.255.255.0]: <<var_controller1_mask>>Should interface e0M take over a partner IP address during failover? [n]: yPlease enter the IPv4 address or interface name to be taken over by e0M []: e0MPlease enter flow control for e0M {none, receive, send, full} [full]: Enter
Note
If additional interface cards are installed in your storage controller, you will have additional questions about the interfaces on those cards.
3.
Enter the following information:
Please enter the name or IP address of the IPv4 default gateway: <<var_controller1_mgmt_gateway>>The administration host is given root access to the storage system's / etc files for system administration. To allow /etc root access to all NFS clients enter RETURN below.Please enter the name or IP address for administrative host: <<var_adminhost_ip>>Please enter timezone [GTM]: <<var_timezone>>Note: Example time zone: America/New_York.Where is the filer located? <<var_location>>Enter the root directory for HTTP files [home/http]: EnterDo you want to run DNS resolver? [n]: yPlease enter DNS domain name []: <<var_dns_domain_name>>Please enter the IP address for first nameserver []: <<var_nameserver_ip>>Do you want another nameserver? [n]:
Note
Optionally enter up to three name server IP addresses.
Do you want to run NIS client? [n]: EnterPress the Return key to continue through AutoSupport messageWould you like to configure SP LAN interface [y]: EnterWould you like to enable DHCP on the SP LAN interface [y]: nPlease enter the IP address for the SP: <<var_sp_ip>>Please enter the netmask for the SP []: <<var_sp_mask>>Please enter the IP address for the SP gateway: <<var_sp_gateway>>Please enter the name or IP address of the mail host [mailhost]: <<var_mailhost>>Please enter the IP address for <<var_mailhost>> []: <<var_mailhost_ip>>New password: <<var_password>>Retype new password <<var_password>>4.
Enter the root password to log in to controller 1.
Controller 2
1.
Enter the configuration values the first time you power on the new system. The configuration values populate these files and configure the installed functionality of the system.
2.
Enter the following information:
Please enter the new hostname []: <<var_controller2>>Do you want to enable IPv6? [n]: EnterDo you want to configure interface groups? [n]: EnterPlease enter the IP address for Network Interface e0a []: EnterNote: Press Enter to accept the blank IP address.Should interface e0a take over a partner IP address during failover? [n]: EnterPlease enter the IP address for the Network Interface e0b []:EnterShould interface e0b take over a partner IP address during failover? [n]: EnterPlease enter the IP address for the Network Interface e1a []:EnterShould interface e1a take over a partner IP address during failover? [n]: EnterPlease enter the IP address for the Network Interface e1b []:EnterShould interface e1b take over a partner IP address during failover? [n]: EnterPlease enter the IP address for Network Interface e0M []: <<var_controller2_e0m_ip>>Please enter the netmaskfor the Network Interface e0M [255.255.255.0]: <<var_controller2_mask>>Should interface e0M take over a partner IP address during failover? [n]: yPlease enter the IPv4 address or interface name to be taken over by e0M []: e0MPlease enter flow control for e0M {none, receive, send, full} [full]: Enter
Note
If additional interface cards are installed in your storage controller, you will have additional questions about the interfaces on those cards.
3.
Enter the following information:
Please enter the name or IP address of the IPv4 default gateway: <<var_controller2_mgmt_gateway>>The administration host is given root access to the storage system's / etc files for system administration. To allow /etc root access to all NFS clients enter RETURN below.Please enter the name or IP address for administrative host: <<var_adminhost_ip>>Please enter timezone [GTM]: <<var_timezone>>Note: Example time zone: America/New_York.Where is the filer located? <<var_location>>Enter the root directory for HTTP files [home/http]: EnterDo you want to run DNS resolver? [n]: yPlease enter DNS domain name []: <<var_dns_domain_name>>Please enter the IP address for first nameserver []: <<var_nameserver_ip>>Do you want another nameserver? [n]:
Note
Optionally enter up to three name server IP addresses.
Do you want to run NIS client? [n]: EnterPress the Return key to continue through AutoSupport messageWould you like to configure SP LAN interface [y]: EnterWould you like to enable DHCP on the SP LAN interface [y]: nPlease enter the IP address for the SP: <<var_sp_ip>>Please enter the netmask for the SP []: <<var_sp_mask>>Please enter the IP address for the SP gateway: <<var_sp_gateway>>Please enter the name or IP address of the mail host [mailhost]: <<var_mailhost>>Please enter the IP address for <<var_mailhost>> []: <<var_mailhost_ip>>New password: <<var_password>>Retype new password <<var_password>>4.
Enter the root password to log in to controller 2.
Upgrade the Service Processor on Each Node to the Latest Release
With Data ONTAP 8.1.2, you must upgrade to the latest Service Processor (SP) firmware to take advantage of the latest updates available for the remote management device.
1.
Using a web browser, connect to: http://support.netapp.com/NOW/cgi-bin/fw.
2.
Navigate to the Service Process Image for installation from the Data ONTAP prompt page for your storage platform.
3.
Proceed to the Download page for the latest release of the SP Firmware for your storage platform.
4.
Using the instructions on this page, update the SPs on both controllers. You will need to download the .zip file to a web server that is reachable from the management interfaces of the controllers.
64-Bit Aggregates in Data ONTAP 7-Mode
A 64-bit aggregate containing the root volume is created during the Data ONTAP setup process. To create additional 64-bit aggregates, determine the aggregate name, the node on which to create it, and how many disks it will contain. Calculate the RAID group size to allow for roughly balanced (same size) RAID groups of between 12 and 20 disks (for SAS disks) within the aggregate. For example, if 52 disks were being assigned to the aggregate, select a RAID group size of 18. A RAID group size of 18 would yield two 18-disk RAID groups and one 16-disk RAID group. Keep in mind that the default RAID group size is 16 disks, and that the larger the RAID group size, the longer the disk rebuild time in case of a failure.
Controller 1
Execute the following command to create a new aggregate:
aggr create aggr1 -B 64 -r <<var_raidsize>> <<var_#_of_disks>>
Note
Leave at least one disk (select the largest disk) in the configuration as a spare. A best practice is to have at least one spare for each disk type and size.
Controller 2
Execute the following command to create a new aggregate:
aggr create aggr1 -B 64 -r <<var_raidsize>> <<var_#_of_disks>>
Note
Leave at least one disk (select the largest disk) in the configuration as a spare. A best practice is to have at least one spare for each disk type and size.
Flash Cache
Controller 1 and Controller 2
Execute the following commands to enable Flash Cache:
options flexscale.enable onoptions flexscale.lopri_blocks offoptions flexscale.normal_data_blocks on
Note
For directions on how to configure Flash Cache in metadata mode or low-priority data caching mode, see TR-3832: Flash Cache and PAM Best Practices Guide at: http://media.netapp.com/documents/tr-3832.pdf. Before customizing the settings, determine whether the custom settings are required or whether the default settings are sufficient.
IFGRP LACP
Since this type of interface group requires two or more Ethernet interfaces and a switch that supports LACP, make sure that the switch is configured properly.
Controller 1 and Controller 2
Run the following command on the command line and also add it to the /etc/rc file, so it is activated upon boot:
ifgrp create lacp ifgrp0 -b port e1a e1bwrfile -a /etc/rc "ifgrp create lacp ifgrp0 -b ip e1a e1b"
Note
All interfaces must be in down status before being added to an interface group.
VLAN
Controller 1 and Controller 2
Follow these steps to create a VLAN interface for NFS data traffic.
vlan create ifgrp0 <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>wrfile -a /etc/rc "vlan create ifgrp0 <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>"IP Config
Controller 1 and Controller 2
Run the following commands on the command line.
ifconfig ifgrp0-<<var_nfs_vlan_id>> <<var_nfs_ip>> netmask <<var_nfs_mask>> mtusize 9000 partner ifgrp0-<<var_nfs_vlan_id>>wrfile -a /etc/rc " ifconfig ifgrp0-<<var_nfs_vlan_id>> <<var_nfs_ip>> netmask <<var_nfs_mask>> mtusize 9000 partner ifgrp0-<<var_nfs_vlan_id>>"Cisco Discovery Protocol
Follow these steps to enable Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on controller 1 and controller 2.
Controller 1 and Controller 2
Enable CDP
options cdpd.enable onActive-Active Controller Configuration
Controller 1 and Controller 2
Enable two storage controllers to an active-active configuration.
1.
Enter the cluster license on both nodes.
license add <<var_cf_license>>2.
Reboot each storage controller.
reboot3.
Log back in to both controllers.
Controller 1
Enable failover on Controller 1, if it is not enabled already.
cf enableNFSv3
Controller 1 and Controller 2
1.
Add a license for NFS.
license add <<var_nfs_license>>2.
Set the following recommended options that enable NFS version 3.
options nfs.tcp.enable onoptions nfs.udp.enable offoptions nfs.v3.enable on3.
Enable NFS.
nfs onFCP
Controller 1 and Controller 2
1.
License FCP.
license add <<var_fc_license>>2.
Start the FCP service.
fcp start3.
Record the WWPN or FC port name for later use.
fcp show adaptersNTP
The following commands configure and enable time synchronization on the storage controller. You must have either a publically available IP address or your company's standard NTP server name or IP address.
Controller 1 and Controller 2
1.
Run the following commands to configure and enable the NTP server:
date <<var_date>>2.
Enter the current date in the format of [[[[CC]yy]mm]dd]hhmm[.ss]].
For example: date 201208311436; would set the date to August 31st 2012 at 14:36.
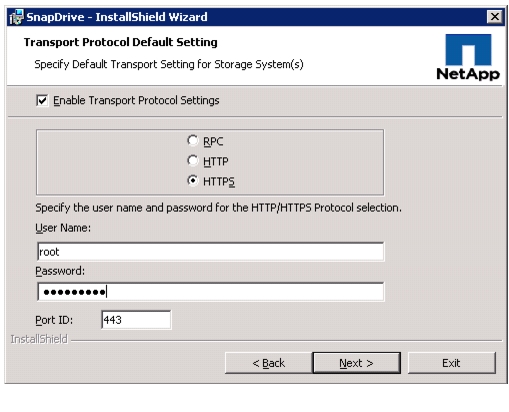
options timed.servers <<var_global_ntp_server_ip>>options timed.enable onData ONTAP SecureAdmin
Secure API access to the storage controller must be configured.
Controller 1
1.
Issue the following as a one-time command to generate the certificates used by the Web services for the API.
secureadmin setup sslSSL Setup has already been done before. Do you want to proceed? [no] yCountry Name (2 letter code) [US]: <<var_country_code>>State or Province Name (full name) [California]: <<var_state>>Locality Name (city, town, etc.) [Santa Clara]: <<var_city>>Organization Name (company) [Your Company]: <<var_org>>Organization Unit Name (division): <<var_unit>>Common Name (fully qualified domain name) [<<var_controller1_fqdn>>]: EnterAdministrator email: <<var_admin_email>>Days until expires [5475] : EnterKey length (bits) [512] : <<var_key_length>>Note: NetApp recommends that your key length be 1024.After the initialization, the CSR is available in the file /etc/keymgr/csr/secureadmin_tmp.pem.2.
Configure and enable SSL and HTTPS for API access using the following options.
options httpd.access noneoptions httpd.admin.enable offoptions httpd.admin.ssl.enable onoptions ssl.enable onController 2
1.
Issue the following as a one-time command to generate the certificates used by the Web services for the API.
secureadmin setup sslSSL Setup has already been done before. Do you want to proceed? [no] yCountry Name (2 letter code) [US]: <<var_country_code>>State or Province Name (full name) [California]: <<var_state>>Locality Name (city, town, etc.) [Santa Clara]: <<var_city>>Organization Name (company) [Your Company]: <<var_org>>Organization Unit Name (division): <<var_unit>>Common Name (fully qualified domain name) [<<var_controller2_fqdn>>]: EnterAdministrator email: <<var_admin_email>>Days until expires [5475] : EnterKey length (bits) [512] : <<var_key_length>>
Note
NetApp recommends that your key length be 1024.
After the initialization, the CSR is available in the file /etc/keymgr/csr/secureadmin_tmp.pem.
2.
Configure and enable SSL and HTTPS for API access using the following options.
options httpd.access noneoptions httpd.admin.enable offoptions httpd.admin.ssl.enable onoptions ssl.enable onSecure Shell
SSH must be configured and enabled.
Controller 1 and Controller 2
1.
Use the following one-time command to generate host keys.
secureadmin disable sshsecureadmin setup -f -q ssh 768 512 10242.
Use the following options to configure and enable SSH.
options ssh.idle.timeout 60options autologout.telnet.timeout 5SNMP
Controller 1 and Controller 2
1.
Run the following commands to configure SNMP basics, such as the local and contact information. When polled, this information displays as the sysLocation and sysContact variables in SNMP.
snmp contact "<<var_admin_email>>"snmp location "<<var_location>>"snmp init 1options snmp.enable on2.
Configure SNMP traps to send them to remote hosts, such as a DFM server or another fault management system.
snmp traphost add <<var_oncommand_server_fqdn>>SNMPv1
Controller 1 and Controller 2
1.
Set the shared secret plain-text password, which is called a community.
snmp community delete allsnmp community add ro <<var_snmp_community>>
Note
Use the delete all command with caution. If community strings are used for other monitoring products, the delete all command will remove them.
SNMPv3
SNMPv3 requires a user to be defined and configured for authentication.
Controller 1 and Controller 2
Create a user called snmpv3user.
useradmin role add snmp_requests -a login-snmpuseradmin group add snmp_managers -r snmp_requestsuseradmin user add snmpv3user -g snmp_managersNew Password: <<var_password>>Retype new password: <<var_password>>AutoSupport HTTPS
AutoSupport™ sends support summary information to NetApp through HTTPS.
Controller 1 and Controller 2
Execute the following commands to configure AutoSupport:
options autosupport.noteto <<var_admin_email>>Security Best Practices
Apply the following commands according to local security policies.
Controller 1 and Controller 2
Run the following commands to enhance security on the storage controller:
options rsh.access noneoptions webdav.enable offoptions security.passwd.rules.maximum 14options security.passwd.rules.minimum.symbol 1options security.passwd.lockout.numtries 6options autologout.console.timeout 5Install Remaining Required Licenses and Enable MultiStore
Controller 1 and Controller 2
Install the following licenses to enable SnapRestore® and FlexClone®.
license add <<var_snaprestore_license>>license add <<var_flex_clone_license>>options licensed_feature.multistore.enable onEnable NDMP
Run the following commands to enable NDMP.
Controller 1 and Controller 2
options ndmpd.enable on
Create FlexVol Volumes
Controller 1
Follow these steps to create two volumes on controller 1:
vol create esxi_boot -s none aggr1 100gsnap reserve esxi_boot 0sis on /vol/esxi_bootvol create infra_swap -s none aggr1 100gsnap reserve infra_swap 0snap sched infra_swap 0 0 0Controller 2
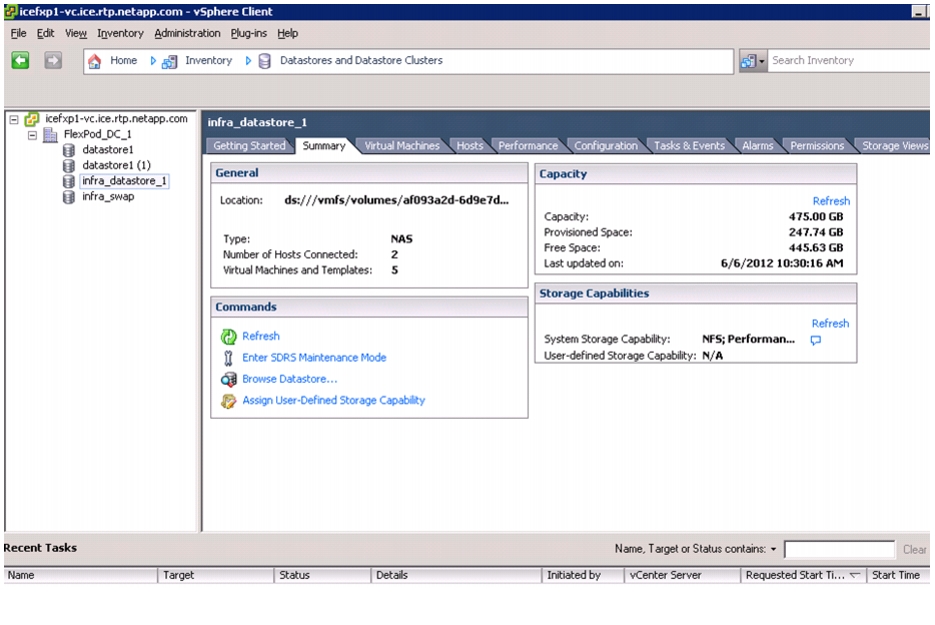
Follow these steps to create two volumes on controller 2:
vol create infra_datastore_1 -s none aggr1 500gsnap reserve infra_datastore_1 0sis on /vol/infra_datastore_1vol create OnCommandDB -s none aggr1 200gsnap reserve OnCommandDB 0sis on /vol/OnCommandDBNFS Exports
Follow these steps to create NFS exports on each controller.
Controller 1
exportfs -p sec=sys,rw=<<var_vm_infra01_nfs_host_ip>>:<<var_vm_infra02_nfs_host_ip>>,root=<<var_vm _infra01_nfs_host_ip>>:<<var_vm_infra02_nfs_host_ip>>,nosuid /vol/infra_swapexportfs -p sec=sys,ro,rw=<<var_adminhost_ip>>:<<var_vm_infra01_nfs_host_ip>>:<<var_vm_infra02_nfs _host_ip>>,root==<<var_adminhost_ip>>:<<var_vm_infra01_nfs_host_ip>>:<<var_vm_infra02_ nfs_host_ip>>,nosuid /vol/vol0Controller 2
exportf s -p sec=sys,rw=<<var_vm_infra01_nfs_host_ip>>:<<var_vm_infra02_nfs_host_ip>>,root=<<var_vm _infra01_nfs_host_ip>>:<<var_vm_infra02_nfs_host_ip>>,nosuid /vol/infra_datastore_1exportfs -p sec=sys,ro,rw=<<var_adminhost_ip>>:<<var_vm_infra01_nfs_host_ip>>:<<var_vm_infra02_nfs _host_ip>>,root==<<var_adminhost_ip>>:<<var_vm_infra01_nfs_host_ip>>:<<var_vm_infra02_ nfs_host_ip>>,nosuid /vol/vol0LUN Creation
Follow these steps to create two LUNs on controller 1.
Controller 1
lun create -s 10g -t vmware -o noreserve /vol/esxi_boot/VM-Host-Infra-01lun create -s 10g -t vmware -o noreserve /vol/esxi_boot/VM-Host-Infra-02Server Configuration
FlexPod Cisco UCS Base
Perform Initial Setup of Cisco UCS 6248 Fabric Interconnect for FlexPod Environments
This section provides detailed procedures for configuring the Cisco Unified Computing System (Cisco UCS) for use in a FlexPod environment. The following steps are necessary to provision the Cisco UCS C-Series and B-Series servers and should be followed precisely to avoid improper configuration.
Cisco UCS 6248UP Fabric Interconnect A
To configure the Cisco UCS for use in a FlexPod environment, follow these steps:
1.
Connect to the console port on the first Cisco UCS 6248 fabric interconnect.
Enter the configuration method: consoleEnter the setup mode; setup newly or restore from backup.(setup/restore)? setupYou have choosen to setup a a new fabric interconnect? Continue? (y/n): yEnforce strong passwords? (y/n) [y]: yEnter the password for "admin": <<var_password>>Enter the same password for "admin": <<var_password>>Is this fabric interconnect part of a cluster (select 'no' for standalone)? (yes/no) [n]: yWhich switch fabric (A|B): AEnter the system name: <<var_ucs_clustername>>Physical switch Mgmt0 IPv4 address: <<var_ucsa_mgmt_ip>>Physical switch Mgmt0 IPv4 netmask: <<var_ucsa_mgmt_mask>>IPv4 address of the default gateway: <<var_ucsa_mgmt_gateway>>Cluster IPv4 address: <<var_ucs_cluster_ip>>Configure DNS Server IPv4 address? (yes/no) [no]: yDNS IPv4 address: <<var_nameserver_ip>>Configure the default domain name? yDefault domain name: <<var_dns_domain_name>>Join centralized management environment (UCS Central)? (yes/no) [n]: Enter2.
Review the settings printed to the console. If they are correct, answer yes to apply and save the configuration.
3.
Wait for the login prompt to make sure that the configuration has been saved.
Cisco UCS 6248UP Fabric Interconnect B
To configure the Cisco UCS for use in a FlexPod environment, follow these steps:
1.
Connect to the console port on the second Cisco UCS 6248 fabric interconnect.
Enter the configuration method: consoleInstaller has detected the presence of a peer Fabric interconnect. This Fabric interconnect will be added to the cluster. Do you want to continue {y|n}? yEnter the admin password for the peer fabric interconnect: <<var_password>>Physical switch Mgmt0 IPv4 address: <<var_ucsb_mgmt_ip>>Apply and save the configuration (select `no' if you want to re-enter)? (yes/no): y2.
Wait for the login prompt to make sure that the configuration has been saved.
FlexPod Cisco UCS FCoE vSphere on Data ONTAP 7-Mode
Log in to Cisco UCS Manager
To log in to the Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS) environment, follow these steps:
1.
Open a Web browser and navigate to the Cisco UCS 6248 fabric interconnect cluster address.
2.
Click the Launch UCS Manager link to download the Cisco UCS Manager software.
3.
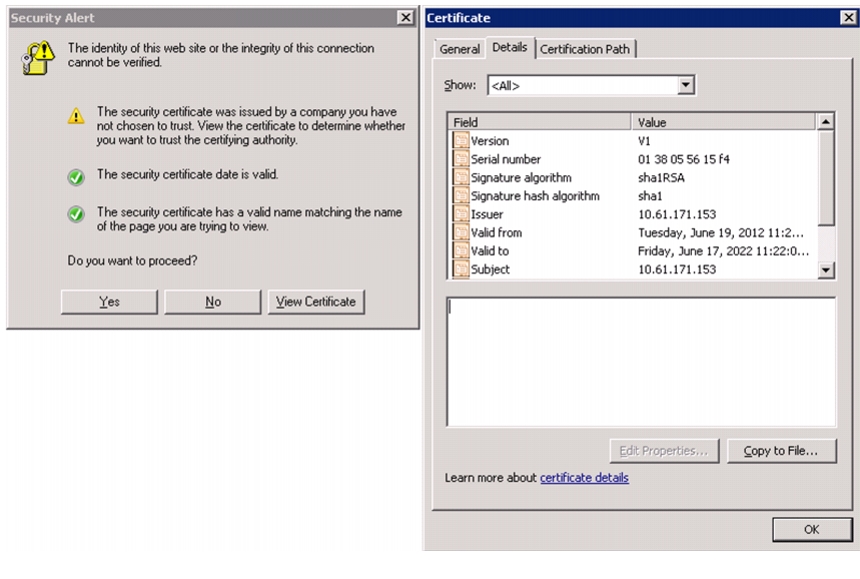
If prompted to accept security certificates, accept as necessary.
4.
When prompted, enter admin as the user name and enter the administrative password.
5.
Click Login to log in to Cisco UCS Manager.
Upgrade Cisco UCS Manager Software to Version 2.1(1b)
This document assumes the use of Cisco UCS 2.1(1b). To upgrade the Cisco UCS Manager software and the UCS 6248 Fabric Interconnect software to version 2.1(1b), see Cisco UCS Manager Install and Upgrade Guides at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/unified_computing/ucs/sw/upgrading/from2.0/to2.1/b_UpgradingCiscoUCSFrom2.0To2.1.html
Add Block of IP Addresses for KVM Access
To create a block of IP addresses for server Keyboard, Video, Mouse (KVM) access in the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
Note
This block of IP addresses should be in the same subnet as the management IP addresses for the Cisco UCS Manager.
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the LAN tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Pools > root > IP Pools > IP Pool ext-mgmt.
3.
In the Actions pane, choose Create Block of IP Addresses.
4.
Enter the starting IP address of the block and the number of IP addresses required, and the subnet and gateway information.
5.
Click OK to create the IP block.
6.
Click OK in the confirmation message window.
Synchronize Cisco UCS to NTP
To synchronize the Cisco UCS environment to the NTP server, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Admin tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose All > Timezone Management.
3.
In the Properties pane, choose the appropriate time zone in the Timezone menu.
4.
Click Save Changes, and then click OK.
5.
Click Add NTP Server.
6.
Enter <<var_global_ntp_server_ip>> and click OK.
7.
Click OK.
Edit Chassis Discovery Policy
Setting the discovery policy simplifies the addition of B-Series Cisco UCS chassis and of additional fabric extenders for further C-Series connectivity.
To modify the chassis discovery policy, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Equipment tab in the navigation pane and choose Equipment in the list on the left.
2.
In the right pane, click the Policies tab.
3.
Under Global Policies, set the Chassis/FEX Discovery Policy to 2-link or set it to match the number of uplink ports that are cabled between the chassis or fabric extenders (FEXes) and the fabric interconnects.
4.
Set the Link Grouping Preference to Port Channel.
5.
Click Save Changes.
6.
Click OK.
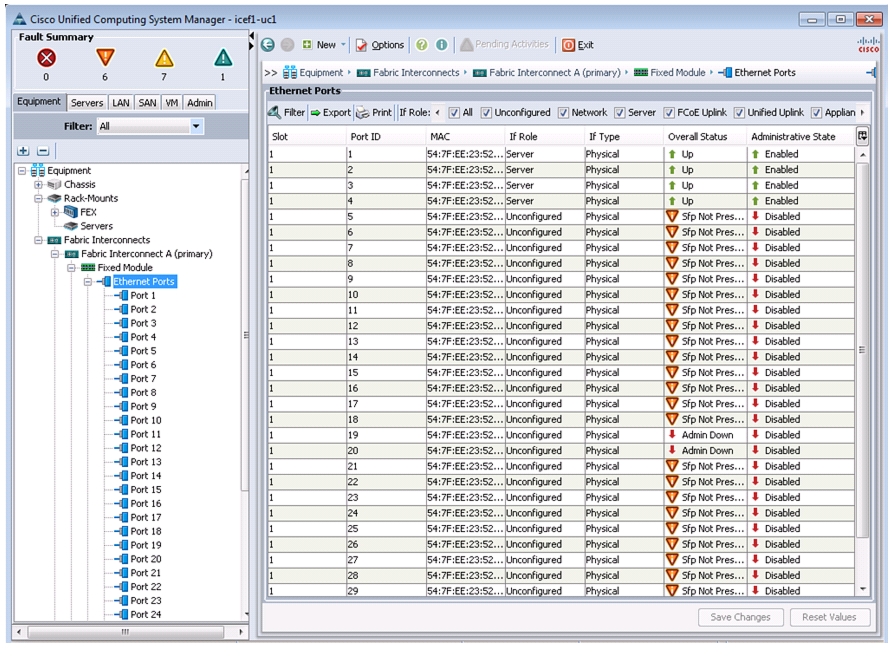
Enable Server and Uplink Ports
To enable server and uplink ports, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Equipment tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Equipment > Fabric Interconnects > Fabric Interconnect A (primary) > Fixed Module.
3.
Expand Ethernet Ports.
4.
Choose the ports that are connected to the chassis or to the Cisco 2232 FEX (two per FEX), right-click them, and choose Configure as Server Port.
5.
Click Yes to confirm server ports and click OK.
6.
Verify that the ports connected to the chassis or to the Cisco 2232 FEX are now configured as server ports.
Figure 3 Configured Server Ports
7.
Choose ports 19 and 20 that are connected to the Cisco Nexus 5548 switches, right-click them, and choose Configure as Uplink Port.
8.
Click Yes to confirm uplink ports and click OK.
9.
Choose ports 31 and 32, which will serve as FCoE uplinks to the Cisco Nexus 5548 switches; right-click them; and choose Configure as FCoE Uplink Port.
10.
Click Yes to confirm FCoE uplink ports and click OK.
11.
Choose Equipment > Fabric Interconnects > Fabric Interconnect B (subordinate) > Fixed Module.
12.
Expand Ethernet Ports.
13.
Choose the ports that are connected to the chassis or to the Cisco 2232 FEX (two per FEX), right-click them, and choose Configure as Server Port.
14.
Click Yes to confirm server ports and click OK.
15.
Choose ports 19 and 20 that are connected to the Cisco Nexus 5548 switches, right-click them, and choose Configure as Uplink Port.
16.
Click Yes to confirm the uplink ports and click OK.
17.
Choose ports 31 and 32 that will serve as FCoE uplinks to the Cisco Nexus 5548 switches, right-click them, and choose Configure as FCoE Uplink Port.
18.
Click Yes to confirm FCoE uplink ports and click OK.
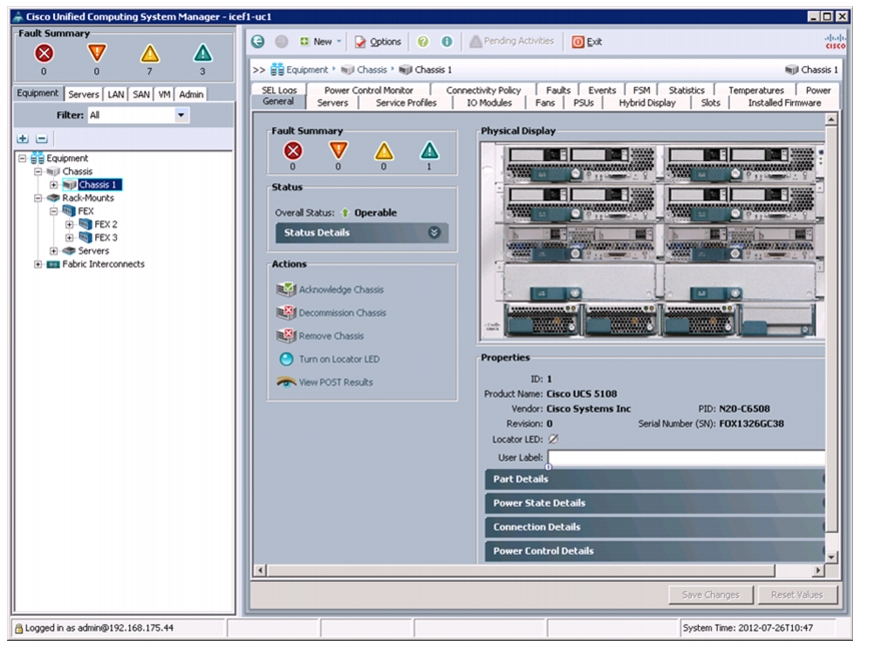
Acknowledge Cisco UCS Chassis and FEX
To acknowledge all Cisco UCS chassis and external 2232 FEX modules, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Equipment tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Expand Chassis.
3.
Choose each chassis that is listed, right-click on each chassis and choose Acknowledge Chassis.
Figure 4 Acknowledging Cisco UCS Chassis
4.
Click Yes and then click OK to complete acknowledging the chassis.
5.
If C-Series servers are part of the configuration, expand Rack Mounts and FEX.
6.
Right-click each FEX that is listed and choose Acknowledge FEX.
Figure 5 Acknowledging Cisco UCS Fabric Extenders
7.
Click Yes and then click OK to complete acknowledging the FEX.
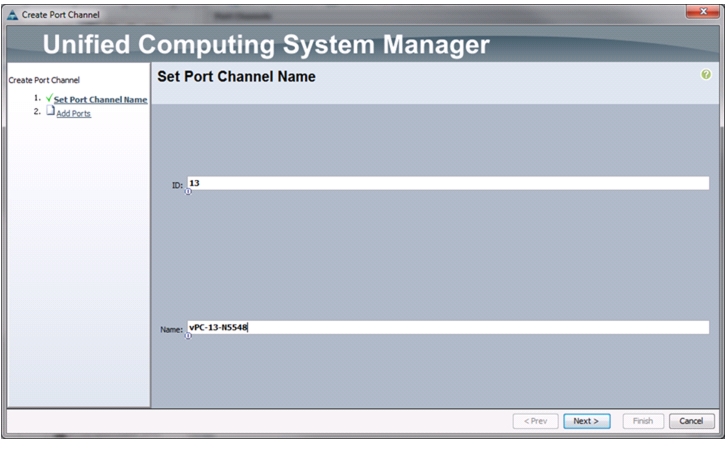
Create Uplink Port Channels to Cisco Nexus 5548 Switches
To configure the necessary port channels out of the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the LAN tab in the navigation pane.
Note
In this procedure, two port channels are created: one from fabric A to both Cisco Nexus 5548 switches and one from fabric B to both Cisco Nexus 5548 switches.
2.
Under LAN > LAN Cloud, expand the Fabric A tree.
3.
Right-click Port Channels.
4.
Choose Create Port Channel.
5.
Enter 13 as the unique ID of the port channel.
6.
Enter vPC-13-N5548 as the name of the port channel.
7.
Click Next.
Figure 6 Creating Port Channels
8.
Choose the following ports to be added to the port channel:
–
Slot ID 1 and port 19
–
Slot ID 1 and port 20
9.
Click >> to add the ports to the port channel.
10.
Click Finish to create the port channel.
11.
Click OK.
12.
In the navigation pane, under LAN > LAN Cloud, expand the fabric B tree.
13.
Right-click Port Channels.
14.
Choose Create Port Channel.
15.
Enter 14 as the unique ID of the port channel.
16.
Enter vPC-14-N5548 as the name of the port channel.
17.
Click Next.
18.
Choose the following ports to be added to the port channel:
–
Slot ID 1 and port 19
–
Slot ID 1 and port 20
19.
Click >> to add the ports to the port channel.
20.
Click Finish to create the port channel.
21.
Click OK.
Create an Organization
Organizations are used to organize resources and restrict access to various groups within the IT organization, thereby enabling multi-tenancy of the compute resources.
Note
Although this document does not assume the use of organizations this procedure provides instructions for creating one.
To configure an organization in the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, from the New menu in the toolbar at the top of the window, choose Create Organization.
2.
Enter a name for the organization.
3.
(Optional) Enter a description for the organization.
4.
Click OK.
5.
Click OK in the confirmation message window.
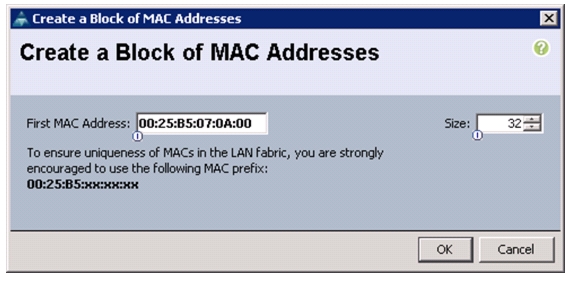
Create MAC Address Pools
To configure the necessary MAC address pools for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the LAN tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Pools > root.
Note
In this procedure, two MAC address pools are created, one for each switching fabric.
3.
Right-click MAC Pools under the root organization.
4.
Choose Create MAC Pool to create the MAC address pool.
5.
Enter MAC_Pool_A as the name of the MAC pool.
6.
(Optional) Enter a description for the MAC pool.
7.
Click Next.
8.
Click Add.
9.
Specify a starting MAC address.
Note
For the FlexPod solution, the recommendation is to place 0A in the next-to-last octet of the starting MAC address to identify all of the MAC addresses as fabric A addresses.
10.
Specify a size for the MAC address pool that is sufficient to support the available blade or server resources.
Figure 7 Creating MAC Address Pool for Fabric A
11.
Click OK.
12.
Click Finish.
13.
In the confirmation message window, click OK.
14.
Right-click MAC Pools under the root organization.
15.
Choose Create MAC Pool to create the MAC address pool.
16.
Enter MAC_Pool_B as the name of the MAC pool.
17.
(Optional) Enter a description for the MAC pool.
18.
Click Next.
19.
Click Add.
20.
Specify a starting MAC address.
Note
For the FlexPod solution, the recommendation is to place 0B in the next to last octet of the starting MAC address to identify all the MAC addresses in this pool as fabric B addresses.
21.
Specify a size for the MAC address pool that is sufficient to support the available blade or server resources.
Figure 8 Creating MAC Address Pool for Fabric B
22.
Click OK.
23.
Click Finish.
24.
In the confirmation message window, click OK.
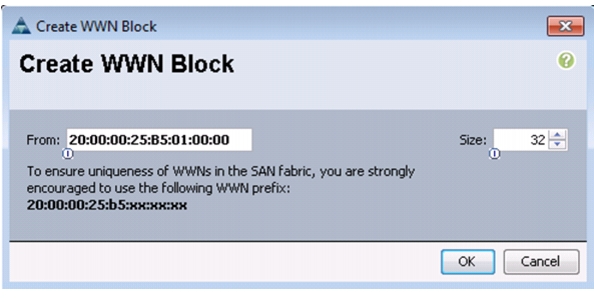
Create WWNN Pools
To configure the necessary World Wide Node Name (WWNN) pools for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the SAN tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Pools > root.
3.
Right-click WWNN Pools.
4.
Choose Create WWNN Pool.
5.
Enter WWNN_Pool as the name of the WWNN pool.
6.
(Optional) Add a description for the WWNN pool.
7.
Click Next.
8.
Click Add to add a block of WWNNs.
9.
Keep the default block of WWNNs, or specify a base WWNN.
10.
Specify a size for the WWNN block that is sufficient to support the available blade or server resources.
Figure 9 Creating WWNN Pool
11.
Click OK.
12.
Click Finish.
13.
Click OK.
Create WWPN Pools
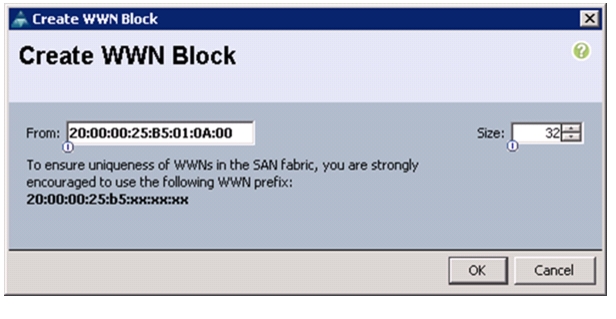
To configure the necessary World Wide Port Name (WWPN) pools for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the SAN tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Pools > root.
Note
In this procedure, two WWPN pools are created: one for fabric A and one for fabric B.
3.
Right-click WWPN Pools.
4.
Choose Create WWPN Pool.
5.
Enter WWPN_Pool_A as the name of the WWPN pool for fabric A.
6.
(Optional) Enter a description for this WWPN pool.
7.
Click Next.
8.
Click Add to add a block of WWPNs.
9.
Specify the starting WWPN in the block for fabric A.
Note
For the FlexPod solution, the recommendation is to place 0A in the next-to-last octet of the starting WWPN to identify all the WWPNs in this pool as fabric A addresses.
10.
Specify a size for the WWPN block that is sufficient to support the available blade or server resources.
Figure 10 Creating WWPN Pool
11.
Click OK.
12.
Click Finish to create the WWPN pool.
13.
Click OK.
14.
Right-click WWPN Pools.
15.
Choose Create WWPN Pool.
16.
Enter WWPN_Pool_B as the name for the WWPN pool for fabric B.
17.
(Optional) Enter a description for this WWPN pool.
18.
Click Next.
19.
Click Add to add a block of WWPNs.
20.
Enter the starting WWPN address in the block for fabric B.
Note
For the FlexPod solution, the recommendation is to place 0B in the next to last octet of the starting WWPN to identify all the WWPNs in this pool as fabric B addresses.
21.
Specify a size for the WWPN block that is sufficient to support the available blade or server resources.
22.
Click OK.
23.
Click Finish.
24.
Click OK.
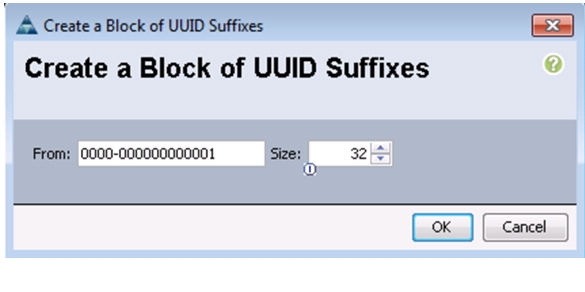
Create UUID Suffix Pool
To configure the necessary universally unique identifier (UUID) suffix pool for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Pools > root.
3.
Right-click UUID Suffix Pools.
4.
Choose Create UUID Suffix Pool.
5.
Enter UUID_Pool as the name of the UUID suffix pool.
6.
(Optional) Enter a description for the UUID suffix pool.
7.
Keep the prefix at the derived option.
8.
Click Next.
9.
Click Add to add a block of UUIDs.
10.
Keep the From field at the default setting.
11.
Specify a size for the UUID block that is sufficient to support the available blade or server resources.
Figure 11 Creating UUID Suffix Pool
12.
Click OK.
13.
Click Finish.
14.
Click OK.
Create Server Pool
To configure the necessary server pool for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
Note
Consider creating unique server pools to achieve the granularity that is required in your environment.
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Pools > root.
3.
Right-click Server Pools.
4.
Choose Create Server Pool.
5.
Enter Infra_Pool as the name of the server pool.
6.
(Optional) Enter a description for the server pool.
7.
Click Next.
8.
Choose two servers to be used for the VMware management cluster and click >> to add them to the Infra_Pool server pool.
9.
Click Finish.
10.
Click OK.
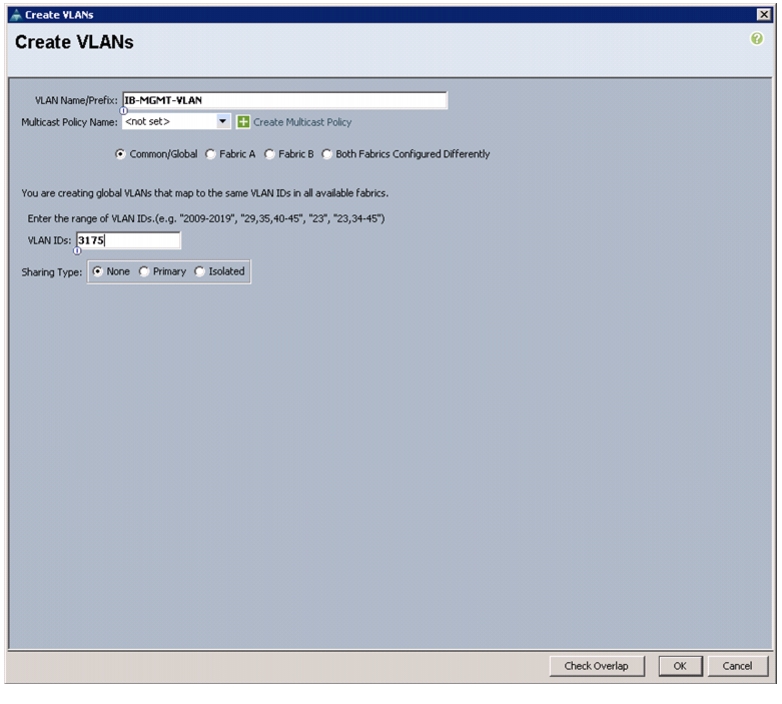
Create VLANs
To configure the necessary virtual local area networks (VLANs) for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the LAN tab in the navigation pane.
Note
In this procedure, five VLANs are created.
2.
Choose LAN > LAN Cloud.
3.
Right-click VLANs.
4.
Choose Create VLANs.
5.
Enter IB-MGMT-VLAN as the name of the VLAN to be used for management traffic.
6.
Keep the Common/Global option selected for the scope of the VLAN.
7.
Enter <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>> as the ID of the management VLAN.
8.
Keep the Sharing Type as None.
9.
Click OK, and then click OK again.
Figure 12 Creating VLAN for Management Traffic
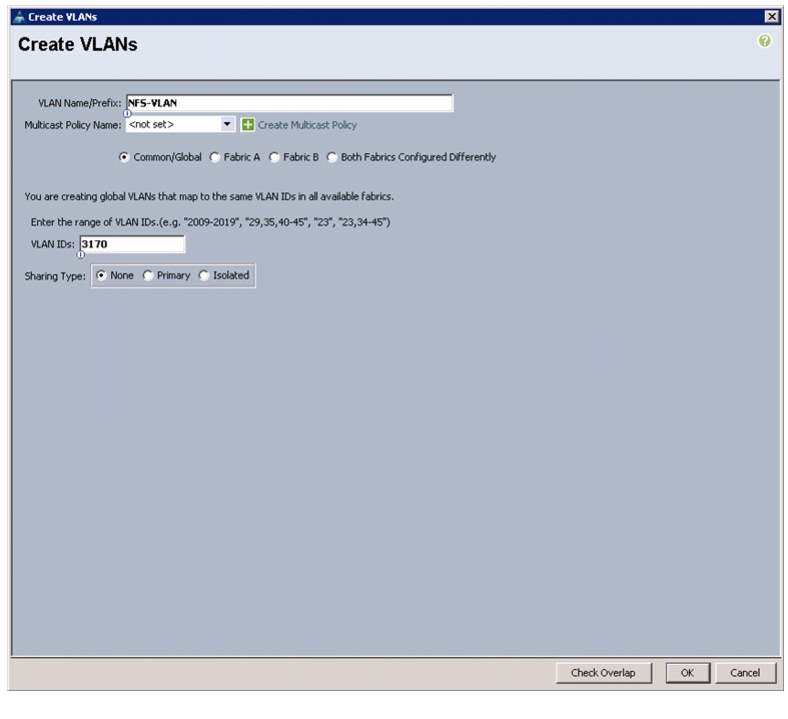
10.
Right-click VLANs.
11.
Choose Create VLANs.
12.
Enter NFS-VLAN as the name of the VLAN to be used for NFS.
13.
Keep the Common/Global option selected for the scope of the VLAN.
14.
Enter the <<var_nfs_vlan_id>> for the NFS VLAN.
15.
Keep the Sharing Type as None.
16.
Click OK, and then click OK again.
Figure 13 Creating VLAN for NFS Traffic
17.
Right-click VLANs.
18.
Choose Create VLANs.
19.
Enter vMotion-VLAN as the name of the VLAN to be used for vMotion.
20.
Keep the Common/Global option selected for the scope of the VLAN.
21.
Enter the <<var_vmotion_vlan_id>> as the ID of the vMotion VLAN.
22.
Keep the Sharing Type as None.
23.
Click OK, and then click OK again.
24.
Right-click VLANs.
25.
Choose Create VLANs.
26.
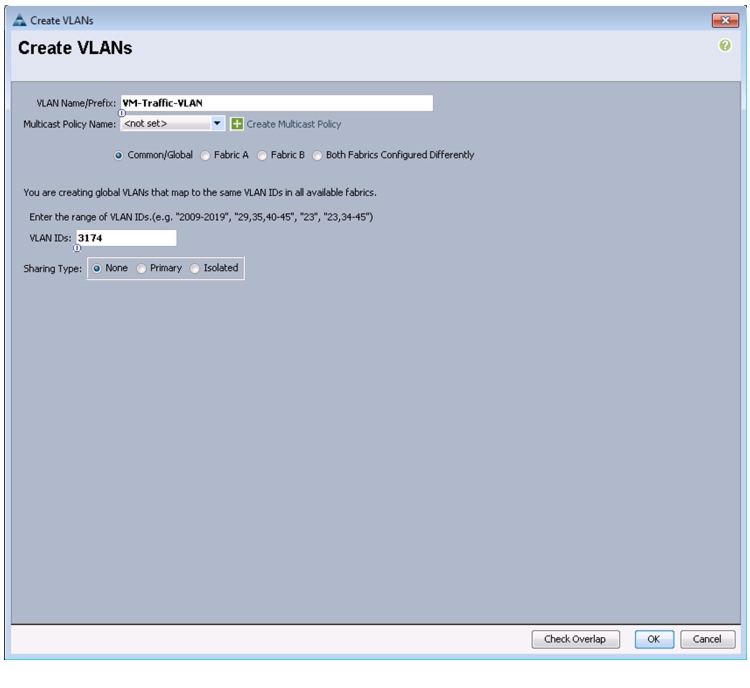
Enter VM-Traffic-VLAN as the name of the VLAN to be used for the VM traffic.
27.
Keep the Common/Global option selected for the scope of the VLAN.
28.
Enter the <<var_vm-traffic_vlan_id>> for the VM Traffic VLAN.
29.
Keep the Sharing Type as None.
30.
Click OK, and then click OK again.
Figure 14 Creating VLAN for VM Traffic
31.
Right-click VLANs.
32.
Choose Create VLANs.
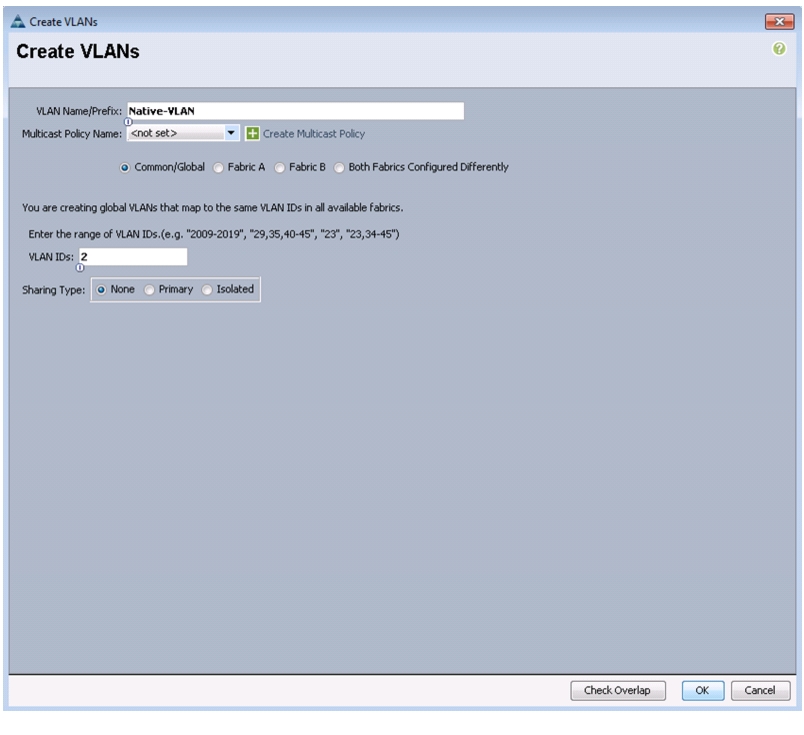
33.
Enter Native-VLAN as the name of the VLAN to be used as the native VLAN.
34.
Keep the Common/Global option selected for the scope of the VLAN.
35.
Enter the <<var_native_vlan_id>> as the ID of the native VLAN.
36.
Keep the Sharing Type as None.
37.
Click OK, and then click OK again.
Figure 15 Creating Native VLAN
38.
Expand the list of VLANs in the navigation pane, right-click the newly created Native-VLAN and choose Set as Native VLAN.
39.
Click Yes, and then click OK.
Create VSANs and FCoE Port Channels
To configure the necessary virtual storage area networks (VSANs) and FCoE uplink port channels for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the SAN tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Expand the SAN > SAN Cloud tree.
3.
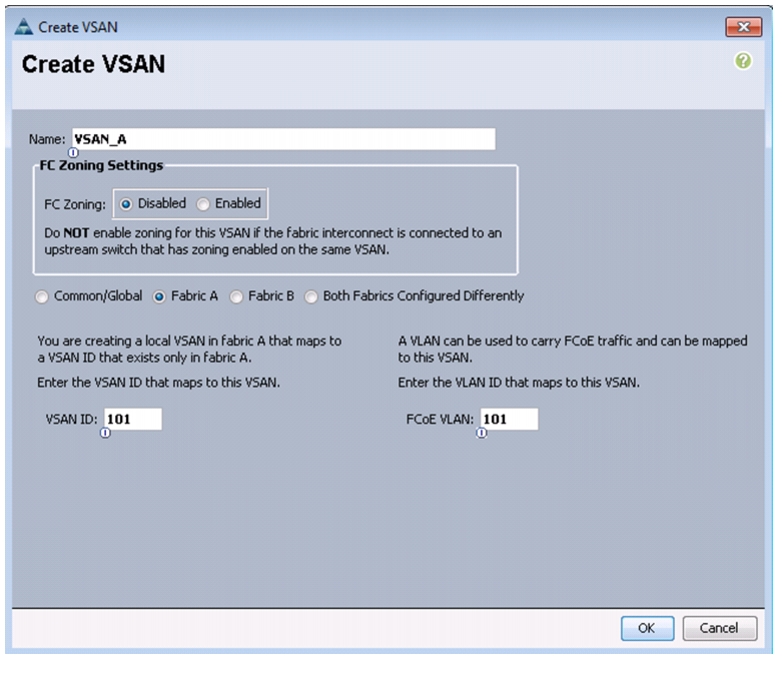
Right-click VSANs.
4.
Choose Create VSAN.
5.
Enter VSAN_A as the name of the VSAN for fabric A.
6.
Keep the Disabled option selected for FC Zoning.
7.
Click the Fabric A radio button.
8.
Enter <<var_vsan_a_id>> as the VSAN ID for fabric A.
9.
Enter <<var_fabric_a_fcoe_vlan_id>> as the FCoE VLAN ID for fabric A.
Note
For the FlexPod solution, it is recommended to use the same ID for the VSAN and the FCoE VLAN required for fabric A.
10.
Click OK, and then click OK again to create the VSAN.
Figure 16 Creating VSAN for Fabric A
11.
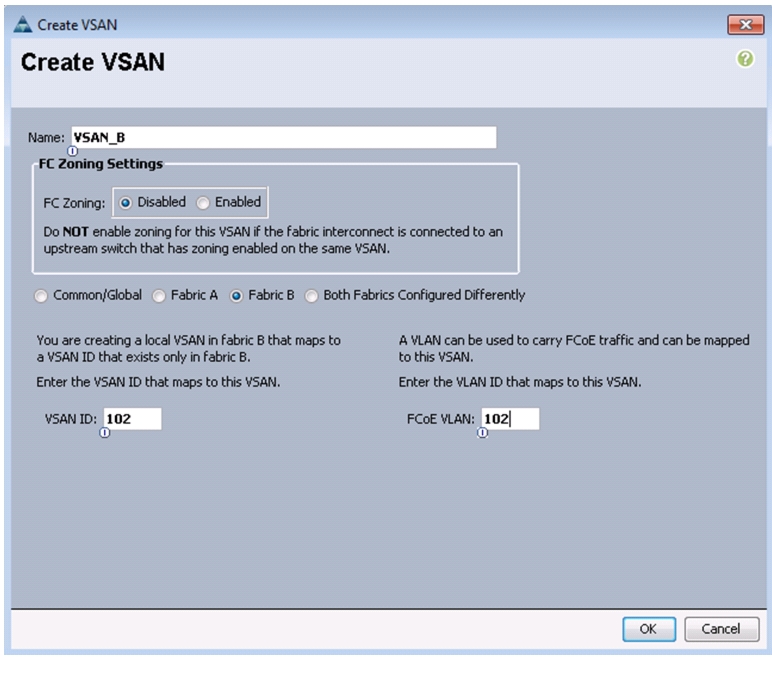
Right-click VSANs.
12.
Choose Create VSAN.
13.
Enter VSAN_B as the name of the VSAN for fabric B.
14.
Keep the Disabled option selected for FC Zoning.
15.
Click the Fabric B radio button.
16.
Enter <<var_vsan_b_id>> as the VSAN ID for fabric B.
17.
Enter <<var_fabric_b_fcoe_vlan_id>> as the FCoE VLAN ID for fabric B.
Note
It is recommended to use the same ID for the VSAN and the FCoE VLAN required for fabric B.
18.
Click OK, and then click OK again to create the VSAN.
Figure 17 Creating VSAN for Fabric B
19.
In the navigation pane, under SAN > SAN Cloud, expand the Fabric A tree.
20.
Right-click FCoE Port Channels.
21.
Choose Create FCoE Port Channel.
22.
Enter 1 for the port channel ID and Po1 for the port channel name.
23.
Click Next.
24.
Choose ports 31 and 32 and click >> to add the ports to the port channel.
25.
Click Finish.
26.
check the check box for Show Navigator for FCoE Port-Channel 1 (Fabric A).
27.
Click OK to create the port channel.
28.
In the right pane, under Properties, choose VSAN VSAN_A for Fabric A in the VSAN list.
29.
Click Apply, and then click OK.
30.
Click OK to close the navigator.
31.
In the navigation pane, under SAN > SAN Cloud, expand the fabric B tree.
32.
Right-click FCoE Port Channels.
33.
Choose Create FCoE Port Channel.
34.
Enter 2 for the port channel ID and Po2 for the port channel name.
35.
Click Next.
36.
Choose ports 31 and 32 and click >> to add the ports to the port channel.
37.
Click Finish.
38.
Check the check box for Show Navigator for FCoE Port-Channel 2 (Fabric B).
39.
Click OK to create the port channel.
40.
In the right pane, under Properties, choose VSAN VSAN_B for Fabric B.
41.
Click Apply, and then click OK.
42.
Click OK to close the navigator.
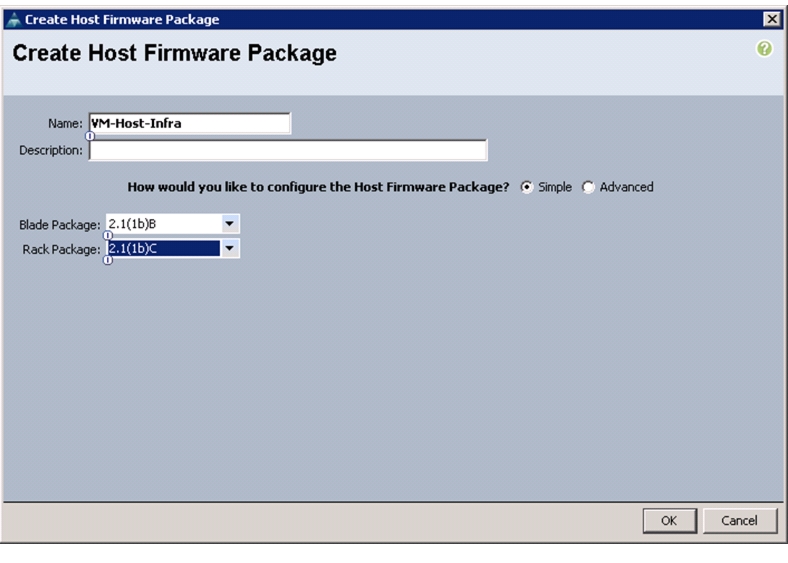
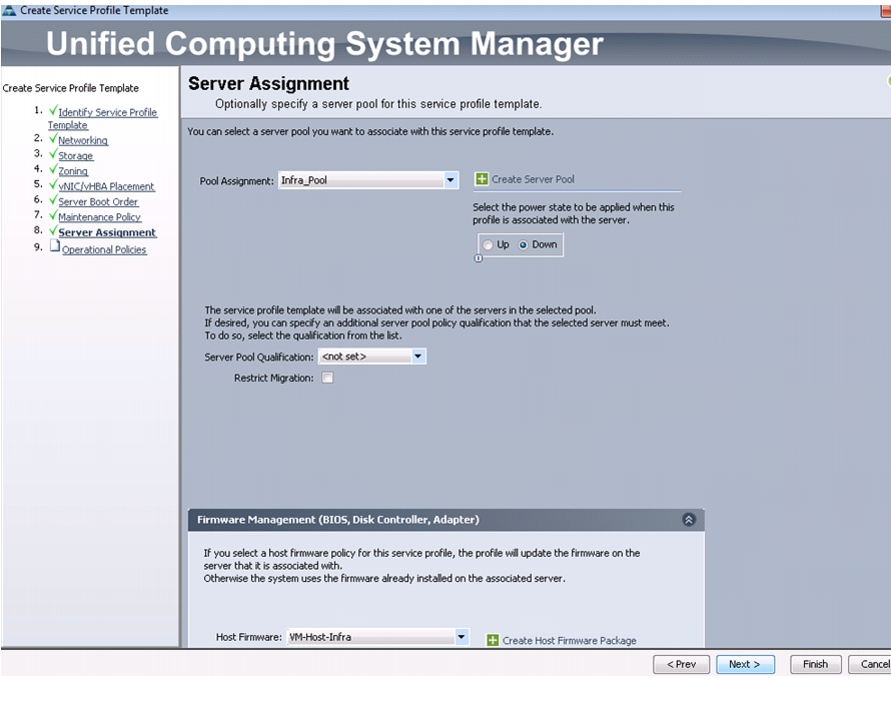
Create Host Firmware Package
Firmware management policies allow the administrator to select the corresponding packages for a given server configuration. These policies often include packages for adapter, BIOS, board controller, FC adapters, host bus adapter (HBA) option ROM, and storage controller properties.
To create a firmware management policy for a given server configuration in the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Policies > root.
3.
Right-click Host Firmware Packages.
4.
Choose Create Host Firmware Package.
5.
Enter VM-Host-Infra as the name of the host firmware package.
6.
Keep the radio button Simple selected.
7.
Choose the version 2.1(1b) for both the Blade and Rack Packages.
8.
Click OK to create the host firmware package.
9.
Click OK.
Figure 18 Creating Host Firmware Package
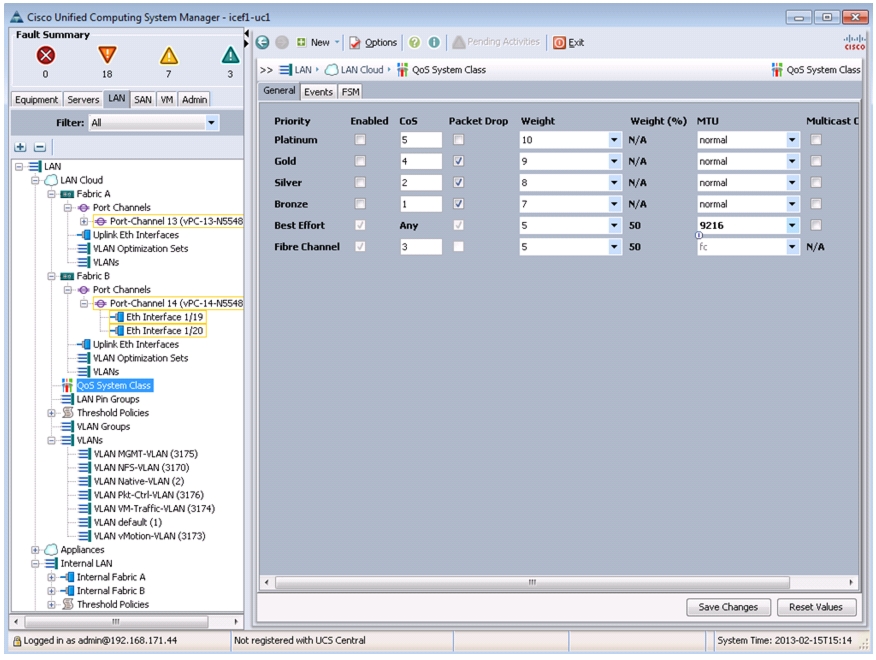
Set Jumbo Frames in Cisco UCS Fabric
To configure jumbo frames and enable quality of service in the Cisco UCS Fabric, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the LAN tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose LAN > LAN Cloud > QoS System Class.
3.
In the right pane, click the General tab.
4.
On the Best Effort row, enter 9216 in the box under the MTU column.
5.
Click Save Changes.
6.
Click OK.
Figure 19 Setting Jumbo Frame
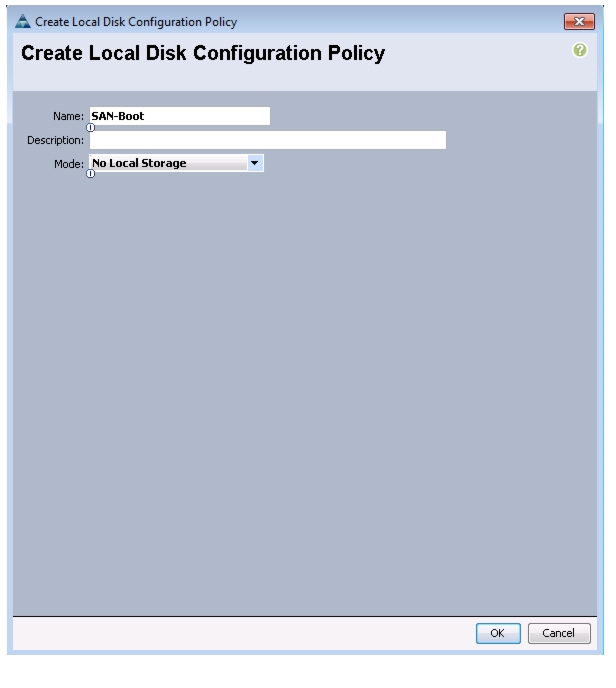
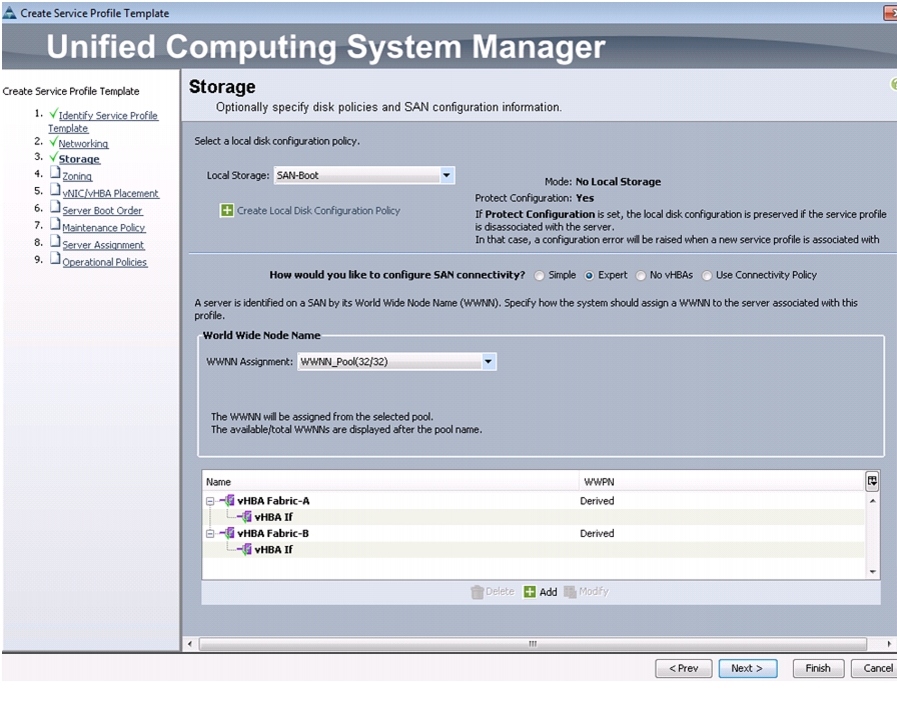
Create Local Disk Configuration Policy (Optional)
A local disk configuration for the Cisco UCS environment is necessary if the servers in the environment do not have a local disk.
Note
This policy should not be used on servers that contain local disks.
To create a local disk configuration policy, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Policies > root.
3.
Right-click Local Disk Config Policies.
4.
Choose Create Local Disk Configuration Policy.
5.
Enter SAN-Boot as the local disk configuration policy name.
6.
Change the mode to No Local Storage.
7.
Click OK to create the local disk configuration policy.
Figure 20 Creating Local Disk Configuration Policy
8.
Click OK.
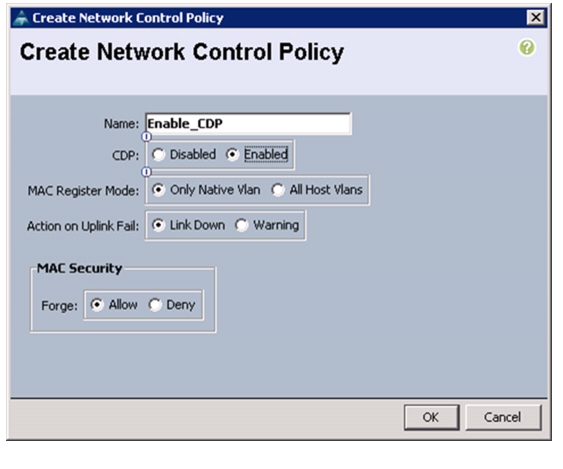
Create Network Control Policy for Cisco Discovery Protocol
To create a network control policy that enables Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on virtual network ports, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the LAN tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Policies > root.
3.
Right-click Network Control Policies.
4.
Choose Create Network Control Policy.
5.
Enter Enable_CDP as the policy name.
6.
For CDP, choose the Enabled option.
7.
Click OK to create the network control policy.
Figure 21 Creating Network Control Policy
8.
Click OK.
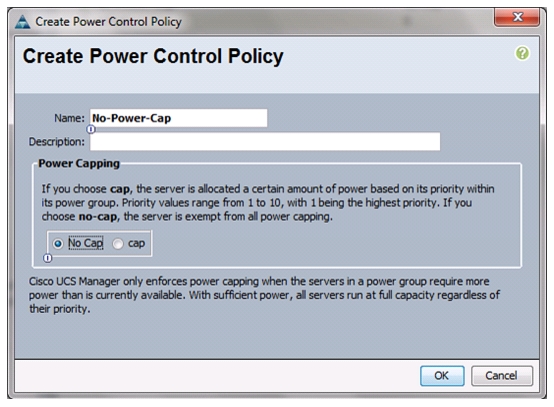
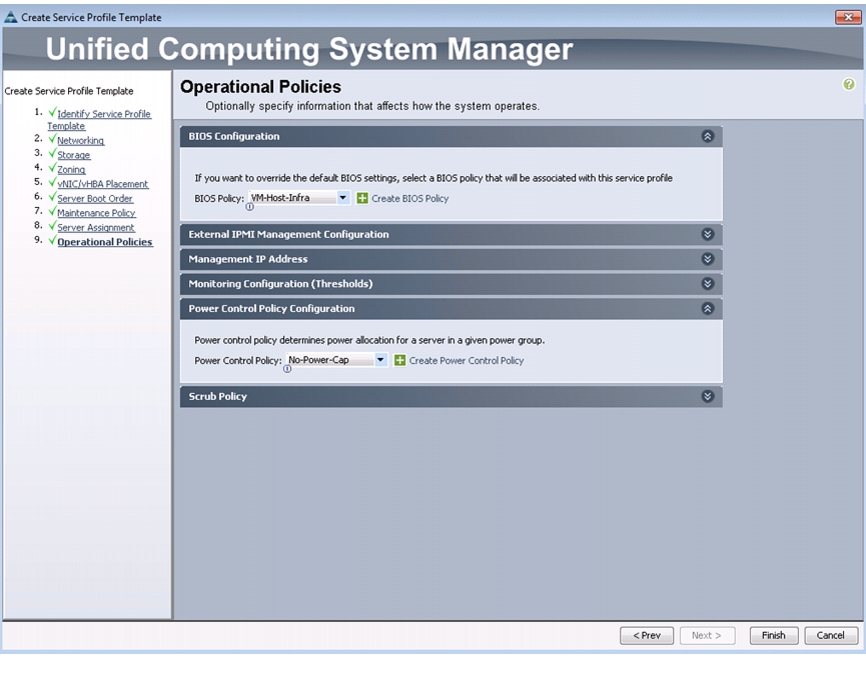
Create Power Control Policy
To create a power control policy for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Policies > root.
3.
Right-click Power Control Policies.
4.
Choose Create Power Control Policy.
5.
Enter No-Power-Cap as the power control policy name.
6.
Change the power capping setting to No Cap.
7.
Click OK to create the power control policy.
8.
Click OK.
Figure 22 Creating Power Control Policy
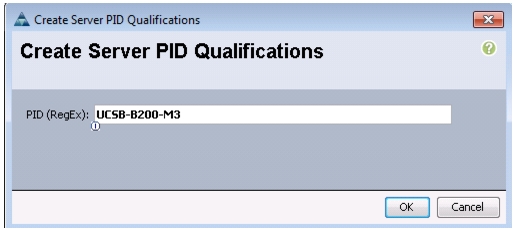
Create Server Pool Qualification Policy (Optional)
To create an optional server pool qualification policy for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
Note
This example creates a policy for a B200-M3 server.
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Policies > root.
3.
Right-click Server Pool Policy Qualifications.
4.
Choose Create Server Pool Policy Qualification.
5.
Enter UCSB-B200-M3 as the name for the policy.
6.
Choose Create Server PID Qualifications.
7.
Enter UCSB-B200-M3 as the PID.
8.
Click OK to create the server pool qualification policy.
9.
Click OK, and then click OK again.
Figure 23 Creating Server PID Qualifications
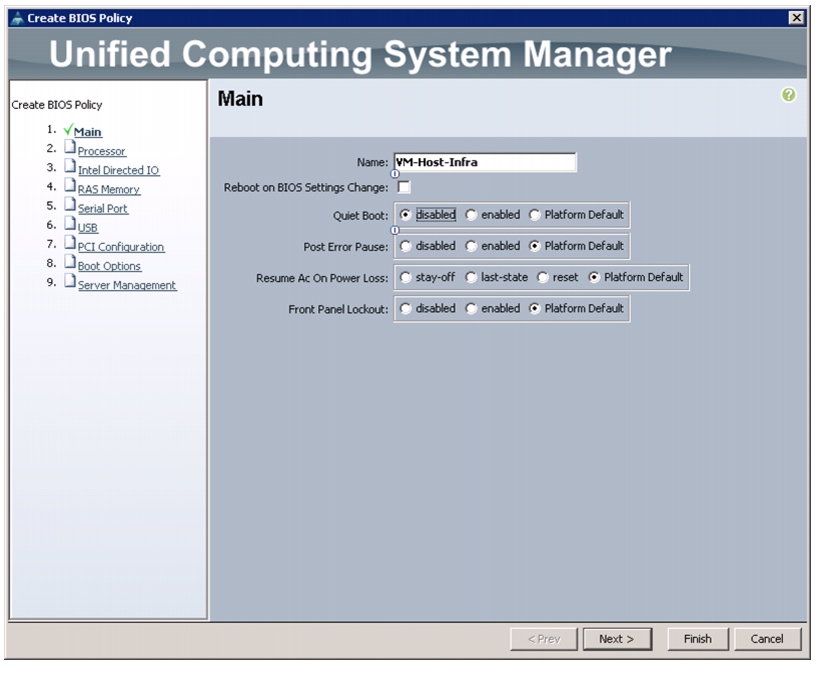
Create Server BIOS Policy
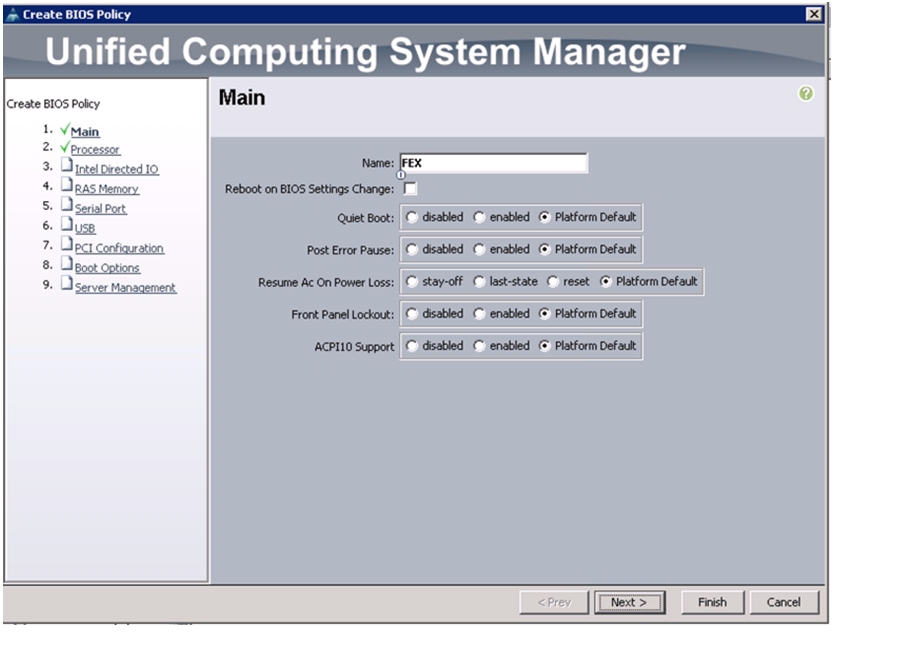
To create a server BIOS policy for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Policies > root.
3.
Right-click BIOS Policies.
4.
Choose Create BIOS Policy.
5.
Enter VM-Host-Infra as the BIOS policy name.
6.
Change the Quiet Boot setting to Disabled.
7.
Click Finish to create the BIOS policy.
Figure 24 Creating BIOS Policy
8.
Click OK.
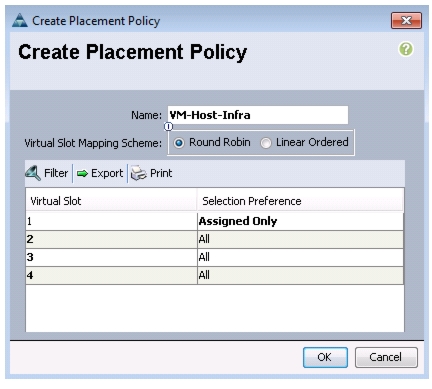
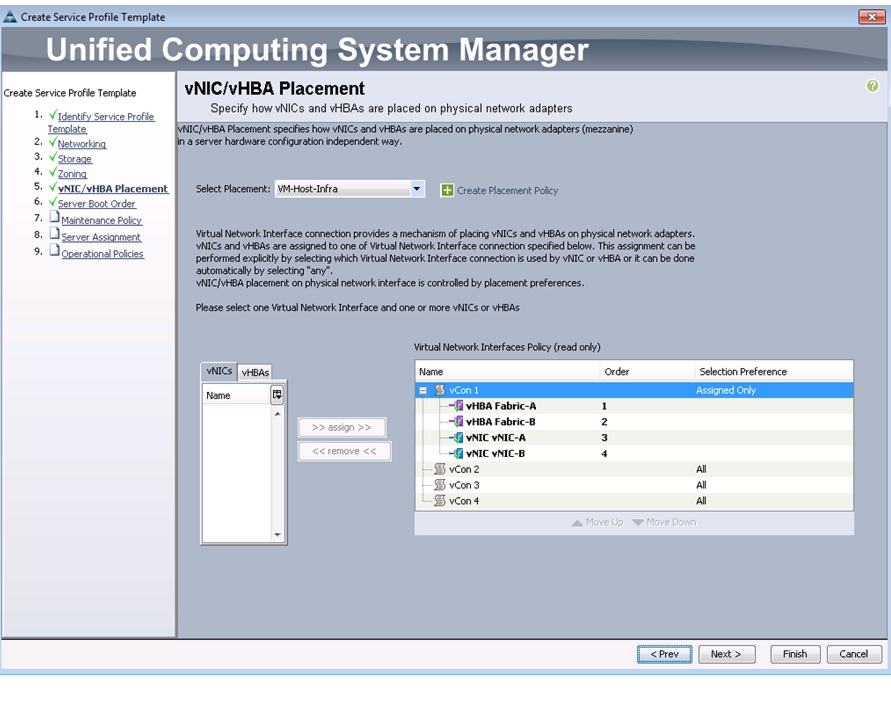
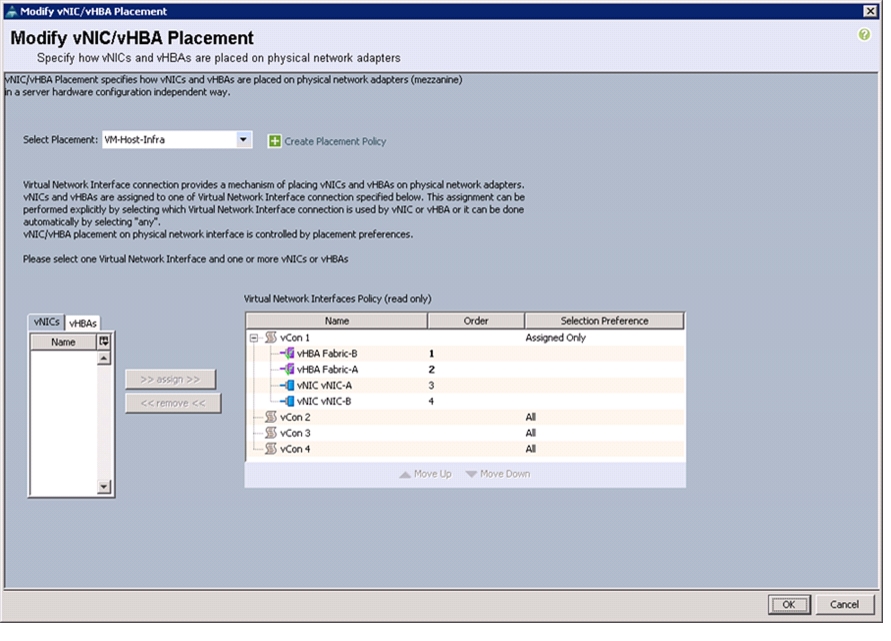
Create vNIC/vHBA Placement Policy for Virtual Machine Infrastructure Hosts
To create a vNIC/vHBA placement policy for the infrastructure hosts, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Policies > root.
3.
Right-click vNIC/vHBA Placement Policies.
4.
Choose Create Placement Policy.
5.
Enter VM-Host-Infra as the name of the placement policy.
6.
Click 1 and Choose Assigned Only.
7.
Click OK, and then click OK again.
Figure 25 Creating Placement Policy
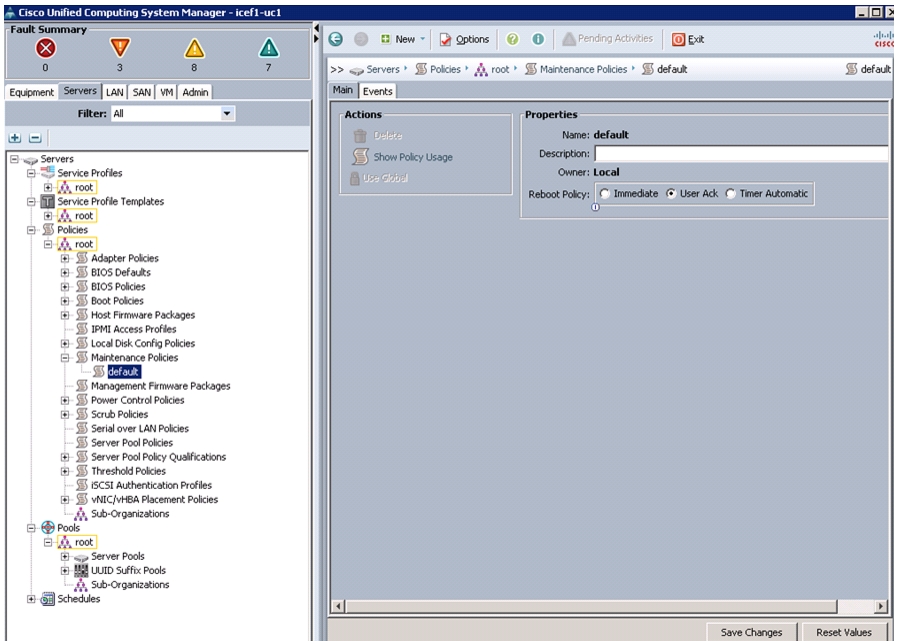
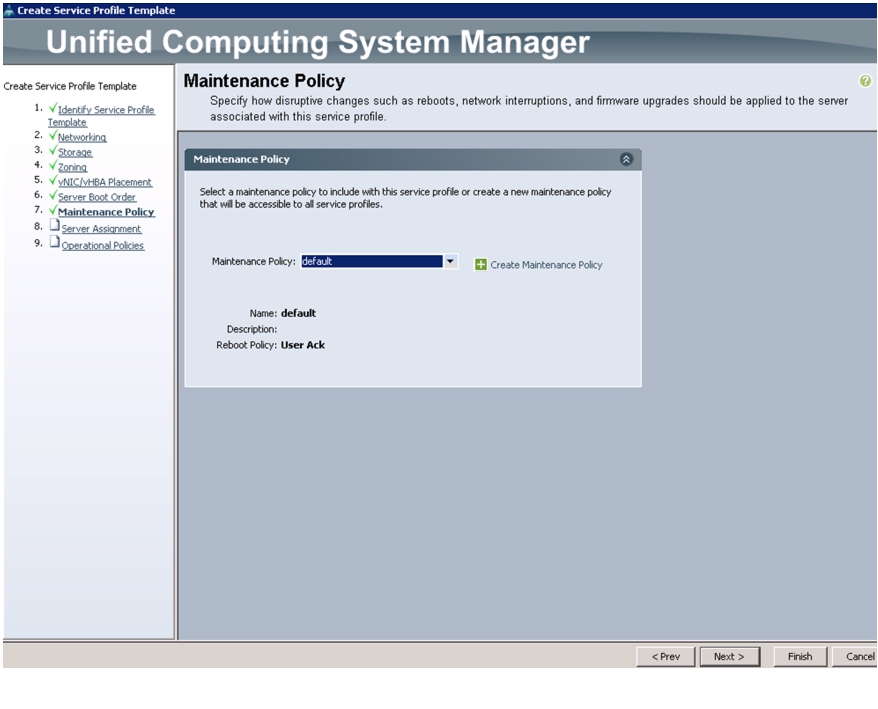
Update default Maintenance Policy
To update the default Maintenance Policy, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Policies > root.
3.
Choose Maintenance Policies > default.
4.
Change the Reboot Policy to User Ack.
5.
Click Save Changes.
6.
Click OK to accept the change.
Figure 26 Updating Maintenance Policy
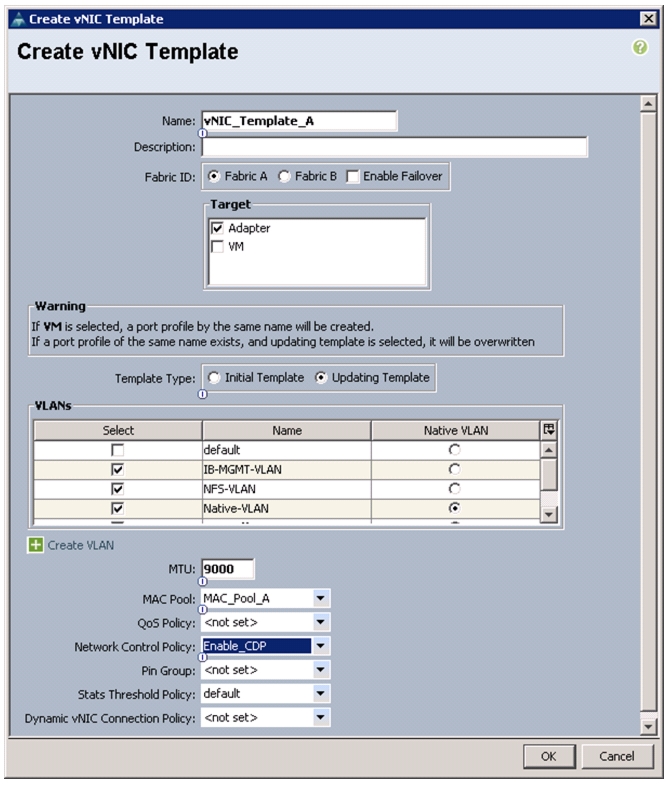
Create vNIC Templates
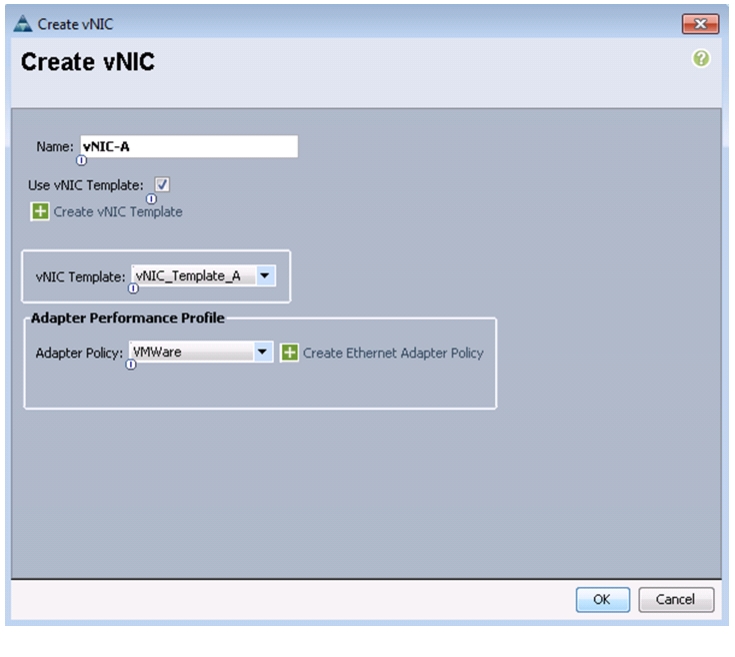
To create multiple virtual network interface card (vNIC) templates for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the LAN tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Policies > root.
3.
Right-click vNIC Templates.
4.
Choose Create vNIC Template.
5.
Enter vNIC_Template_A as the vNIC template name.
6.
Keep the radio button Fabric A selected.
7.
Do not check the Enable Failover check box.
8.
Under Target, make sure that the VM check box is not checked.
9.
Click the Updating Template radio button as the Template Type.
10.
Under VLANs, check the check boxes for IB-MGMT-VLAN, NFS-VLAN, Native-VLAN, VM-Traffic-VLAN, and vMotion-VLAN.
11.
Set Native-VLAN as the native VLAN.
12.
For MTU, enter 9000.
13.
In the MAC Pool list, Choose MAC_Pool_A.
14.
In the Network Control Policy list, Choose Enable_CDP.
15.
Click OK to create the vNIC template.
16.
Click OK.
Figure 27 Creating vNIC Template for Fabric A
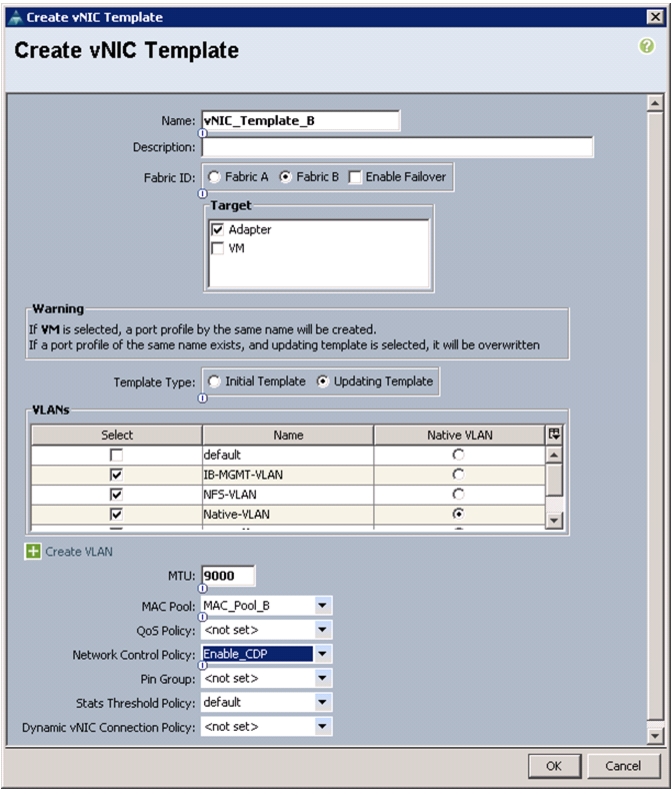
17.
In the navigation pane, click the LAN tab.
18.
Choose Policies > root.
19.
Right-click vNIC Templates.
20.
Choose Create vNIC Template.
21.
Enter vNIC_Template_B as the vNIC template name.
22.
Click the radio button Fabric B.
23.
Do not check the Enable Failover check box.
24.
Under Target, make sure the VM check box is not checked.
25.
Click the Updating Template radio button as the template type.
26.
Under VLANs, check the check boxes for IB-MGMT-VLAN, NFS-VLAN, Native-VLAN, VM-Traffic-VLAN, and vMotion-VLAN.
27.
Set Native-VLAN as the native VLAN.
28.
For MTU, enter 9000.
29.
In the MAC Pool list, Choose MAC_Pool_B.
30.
In the Network Control Policy list, Choose Enable_CDP.
31.
Click OK to create the vNIC template.
32.
Click OK.
Figure 28 Creating vNIC Template for Fabric B
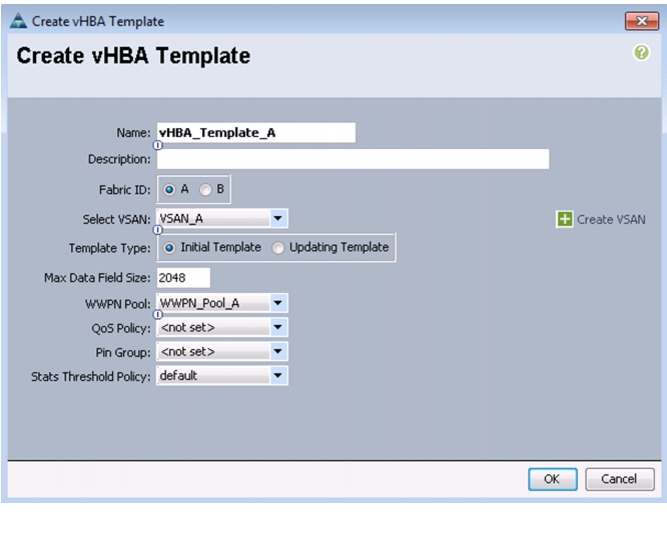
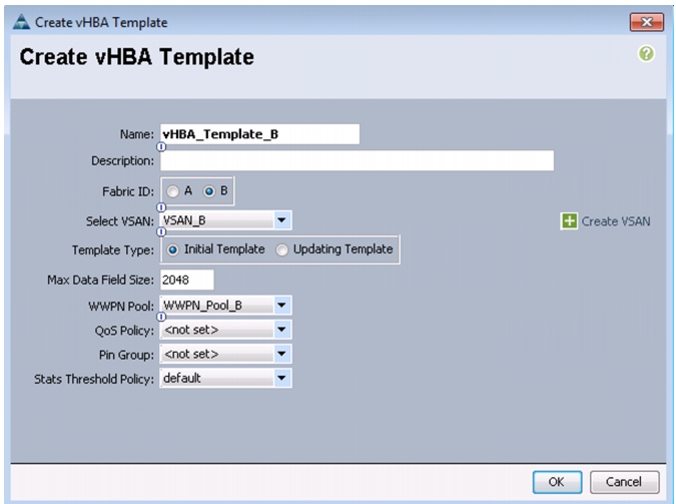
Create vHBA Templates for Fabric A and Fabric B
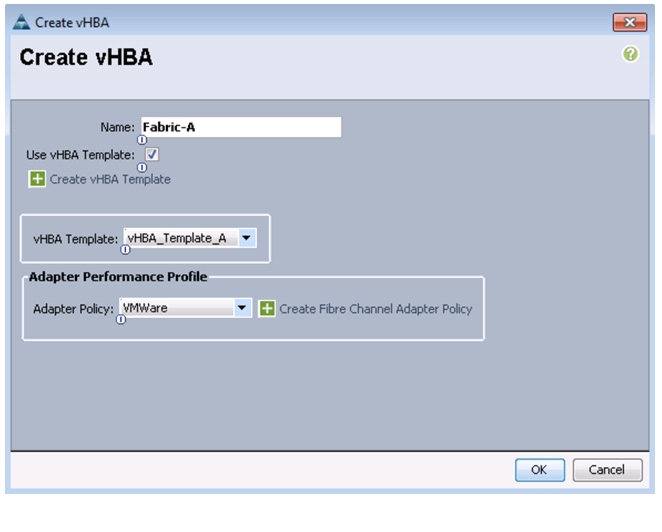
To create multiple virtual host bus adapter (vHBA) templates for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the SAN tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Policies > root.
3.
Right-click vHBA Templates.
4.
Choose Create vHBA Template.
5.
Enter vHBA_Template_A as the vHBA template name.
6.
Click the radio button Fabric A.
7.
In the Select VSAN list, Choose VSAN_A.
8.
In the WWPN Pool list, Choose WWPN_Pool_A.
9.
Click OK to create the vHBA template.
10.
Click OK.
Figure 29 Creating vHBA Template for Fabric A
11.
In the navigation pane, click the SAN tab.
12.
Choose Policies > root.
13.
Right-click vHBA Templates.
14.
Choose Create vHBA Template.
15.
Enter vHBA_Template_B as the vHBA template name.
16.
Click the radio button Fabric B.
17.
In the Select VSAN list, Choose VSAN_B.
18.
In the WWPN Pool, Choose WWPN_Pool_B.
19.
Click OK to create the vHBA template.
20.
Click OK.
Figure 30 Creating vHBA Template for Fabric B
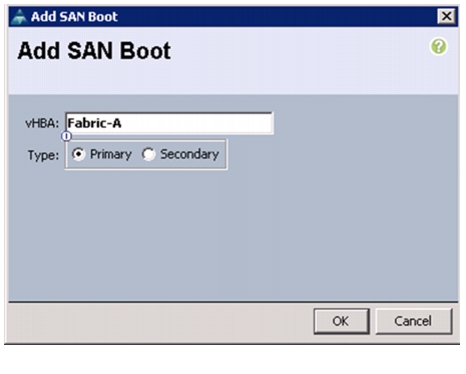
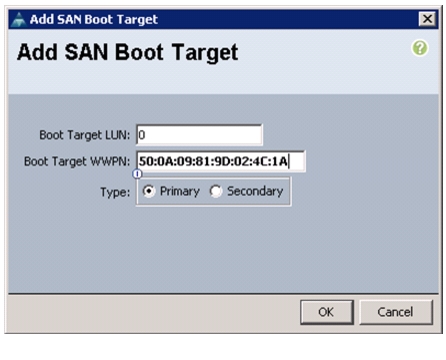
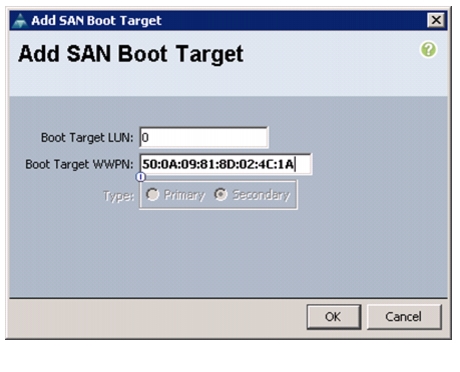
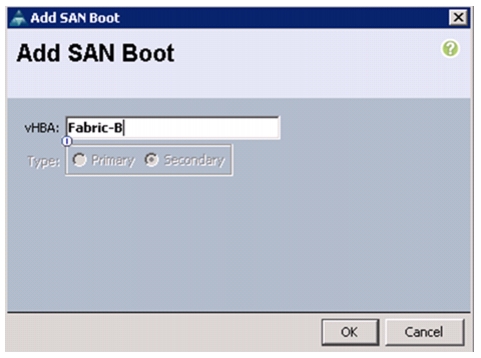
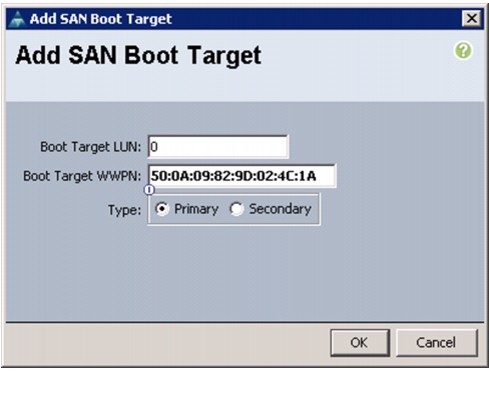
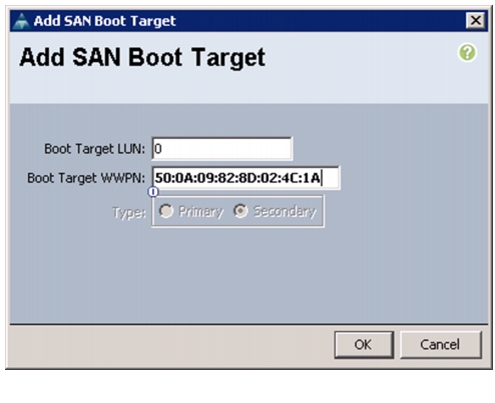
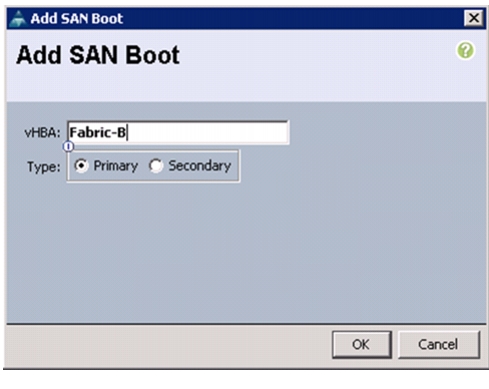
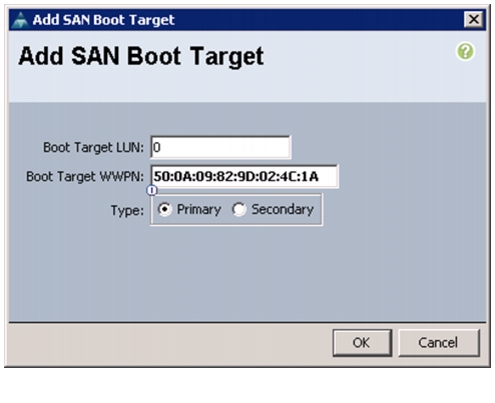
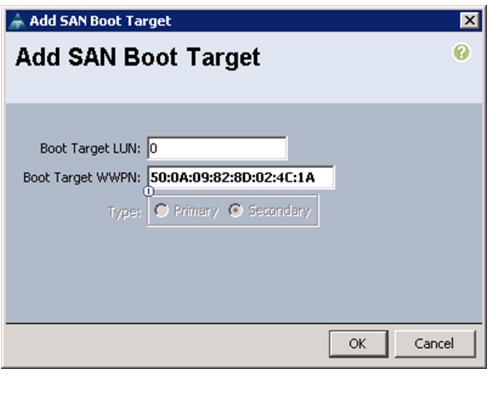
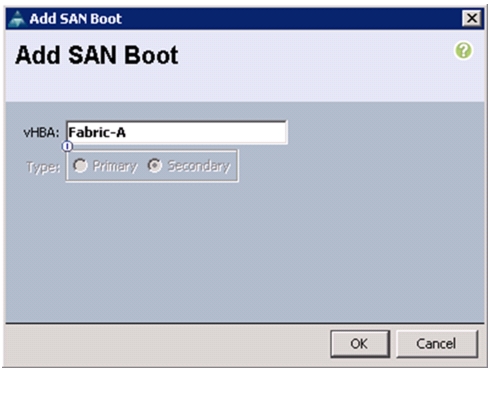
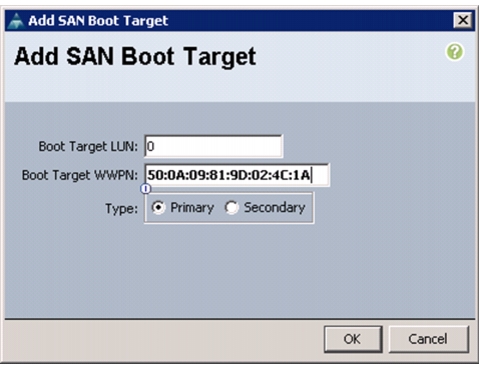
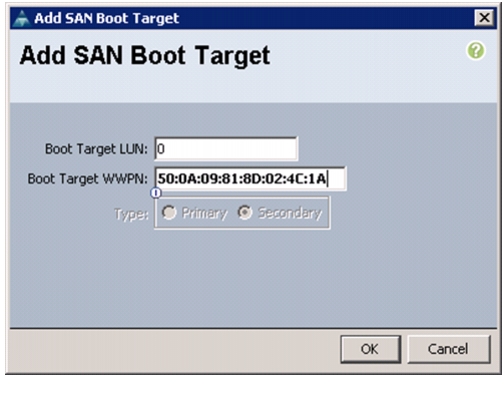
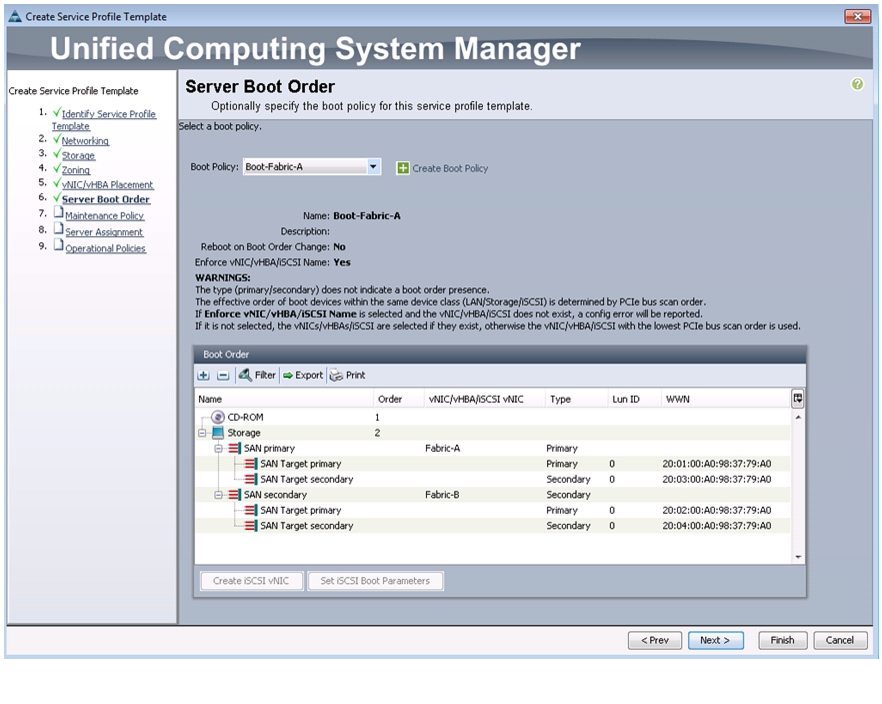
Create Boot Policies
This procedure applies to a Cisco UCS environment in which the storage FCoE ports are configured in the following ways:
•
The FCoE ports 1a on storage controllers 1 and 2 are connected to the Cisco Nexus 5548 switch A.
•
The FCoE ports 1b on storage controllers 1 and 2 are connected to the Cisco Nexus 5548 switch B.
Two boot policies are configured in this procedure:
•
The first configures the primary target to be FCoE port 1a on storage controller 1.
•
The second configures the primary target to be FCoE port 1b on storage controller 1.
To create boot policies for the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Policies > root.
3.
Right-click Boot Policies.
4.
Choose Create Boot Policy.
5.
Enter Boot-Fabric-A as the name of the boot policy.
6.
(Optional) Enter a description for the boot policy.
7.
Keep the Reboot on Boot Order Change check box unchecked.
8.
Expand the Local Devices drop-down menu and Choose Add CD-ROM.
9.
Expand the vHBAs drop-down menu and Choose Add SAN Boot.
10.
In the Add SAN Boot dialog box, enter Fabric-A in the vHBA field.
11.
Make sure that the Primary radio button is selected as the SAN boot type.
12.
Click OK to add the SAN boot initiator.
Figure 31 Adding SAN Boot Initiator for Fabric A
13.
From the vHBA drop-down menu, choose Add SAN Boot Target.
14.
Keep 0 as the value for Boot Target LUN.
15.
Enter the WWPN for FCoE port 1a on storage controller 1.
Note
To obtain this information, log in to storage controller 1 and run the fcp show adapters command. Make sure you enter the port name and not the node name.
16.
Keep the Primary radio button selected as the SAN boot target type.
17.
Click OK to add the SAN boot target.
Figure 32 Adding SAN Boot Target for Fabric A
18.
From the vHBA drop-down menu, choose Add SAN Boot Target.
19.
Keep 0 as the value for Boot Target LUN.
20.
Enter the WWPN for FCoE port 1a on storage controller 2.
Note
To obtain this information, log in to storage controller 2 and run the fcp show adapters command. Make sure you enter the port name and not the node name.
21.
Click OK to add the SAN boot target.
Figure 33 Adding Secondary SAN Boot Target for Fabric A
22.
From the vHBA drop-down menu, choose Add SAN Boot.
23.
In the Add SAN Boot dialog box, enter Fabric-B in the vHBA box.
24.
The SAN boot type should automatically be set to Secondary, and the Type option should be unavailable.
25.
Click OK to add the SAN boot initiator.
Figure 34 Adding SAN Boot Initiator for Fabric B
26.
From the vHBA drop-down menu, choose Add SAN Boot Target.
27.
Keep 0 as the value for Boot Target LUN.
28.
Enter the WWPN for FCoE port 1b on storage controller 1.
Note
To obtain this information, log in to storage controller 1 and run the fcp show adapters command. Make sure you enter the port name and not the node name.
29.
Keep Primary as the SAN boot target type.
30.
Click OK to add the SAN boot target.
Figure 35 Adding Primary SAN Boot Target for Fabric B
31.
From the vHBA drop-down menu, choose Add SAN Boot Target.
32.
Keep 0 as the value for Boot Target LUN.
33.
Enter the WWPN for FCoE port 1b on storage controller 2.
Note
To obtain this information, log in to storage controller 2 and run the fcp show adapters command. Make sure you enter the port name and not the node name.
34.
Click OK to add the SAN boot target.
Figure 36 Adding Secondary SAN Boot Target
35.
Click OK, and then OK again to create the boot policy.
36.
Right-click Boot Policies again.
37.
Choose Create Boot Policy.
38.
Enter Boot-Fabric-B as the name of the boot policy.
39.
(Optional) Enter a description of the boot policy.
40.
Keep the Reboot on Boot Order Change check box unchecked.
41.
From the Local Devices drop-down menu choose Add CD-ROM.
42.
From the vHBA drop-down menu choose Add SAN Boot.
43.
In the Add SAN Boot dialog box, enter Fabric-B in the vHBA box.
44.
Make sure that the Primary radiobutton is selected as the SAN boot type.
45.
Click OK to add the SAN boot initiator.
Figure 37 Adding SAN Boot Initiator for Fabric B
46.
From the vHBA drop-down menu, choose Add SAN Boot Target.
47.
Keep 0 as the value for Boot Target LUN.
48.
Enter the WWPN for FCoE port 1b on storage controller 1.
Note
To obtain this information, log in to storage controller 1 and run the fcp show adapters command. Make sure you enter the port name and not the node name.
49.
Keep Primary as the SAN boot target type.
50.
Click OK to add the SAN boot target.
Figure 38 Adding Primary SAN Boot Target for Fabric B
51.
From the vHBA drop-down menu, choose Add SAN Boot Target.
52.
Keep 0 as the value for Boot Target LUN.
53.
Enter the WWPN for FCoE port 1b on storage controller 2.
Note
To obtain this information, log in to storage controller 2 and run the fcp show adapters command. Make sure you enter the port name and not the node name.
54.
Click OK to add the SAN boot target.
Figure 39 Adding Secondary SAN Boot Target for Fabric B
55.
From the vHBA menu, choose Add SAN Boot.
56.
In the Add SAN Boot dialog box, enter Fabric-A in the vHBA box.
57.
The SAN boot type should automatically be set to Secondary, and the Type option should be unavailable.
58.
Click OK to add the SAN boot initiator.
Figure 40 Adding SAN Boot for Fabric A
59.
From the vHBA menu, choose Add SAN Boot Target.
60.
Keep 0 as the value for Boot Target LUN.
61.
Enter the WWPN for FCoE port 1a on storage controller 1.
Note
To obtain this information, log in to storage controller 1 and run the fcp show adapters command. Make sure you enter the port name and not the node name.
62.
Keep Primary as the SAN boot target type.
63.
Click OK to add the SAN boot target.
Figure 41 Adding Primary SAN Boot Target for Fabric A
64.
From the vHBA drop-down menu, choose Add SAN Boot Target.
65.
Keep 0 as the value for Boot Target LUN.
66.
Enter the WWPN for FCoE port 1a on storage controller 2.
Note
To obtain this information, log in to storage controller 2 and run the fcp show adapters command. Make sure you enter the port name and not the node name.
67.
Click OK to add the SAN boot target.
Figure 42 Adding Secondary SAN Boot Target for Fabric A
68.
Click OK, and then click OK again to create the boot policy.
Create Service Profile Templates
In this procedure, two service profile templates are created: one for fabric A boot and one for fabric B boot. The first profile is created and then cloned and modified for the second host.
To create service profile templates, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Service Profile Templates > root.
3.
Right-click root.
4.
Choose Create Service Profile Template to open the Create Service Profile Template wizard.
5.
Identify the Service Profile Template:
a.
Enter VM-Host-Infra-Fabric-A as the name of the service profile template. This service profile template is configured to boot from node 1 on fabric A.
b.
Click the Updating Template radio button.
c.
Under UUID, choose UUID_Pool as the UUID pool.
d.
Click Next.
Figure 43 Details for Creating Service Profile Template
6.
Configure the Networking options:
a.
Keep the default setting for Dynamic vNIC Connection Policy.
b.
Click the Expert radio button to configure the LAN connectivity.
c.
Click Add to add a vNIC to the template.
d.
In the Create vNIC dialog box, enter vNIC-A as the name of the vNIC.
e.
Check the Use vNIC Template check box.
f.
In the vNIC Template list, choose vNIC_Template_A.
g.
In the Adapter Policy list, choose VMWare.
h.
Click OK to add this vNIC to the template.
Figure 44 Creating vNIC Using vNIC Template
i.
On the Networking page of the wizard, click Add to add another vNIC to the template.
j.
In the Create vNIC box, enter vNIC-B as the name of the vNIC.
k.
Check the Use vNIC Template check box.
l.
In the vNIC Template list, choose vNIC_Template_B.
m.
In the Adapter Policy list, choose VMWare.
n.
Click OK to add the vNIC to the template.
o.
Review the table in the Networking page to make sure that both vNICs were created.
p.
Click Next.
Figure 45 LAN Configuration Details
7.
Configure the Storage options:
a.
Choose a local disk configuration policy:
–
If the server in question has local disks, choose default in the Local Storage list.
–
If the server in question does not have local disks, choose SAN-Boot.
b.
Click the Expert radio button to configure the SAN connectivity.
c.
In the WWNN Assignment list, choose WWNN_Pool.
d.
Click Add at the bottom of the page to add a vHBA to the template.
e.
In the Create vHBA dialog box, enter Fabric-A as the name of the vHBA.
f.
Check the Use vHBA Template check box.
g.
In the vHBA Template list, choose vHBA_Template_A.
h.
In the Adapter Policy list, choose VMware.
i.
Click OK to add this vHBA to the template.
Figure 46 Creating vHBA Using vHBA Template
j.
On the Storage page of the wizard, click Add at the bottom of the page to add another vHBA to the template.
k.
In the Create vHBA dialog box, enter Fabric-B as the name of the vHBA.
l.
Check the check box for Use HBA Template.
m.
In the vHBA Template list, choose vHBA_Template_B.
n.
In the Adapter Policy list, choose VMware.
o.
Click OK to add the vHBA to the template.
p.
Review the table in the Storage page to verify that both vHBAs were created.
q.
Click Next.
Figure 47 Storage Window Showing Created vHBAs
8.
Set no Zoning options and click Next.
9.
Set the vNIC/vHBA placement options.
a.
In the Select Placement list, choose the VM-Host-Infra placement policy.
b.
Choose vCon1 and assign the vHBAs/vNICs to the virtual network interfaces policy in the following order:
–
vHBA Fabric-A
–
vHBA Fabric-B
–
vNIC-A
–
vNIC-B
c.
Review the table to verify that all vNICs and vHBAs were assigned to the policy in the appropriate order.
d.
Click Next.
Figure 48 Placing vNIC and vHBA on Physical Adapters
10.
Set the Server Boot Order:
a.
In the Boot Policy list, choose Boot-Fabric-A.
b.
Review the table to verify that all boot devices were created and identified. Verify that the boot devices are in the correct boot sequence.
c.
Click Next.
Figure 49 Setting Boot Order for the Service Profile Template
11.
Add a Maintenance Policy:
a.
Choose the Default Maintenance Policy.
b.
Click Next.
Figure 50 Choosing a Maintenance Policy
12.
Specify the Server Assignment:
a.
In the Pool Assignment list, choose Infra_Pool.
b.
(Optional) Choose a Server Pool Qualification policy.
c.
Choose Down as the power state to be applied when the profile is associated with the server.
d.
Expand Firmware Management at the bottom of the page and choose VM-Host-Infra from the Host Firmware list.
e.
Click Next.
Figure 51 Assigning a Server Pool to the Service Profile Template
13.
Add Operational Policies:
a.
In the BIOS Policy list, choose VM-Host-Infra.
b.
Expand Power Control Policy Configuration and choose No-Power-Cap in the Power Control Policy list.
Figure 52 Setting Operational Policy
14.
Click Finish to create the service profile template.
15.
Click OK in the confirmation message.
16.
Click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
17.
Choose Service Profile Templates > root.
18.
Right-click the previously created VM-Host-Infra-Fabric-A template.
19.
Choose Create a Clone.
20.
In the dialog box, enter VM-Host-Infra-Fabric-B as the name of the clone, choose the root Org, and click OK.
Figure 53 Cloning a Service Profile Template
21.
Click OK.
22.
Choose the newly cloned service profile template and click the Boot Order tab.
23.
Click Modify Boot Policy.
24.
In the Boot Policy list, choose Boot-Fabric-B.
Figure 54 Modifying Boot Policy
25.
Click OK, and then click OK again.
26.
In the right pane, click the Network tab and then click Modify vNIC/HBA Placement.
27.
Expand vCon 1 and move vHBA Fabric-B ahead of vHBA Fabric-A in the placement order.
Figure 55 Modifying Placement Policy
28.
Click OK, and then click OK again.
Create Service Profiles
To create service profiles from the service profile template, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Service Profile Templates > root > Service Template VM-Host-Infra-Fabric-A.
3.
Right-click VM-Host-Infra-Fabric-A and choose Create Service Profiles from Template.
4.
Enter VM-Host-Infra-0 as the service profile prefix.
5.
Enter 1 as the number of service profiles to create.
6.
Click OK to create the service profile.
Figure 56 Creating Service Profile from a Service Profile Template
7.
Click OK in the confirmation message.
8.
Choose Service Profile Templates > root > Service Template VM-Host-Infra-Fabric-B.
9.
Right-click VM-Host-Infra-Fabric-B and choose Create Service Profiles from Template.
10.
Enter VM-Host-Infra-0 as the service profile prefix.
11.
Enter 1 as the number of service profiles to create.
12.
Click OK to create the service profile.
Figure 57 Creating Service Profile from a Service Profile Template
13.
Click OK in the confirmation message.
Verify that the service profiles VM-Host-Infra-01 and VM-Host-Infra-02 have been created. The service profiles are automatically associated with the servers in their assigned server pools.
14.
(Optional) Choose each newly created service profile and enter the server host name or the FQDN in the User Label field in the General tab. Click Save Changes to map the server host name to the service profile name.
Add More Servers to FlexPod Unit
Additional server pools, service profile templates, and service profiles can be created in the respective organizations to add more servers to the FlexPod unit. All other pools and policies are at the root level and can be shared among the organizations.
Gather Necessary Information
After the Cisco UCS service profiles have been created, each infrastructure blade in the environment will have a unique configuration. To proceed with the FlexPod deployment, specific information must be gathered from each Cisco UCS blade and from the NetApp controllers. Insert the required information into Table 20 and Table 21.
Table 20 FC Port Names for Storage Controllers 1 and 2
1
1a
1
1b
2
1a
2
1b
Note
To gather the FC port name information, run the fcp show adapters command on the storage controller.
Table 21 vHBA WWPNs for Fabric A and Fabric B
VM-Host-infra-01
VM-Host-infra-02
Note
To gather the vHBA WWPN information, launch the Cisco UCS Manager GUI. In the navigation pane, click the Servers tab. Expand Servers > Service Profiles > root. Click each service profile and then click the Storage tab in the right pane. In Table 21, record the WWPN information that is displayed in the right pane for both the Fabric A vHBA and the Fabric B vHBA for each service profile.
Storage Networking
FlexPod Cisco Nexus Base
Table 22 Flexpod Cisco Nexus Base Prerequisite
The Cisco Nexus switch must be running Cisco Nexus NX-OS 5.2(1)N1(3) or late
The following procedures describe how to configure the Cisco Nexus switches for use in a base FlexPod environment. Follow these steps precisely; failure to do so might result in an improper configuration.
Set Up Initial Configuration
Cisco Nexus A
To set up the initial configuration for the Cisco Nexus A switch on <<var_nexus_A_hostname>>, follow these steps:
Configure the switch.
Note
On initial boot and connection to the serial or console port of the switch, the NX-OS setup should automatically start and attempt to enter Power on Auto Provisioning.
Abort Power on Auto Provisioning and continue with normal setup? (yes/no) [no]: yesDo you want to enforce secure password standard (yes/no): yesEnter the password for the "admin": <<var_password>>Confirm the password for "admin": <<var_password>>Would you like to enter the basic configuration dialog (yes/no): yesCreate another login account (yes/no) [n]: EnterConfigure read-only SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: EnterConfigure read-write SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: EnterEnter the switch name: <<var_nexus_A_hostname>>Continue with out-of-band (mgmt0) management configuration? (yes/no) [y]: EnterMgmt0 IPv4 address: <<var_nexus_A_mgmt0_ip>>Mgmt0 IPv4 netmask: <<var_nexus_A_mgmt0_netmask>>Configure the default gateway? (yes/no) [y]: EnterIPv4 address of the default gateway: <<var_nexus_A_mgmt0_gw>>Enable the telnet service? (yes/no) [n]: EnterEnable the ssh service? (yes/no) [y]: EnterType of ssh key you would like to generate (dsa/rsa): rsaNumber of key bits <768-2048> : 1024Configure the ntp server? (yes/no) [n]: yNTP server IPv4 address: <<var_global_ntp_server_ip>>Enter basic FC configurations (yes/no) [n]: EnterWould you like to edit the configuration? (yes/no) [n]: Enter2. Review the configuration summary before enabling the configuration.Use this configuration and save it? (yes/no) [y]: EnterCisco Nexus B
To set up the initial configuration for the Cisco Nexus B switch on <<var_nexus_B_hostname>>, follow these steps:
1.
Configure the switch.
Note
On initial boot and connection to the serial or console port of the switch, the NX-OS setup should automatically start and attempt to enter Power on Auto Provisioning.
Abort Power on Auto Provisioning and continue with normal setup? (yes/no) [no]: yesDo you want to enforce secure password standard (yes/no): yesEnter the password for the "admin": <<var_password>>Confirm the password for "admin": <<var_password>>Would you like to enter the basic configuration dialog (yes/no): yesCreate another login account (yes/no) [n]: EnterConfigure read-only SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: EnterConfigure read-write SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: EnterEnter the switch name: <<var_nexus_B_hostname>>Continue with out-of-band (mgmt0) management configuration? (yes/no) [y]: EnterMgmt0 IPv4 address: <<var_nexus_B_mgmt0_ip>>Mgmt0 IPv4 netmask: <<var_nexus_B_mgmt0_netmask>>Configure the default gateway? (yes/no) [y]: EnterIPv4 address of the default gateway: <<var_nexus_B_mgmt0_gw>>Enable the telnet service? (yes/no) [n]: EnterEnable the ssh service? (yes/no) [y]: EnterType of ssh key you would like to generate (dsa/rsa): rsaNumber of key bits <768-2048> : 1024Configure the ntp server? (yes/no) [n]: yNTP server IPv4 address: <<var_global_ntp_server_ip>>Enter basic FC configurations (yes/no) [n]: EnterWould you like to edit the configuration? (yes/no) [n]: Enter2.
Review the configuration summary before enabling the configuration.
Use this configuration and save it? (yes/no) [y]: EnterFlexPod Cisco Nexus FCoE Storage vSphere on Data ONTAP 7-Mode
Enable Licenses
Cisco Nexus A
To license the Cisco Nexus A switch on <<var_nexus_A_hostname>>, follow these steps:
1.
Log in as admin.
2.
Run the following commands:
config tfeature fcoefeature npivfeature lacpfeature vpcCisco Nexus B
To license the Cisco Nexus B switch on <<var_nexus_B_hostname>>, follow these steps:
1.
Log in as admin.
2.
Run the following commands:
config tfeature fcoefeature npivfeature lacpfeature vpcSet Global Configurations
Cisco Nexus 5548 A and Cisco Nexus 5548 B
To set global configurations, follow these steps on both switches:
Run the following commands to set global configurations and jumbo frames in QoS:
spanning-tree port type network defaultspanning-tree port type edge bpduguard defaultport-channel load-balance ethernet source-dest-portpolicy-map type network-qos jumboclass type network-qos class-defaultmtu 9216exitclass type network-qos class-fcoepause no-dropmtu 2158exitexitsystem qosservice-policy type network-qos jumboexitcopy run startCreate VLANs
Cisco Nexus 5548 A and Cisco Nexus 5548 B
To create the necessary virtual local area networks (VLANs), follow these steps on both switches:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands:
vlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>name IB-MGMT-VLANexitvlan <<var_native_vlan_id>>name Native-VLANexitvlan <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>name NFS-VLANexitvlan <<var_pkt-ctrl_vlan_id>>name Packet-Control-VLANexitvlan <<var_vmotion_vlan_id>>name vMotion-VLANexitvlan <<var_vm-traffic_vlan_id>>name VM-Traffic-VLANexitAdd Individual Port Descriptions for Troubleshooting
Cisco Nexus 5548 A
To add individual port descriptions for troubleshooting activity and verification for switch A, follow these steps:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands:
interface Eth1/1description <<var_node01>>:e3aexitinterface Eth1/2description <<var_node02>>:e3aexitinterface Eth1/11description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-A:1/19exitinterface Eth1/12description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-B:1/19exitinterface Eth1/13description <<var_nexus_B_hostname>>:1/13exitinterface Eth1/14description <<var_nexus_B_hostname>>:1/14exitinterface eth1/31description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-A:1/31exitinterface eth1/32description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-A:1/32exitCisco Nexus 5548 B
To add individual port descriptions for troubleshooting activity and verification for switch B, follow these steps:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands:
interface Eth1/1description <<var_node01>>:e4aexitinterface Eth1/2description <<var_node02>>:e4aexitinterface Eth1/11description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-A:1/20exitinterface Eth1/12description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-B:1/20exitinterface Eth1/13description <<var_nexus_A_hostname>>:1/13exitinterface Eth1/14description <<var_nexus_A_hostname>>:1/14exitinterface eth1/31description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-B:1/31exitinterface eth1/32description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-B:1/32exitCreate Port Channels
Cisco Nexus 5548 A and Cisco Nexus 5548 B
To create the necessary port channels between devices, follow these steps on both switches:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands:
interface Po10description vPC peer-linkexitinterface Eth1/13-14channel-group 10 mode activeno shutdownexitinterface Po11description <<var_node01>>exitinterface Eth1/1channel-group 11 mode activeno shutdownexitinterface Po12description <<var_node02>>exitinterface Eth1/2channel-group 12 mode activeno shutdownexitinterface Po13description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-Aexitinterface Eth1/11channel-group 13 mode activeno shutdownexitinterface Po14description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-Bexitinterface Eth1/12channel-group 14 mode activeno shutdownexitcopy run startConfigure Port Channels
Cisco Nexus 5548 A and Cisco Nexus 5548 B
To configure the port channels, follow these steps on both switches:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands:
interface Po10switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan <<var_native_vlan_id>>switchport trunk allowed vlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>, <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>, <<var_pkt-ctrl_vlan_id>>, <<var_vmotion_vlan_id>>, <<var_vm-traffic_vlan_id>>spanning-tree port type networkno shutdownexitinterface Po11switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan <<var_native_vlan_id>>switchport trunk allowed vlan <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>spanning-tree port type edge trunkno shutdownexitinterface Po12switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan <<var_native_vlan_id>>switchport trunk allowed vlan <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>spanning-tree port type edge trunkno shutdownexitinterface Po13switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan <<var_native_vlan_id>>switchport trunk allowed vlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>, <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>, <<var_vmotion_vlan_id>>, <<var_vm-traffic_vlan_id>>spanning-tree port type edge trunkno shutdownexitinterface Po14switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan <<var_native_vlan_id>>switchport trunk allowed vlan<<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>, <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>, <<var_vmotion_vlan_id>>, <<var_vm-traffic_vlan_id>>spanning-tree port type edge trunkno shutdownexitcopy run startConfigure Virtual Port Channels
Cisco Nexus 5548 A
To configure virtual port channels (vPCs) for switch A, follow these steps:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands:
vpc domain <<var_nexus_vpc_domain_id>>role priority 10peer-keepalive destination <<var_nexus_B_mgmt0_ip>> source <<var_nexus_A_mgmt0_ip>>auto-recoveryexitinterface Po10vpc peer-linkexitinterface Po11vpc 11exitinterface Po12vpc 12exitinterface Po13vpc 13exitinterface Po14vpc 14exitcopy run startCisco Nexus 5548 B
To configure vPCs for switch B, follow these steps:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands.
vpc domain <<var_nexus_vpc_domain_id>>role priority 20peer-keepalive destination <<var_nexus_A_mgmt0_ip>> source <<var_nexus_B_mgmt0_ip>>auto-recoveryexitinterface Po10vpc peer-linkexitinterface Po11vpc 11exitinterface Po12vpc 12exitinterface Po13vpc 13exitinterface Po14vpc 14exitcopy run startConfigure Ports for Cisco Nexus 1110-X Virtual Appliances
Cisco Nexus 5548 A
To configure the ports in switch A that are connected to the Cisco Nexus 1110-X, follow these steps:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands:
interface Eth1/15description <<var_nexus_1110x-1>>:Eth1switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk allowed vlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>, <<var_pkt-ctrl_vlan_id>>speed 1000spanning-tree port type edge trunkno shutdownexitinterface Eth1/16description <<var_nexus_1110x-2>>:Eth1switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk allowed vlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>, <<var_pkt-ctrl_vlan_id>>speed 1000spanning-tree port type edge trunkno shutdownexitcopy run startCisco Nexus 5548 B
To configure the ports in switch B that are connected to the Cisco Nexus 1110-X, follow these steps:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands:
interface Eth1/15description <<var_nexus_1110x-1>>:Eth2switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk allowed vlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>, <<var_pkt-ctrl_vlan_id>>speed 1000spanning-tree port type edge trunkno shutdownexitinterface Eth1/16description <<var_nexus_1110x-2>>:Eth2switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk allowed vlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>, <<var_pkt-ctrl_vlan_id>>speed 1000spanning-tree port type edge trunkno shutdownexitcopy run startUplink into Existing Network Infrastructure
Depending on the available network infrastructure, several methods and features can be used to uplink the FlexPod environment. If an existing Cisco Nexus environment is present, NetApp recommends using vPCs to uplink the Cisco Nexus 5548 switches included in the FlexPod environment into the infrastructure. The previously described procedures can be used to create an uplink vPC to the existing environment. Make sure to run copy run start to save the configuration on each switch after configuration is completed.
Create VSANs, Assign and Enable Virtual Fibre Channel Ports
This procedure sets up Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) connections between the Cisco Nexus 5548 switches, the Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects, and the NetApp storage systems.
Cisco Nexus 5548 A
To configure virtual storage area networks (VSANs), assign virtual Fibre Channel (vFC) ports, and enable vFC ports on switch A, follow these steps:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands:
vlan <<var_fabric_a_fcoe_vlan_id>>name FCoE_Fabric_Afcoe vsan <<var_vsan_a_id>>exitinterface po11switchport trunk allowed vlan add <<var_fabric_a_fcoe_vlan_id>>exitinterface vfc11switchport description <<var_node01>>:3abind interface Eth1/1switchport trunk allowed vsan <<var_vsan_a_id>>no shutdownexitinterface po12switchport trunk allowed vlan add <<var_fabric_a_fcoe_vlan_id>>exitinterface vfc12switchport description <<var_node02>>:3abind interface Eth1/2switchport trunk allowed vsan <<var_vsan_a_id>>no shutdownexitinterface po15description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-A:FCoEexitinterface Eth1/31-32channel-group 15 mode activeexitinterface po15switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan <<var_native_vlan_id>>switchport trunk allowed vlan <<var_fabric_a_fcoe_vlan_id>>spanning-tree port type edge trunkno shutdownexitinterface vfc15switchport description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-A:FCoEbind interface po15switchport trunk allowed vsan <<var_vsan_a_id>>no shutdownvsan databasevsan <<var_vsan_a_id>> name Fabric_Avsan <<var_vsan_a_id>> interface vfc11vsan <<var_vsan_a_id>> interface vfc12vsan <<var_vsan_a_id>> interface vfc15exitCisco Nexus 5548 B
To configure VSANs, assign vFC ports, and enable vFC ports on switch B, follow these steps:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands:
vlan <<var_fabric_b_fcoe_vlan_id>>name FCoE_Fabric_Bfcoe vsan <<var_vsan_b_id>>exitinterface po11switchport trunk allowed vlan add <<var_fabric_b_fcoe_vlan_id>>exitinterface vfc11switchport description <<var_node01>>:4abind interface Eth1/1switchport trunk allowed vsan <<var_vsan_b_id>>no shutdownexitinterface po12switchport trunk allowed vlan add <<var_fabric_b_fcoe_vlan_id>>exitinterface vfc12switchport description <<var_node02>>:4abind interface Eth1/2switchport trunk allowed vsan <<var_vsan_b_id>>no shutdownexitinterface po15description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-B:FCoEexitinterface Eth1/31-32channel-group 15 mode activeexitinterface po15switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan <<var_native_vlan_id>>switchport trunk allowed vlan <<var_fabric_b_fcoe_vlan_id>>spanning-tree port type edge trunkno shutdownexitinterface vfc15switchport description <<var_ucs_clustername>>-B:FCoEbind interface po15switchport trunk allowed vsan <<var_vsan_b_id>>no shutdownvsan databasevsan <<var_vsan_b_id>> name Fabric_Bvsan <<var_vsan_b_id>> interface vfc11vsan <<var_vsan_b_id>> interface vfc12vsan <<var_vsan_b_id>> interface vfc15exitCreate Device Aliases
Cisco Nexus 5548 A
To configure device aliases and zones for the primary boot paths of switch A on <<var_nexus_A_hostname>>, follow these steps:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands:
device-alias databasedevice-alias name VM-Host-Infra-01_A pwwn <<var_vm_host_infra_01_A_wwpn>>device-alias name VM-Host-Infra-02_A pwwn <<var_vm_host_infra_02_A_wwpn>>device-alias name <<var_controller1>>_1a pwwn <<var_controller1_1a_wwpn>>device-alias name <<var_controller2>>_1a pwwn <<var_controller2_1a_wwpn>>exitdevice-alias commitCisco Nexus 5548 B
To configure device aliases and zones for the boot paths of switch B on <<var_nexus_B_hostname>>, follow these steps:
From the global configuration mode, run the following commands:
device-alias databasedevice-alias name VM-Host-Infra-01_B pwwn <<var_vm_host_infra_01_B_wwpn>>device-alias name VM-Host-Infra-02_B pwwn <<var_vm_host_infra_02_B_wwpn>>device-alias name <<var_controller1>>_1b pwwn <<var_controller1_1b_wwpn>>device-alias name <<var_controller2>>_1b pwwn <<var_controller2_1b_wwpn>>exitdevice-alias commitCreate Zones
Cisco Nexus 5548 A
To create zones for the service profiles on switch A, follow these steps:
1.
Create a zone for each service profile.
zone name VM-Host-Infra-01_A vsan <<var_vsan_a_id>>member device-alias VM-Host-Infra-01_Amember device-alias <<var_controller1>>_1amember device-alias <<var_controller2>>_1aexitzone name VM-Host-Infra-02_A vsan <<var_ vsan_a_id>>member device-alias VM-Host-Infra-02_Amember device-alias <<var_controller1>>_1amember device-alias <<var_controller2>>_1aexit2.
After the zone for the Cisco UCS service profiles has been created, create the zone set and add the necessary members.
zoneset name FlexPod vsan <<var_ vsan_a_id>>member VM-Host-Infra-01_Amember VM-Host-Infra-02_Aexit3.
Activate the zone set.
zoneset activate name FlexPod vsan <<var_ vsan_a_id>>exitcopy run startCisco Nexus 5548 B
To create zones for the service profiles on switch B, follow these steps:
1.
Create a zone for each service profile.
zone name VM-Host-Infra-01_B vsan <<var_ vsan_b_id>>member device-alias VM-Host-Infra-01_Bmember device-alias <<var_controller1>>_1bmember device-alias <<var_controller2>>_1bexitzone name VM-Host-Infra-02_B vsan <<var_ vsan_b_id>>member device-alias VM-Host-Infra-02_Bmember device-alias <<var_controller1>>_1bmember device-alias <<var_controller2>>_1bexit2.
After all of the zones for the Cisco UCS service profiles have been created, create the zone set and add the necessary members.
zoneset name FlexPod vsan <<var_ vsan_b_id>>member VM-Host-Infra-01_Bmember VM-Host-Infra-02_Bexit3.
Activate the zone set.
zoneset activate name FlexPod vsan <<var_ vsan_b_id>>exitcopy run startStorage Part 2
Data ONTAP 7-Mode SAN Boot Storage Setup
The following subsections create initiator groups (igroups) on storage controller 1 and map the SAN boot LUNs to these igroups so that VMware ESXi can be installed on the LUNs for the two management hosts created.
Create Igroups
Enter the following commands to create two igroups:
Controller 1 Command Line Interface
igroup create -f -t vmware VM-Host-Infra-01 <<var_vm_host_infra_01_A_wwpn >> <<var_vm_host_infra_01_B_wwpn >>igroup create -f -t vmware VM-Host-Infra-02 <<var_vm_host_infra_02_A__wwpn >> <<var_vm_host_infra_02_B_wwpn >>
Note
To view the two igroups just created, type igroup show.
Controller 2 Command Line Interface
igroup create -f -t vmware MGMT-Hosts <<var_vm_host_infra_01_A_wwpn >> <<var_vm_host_infra_01_B_wwpn >> <<var_vm_host_infra_02_A_wwpn >> <<var_vm_host_infra_02_B_wwpn >>
Note
To view the three igroups just created, type igroup show.
Map Boot LUNs to Igroups
Enter the following commands to map the boot LUNS to igroups.
Controller 1 Command Line Interface
lun map /vol/esxi_boot/VM-Host-Infra-01 VM-Host-Infra-01 0lun map /vol/esxi_boot/VM-Host-Infra-02 VM-Host-Infra-02 0VMware vSphere 5.1 Setup
FlexPod VMware ESXi 5.1 FCoE 7-Mode
This section provides detailed instructions for installing VMware ESXi 5.1 in a FlexPod environment. After the procedures are completed, two FCP-booted ESXi hosts will be provisioned. These deployment procedures are customized to include the environment variables.
Note
Several methods exist for installing ESXi in a VMware environment. These procedures focus on how to use the built-in Keyboard, Video, Mouse (KVM) console and virtual media features in Cisco UCS Manager to map remote installation media to individual servers and connect to their Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) boot Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs).
Log in to Cisco UCS 6200 Fabric Interconnect
Cisco UCS Manager
The IP KVM enables the administrator to begin the installation of the operating system (OS) through remote media. It is necessary to log in to the UCS environment to run the IP KVM.
To log in to the Cisco UCS environment, follow these steps:
1.
Open a Web browser and enter the IP address for the Cisco UCS cluster address. This step launches the Cisco UCS Manager application.
2.
Log in to Cisco UCS Manager by using the admin user name and password.
3.
From the main menu, click the Servers tab.
4.
Choose Servers > Service Profiles > root > VM-Host-Infra-01.
5.
Right-click VM-Host-Infra-01 and choose KVM Console.
6.
Choose Servers > Service Profiles > root > VM-Host-Infra-02.
7.
Right-click VM-Host-Infra-02 and choose KVM Console Actions > KVM Console.
Set Up VMware ESXi Installation
ESXi Hosts VM-Host-Infra-01 and VM-Host-Infra-02
To prepare the server for the OS installation, follow these steps on each ESXi host:
1.
In the KVM window, click the Virtual Media tab.
2.
Click Add Image.
3.
Browse to the ESXi installer ISO image file and click Open.
4.
Check the Mapped check box to map the newly added image.
5.
Click the KVM tab to monitor the server boot.
6.
Boot the server by selecting Boot Server and click OK. Then click OK again.
Install ESXi
ESXi Hosts VM-Host-Infra-01 and VM-Host-Infra-02
To install VMware ESXi to the SAN-bootable LUN of the hosts, follow these steps on each host:
1.
On reboot, the machine detects the presence of the ESXi installation media. Choose the ESXi installer from the menu that is displayed.
2.
After the installer is finished loading, press Enter to continue with the installation.
3.
Read and accept the end-user license agreement (EULA). Press F11 to accept and continue.
4.
Choose the NetApp LUN that was previously set up as the installation disk for ESXi and press Enter to continue with the installation.
5.
Choose the appropriate keyboard layout and press Enter.
6.
Enter and confirm the root password and press Enter.
7.
The installer issues a warning that existing partitions will be removed from the volume. Press F11 to continue with the installation.
8.
After the installation is complete, uncheck the Mapped check box (located in the Virtual Media tab of the KVM console) to unmap the ESXi installation image.
Note
The ESXi installation image must be unmapped to make sure that the server reboots into ESXi and not into the installer.
9.
The Virtual Media window might issue a warning stating that it is preferable to eject the media from the guest. Because the media cannot be ejected and it is read-only, simply click Yes to unmap the image.
10.
From the KVM tab, press Enter to reboot the server.
Set Up Management Networking for ESXi Hosts
Adding a management network for each VMware host is necessary for managing the host. To add a management network for the VMware hosts, follow these steps on each ESXi host:
ESXi Host VM-Host-Infra-01
To configure the VM-Host-Infra-01 ESXi host with access to the management network, follow these steps:
1.
After the server has finished rebooting, press F2 to customize the system.
2.
Log in as root and enter the corresponding password.
3.
Choose the Configure the Management Network option and press Enter.
4.
(Optional) Choose the VLAN option and press Enter.
5.
Enter the <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>> and press Enter.
6.
From the Configure Management Network menu, choose IP Configuration and press Enter.
7.
Choose the Set Static IP Address and Network Configuration option by using the space bar.
8.
Enter the IP address for managing the first ESXi host: <<var_vm_host_infra_01_ip>>.
9.
Enter the subnet mask for the first ESXi host.
10.
Enter the default gateway for the first ESXi host.
11.
Press Enter to accept the changes to the IP configuration.
12.
Choose the IPv6 Configuration option and press Enter.
13.
Using the spacebar, deselect Enable IPv6 (restart required) and press Enter.
14.
Choose the DNS Configuration option and press Enter.
Note
Because the IP address is assigned manually, the DNS information must also be entered manually.
15.
Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server.
16.
(Optional) Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server.
17.
Enter the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the first ESXi host.
18.
Press Enter to accept the changes to the DNS configuration.
19.
Press Esc to exit the Configure Management Network submenu.
20.
Press Y to confirm the changes and return to the main menu.
21.
The ESXi host reboots. After reboot, press F2 and log back in as root.
22.
Choose Test Management Network to verify that the management network is set up correctly and press Enter.
23.
Press Enter to run the test.
24.
Press Enter to exit the window.
25.
Press Esc to log out of the VMware console.
ESXi Host VM-Host-Infra-02
To configure the VM-Host-Infra-02 ESXi host with access to the management network, follow these steps:
1.
After the server has finished rebooting, press F2 to customize the system.
2.
Log in as root and enter the corresponding password.
3.
Choose the Configure the Management Network option and press Enter.
4.
Choose the VLAN (Optional) option and press Enter.
5.
Enter the <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>> and press Enter.
6.
From the Configure Management Network menu, choose IP Configuration and press Enter.
7.
Choose the Set Static IP Address and Network Configuration option by using the space bar.
8.
Enter the IP address for managing the second ESXi host: <<var_vm_host_infra_02_ip>>.
9.
Enter the subnet mask for the second ESXi host.
10.
Enter the default gateway for the second ESXi host.
11.
Press Enter to accept the changes to the IP configuration.
12.
Choose the IPv6 Configuration option and press Enter.
13.
Using the spacebar, deselect Enable IPv6 (restart required) and press Enter.
14.
Choose the DNS Configuration option and press Enter.
Note
Because the IP address is assigned manually, the DNS information must also be entered manually.
15.
Enter the IP address of the primary DNS server.
16.
(Optional) Enter the IP address of the secondary DNS server.
17.
Enter the FQDN for the second ESXi host.
18.
Press Enter to accept the changes to the DNS configuration.
19.
Press Esc to exit the Configure Management Network submenu.
20.
Press Y to confirm the changes and return to the main menu.
21.
The ESXi host reboots. After reboot, press F2 and log back in as root.
22.
Choose Test Management Network to verify that the management network is set up correctly and press Enter.
23.
Press Enter to run the test.
24.
Press Enter to exit the window.
25.
Press Esc to log out of the VMware console.
Download VMware vSphere Client and vSphere Remote CLI
To download the VMware vSphere Client and install Remote CLI, follow these steps:
1.
Open a Web browser on the management workstation and navigate to the VM-Host-Infra-01 management IP address.
2.
Download and install both the vSphere Client and the Windows version of vSphere Remote Command Line.
Note
These applications are downloaded from the VMware Web site and Internet access is required on the management workstation.
Log in to VMware ESXi Hosts by Using VMware vSphere Client
ESXi Host VM-Host-Infra-01
To log in to the VM-Host-Infra-01 ESXi host by using the VMware vSphere Client, follow these steps:
1.
Open the recently downloaded VMware vSphere Client and enter the IP address of VM-Host-Infra-01 as the host you are trying to connect to: <<var_vm_host_infra_01_ip>>.
2.
Enter root for the user name.
3.
Enter the root password.
4.
Click Login to connect.
ESXi Host VM-Host-Infra-02
To log in to the VM-Host-Infra-02 ESXi host by using the VMware vSphere Client, follow these steps:
1.
Open the recently downloaded VMware vSphere Client and enter the IP address of VM-Host-Infra-02 as the host you are trying to connect to: <<var_vm_host_infra_02_ip>>.
2.
Enter root for the user name.
3.
Enter the root password.
4.
Click Login to connect.
Download Updated Cisco VIC enic and fnic Drivers
To download the Cisco virtual interface card (VIC) enic and fnic drivers, follow these steps:
Note
The enic version used in this configuration is 2.1.2.38, and the fnic version is 1.5.0.20.
1.
Open a Web browser on the management workstation and navigate to http://software.cisco.com/download/release.html?mdfid=283853163&softwareid=283853158&release=2.0(5)&relind=AVAILABLE&rellifecycle=&reltype=latest
Login and choose the driver ISO for version 2.1(1a). Download the ISO file. Once the ISO file is downloaded, either burn the ISO to a CD or map the ISO to a drive letter. Extract the following files from within the VMware directory for ESXi 5.1:
–
Network - net-enic-2.1.2.38-1OEM.500.0.0.472560.x86_64.zip
–
Storage - scsi-fnic-1.5.0.20-1OEM.500.0.0.472560.x86_64.zip
2.
Document the saved location.
Load Updated Cisco VIC enic and fnic Drivers
ESXi Hosts VM-Host-Infra-01 and VM-Host-Infra-02
To load the updated versions of the enic and fnic drivers for the Cisco VIC, follow these steps for the hosts on each vSphere Client:
1.
From each vSphere Client, choose the host in the inventory.
2.
Click the Summary tab to view the environment summary.
3.
From Resources > Storage, right-click datastore1 and choose Browse Datastore.
4.
Click the fourth button and choose Upload File.
5.
Navigate to the saved location for the downloaded enic driver version and choose net-enic-2.1.2.38-1OEM.500.0.0.472560.x86_64.zip.
6.
Click Open to open the file.
7.
Click Yes to upload the .zip file to datastore1.
8.
Click the fourth button and choose Upload File.
9.
Navigate to the saved location for the downloaded fnic driver version and choose scsi-fnic-1.5.0.20-1OEM.500.0.0.472560.x86_64.zip.
10.
Click Open to open the file.
11.
Click Yes to upload the .zip file to datastore1.
12.
From the management workstation, open the VMware vSphere Remote CLI that was previously installed.
13.
At the command prompt, run the following commands to account for each host (enic):
esxcli -s <<var_vm_host_infra_01_ip>> -u root -p <<var_password>> software vib install --no-sig-check -d /vmfs/volumes/datastore1/net-enic-2.1.2.38-1OEM.500.0.0.472560.x86_64.zipesxcli -s <<var_vm_host_infra_02_ip>> -u root -p <<var_password>> software vib install --no-sig-check -d /vmfs/volumes/datastore1/net-enic-2.1.2.38-1OEM.500.0.0.472560.x86_64.zip14.
At the command prompt, run the following commands to account for each host (fnic):
esxcli -s <<var_vm_host_infra_01_ip>> -u root -p <<var_password>> software vib install --no-sig-check -d /vmfs/volumes/datastore1/scsi-fnic-1.5.0.20-1OEM.500.0.0.472560.x86_64.zipesxcli -s <<var_vm_host_infra_02_ip>> -u root -p <<var_password>> software vib install --no-sig-check -d /vmfs/volumes/datastore1/scsi-fnic-1.5.0.20-1OEM.500.0.0.472560.x86_64.zip15.
From the vSphere Client, right-click each host in the inventory and choose Reboot.
16.
Choose Yes to continue.
17.
Enter a reason for the reboot and click OK.
18.
After the reboot is complete, log back in to both hosts using the vSphere Client.
Set Up VMkernel Ports and Virtual Switch
ESXi Host VM-Host-Infra-01
To set up the VMkernel ports and the virtual switches on the VM-Host-Infra-01 ESXi host, follow these steps:
1.
From each vSphere Client, choose the host in the inventory.
2.
Click the Configuration tab.
3.
Click Networking in the Hardware pane.
4.
Click Properties on the right side of vSwitch0.
5.
Choose the vSwitch configuration and click Edit.
6.
From the General tab, change the MTU to 9000.
7.
Click OK to close the properties for vSwitch0.
8.
Choose the Management Network configuration and click Edit.
9.
Change the network label to VMkernel-MGMT and check the Management Traffic check box.
10.
Click OK to finalize the edits for Management Network.
11.
Choose the VM Network configuration and click Edit.
12.
Change the network label to IB-MGMT Network and enter <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>> in the VLAN ID (Optional) field.
13.
Click OK to finalize the edits for VM Network.
14.
Click Add to add a network element.
15.
Choose VMkernel and click Next.
16.
Change the network label to VMkernel-NFS and enter <<var_nfs_vlan_id>> in the VLAN ID (Optional) field.
17.
Click Next to continue with the NFS VMkernel creation.
18.
Enter the IP address <<var_nfs_vlan_id_ip_host-01>> and the subnet mask <<var_nfs_vlan_id_mask_host01>> for the NFS VLAN interface for VM-Host-Infra-01.
19.
Click Next to continue with the NFS VMkernel creation.
20.
Click Finish to finalize the creation of the NFS VMkernel interface.
21.
Choose the VMkernel-NFS configuration and click Edit.
22.
Change the MTU to 9000.
23.
Click OK to finalize the edits for the VMkernel-NFS network.
24.
Click Add to add a network element.
25.
Choose VMkernel and click Next.
26.
Change the network label to VMkernel-vMotion and enter <<var_vmotion_vlan_id>> in the VLAN ID (Optional) field.
27.
Check the Use This Port Group for vMotion check box.
28.
Click Next to continue with the vMotion VMkernel creation.
29.
Enter the IP address <<var_vmotion_vlan_id_ip_host-01>> and the subnet mask <<var_vmotion_vlan_id_mask_host-01>> for the vMotion VLAN interface for VM-Host-Infra-01.
30.
Click Next to continue with the vMotion VMkernel creation.
31.
Click Finish to finalize the creation of the vMotion VMkernel interface.
32.
Choose the VMkernel-vMotion configuration and click Edit.
33.
Change the MTU to 9000.
34.
Click OK to finalize the edits for the VMkernel-vMotion network.
35.
Close the dialog box to finalize the ESXi host networking setup. The networking for the ESXi host should be similar to Figure 58.
Figure 58 vSphere Client Showing VMKernel Ports and Virtual Switch
ESXi Host VM-Host-Infra-02
To set up the VMkernel ports and the virtual switches on the VM-Host-Infra-02 ESXi host, follow these steps:
1.
From each vSphere Client, choose the host in the inventory.
2.
Click the Configuration tab.
3.
Click Networking in the Hardware pane.
4.
Click Properties on the right side of vSwitch0.
5.
Choose the vSwitch configuration and click Edit.
6.
From the General tab, change the MTU to 9000.
7.
Click OK to close the properties for vSwitch0.
8.
Choose the Management Network configuration and click Edit.
9.
Change the network label to VMkernel-MGMT and check the Management Traffic check box.
10.
Click OK to finalize the edits for Management Network.
11.
Choose the VM Network configuration and click Edit.
12.
Change the network label to IB-MGMT Network and enter <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>> in the VLAN ID (Optional) field.
13.
Click OK to finalize the edits for VM Network.
14.
Click Add to add a network element.
15.
Choose VMkernel and click Next.
16.
Change the network label to VMkernel-NFS and enter <<var_nfs_vlan_id>> in the VLAN ID (Optional) field.
17.
Click Next to continue with the NFS VMkernel creation.
18.
Enter the IP address <<var_nfs_vlan_id_ip_host-02>> and the subnet mask <<var_nfs_vlan_id_mask_host02>> for the NFS VLAN interface for VM-Host-Infra-02.
19.
Click Next to continue with the NFS VMkernel creation.
20.
Click Finish to finalize the creation of the NFS VMkernel interface.
21.
Choose the VMkernel-NFS configuration and click Edit.
22.
Change the MTU to 9000.
23.
Click OK to finalize the edits for the VMkernel-NFS network.
24.
Click Add to add a network element.
25.
Choose VMkernel and click Next.
26.
Change the network label to VMkernel-vMotion and enter <<var_vmotion_vlan_id>> in the VLAN ID (Optional) field.
27.
Check the Use This Port Group for vMotion check box.
28.
Click Next to continue with the vMotion VMkernel creation.
29.
Enter the IP address <<var_vmotion_vlan_id_ip_host-02>> and the subnet mask <<var_vmotion_vlan_id_mask_host-02>> for the vMotion VLAN interface for VM-Host-Infra-02.
30.
Click Next to continue with the vMotion VMkernel creation.
31.
Click Finish to finalize the creation of the vMotion VMkernel interface.
32.
Choose the VMkernel-vMotion configuration and click Edit.
33.
Change the MTU to 9000.
34.
Click OK to finalize the edits for the VMkernel-vMotion network.
35.
Close the dialog box to finalize the ESXi host networking setup. The networking for the ESXi host should be similar to Figure 59.
Figure 59 vSphere Client Showing VMKernel Ports and Virtual Switch
Mount Required Datastores
ESXi Hosts VM-Host-Infra-01 and VM-Host-Infra-02
To mount the required datastores, follow these steps on each ESXi host:
1.
From each vSphere Client, choose the host in the inventory.
2.
Click the Configuration tab to enable configurations.
3.
Click Storage in the Hardware pane.
4.
From the Datastore area, click Add Storage to open the Add Storage wizard.
5.
Choose Network File System and click Next.
6.
The wizard prompts for the location of the NFS export. Enter <<var_controller2_nfs_ip>> as the IP address for NFSIP Address for Controller 2.
7.
Enter /vol/infra_datastore_1 as the path for the NFS export.
8.
Make sure that the Mount NFS read only check box is unchecked.
9.
Enter infra_datastore_1 as the datastore name.
10.
Click Next to continue with the NFS datastore creation.
11.
Click Finish to finalize the creation of the NFS datastore.
12.
From the Datastore area, click Add Storage to open the Add Storage wizard.
13.
Choose Network File System and click Next.
14.
The wizard prompts for the location of the NFS export. Enter <<var_controller1_nfs_ip>> as the IP address for NFSIP Address for Controller 1.
15.
Enter /vol/infra_swap as the path for the NFS export.
16.
Make sure that the Mount NFS read only check box is unchecked.
17.
Enter infra_swap as the datastore name.
18.
Click Next to continue with the NFS datastore creation.
19.
Click Finish to finalize the creation of the NFS datastore.
Configure NTP on ESXi Hosts
ESXi Hosts VM-Host-Infra-01 and VM-Host-Infra-02
To configure Network Time Protocol (NTP) on the ESXi hosts, follow these steps on each host:
1.
From each vSphere Client, choose the host in the inventory.
2.
Click the Configuration tab to enable configurations.
3.
Click Time Configuration in the Software pane.
4.
Click Properties at the upper right side of the window.
5.
At the bottom of the Time Configuration dialog box, click Options.
6.
In the NTP Daemon Options dialog box, follow these steps:
a.
Click General in the left pane and choose Start and stop with host.
b.
Click NTP Settings in the left pane and click Add.
7.
In the Add NTP Server dialog box, enter <<var_global_ntp_server_ip>> as the IP address of the NTP server and click OK.
8.
In the NTP Daemon Options dialog box, check the Restart NTP Service to Apply Changes check box and click OK.
9.
In the Time Configuration dialog box, follow these steps:
a.
Check the NTP Client Enabled check box and click OK.
b.
Verify that the clock is now set to approximately the correct time.
Note
The NTP server time may vary slightly from the host time.
Move VM Swap File Location
ESXi Hosts VM-Host-Infra-01 and VM-Host-Infra-02
To move the VM swap file location, follow these steps on each ESXi host:
1.
From each vSphere Client, choose the host in the inventory.
2.
Click the Configuration tab to enable configurations.
3.
Click Virtual Machine Swapfile Location in the Software pane.
4.
Click Edit at the upper right side of the window.
5.
Choose Store the swapfile in a swapfile datastore selected below.
6.
Select infra_swap as the datastore in which to house the swap files.
7.
Click OK to finalize moving the swap file location.
FlexPod VMware vCenter 5.1
The procedures in the following subsections provide detailed instructions for installing VMware vCenter 5.1 in a FlexPod environment. After the procedures are completed, a VMware vCenter Server will be configured along with a Microsoft SQL Server database to provide database support to vCenter. These deployment procedures are customized to include the environment variables.
Note
This procedure focuses on the installation and configuration of an external Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 database, but other types of external databases are also supported by vCenter. For information about how to configure the database and integrate it into vCenter, see the VMware vSphere5.1 documentation at: http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs/vsphere-esxi-vcenter-server-pubs.html
To install VMware vCenter 5.1, an accessible Windows Active Directory® (AD) Domain is necessary. If an existing AD Domain is not available, an AD virtual machine, or AD pair, can be set up in this FlexPod environment. See "Appendix" section for this setup.
Build Microsoft SQL Server VM
ESXi Host VM-Host-Infra-01
To build a SQL Server virtual machine (VM) for the VM-Host-Infra-01 ESXi host, follow these steps:
1.
Log in to the host by using the VMware vSphere Client.
2.
In the vSphere Client, choose the host in the inventory pane.
3.
Right-click the host and choose New Virtual Machine.
4.
Click Custom and then click Next.
5.
Enter a name for the VM. Click Next.
6.
Choose infra_datastore_1. Click Next.
7.
Choose Virtual Machine Version: 8. Click Next.
8.
Verify that the Windows option and the Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 (64-bit) version are selected. Click Next.
9.
Choose two virtual sockets and one core per virtual socket. Click Next.
10.
Choose 4GB of memory. Click Next.
11.
Choose one network interface card (NIC).
12.
For NIC 1, choose the IB-MGMT Network option and the VMXNET 3 adapter. Click Next.
13.
Keep the LSI Logic SAS option for the SCSI controller selected. Click Next.
14.
Keep the Create a New Virtual Disk option selected. Click Next.
15.
Make the disk size at least 60GB. Click Next.
16.
Click Next.
17.
Check the Edit the Virtual Machine Settings Before Completion check box. Click Continue.
18.
Choose the Options tab.
19.
Choose Boot Options.
20.
Check the Force BIOS Setup check box.
21.
Click Finish.
22.
From the left pane, expand the host field by clicking the plus sign (+).
23.
Right-click the newly created SQL Server VM and click Open Console.
24.
Click the third button (green right arrow) to power on the VM.
25.
Click the ninth button (CD with a wrench) to map the Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 ISO, and then choose Connect to ISO Image on Local Disk.
26.
Navigate to the Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 ISO, select it, and click Open.
27.
In the BIOS Setup Utility window and use the right arrow key to navigate to the Boot menu. Use the down arrow key to select CD-ROM Drive. Press the plus (+) key twice to move CD-ROM Drive to the top of the list. Press F10 and Enter to save the selection and exit the BIOS Setup Utility.
28.
The Windows Installer boots. Choose the appropriate language, time and currency format, and keyboard. Click Next.
29.
Click Install Now.
30.
Make sure that the Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard (Full Installation) option is selected. Click Next.
31.
Read and accept the license terms and click Next.
32.
Choose Custom (Advanced). Make sure that Disk 0 Unallocated Space is selected. Click Next to allow the Windows installation to complete.
33.
After the Windows installation is complete and the VM has rebooted, click OK to set the Administrator password.
34.
Enter and confirm the Administrator password and choose the blue arrow to log in. Click OK to confirm the password change.
35.
After logging in to the VM desktop, from the VM console window, choose the VM menu. Under Guest, choose Install/Upgrade VMware Tools. Click OK.
36.
If prompted to eject the Windows installation media before running the setup for the VMware tools, click OK, then click OK.
37.
In the dialog box, choose Run setup64.exe.
38.
In the VMware Tools installer window, click Next.
39.
Make sure that Typical is selected and click Next.
40.
Click Install.
41.
Click Finish.
42.
Click Yes to restart the VM.
43.
After the reboot is complete, choose the VM menu. Under Guest, choose Send Ctrl+Alt+Del and then enter the password to log in to the VM.
44.
Set the time zone for the VM, IP address, gateway, and host name. Add the VM to the Windows AD domain.
Note
A reboot is required.
45.
If necessary, activate Windows.
46.
Log back in to the VM and download and install all required Windows updates.
Note
This process requires several reboots.
Install Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2
vCenter SQL Server VM
To install SQL Server on the vCenter SQL Server VM, follow these steps:
1.
Connect to an AD Domain Controller in the FlexPod Windows Domain and add an admin user for the FlexPod using the Active Directory Users and Computers tool. This user should be a member of the Domain Administrators security group.
2.
Log in to the vCenter SQL Server VM as the FlexPod admin user and open Server Manager.
3.
Expand Features and click Add Features.
4.
Expand .NET Framework 3.5.1 Features and choose only .NET Framework 3.5.1.
Figure 60 Adding Features for Installing SQL Server
5.
Click Next.
6.
Click Install.
7.
Click Close.
8.
Open Windows Firewall with Advanced Security by navigating to Start > Administrative Tools > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
9.
Choose Inbound Rules and click New Rule.
10.
Choose Port and click Next.
11.
Choose TCP and enter the specific local port 1433. Click Next.
12.
Choose Allow the Connection. Click Next, and then click Next again.
13.
Name the rule SQL Server and click Finish.
14.
Close Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
15.
In the vCenter SQL Server VMware console, click the ninth button (CD with a wrench) to map the Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 ISO. Choose Connect to ISO Image on Local Disk.
16.
Navigate to the SQL Server 2008 R2 ISO, select it, and click Open.
17.
In the dialog box, click Run setup.exe.
18.
In the SQL Server Installation Center window, click Installation on the left.
19.
Choose New Installation or Add Features to an Existing Installation.
20.
Click OK.
21.
Choose Enter the Product Key. Enter a product key and click Next.
22.
Read and accept the license terms and choose whether to check the second check box. Click Next.
23.
Click Install to install the setup support files.
24.
Address any warnings except for the Windows firewall warning. Click Next.
Note
The Windows firewall issue was addressed in Step 13.
25.
Choose SQL Server Feature Installation and click Next.
26.
Under Instance Features, choose only Database Engine Services.
27.
Under Shared Features, choose Management Tools > Basic and Management Tools > Complete. Click Next.
Figure 61 Selecting SQL Server Features
28.
Click Next.
29.
Keep Default Instance selected. Click Next.
Figure 62 SQL Server Instance Configuration
30.
Click Next for Disk Space Requirements.
31.
For the SQL Server Agent service, click in the first cell in the Account Name column and then click <<Browse...>>.
32.
Enter the local machine administrator name (for example, systemname\Administrator), click Check Names, and click OK.
33.
Enter the administrator password in the first cell under Password.
34.
Change the startup type for SQL Server Agent to Automatic.
35.
For the SQL Server Database Engine service, choose Administrator in the Account Name column and enter the administrator password again. Click Next.
Figure 63 Configuring SQL Server
36.
Choose Mixed Mode (SQL Server Authentication and Windows Authentication). Enter and confirm the password for the SQL Server system administrator (sa) account, click Add Current User, and Click Next.
Figure 64 Configuring Database Engine
37.
Choose whether to send error reports to Microsoft. Click Next.
38.
Click Next.
39.
Click Install.
40.
After the installation is complete, click Close to close the SQL Server installer.
41.
Close the SQL Server Installation Center.
42.
Install all available Microsoft Windows updates by navigating to Start > All Programs > Windows Update.
43.
Choose Start > All Programs > Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 > SQL Server Management Studio to open the SQL Server Management Studio.
44.
Under Server Name, choose the local machine name. Under Authentication, choose SQL Server Authentication. Enter sa in the Login field and enter the sa password. Click Connect.
45.
Click New Query.
46.
Run the following script, substituting the vpxuser password for <Password>:
use [master]goCREATE DATABASE [VCDB] ON PRIMARY(NAME = N'vcdb', FILENAME = N'C:\VCDB.mdf', SIZE = 2000KB, FILEGROWTH = 10% )LOG ON(NAME = N'vcdb_log', FILENAME = N'C:\VCDB.ldf', SIZE = 1000KB, FILEGROWTH = 10%)COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_ASgouse VCDBgosp_addlogin @loginame=[vpxuser], @passwd=N'<Password>', @defdb='VCDB',@deflanguage='us_english'goALTER LOGIN [vpxuser] WITH CHECK_POLICY = OFFgoCREATE USER [vpxuser] for LOGIN [vpxuser]gouse MSDBgoCREATE USER [vpxuser] for LOGIN [vpxuser]gouse VCDBgosp_addrolemember @rolename = 'db_owner', @membername = 'vpxuser'gouse MSDBgosp_addrolemember @rolename = 'db_owner', @membername = 'vpxuser'go
Note
Figure 65 illustrates the script.
Figure 65 Executing the Query
47.
Click Execute and verify that the query executes successfully.
48.
Close Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio.
49.
Disconnect the Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 ISO from the SQL Server VM.
Build and Set Up VMware vCenter VM
Build VMware vCenter VM
To build the VMware vCenter VM, follow these steps:
1.
Using the instructions for building a SQL Server VM provided in the section "Build Microsoft SQL Server VM," build a VMware vCenter VM with the following configuration in the <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>> VLAN:
–
4GB RAM
–
Two CPUs
–
One virtual network interface
2.
Start the VM, install VMware Tools, and assign an IP address and host name to it in the Active Directory domain.
Set Up VMware vCenter VM
To set up the newly built VMware vCenter VM, follow these steps:
1.
Log in to the vCenter VM as the FlexPod admin user and open Server Manager.
2.
Expand Features and click Add Features.
3.
Expand .NET Framework 3.5.1 Features and choose only .NET Framework 3.5.1.
4.
Click Next.
5.
Click Install.
6.
Click Close to close the Add Features wizard.
7.
Close Server Manager.
8.
Download and install the client components of the Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 Native Client from the Microsoft Download Center.
9.
Create the vCenter database data source name (DSN). Choose Start > Administrative Tools > Data Sources (ODBC) to open Data Sources (ODBC).
10.
Choose the System DSN tab.
11.
Click Add.
12.
Choose SQL Server Native Client 10.0 and click Finish.
13.
Name the data source VCDB. In the Server field, enter the IP address of the vCenter SQL server. Click Next.
Figure 66 Creating New Data Source
14.
Choose With SQL Server authentication using a login ID and password entered by the user. Enter vpxuser as the login ID and the vpxuser password. Click Next.
Figure 67 Login Credentials for SQL Server
15.
Choose Change the Default Database To and choose VCDB from the list. Click Next.
Figure 68 Setting Up the Database
16.
Click Finish.
17.
Click Test Data Source. Verify that the test completes successfully.
Figure 69 Verifying ODBC Data Source
18.
Click OK and then click OK again.
19.
Click OK to close the ODBC Data Source Administrator window.
20.
Install all available Microsoft Windows updates by navigating to Start > All Programs > Windows Update.
Note
A restart might be required.
Install VMware vCenter Server
vCenter Server VM
To install vCenter Server on the vCenter Server VM, follow these steps:
1.
In the vCenter Server VMware console, click the ninth button (CD with a wrench) to map the VMware vCenter ISO and choose Connect to ISO Image on Local Disk.
2.
Navigate to the VMware vCenter 5.1 (VIMSetup) ISO, select it, and click Open.
3.
In the dialog box, click Run autorun.exe.
4.
In the VMware vCenter Installer window, make sure that VMware vCenter Simple Install is selected and click Install.
Figure 70 Installing VMware vSphere
5.
Click Yes at the User Account Control warning.
6.
Click Next to install vCenter Single Sign On.
7.
Click Next.
8.
Accept the terms of the license agreement and click Next.
9.
Enter and confirm <<var_password>> for admin@System-Domain. Click Next.
10.
Keep the radio button checked to install a local Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 Express instance and click Next.
11.
Enter and confirm <<var_password>> for both user names. Click Next.
12.
Verify the vCenter VM FQDN and click Next.
13.
Leave Use network service account selected and click Next.
14.
Click Next to select the default destination folder.
15.
Click Next to select the default HTTPS port.
16.
Click Install to install vCenter Single Sign On.
17.
Click Yes at the User Account Control warning.
18.
Click Yes at the User Account Control warning.
19.
Enter the vCenter 5.1 license key and click Next.
20.
Choose Use an Existing Supported Database. Choose VCDB from the Data Source Name list and click Next.
Figure 71 Selecting Database for VMware vSphere
21.
Enter the vpxuser password and click Next.
Figure 72 Entering Database Login Credentials
22.
Review the warning and click OK.
23.
Click Next to use the SYSTEM Account.
24.
Click Next to accept the default ports.
25.
Choose the appropriate inventory size. Click Next.
26.
Click Install.
27.
Click Finish.
28.
Click OK to confirm the installation.
29.
Click Exit in the VMware vCenter Installer window.
30.
Disconnect the VMware vCenter ISO from the vCenter VM.
31.
Install all available Microsoft Windows updates by navigating to Start > All Programs > Windows Updates.
Note
A restart might be required.
Set Up vCenter Server
vCenter Server VM
To set up vCenter Server on the vCenter Server VM, follow these steps:
1.
Using the vSphere Client, log in to the newly created vCenter Server as the FlexPod admin user.
2.
Click Create a data center.
3.
Enter FlexPod_DC_1 as the data center name.
4.
Right-click the newly created FlexPod_DC_1 data center and choose New Cluster.
5.
Name the cluster FlexPod_Management and click the check boxes for Turn On vSphere HA and Turn on vSphere DRS. Click Next.
Figure 73 Selecting Cluster Features
6.
Accept the defaults for vSphere DRS. Click Next.
7.
Accept the defaults for Power Management. Click Next.
8.
Accept the defaults for vSphere HA. Click Next.
9.
Accept the defaults for Virtual Machine Options. Click Next.
10.
Accept the defaults for VM Monitoring. Click Next.
11.
Accept the defaults for VMware EVC. Click Next.
Note
If mixing UCS B or C-Series M2 and M3 servers within a vCenter cluster, it is necessary to enable VMware Enhanced vMotion Compatibility (EVC) mode. For more information about setting up EVC mode, see Enhanced vMotion Compatibility (EVC) Processor Support at: http://kb.vmware.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?language=en_US&cmd=displayKC&externalId=1003212
12.
Choose Store the swapfile in the datastore specified by the host. Click Next.
13.
Click Finish.
14.
Right-click the newly created FlexPod_Management cluster and choose Add Host.
15.
In the Host field, enter either the IP address or the host name of the VM-Host-Infra_01 host. Enter root as the user name and the root password for this host. Click Next.
16.
Click Yes.
17.
Click Next.
18.
Choose Assign a New License Key to the Host. Click Enter Key and enter a vSphere license key. Click OK, and then click Next.
19.
Click Next.
20.
Click Next.
21.
Click Finish. VM-Host-Infra-01 is added to the cluster.
22.
Repeat this procedure to add VM-Host-Infra-02 to the cluster.
FlexPod Cisco Nexus 1110-X and 1000V vSphere
The following sections provide detailed procedures for installing a pair of high-availability (HA) Cisco Nexus 1110-X Virtual Services Appliances (VSAs) in a FlexPod configuration. Primary and standby Cisco Nexus 1000V Virtual Supervisor Modules (VSMs) are installed on the 1110-Xs. By the end of this section, a Cisco Nexus 1000V distributed virtual switch (DVS) will be provisioned. This procedure assumes that the Cisco Nexus 1000V software version 4.2(1)SV2(1.1a) has been downloaded from www.cisco.com and expanded. This procedure also assumes that VMware vSphere 5.1 Enterprise Plus licensing is installed.
Configure CIMC Interface on Both Cisco Nexus 1110-Xs
Cisco Nexus 1110-X A and Cisco Nexus 1110-X B
To configure the Cisco Integrated Management Controller (CIMC) interface on the Cisco Nexus 1110-X VSAs, follow these steps:
1.
Using the supplied dongle, connect a monitor and USB keyboard to the KVM console port on the front of the Cisco Nexus 1110-X virtual appliance.
2.
Reboot the virtual appliance.
3.
Press F8 when prompted to configure the CIMC interface.
4.
Using the spacebar, set the NIC mode to Dedicated.
5.
Clear the check box for DHCP enabled.
6.
Set the CIMC IP address (<<var_cimc_ip>>) in the out-of -band management VLAN.
7.
Set the CIMC subnet mask (<<var_cimc_mask>>).
8.
Set the CIMC gateway (<<var_cimc_gateway>>).
9.
Set the NIC redundancy to None.
10.
Set and reenter the CIMC default password (<<var_password>>).
11.
Press F10 to save the configuration.
12.
Continue pressing F5 until Network settings configured is shown.
13.
Press Esc to reboot the virtual appliance.
Configure Serial over LAN for Both Cisco Nexus 1110-Xs
Cisco Nexus 1110-X A and Cisco Nexus 1110-X B
To configure serial over LAN on the Cisco Nexus 1110-X VSAs, follow these steps:
1.
Use a Web browser to open the URL at http://<<var_cimc_ip>>.
2.
Log in to the CIMC with the admin user id and the CIMC default password (<<var_password>>).
3.
In the left column, click Remote Presence.
4.
Click the Serial over LAN tab.
5.
Check the Enabled check box for Serial over LAN Properties.
6.
From the Baud Rate drop-down menu, choose 9600 bps.
7.
Click Save Changes.
Figure 74 Configuring Serial Over LAN on Cisco Nexus 1110-Xs
8.
Log out of the CIMC Web interface.
9.
Use an SSH client to connect to <<var_cimc_ip>> with the default CIMC user name and password.
10.
Run connect host.
Figure 75 Execute Command for Connecting the Host
Configure Cisco Nexus 1110-X Virtual Appliances
Cisco Nexus 1110-X A
To configure Cisco Nexus 1110-X A, follow these steps:
1.
Reboot the virtual appliance. The appliance should boot into a setup mode.
Enter the password for "admin": <<var_password>>Confirm the password for "admin": <<var_password>>Enter HA role[primary/secondary]: primaryEnter network-uplink type <1-5>: 1Enter control VLAN <1-3967, 4048-4093>: <<var_pkt-ctrl_vlan_id>>Enter the domain<1-4095>: <<var_1110x_domain_id>>Enter management vlan <1-3967, 4048-4093>: <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>Would you like to enter the basic system configuration dialogue (yes/no): yesCreate another login account (yes/no) [n]: EnterConfigure read-only SNMP community string (yes/no)[n]: EnterConfigure read-write SNMP community string (yes/no)[n]: EnterEnter the VSA name : <<var_1110x_vsa>>Continue with Out-of-band (mgmt0) management configuration? (yes/no) [y]: EnterMgmt0 IP address type V4/V6? (V4): EnterMgmt0 IPv4 address : <<var_1110x_vsa_ip>>Mgmt0 IPv4 netmask : <<var_1110x_vsa_mask>>Configure the default gateway? (yes/no) [y]: EnterIPv4 address of the default gateway : <<var_1110x_vsa_gateway>>Configure advanced IP options? (yes/no) [n]: EnterEnable the telnet service? (yes/no) [n]: EnterEnable the ssh service? (yes/no) [y]: EnterType of ssh key you would like to generate (das/rsa) [rsa]: EnterNumber of rsa key bits <768-2048> [1024]: EnterEnable the http server? (yes/no) [y]: EnterConfigure the ntp server? (yes/no) [n]: yNTP server IPv4 address: <<var_global_ntp_server_ip>>2.
Review the configuration summary. If everything is correct, enter no to skip editing the configuration.
Would you like to edit the configuration? (yes/no) [n]: EnterUse this configuration and save it? (yes/no) [y]: Enter3.
The Cisco Nexus 1110-X saves the configuration and reboots. After reboot, log back in as admin.
Cisco Nexus 1110-X B
To configure the Cisco Nexus 1110-X B, follow these steps:
1.
Reboot the virtual appliance. The appliance should boot into a setup mode.
Enter the password for "admin": <<var_password>>
Note
This is the same password that you entered on the primary Cisco Nexus 1110-X.
2.
Enter the admin password again to confirm: <<var_password>>.
Enter HA role[primary/secondary]: secondaryEnter network-uplink type <1-5>: 1Enter control vlan <1-3967, 4048-4093>: <<var_pkt-ctrl_vlan_id>>Enter the domain id<1-4095>: <<var_1110x_domain_id>>
Note
This is the same unique Cisco Nexus 1110 domain ID entered on Cisco Nexus 1110-X A.
Enter management vlan <1-3967, 4048-4093>: <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>3.
The Cisco Nexus 1110-X saves the configuration and reboots.
Set Up the Primary Cisco Nexus 1000V VSM
Cisco Nexus 1110-X A
To set up the primary Cisco Nexus 1000V VSM on the Cisco Nexus 1110-X A, follow these steps:
1.
Continue periodically running the following command until module 2 (Cisco Nexus 1110-X B) has a status of ha-standby.
show module2.
Enter the global configuration mode and create a virtual service blade.
config tvirtual-service-blade VSM-1dir /repository3.
If the desired Cisco Nexus 1000V ISO file (nexus-1000v.4.2.1.SV2.1.1a.iso) is not present on the Cisco Nexus 1110-X, run the copy command to copy it to the Cisco Nexus 1110-X disk. You must place the file either on an FTP server or on a UNIX® or Linux® machine (using scp) that is accessible from the Cisco Nexus 1110-X management interface. An example copy command from an FTP server is copy ftp://<<var_ftp_server>>/nexus-1000v.4.2.1.SV2.1.1a.iso /repository/.
virtual-service-blade-type new nexus-1000v.4.2.1.SV2.1.1a.isointerface control vlan <<var_pkt-ctrl_vlan_id>>interface packet vlan <<var_pkt-ctrl_vlan_id>>enable primaryEnter vsb image:[nexus-1000v.4.2.1.SV2.1.1a.iso] EnterEnter domain id[1-4095]: <<var_vsm_domain_id>>
Note
This domain ID should be different than the VSA domain ID.
Enter SVS Control mode (L2 / L3): [L3] EnterManagement IP version [V4/V6]: [V4] EnterEnter Management IP address: <<var_vsm_mgmt_ip>>Enter Management subnet mask: <<var_vsm_mgmt_mask>>IPv4 address of the default gateway: <<var_vsm_mgmt_gateway>>Enter HostName: <<var_vsm_hostname>>Enter the password for 'admin': <<var_password>>copy run start4.
Run show virtual-service-blade summary. Continue periodically entering this command until the primary VSM-1 has a state of VSB POWERED ON.
Set Up the Secondary Cisco Nexus 1000V VSM
To set up the secondary Cisco Nexus 1000V VSM on Cisco Nexus 1110-X B, follow these steps in two subsections:
Cisco Nexus 1110-X A
Run system switchover to activate Cisco Nexus 1110-X B.
Cisco Nexus 1110-X B
1.
Log in to Cisco Nexus 1110-X B as the admin user.
config tvirtual-service-blade VSM-1dir /repository2.
If the desired Cisco Nexus 1000V ISO file (nexus-1000v.4.2.1.SV2.1.1a.iso) is not present on the Cisco Nexus 1110-X, run the copy command to copy it to the Cisco Nexus 1110-X disk. You must place the file either on an FTP server or on a UNIX or Linux machine (using the scp command) that is accessible from the Cisco Nexus 1110-X management interface. An example copy command from an FTP server is copy ftp:// <<var_ftp_server>>/nexus-1000v.4.2.1.SV2.1.1a.iso /repository/.
enable secondaryEnter vsb image: [nexus-1000v.4.2.1.SV2.1.1a.iso] EnterEnter domain id[1-4095]: <<var_vsm_domain_id>>Enter SVS Control mode (L2 / L3): [L3] EnterManagement IP version [V4/V6]: [V4] EnterEnter Management IP address: <<var_vsm_ mgmt_ip>>Enter Management subnet mask: <<var_vsm_ mgmt_mask>>IPv4 address of the default gateway: <<var_vsm_mgmt_gateway>>Enter HostName: <<var_vsm_hostname>>3.
Enter the admin password <<var_password>>.
4.
Type show virtual-service-blade summary. Continue periodically entering this command until both the primary and secondary VSM-1s have a state of VSB POWERED ON.
copy run start5.
Run system switchover on Cisco Nexus 1110-X B to activate Cisco Nexus 1110-X A. This causes Cisco Nexus 1110-X B to reboot.
Install Virtual Ethernet Module on Each ESXi Host
vCenter Server VM
To install the Virtual Ethernet Module (VEM) on the ESXi hosts, follow these steps:
1.
Launch a Web browser to http://<<var_vsm_mgmt_ip>>.
2.
Right-click the cross_cisco-vem-v152-4.2.1.2.1.1a.0-3.1.1.vib hyperlink and choose Save target as.
3.
Save the file as cross_cisco-vem-v152-4.2.1.2.1.1a.0-3.1.1.vib, type All Files, on the Desktop of the management workstation.
4.
From the main window in the vSphere Client connected to vCenter, choose the first server in the list under the FlexPod Management cluster.
5.
Click the Summary tab.
6.
Under Storage on the right, right-click infra_datastore_1 and choose Browse Datastore.
7.
Choose the root folder (/) and click the third button at the top to add a folder.
8.
Name the folder VEM and click OK.
9.
On the left, choose the VEM folder.
10.
Click the fourth button at the top and choose Upload File.
11.
Navigate to the cross_cisco-vem-v152-4.2.1.2.1.1a.0-3.1.1.vib file and click Open.
12.
Click Yes. The VEM file should now appear in the VEM folder in the datastore.
13.
Open the VMware vSphere CLI command prompt.
14.
For each ESXi host in the VMware vSphere CLI, run the following command:
esxcli -s <Host Server IP> -u root -p <Root Password> software vib install -v /vmfs/volumes/infra_datastore_1/VEM/cross_cisco-vem-v152-4.2.1.2.1.1a.0-3.1.1.vibFigure 76 Executing Command for Each ESXi Hosts
Register Cisco Nexus 1000V as a vCenter Plug-in
To register the Cisco Nexus 1000V as a vCenter plug-in, follow these steps:
1.
Using a Web browser, navigate to the <<var_vsm_mgmt_ip>> using http://<<var_vsm_mgmt_ip>>.
2.
Right-click the cisco_nexus_1000v_extension.xml hyperlink and choose Save target as.
3.
Save the XML file to the local desktop.
4.
In the vSphere Client connected to vCenter, choose Plug-ins > Manage Plug-ins.
5.
Right-click the white space in the window and choose New Plug-in.
6.
Browse to the desktop and choose the cisco_nexus_1000v_extension.xml document that was previously saved. Click Open.
7.
Click Register Plug-in.
8.
Click Ignore.
9.
Click OK.
10.
The Cisco_Nexus_1000V should now appear in the list of available plug-ins.
11.
Click Close to close the Plug-in Manager.
Perform Base Configuration of the Primary VSM
To perform the base configuration of the primary VSM, follow these steps:
1.
Using an SSH client, log in to the primary Cisco Nexus 1000V VSM as admin.
2.
Run the following configuration commands.
config tsvs connection vCenterprotocol vmware-vimremote ip address <<var_vcenter_server_ip>> port 80vmware dvs datacenter-name FlexPod_DC_1connectexitntp server <<var_global_ntp_server_ip>> use-vrf managementvlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>name IB-MGMT-VLANvlan <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>name NFS-VLANvlan <<var_vmotion_vlan_id>>name vMotion-VLANvlan <<var_vm-traffic_vlan_id>>name VM-Traffic-VLANvlan <<var_native_vlan_id>>name Native-VLANexitport-profile type ethernet system-uplinkvmware port-groupswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan <<var_native_vlan_id>>switchport trunk allowed vlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>, <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>, <<var_vmotion_vlan_id>>, <<var_vm-traffic_vlan_id>>channel-group auto mode on mac-pinningno shutdownsystem vlan <<var_mgmt_vlan_id>>, <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>, <<var_vmotion_vlan_id>>, <<var_vm-traffic_vlan_id>>system mtu 9000state enabledport-profile type vethernet IB-MGMT-VLANvmware port-groupswitchport mode accessswitchport access vlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>no shutdownsystem vlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>state enabledport-profile type vethernet NFS-VLANvmware port-groupswitchport mode accessswitchport access vlan <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>no shutdownsystem vlan <<var_nfs_vlan_id>>state enabledport-profile type vethernet vMotion-VLANvmware port-groupswitchport mode accessswitchport access vlan <<var_vmotion_vlan_id>>no shutdownsystem vlan <<var_vmotion_vlan_id>>state enabledport-profile type vethernet VM-Traffic-VLANvmware port-groupswitchport mode accessswitchport access vlan <<var_vm-traffic_vlan_id>>no shutdownsystem vlan <<var_vm-traffic_vlan_id>>state enabledport-profile type vethernet n1kv-L3capability l3controlvmware port-groupswitchport mode accessswitchport access vlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>no shutdownsystem vlan <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>>state enabledexitcopy run startMigrate Networking Components for ESXi Hosts to Cisco Nexus 1000V
vSphere Client Connect to vCenter
To migrate the networking components for the ESXi hosts to the Cisco Nexus 1000V, follow these steps:
1.
In the VMware vSphere Client connected to vCenter, choose Home > Networking.
2.
Expand the vCenter, DataCenter, and Cisco Nexus 1000V folders. choose the Cisco Nexus 1000V switch.
3.
Under Basic Tasks for the vSphere distributed switch, choose Add a Host.
4.
For both hosts, choose vmnic1 and choose the system-uplink Uplink port group. Click Next.
Figure 77 Adding Host to the vSphere Distributed Switch
5.
For all VMkernel ports, choose the appropriate Destination Port Group from the Cisco Nexus1000V, making sure to choose the "n1kv-L3" destination port group for the MGMT VMkernel ports. Click Next.
Figure 78 Assigning Port Groups
6.
Choose the Migrate Virtual Machine Networking check box. Expand each VM and choose the port groups for migration individually. Click Next.
Figure 79 Choosing Port Groups for Each VMs
7.
Click Finish. Wait for the migration process to complete.
8.
In the vSphere Client window, choose Home > Hosts and Clusters.
9.
Choose the first ESXi host and click the Configuration tab. In the Hardware box, choose Networking.
10.
Make sure that vSphere Standard Switch is selected at the top next to View. vSwitch0 should not have any active VMkernel or VM Network ports on it. On the upper right of vSwitch0, click Remove.
11.
Click Yes.
12.
After vSwitch0 has disappeared from the screen, click vSphere Distributed Switch at the top next to View.
13.
Click Manage Physical Adapters.
14.
Scroll down to the system-uplink box and click Add NIC.
15.
choose vmnic0 and click OK.
16.
Click OK to close the Manage Physical Adapters window. Two system uplinks should now be present.
17.
choose the second ESXi host and click the Configuration tab. In the Hardware field, click Networking.
18.
Make sure vSphere Standard Switch is selected at the top next to View. vSwitch0 should have no active VMkernel or VM Network ports on it. On the upper right of vSwitch0, click Remove.
19.
Click Yes.
20.
After vSwitch0 has disappeared from the screen, click vSphere Distributed Switch at the top next to View.
21.
Click Manage Physical Adapters.
22.
Scroll down to the system-uplink box and click Add NIC.
23.
choose vmnic0 and click OK.
24.
Click OK to close the Manage Physical Adapters window. Two system-uplinks should now be present.
25.
From the SSH client that is connected to the Cisco Nexus 1000V, run show interface status to verify that all interfaces and port channels have been correctly configured.
Figure 80 Verifying Interfaces and Port Channels
26.
Run show module and verify that the two ESXi hosts are present as modules.
Figure 81 Verifying the ESXi Hosts are Shown as Modules
27.
Run copy run start.
28.
Type exit two times to log out of the Cisco Nexus 1000v.
FlexPod Management Tool Setup
NetApp Virtual Storage Console (VSC) 4.1 Deployment Procedure
VSC 4.1 Preinstallation Considerations
The following licenses are required for VSC on storage systems running Data ONTAP 8.1.2 7-mode:
•
Protocol licenses (NFS and FCP)
•
FlexClone (for provisioning and cloning only)
•
SnapRestore (for backup and recovery)
•
SnapManager suite
Install VSC 4.1
To install the VSC 4.1 software, follow these steps:
1.
Using the instructions in section "Build Microsoft SQL Server VM," build a VSC and an OnCommand virtual machine with 4GB RAM, two CPUs, and one virtual network interface in the <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>> VLAN. The virtual network interface should be a VMXNET 3 adapter. Bring up the VM, install VMware Tools, assign IP addresses, and join the machine to the Active Directory domain. Install the current version of Adobe Flash Player on the VM. Install all Windows updates on the VM.
2.
Log in to the VSC and OnCommand VM as the FlexPod admin user.
3.
Download the x64 version of the Virtual Storage Console 4.1 at: http://support.netapp.com/NOW/cgi-bin/software/?product=Virtual+Storage+Console&platform=VMware+vSphere from the NetApp Support site.
4.
Right-click the file downloaded in step 3 and choose Run As Administrator.
5.
Click Yes at the User Access Control warning.
6.
On the Installation wizard Welcome page, click Next.
7.
choose the backup and recovery capability. Click Next.
Note
The backup and recovery capability requires an additional license.
Figure 82 Selecting the Desired Capabilities of VSC 4.1
8.
Click Next to accept the default installation location.
Figure 83 Installation Location
9.
Click Install.
10.
Click Finish.
Figure 84 Ready to Install VSC 4.1
Register VSC with vCenter Server
To register the VSC with the vCenter Server, follow these steps:
1.
A browser window with the registration URL opens automatically when the installation phase is complete.
2.
Click Continue to this website (not recommended).
3.
In the Plug-in Service Information section, choose the local IP address that the vCenter Server uses to access the VSC server from the drop-down list.
4.
In the vCenter Server Information section, enter the host name or IP address, user name (FlexPod admin user), and user password for the vCenter Server. Click Register to complete the registration.
Figure 85 Registering VSC with vCenter Server
Discover and Add Storage Resources
To discover storage resources for the Monitoring and Host Configuration and the Provisioning and Cloning capabilities, follow these steps:
1.
Using the vSphere Client, log in to the vCenter Server as FlexPod admin user. If the vSphere Client was previously opened, close it and then reopen it.
2.
Click the Home tab in the left side of the vSphere Client window.
3.
Under Solutions and Applications, click NetApp.
Figure 86 Adding Storage Resource
4.
Click Yes when the security certificate warning appears. To view the certificate, click View Certificate.
Figure 87 Certificate Details
5.
In the navigation pane, choose Monitoring and Host Configuration if it is not selected by default
6.
In the list of storage controllers, right-click the first controller listed and choose Modify Credentials.
7.
Enter the storage cluster management IP address in the Management IP address field. Enter admin for the User name, and the admin password for the Password. Make sure that Use SSL is selected. Click OK.
8.
Click OK to accept the controller privileges.
Figure 88 vSphere Client Showing Storage Controllers
Optimal Storage Settings for ESXi Hosts
VSC allows for the automated configuration of storage-related settings for all ESXi hosts that are connected to NetApp storage controllers. To use these settings, follow these steps:
1.
Choose individual or multiple ESXi hosts.
2.
Right-click and choose Set Recommended Values for these hosts.
Figure 89 Setting Recommended Values for the Hosts
3.
Check the settings to apply to selected vSphere hosts. Click OK to apply the settings.
This functionality sets values for HBAs and CNAs, sets appropriate paths and path-selection plug-ins, and verifies appropriate settings for software-based I/O (NFS and iSCSI).
Figure 90 Recommended Settings for NetApp Storage System
Note
Depending on what changes have been made, the servers might require a restart for network-related parameter changes to take effect. If no reboot is required, the Status value is set to Normal. If a reboot is required, the Status value is set to Pending Reboot. If a reboot is required, the ESX or ESXi servers should be placed into Maintenance Mode, evacuate (if necessary), and be restarted before proceeding.
VSC 4.1 Provisioning and Cloning Setup
Provisioning and cloning in VSC 4.1 helps administrators to provision both VMFS and NFS datastores at the data center, datastore cluster, or host level in VMware environments.
1.
In a vSphere Client connected to vCenter, choose Home > Solutions and Applications > NetApp and click the Provisioning and Cloning tab on the left. Choose Storage controllers.
2.
In the main part of the window, right-click <<var_controller1>> and choose Resources.
3.
In the <<var_controller1>> resources window, use the arrows to move volumes ifgrp0-<<var_nfs_vlan_id>>, esxi_boot and aggr1 to the right. Also choose the Prevent further changes check box as shown in Figure 91.
Figure 91 List of Parameters of Storage Controller 1 Ready for Provisioning and Cloning
4.
Click Save.
5.
In the main part of the window, right-click <<var_controller2>> and choose Resources.
6.
In the <<var_controller2>> resources window, use the arrows to move volumes ifgrp0-<<var_nfs_vlan_id>>, infra_datastore_1 and aggr1 to the right. choose the Prevent Further changes check box as shown in Figure 92.
Figure 92 List of Parameters of Storage Controller 2 Ready for Provisioning and Cloning
7.
Click Save.
VSC 4.1 Backup and Recovery
Adding Storage Systems to the Backup and Recovery Capability
Before you begin using the Backup and Recovery capability to schedule backups and restore your datastores, virtual machines, or virtual disk files, you must add the storage systems that contain the datastores and virtual machines for which you are creating backups.
Note
The Backup and Recovery capability does not use the user credentials from the Monitoring and Host Configuration capability.
Follow these steps to add the storage systems to the Backup and Recovery capability:
Figure 93 Adding Storage System to Backup and Recovery Capability
1.
Click Backup and Recovery and then click Setup.
2.
Click Add. The Add Storage System dialog box appears.
3.
Type the DNS name or IP address and the user credentials of the storage cluster.
4.
Click Add to add the storage cluster.
Backup and Recovery Configuration
To configure a backup job for a datastore, follow these steps:
1.
Click Backup and Recovery, then choose Backup.
2.
Click Add. The Backup wizard appears.
Figure 94 Configuring Backup
3.
Type a backup job name and description.
4.
If you want to create a VMware snapshot for each backup, choose Perform VMware consistency snapshot in the options pane.
5.
Click Next.
6.
choose infra_datastore_1 and then click
to move it to the selected entities. Click Next.
Figure 95 Selecting Entities to Backup
7.
choose one or more backup scripts if available and click Next.
8.
choose the hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly schedule that you want for this backup job and click Next.
Figure 96 Setting Schedule for Backup
9.
Use the default vCenter credentials or type the user name and password for the vCenter Server and click Next.
10.
Specify backup retention details as per requirements. Enter an e-mail address for receiving e-mail alerts. You can add multiple e-mail addresses by using semicolons to separate e-mail addresses. Click Next.
Figure 97 Specifying Backup Retention Period
11.
Review the summary page and click Finish. If you want to run the job immediately, choose the Run Job Now option and then click Finish.
Figure 98 Summary of Backup Settings
12.
On the management interface of storage controller 2, automatic Snapshot copies of the infrastructure datastore volume can be disabled by typing the command:
snap sched infra_datastore_1 0 0 013.
Also, to delete any existing automatic Snapshot copies that have been created on the volume type the following command:
snap list infra_datastore_1snap delete infra_datastore_1 <snapshot name>OnCommand Unified Manager 5.1
Create Raw Device Mapping (RDM) Datastore
From the VMware vCenter Client, do as follows:
1.
In the VMware vCenter Client, from Home > Inventory > Hosts and Clusters, right-click the FlexPod_Management cluster.
2.
choose NetApp > Provisioning and Cloning > Provision Datastore.
3.
Make sure the Infra_Vserver is selected in Vserver drop-down menu and click Next.
4.
choose VMFS as the Datastore type and click Next.
5.
choose FCP as the Protocol type, set the Size to 100, enter the datastore name as RDM_Map, check the check box to create new volume container, choose aggr02 as the Aggregate, check the Thin Provision check box, and click Next.
6.
Verify settings and click Apply.
Install .NET Framework 3.5.1 Feature
From the Virtual Storage Console (VSC) and OnCommand VM:
1.
Log in to the VSC and OnCommand VM as the FlexPod admin and open Server Manager.
2.
Click Features and click Add Features.
3.
Expand .NET Framework 3.5.1 Features and choose only .NET Framework 3.5.1.
Figure 99 Selecting Features to be Installed on the Server
4.
Click Next.
5.
Click Install.
6.
Click Close.
7.
Close Server Manager.
Install SnapDrive 6.4.2
Follow these steps to install SnapDrive® 6.4.2:
1.
Download SnapDrive 6.4.2 from the NetApp Support Site.
2.
Browse to the location of the SnapDrive installation package and double-click the executable file. This launches the SnapDrive installation wizard and opens the Welcome page.
3.
Click Next in the Welcome page of the SnapDrive installation wizard.
4.
If this is a new SnapDrive installation, read and accept the license agreement. Click Next.
5.
If this is a SnapDrive upgrade, choose Modify/Upgrade in the Program Maintenance page. Click Next.
6.
choose "Per Storage System" as the license type. Click Next.
Note
•
In the case of upgrading SnapDrive, the license information will already be populated.
•
In the case of selecting storage system licensing, SnapDrive can be installed without entering a license key. SnapDrive operations can be executed only on storage systems that have a SnapDrive or SnapManager license installed.
•
In the case of clustered Data ONTAP 8.1-based systems, the storage system licensing for SnapDrive is bundled with the other SnapManager product licenses. They are now a single license called the SnapManager_suite license.
7.
In the Customer Information page, type the user name and organization name. Click Next.
8.
The Destination Folder page prompts for a directory in which to install SnapDrive on the host. For new installations, by default this directory is C:\Program Files\NetApp\SnapDrive\.To accept the default, click Next.
9.
Check the Enable VirtualCenter or ESX Server Settings check box. Enter the IP address, user name, and password for the vCenter Server and click Next.
Note
Selecting Enable VirtualCenter or ESX Server Settings enables SnapDrive to use RDM pass-through LUNs. choose this option to use RDM pass-through disks. By default, this option is not selected.
Figure 100 Specifying Account Information for Installing SnapDrive 6.4.2
10.
Check the Enable SnapManager for Virtual Infrastructure Configuration Details check box. Enter the IP address of the VSC and OnCommand Server, and accept the default port. Click Next.
Figure 101 Specifying Virtual Infrastructure Details
11.
Enter your credentials or follow these steps to select a user account:
a.
In the Enter object name to select box, enter the local machine administrator in Domain name\user name format. Click Add.
b.
Click Check Names.
c.
Click OK.
d.
Enter the Administrator password.
e.
Click Next.
f.
Click OK.
Figure 102 Specifying SnapDrive Service Credentials
Note
The specified account must be a member of the local administrators' group of this system.
12.
In the SnapDrive Web Service Configuration page, keep the default ports unless any of them are already being used exclusively by another service. Click Next.
Figure 103 SnapDrive Web Service Configuration
13.
In the Transport Protocol Default Setting screen:
a.
choose Enable Transport Protocol Settings.
b.
choose HTTPS as the transport protocol.
c.
Enter the user name (vsadmin) and password for the Infra_Vserver vserver.
d.
Verify that port ID is set to 443 and click Next.
Figure 104 Transport Protocol Settings
14.
Click Next > Next > Install > Finish.
15.
From the Start menu, open SnapDrive.
16.
In the left pane, expand the local machine and choose Disks.
17.
In the right pane, choose Create Disk.
18.
In the create disk Wizard Window, click Next.
19.
In the storage system name field, enter the Infra_Vserver management IP address, and click Add.
20.
In the list that appears, choose OnCommandDB.
21.
Enter OnCommandDB for the LUN Name and click Next.
Figure 105 Adding LUN Information
22.
Make sure the LUN type is set to Dedicated and click Next.
23.
Assign drive letter O and set LUN size to 100GB. Click Next.
Figure 106 Entering LUN Properties
24.
Choose all initiators on the Initiator List, and click Next.
25.
Choose manual as the Initiator group management, and click Next.
26.
Choose the MGMT-Hosts igroup, and click Next.
Figure 107 Specifying igroups for the LUN
27.
Choose the RDM_Map Datastore in the Select Datastore section. Click Next.
Figure 108 Selecting a Datastore to Store LUN Mapping
28.
Click Finish to create the disk.
29.
Close SnapDrive.
Install NetApp OnCommand Core Package
To install the OnCommand Unified Manager Core Package, follow these steps:
1.
To download the OnCommand Unified Manager Core Package for Windows, click here.
2.
Using the FlexPod admin credentials, log in to the VSC and OnCommand VM.
3.
Identify the DataFabric® Manager Server license key before starting the installation.
The DataFabric Manager Server license key
4.
Navigate to the path or directory containing the downloaded file and launch the file.
5.
In the Security Warning message, click Yes to start the installation.
6.
In the Welcome screen, click Next.
7.
Accept the AutoSupport notice and click Next.
8.
Identify whether the OnCommand Unified Manager instance should manage systems with clustered Data ONTAP or 7-Mode and click Next.
Note
•
For a 7-Mode environment, either the Express edition or the Standard edition of the software is available.
•
If the infrastructure has both 7-Mode and clustered Data ONTAP systems, two OnCommand instances are needed to manage the respective 7-Mode or clustered Data ONTAP systems.
9.
choose Standard edition and click Next.
10.
Enter the 14-character license key when prompted and click Next.
11.
choose the installation location, if different from the default.
Note
Do not change the default location of the local Temp Folder directory, or the installation will fail. The installer automatically extracts the installation files to the %TEMP% location.
12.
Follow the remaining setup prompts to complete the installation.
From an MS-DOS command prompt, follow these steps as an administrator:
13.
In preparation for the database movement to the previously created LUN from local storage, stop all OnCommand Unified Manager services and verify that the services have stopped.
dfm service stopdfm service list14.
Move the data to the previously created LUN.
Note
The dfm datastore setup help command provides switch options available with the command.
dfm datastore setup O:\15.
Start OnCommand Unified Manager and then verify that all services have started.
dfm service startdfm service list16.
Generate an SSL key.
dfm ssl server setupKey Size (minimum = 512..1024..2048..) [default=512]: 1024Certificate Duration (days) [default=365]: EnterCountry Name (e.g., 2 letter code): <<var_country_code>>State or Province Name (full name): <<var_state>>Locality Name (city): <<var_city>>Organization Name (e.g., company): <<var_org>>Organizational Unit Name (e.g., section): <<var_ unit>>Common Name (fully-qualified hostname): <<var_oncommand_server_fqdn>>Email Address: <<var_admin_email>>
Note
The SSL key command fails if certain command line option inputs do not follow specified character lengths (for example, a two-letter country code), and any multiword entries must be encased in double quotation marks, for example, "North Carolina."
17.
Turn off automatic discovery.
dfm option set discoverEnabled=no18.
Set the protocol security options for communication with various devices.
dfm service stop httpdfm option set httpsEnabled=yesdfm option set httpEnabled=nodfm option set httpsPort=8443dfm option set hostLoginProtocol=sshdfm option set hostAdminTransport=https
Note
The HTTPS and SSH protocols must be enabled on the storage controllers that are monitored by OnCommand Unified Manager.
19.
Restart the DataFabric Manager HTTP services to make sure that the security options take effect.
dfm service start http20.
Configure OnCommand Unified Manager to use SNMPv3 to poll configuration information from the storage devices. Use the user name and password generated for SNMPv3.
dfm snmp modify -v 3 -c <<var_snmp_community>> -U snmpv3user -P <<var_password>> -A MD5 -X <<var_password>> default21.
Set up OnCommand Unified Manager to send AutoSupport through HTTPS to NetApp.
dfm option set SMTPServerName=<<var_mailhost>>dfm option set autosupportAdminContact=<<var_storage_admin_email>>dfm option set autosupportContent=completedfm option set autosupportProtocol=https22.
Manually add the storage cluster to the OnCommand server.
dfm host add <<var_cluster1>>dfm host add <<var_cluster2>>23.
Set the array login and password credentials in OnCommand Unified Manager. This is the root or administrator account.
dfm host set <<var_cluster1>> hostlogin=rootdfm host set <<var_cluster1>> hostPassword=<<var_password>>dfm host set <<var_cluster2>> hostlogin=rootdfm host set <<var_cluster2>> hostPassword=<<var_password>>24.
List the storage systems discovered by OnCommand Unified Manager and their properties.
dfm host listdfm host get <<var_cluster1>>dfm host get <<var_cluster2>>25.
Test the network configuration and connectivity between the OnCommand server and the named host. This test helps identify misconfigurations that prevent the OnCommand server from monitoring or managing a particular appliance. The test should be the first command used if a problem using the OnCommand server occurs with only some of the appliances.
dfm host diag <<var_cluster1>>dfm host diag <<var_cluster2>>26.
(optional) Configure an SNMP trap host.
dfm alarm create -T <<var_oncommand_server_fqdn>>27.
Configure OnCommand Unified Manager to generate and send e-mails for every event whose importance ranks as critical or higher.
dfm alarm create -E <<var_admin_email>> -v Critical28.
Create a manual backup.
dfm backup create -t snapshot29.
Schedule backups to a virtual backup directory on the 100GB FC LUN.
dfm option set backupRetentionCount=20dfm backup schedule set -t snapshot -D 21:0030.
To open Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, click Start > Administrative Tools > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
31.
Choose Inbound Rules.
32.
Click New Rule.
33.
Choose Port and click Next.
34.
Leave TCP selected and enter 8443 in the Specific local ports text box. Click Next.
35.
Click Next.
36.
Click Next.
37.
Name the rule OnCommand Console External Access and click Finish.
38.
Click New Rule.
39.
Choose Port and click Next.
40.
Choose UDP and enter 162 in the Specific local ports text box. Click Next.
41.
Click Next.
42.
Click Next.
43.
Name the rule OnCommand SNMP Trap and click Finish.
44.
Close Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
NetApp NFS Plug-In 1.0 for VMware VAAI
Enable VMware vStorage for NFS in Data ONTAP 7-Mode
To enable VMware vStorage for NFS when Data ONTAP is operating in 7-mode, follow these steps:
1.
From a Secure Shell (SSH) session on each storage controller, log in with the root user name and password.
2.
Enable vStorage on the storage system.
options nfs.vstorage.enable onInstall NetApp NFS Plug-In for VMware VAAI
To install the NetApp NFS plug-in for VMware vStorage APIs for Array Integration (VAAI), follow these steps:
1.
From the vSphere console of the VSC and OnCommand virtual machine (VM), go to the Software Downloads page in the NetApp Support site.
2.
Scroll down to locate the NetApp NFS Plug-in for VMware VAAI, choose the ESXi platform, and click Go.
3.
Download the .vib file of the most recent plug-in version.
4.
Verify that the file name of the .vib file matches the predefined name that VSC 4.1 for VMware vSphere uses: NetAppNasPlugin.vib.
Note
If the .vib file name does not match the predefined name, rename the .vib file. Neither the VSC client nor the NetApp vSphere Plug-in Framework (NVPF) service needs to be restarted after the .vib file is renamed.
5.
Copy the plug-in .vib file (NetAppNasPlugin.vib) to C:\Program Files\Virtual Storage Console\etc\vsc\web.
Note
The default directory path is C:\Program Files\NetApp\Virtual Storage Console\. However, VSC 4.1 for VMware vSphere lets you change this directory. For example, if you are using the default installation directory, the path to the NetAppNasPlugin.vib file is the following: C:\Program Files\Virtual Storage Console\etc\vsc\web\NetAppNasPlugin.vib.
6.
In the VMware vSphere Client connected to the vCenter Server, choose Home > Solutions and Applications > NetApp.
7.
In the Monitoring and Host Configuration capability navigation pane, choose Tools.
8.
Under NFS Plug-in for VMware VAAI, click Install on Host.
Figure 109 Installing NFS Plug-in for VMware VAAI on Host
9.
Choose all ESXi hosts and click Install, and then click Yes.
Note
The Monitoring and Host Configuration capability automatically installs the plug-in on the hosts selected.
Figure 110 Selecting All the ESXi Host for Installing NFS Plug-in
10.
Choose Home > Inventory > Host and Clusters.
11.
For each host (one at a time), right-click the host and choose Enter Maintenance Mode.
Figure 111 Entering Maintenance Mode in vSPhere Client
12.
Click Yes, click Yes again, and then click OK.
Note
It might be necessary to migrate all VMs away from the host.
13.
After the host is in maintenance mode, right-click the host and choose Reboot.
14.
Enter a reason for the reboot and click OK.
15.
After the host reconnects to the vCenter Server, right-click the host and choose Exit Maintenance Mode.
16.
Make sure that all ESXi hosts get rebooted.
NetApp VASA Provider
Install NetApp VASA Provider
To install NetApp VASA Provider, follow these steps:
1.
Using the previous instructions for virtual machine creation, build a VASA Provider virtual machine with 2GB RAM, two CPUs, and one virtual network interface in the <<var_ib-mgmt_vlan_id>> VLAN. The virtual network interface should be a VMXNET 3 adapter. Bring up the VM, install VMware Tools, assign IP addresses, and join the machine to the Active Directory domain.
2.
Log into the VASA Provider VM as the FlexPod admin user.
3.
Download NetApp VASA Provider from the NetApp Support site.
4.
Run the executable file netappvp-1-0-winx64.exe to start the installation.
Figure 112 Preparing to Install NetApp VASA provider
5.
On the Welcome page of the installation wizard, click Next.
6.
Choose the installation location and click Next.
Figure 113 NetApp VASA Provider Installation Location
7.
On the Ready to Install page, click Install.
Figure 114 Ready to Install NetApp VASA Provider
8.
Click Finish to complete the installation.
Figure 115 Installation Completed
Configure NetApp VASA Provider
After NetApp VASA Provider is installed, it must be configured to communicate with the vCenter Server and retrieve storage system data. During configuration, specify a user name and password to register NetApp VASA Provider with the vCenter Server, and then add the storage systems before completing the process.
Add Storage Systems
The NetApp VASA Provider dialog box can be used to add the storage systems from which NetApp VASA Provider collects storage information. Storage systems can be added at any time.
To add a storage system, follow these steps:
1.
Double-click the VASA Configuration icon on your Windows desktop or right-click the icon and choose Open to open the NetApp FAS/V-Series VASA Provider dialog box.
2.
Click Add to open the Add Storage System dialog box.
Figure 116 Adding Storage Systems
3.
Enter the host name or IP address, port number, and user name and password for the storage system.
Figure 117 Entering Storage System Login Credentials
4.
Click OK to add the storage system.
5.
Add both storage systems to the VASA Provider.
Register NetApp VASA Provider with vCenter Server
To establish a connection between the vCenter Server and NetApp VASA Provider, NetApp VASA Provider must be registered with the vCenter Server. The vCenter Server communicates with NetApp VASA Provider to obtain the information that NetApp VASA Provider collects from registered storage systems.
To register NetApp VASA Provider with the vCenter Server, follow these steps:
1.
Under Alarm Thresholds, accept or change the default threshold values for volume and aggregate. These values specify the percentages at which a volume or aggregate is full or nearly full.
The default threshold values are the following:
–
85% for a nearly full volume
–
90% for a full volume
–
90% for a nearly full aggregate
–
95% for a full aggregate
Note
After you finish registering NetApp VASA Provider with the vCenter Server, any changes made to the default threshold values are saved only when you click OK.
2.
Under VMware vCenter, enter the host name or IP address of the vCenter Server machine and the user name and password for the vCenter Server.
3.
Specify the port number to use, or accept the default port number for the vCenter Server.
4.
Click Register Provider.
5.
Click OK to commit all the details and register NetApp VASA Provider with the vCenter Server.
Note
To use the vSphere Client to register NetApp VASA Provider with the vCenter Server, copy the URL from the VASA URL field and paste it into the vCenter Server.
Figure 118 Registering NetApp VASA Provider with VMware vCenter
6.
Click OK to close the VASA Configuration.
Verify VASA Provider in vCenter
1.
Log in to vCenter using vSphere Client.
2.
Click the Home tab at the upper-left portion of the window.
3.
In the Administration section, click Storage Providers.
4.
Click Refresh All. The NetApp VASA Provider (NVP) should now appear as a vendor provider.
Figure 119 NetApp VASA Provider is Listed as Vendor Provider
5.
Click the Home tab in the upper-left portion of the window.
6.
In the Inventory section, click Datastores and Datastore Clusters.
7.
Expand the vCenter and the data center. Choose a datastore.
8.
Click the Summary tab. Verify that a System Storage Capability appears under Storage Capabilities.
Figure 120 Summary Showing System Storage Capability Under Storage Capabilities
Appendix
Build Windows Active Directory Server VM(s)
ESXi Host VM-Host-Infra-01
To build an Active Directory Server virtual machine (VM) for the VM-Host-Infra-01 ESXi host, follow these steps:
1.
Log in to the host by using the VMware vSphere Client.
2.
In the vSphere Client, choose the host in the inventory pane.
3.
Right-click the host and choose New Virtual Machine.
4.
Choose Custom and click Next.
5.
Enter a name for the VM. Click Next.
6.
Choose infra_datastore_1. Click Next.
7.
Choose Virtual Machine Version: 8. Click Next.
8.
Verify that the Windows option and the Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 (64-bit) version are selected. Click Next.
9.
Choose two virtual sockets and one core per virtual socket. Click Next.
10.
Choose 4GB of memory. Click Next.
11.
Choose one network interface card (NIC).
12.
For NIC 1, choose the IB-MGMT Network option and the VMXNET 3 adapter. Click Next.
13.
Keep the LSI Logic SAS option for the SCSI controller selected. Click Next.
14.
Keep the Create a New Virtual Disk option selected. Click Next.
15.
Make the disk size at least 60GB. Click Next.
16.
Click Next.
17.
Check the check box for Edit the Virtual Machine Settings Before Completion. Click Continue.
18.
Click the Options tab.
19.
choose Boot Options.
20.
Check the Force BIOS Setup check box.
21.
Click Finish.
22.
From the left pane, expand the host field by clicking the plus sign (+).
23.
Right-click the newly created AD Server VM and click Open Console.
24.
Click the third button (green right arrow) to power on the VM.
25.
Click the ninth button (CD with a wrench) to map the Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 ISO, and then choose Connect to ISO Image on Local Disk.
26.
Navigate to the Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 ISO, select it, and click Open.
27.
In the BIOS Setup Utility window and use the right arrow key to navigate to the Boot menu. Use the down arrow key to choose CD-ROM Drive. Press the plus (+) key twice to move CD-ROM Drive to the top of the list. Press F10 and Enter to save the selection and exit the BIOS Setup Utility.
28.
The Windows Installer boots. Choose the appropriate language, time and currency format, and keyboard. Click Next.
29.
Click Install now.
30.
Make sure that the Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard (Full Installation) option is selected. Click Next.
31.
Read and accept the license terms and click Next.
32.
Choose Custom (Advanced). Make sure that Disk 0 Unallocated Space is selected. Click Next to allow the Windows installation to complete.
33.
After the Windows installation is complete and the VM has rebooted, click OK to set the Administrator password.
34.
Enter and confirm the Administrator password and click the blue arrow to log in. Click OK to confirm the password change.
35.
After logging in to the VM desktop, from the VM console window, choose the VM menu. Under Guest, choose Install/Upgrade VMware Tools. Click OK.
36.
If prompted to eject the Windows installation media before running the setup for the VMware tools, click OK, then click OK.
37.
In the dialog box, choose Run setup64.exe.
38.
In the VMware Tools installer window, click Next.
39.
Make sure that Typical is selected and click Next.
40.
Click Install.
41.
Click Finish.
42.
Click Yes to restart the VM.
43.
After the reboot is complete, choose the VM menu. Under Guest, choose Send Ctrl+Alt+Del. Then enter the password to log in to the VM.
44.
Set the time zone for the VM, IP address, gateway, and host name.
Note
A reboot is required.
45.
If necessary, activate Windows.
46.
Download and install all required Windows updates.
Note
This process requires several reboots.
47.
Open Server Manager.
48.
On the left, click Roles, the choose Add Roles on the right.
49.
Click Next.
50.
In the list, check the check box next to Active Directory Domain Services.
51.
In the popup, click Add Required Features to add .NET Framework 3.5.1.
Figure 121 Selecting Roles to Install on the Server
52.
Click Next.
53.
Click Next.
Figure 122 Confirming Installation Selections
54.
Click Install.
Figure 123 Installation Completion Summary
55.
In the middle of the window, click Close this wizard and launch the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard (dcpromo.exe).
56.
In the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard, click Next.
57.
Click Next.
58.
Choose Create a new domain in a new forest and click Next.
Figure 124 Creating a Domain Controller for a New Forest
59.
Type the FQDN of the Windows domain for this FlexPod and click Next.
Figure 125 Naming the Forest Root Domain
60.
Choose the appropriate forest functional level and click Next.
61.
Keep DNS server selected and click Next.
Figure 126 Selecting Additional Options for the Domain Controller
62.
If one or more DNS servers exist that this domain can resolve from, Click Yes to create a DNS delegation. If this is AD server is being created on an isolated network, click No, to not create a DNS delegation. The remaining steps in this procedure assume a DNS delegation is not created. Click Next.
63.
Click Next to accept the default locations for database and log files.
64.
Enter and confirm <<var_password>> for the Directory Services Restore Mode Administrator Password. Click Next.
65.
Review the Summary information and click Next. Active Directory Domain Services will install.
66.
Click Finish.
67.
Click Restart Now to restart the AD Server.
68.
After the machine has rebooted, log in as the domain Administrator.
69.
Open the DNS Manager by clicking Start > Administrative Tools > DNS.
70.
(Optional) Add Reverse Lookup Zones for your IP address ranges.
71.
Expand the Server and Forward Lookup Zones. Choose the zone for the domain. Right-click and choose New Host (A or AAAA). Populate the DNS Server with Host Records for all components in the FlexPod.
72.
(Optional) Build a second AD server VM. Add this server to the newly created Windows Domain and activate Windows. Install Active Directory Domain Services on this machine. Launch dcpromo.exe at the end of this installation. Choose to add a domain controller to a domain in an existing forest. Add this domain controller to the domain created earlier. Complete the installation of this second domain controller. After vCenter Server is installed, affinity rules can be created to keep the two AD servers running on different hosts.
Configuring Cisco VM-FEX with the UCS Manager
Background
FlexPod for VMware utilizes distributed virtual switching to manage the virtual access layer from a central point. While previous versions of FlexPod have only described the use of the Cisco Nexus 1000V, there exists an option to use the built-in virtual switching functionality delivered through hardware on the Cisco UCS known as VM-FEX. This has several advantages:
•
There is no need for extra HW such as Cisco Nexus 1110-X.
•
Cisco UCS provides a central configuration environment with which the administrator is already familiar.
•
Compared to using the Cisco Nexus 1000v as virtual appliances within vCenter itself, this setup avoids an SPOF and common restart issues when running the distributed switches in an environment in which they are required for the network functionality of the ESX servers on which they are running. This is a common problem that needs to be addressed in the solution design.
In other words, it dramatically simplifies the hardware setup and operation by optimally utilizing the new hardware features.
Process Overview
This section provides a detailed overview of VM-FEX setup, configuration, and operation using Cisco UCS Manager.
This section describes:
•
Initial setup and configuration
•
Operation, that is, adding networks for additional tenants
For configuration details, see Configuration Guide: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/unified_computing/ucs/sw/vm_fex/vmware/gui/config_guide/2.1/b_GUI_VMware_VM-FEX_UCSM_Configuration_Guide_2_1.html
Initial Setup
For initial setup, follow these steps:
1.
Create a vNIC connection policy in Cisco UCS Manager.
2.
Create a server BIOS policy.
3.
Clone an existing service profile.
4.
Install the VEM software on the ESX server.
5.
Install the plug-in into vCenter.
Create a Dynamic vNIC Connection Policy
To define the dynamic vNIC connection policy that vNICs created from a vNIC template should use, follow these steps in Cisco UCS Manager:
1.
Log in to Cisco UCS Manager.
2.
Click the LAN tab in the left navigation pane and click LAN > Policies > root > Sub-organizations (name of the suborganization if applicable) > Dynamic vNIC Connection Profile.
3.
Right-click and choose Create Dynamic vNIC Connection Policy to start the wizard.
4.
Type a name and description for the vNIC connection policy. Choose VMWare from the Adapter Policy drop-down menu. Choose the Protected option. Click OK.
Note
•
The Protected option allows the vNIC to use both fabric A and fabric B.
•
With Cisco UCS C-Series servers, the number of dynamic vNICs that can be used depends on the hardware in use. Refer to appendix 13.3, "VM-FEX Virtual Interfaces."
Figure 127 Creating Dynamic vNIC Policy
Create a Server BIOS Policy
To define the BIOS policy for a service profile that supports VM-FEX on ESXi, follow these steps in Cisco UCS Manager:
1.
Click the Server tab in the left navigation pane, and choose Server > Policies > root > Sub-organizations (name of the suborganization if applicable) > BIOS Policies.
2.
Right-click and choose Create BIOS Policy to start the wizard.
3.
Type a name for the policy and retain the platform defaults.
Figure 128 Creating BIOS Policy
4.
For Virtualization Technology (VT) and Direct Cache Access, choose enabled.
Figure 129 Processor Settings for BIOS Policy
5.
Click Next.
6.
For VT For Directed IO, choose enabled.
Figure 130 Intel Directed IO Settings for BIOS Policy
7.
Click Next.
8.
The remaining sections of the Create BIOS Policy wizard (RAS Memory, Serial Port, USB, PCI Configuration, Boot Options, and Server Management) can retain the Platform Default option. Click Next on each of these windows and then click Finish to complete the wizard.
Create a VM-FEX Enabled Service Profile Template
To create a Cisco UCS service profile using VM-FEX, clone a previously defined Cisco UCS service profile and apply the dynamic vNIC and BIOS policies by following these steps in the Cisco UCS Manager:
1.
Click the Servers tab in the left navigation pane and expand the Service Profile Templates.
2.
Right-click VM-Host-Infra-Fabric-A and choose Create a Clone.
3.
Type a clone name and choose an organizational owner for the new service profile template.
Figure 131 Cloning Service Profile Template
4.
Click OK when notified that the service profile clone was successfully created. The Service Template navigation window appears.
5.
Click the Network tab and choose Change Dynamic vNIC Connection Policy under the Actions section of the working pane. The Change Dynamic vNIC Connection Policy form appears.
6.
Choose Use a Dynamic vNIC Connection Policy from the drop-down menu and the previously created Dynamic vNIC policy. Click OK.
Figure 132 Changing the Dynamic vNIC Connection Policy
7.
Click OK when notified that the vNIC connection policy was successfully modified.
8.
From the Service Template properties window, click the Policies tab.
9.
Expand the BIOS Policies in the Policies section of the working pane.
10.
Choose the previously defined FEX BIOS policy and click OK.
Figure 133 Choosing a BIOS Policy
Create VM-FEX Service Profile
To create service profiles from the service profile template, follow these steps:
1.
In Cisco UCS Manager, click the Servers tab in the navigation pane.
2.
Choose Service Profile Templates > Service Template VM-Host-Infra-VMFEX-Fabric-A.
3.
Right-click VM-Host-Infra-FEX-Fabric-A and choose Create Service Profiles from Template.
4.
Enter VM-Host-FEX-0 as the service profile prefix.
5.
Enter 1 as the number of service profiles to create.
6.
Click OK to create the service profile.
Figure 134 Creating Service Profile from Template
7.
Click OK in the confirmation message.
8.
Verify that the service profile VM-Host-FEX-1 has been created. The service profile is automatically associated with the servers in their assigned server pools.
Install and Set Up VMware ESXi
Refer to section 11.1 to install and completely set up VMware ESXi version 5.1 on the two ESXi hosts. After ESXi setup is complete, add the two new hosts to VMware vCenter.
Download Cisco VEM Software Bundle
To download the Cisco UCS B-Series or C-Series server drivers, follow these steps:
Note
The following bundle was used during validation cisco-vem-v151-5.1-1.1.1.1.vib.
1.
Open a Web browser on the management workstation and navigate to the following Cisco Download Software pages:
a.
Downloads Home > Products > Servers - Unified Computing > Cisco UCS B-Series Blade Server Software > Unified Computing System (UCS) Drivers-2.1(1d)
b.
Downloads Home > Products > Servers - Unified Computing > Cisco UCS C-Series Rack-Mount UCS-Managed Server Software > Unified Computing System (UCS) Drivers-1.4(5b)
2.
Follow the steps necessary to download the software bundles located on the ISO image.
3.
Mount the ISO image and copy the appropriate vib file from the VMware > VM-FEX > Cisco directory to the local machine.
4.
From the vCenter vSphere Client, choose the infra_datastore_1 in the Inventory > Datastores and Datastore Clusters navigation menu.
5.
Under the Basic Tasks choose Browse this Datastore
6.
Choose the root folder (/) and click the third button at the top to add a folder.
7.
Name the folder VM-FEX and click OK.
8.
On the left, choose the VM-FEX folder.
9.
Click the fourth button at the top and choose Upload File.
10.
Navigate to the cisco-vem-v151-5.1-1.1.1.1.vib file and click Open.
11.
Click Yes to upload the .vib file to infra_datastore_1.
The VM-FEX file should now appear in the VM-FEX folder in the datastore.
Install the FEX Virtual Ethernet Module on Each ESXi Host
To install the Virtual Ethernet Module (VEM) on the ESXi hosts, follow these steps:
1.
Open the VMware vSphere CLI command prompt.
2.
For each ESXi host in the VMware vSphere CLI, run the following command:
esxcli -s <host_ip> -u root -p <host_password> software vib install -v /vmfs/volumes/infra_datastore_1/VM-FEX/cisco-vem-v151-5.1-1.1.1.1.vibIntegrate Cisco UCS with vCenter
To integrate Cisco UCS Manager and vCenter, follow these steps:
1.
Log in to the Cisco UCS Manager.
2.
In the navigation pane, click the VM tab, and in the VM tab, expand the All folder. Choose the VMware node, and in the Working Area, click the General tab.
3.
Choose Configure VMware Integration in the Actions area to start the Configuration wizard.
Figure 135 Configuring VMware Integration
4.
Follow the instructions and click Export and complete the steps to install the UCSM extension file in vCenter.
Figure 136 Exporting vCenter Extension Plug-in
5.
Click Next.
6.
Enter the VMware vCenter Server name, vCenter Server host name or IP address, vCenter data center name, DVS folder, and DVS name.
7.
Click Next.
Figure 137 Defining VMware DVS
8.
Create the FEX-MGMT port profile, choose the MGMT-VLAN, and indicate it is the native VLAN.
Figure 138 Defining Port Profile for VMware Integration
9.
Click Next.
10.
When finishing the wizard, the Cisco UCS Manager connects to vCenter and adds the plug-in.
Figure 139 VMware Integration is succesful
Note
The ESXi host will require additional hypervisor vNICs to support VMware vMotion, and NFS traffic uses the generic port-profile creation steps documented in section "Standard Operations" to establish a FEX-vMotion and FEX-NFS Port Profile.
Validate Setting in VMware vCenter
To validate the successful installation of the Cisco UCS Manager plug-in, follow these steps:
1.
Log in to the vCenter Server.
2.
In the Main menu, choose Plug-ins > Manage Plug-ins.
The popup windows shows that the Cisco UCS Manager is already integrated in vCenter.
Figure 140 Cisco UCS Manager Integrated in vCenter
3.
Click Inventory > Networking to see FEX added to distributed switch from Cisco UCS Manager.
Figure 141 Verifying FEX-DVS in Cisco UCS Manager
Standard Operations
The VM-FEX environment supports the addition of port profiles to the distributed switch. The following section describes how to add these distributed port groups.
Add Distributed Port Group to the VDS (vSphere Distributed Switch)
Port Profiles
Port profiles contain the properties and settings that you can use to configure virtual interfaces in Cisco UCS for VM-FEX. The port profiles are created and administered in Cisco UCS Manager. After a port profile is created, assigned to, and actively used by one or more distributed virtual switches (DVSs), any changes made to the networking properties of the port profile in Cisco UCS Manager are immediately applied to those DVSs.
In VMware vCenter, a port profile is represented as a port group. Cisco UCS Manager pushes the port profile names to VMware vCenter, which displays the names as port groups. None of the specific networking properties or settings in the port profile is visible in VMware vCenter. You must configure at least one port profile client for a port profile if you want Cisco UCS Manager to push the port profile to VMware vCenter.
Port Profile Client
The port profile client determines the DVSs to which a port profile is applied. By default, the port profile client specifies that the associated port profile applies to all DVSs in VMware vCenter. However, you can configure the client to apply the port profile to all DVSs in a specific data center or data center folder or to only one DVS.
Create a VM-FEX Port Profile
Follow these steps to create VM-FEX port profiles for use on the Cisco UCS distributed virtual switch.
1.
Log in to Cisco UCS Manager.
2.
Click the VM tab.
3.
Right-click Port Profile > Create Port Profile.
4.
Enter the name of the Port Profile.
5.
(Optional) Enter a description.
6.
(Optional) Choose a QoS policy.
7.
(Optional) Choose a network control policy.
8.
Enter the maximum number of ports that can be associated with this port profile. The default is 64 ports.
Note
The maximum number of ports that can be associated with a single DVS is 4096. If the DVS has only one associated port profile, that port profile can be configured with up to 4096 ports. However, if the DVS has more than one associated port profile, the total number of ports associated with all of those port profiles combined cannot exceed 4096.
9.
(Optional) Choose High Performance.
Note
Select None—Traffic to and from a virtual machine passes through the DVS.
Select High Performance— Traffic to and from a virtual machine bypasses the DVS and hypervisor and travels directly between the virtual machines and a virtual interface card (VIC) adapter.
10.
Choose the VLAN.
11.
Choose Native-VLAN.
12.
Click OK.
Figure 142 Creating Port Profile
Or
Figure 143 Creating Port Profile with High Performance
The port profile created will appear in the working pane.
Create the Port Profile Client
To create the client profile for use in the Cisco UCS virtual distributed switch, follow these steps:
1.
In the navigation pane under the VM tab, expand All > Port Profiles. Right-click the Port Profile and click Create Profile Client.
2.
Choose the data center created in your vCenter Server, folder, and distributed virtual switch created in section "Integrate Cisco UCS with vCenter."
3.
Click OK.
Figure 144 Creating Profile Client
Or
Figure 145 Creating Profile Client for DVS-FEX
The client profile created will appear in your distributed virtual switch DVS-FEX in vCenter as a port group.
Repeat these steps as necessary for the workloads in the environment.
Migrate Networking Components for ESXi Hosts to Cisco DVS-FEX
vCenter Server VM
To migrate the networking components for the ESXi hosts to the Cisco FEX-DVS, follow these steps:
1.
In the VMware vSphere client connected to vCenter, choose Home > Networking.
2.
Expand the vCenter, DataCenter, and DVS-FEX folders. choose the DVS-FEX switch.
3.
Under Basic Tasks for the vSphere distributed switch, choose Add a Host.
4.
For both hosts, choose vmnic1 and choose the uplink-pg-DVS-FEX Uplink port group. Click Next.
Figure 146 Selecting Physical Adapters to Add to the Vsphere Distributed Switch
5.
For all VMkernel ports, choose the appropriate destination Port Group from the Cisco DVS-FEX. Click Next.
Figure 147 Selecting Destination Port Groups
6.
Check the Migrate Virtual Machine Networking check box. Expand each VM and choose the port groups for migration individually. Click Next.
Figure 148 Selecting Port Groups on Each VM to Migrate Individually
7.
Click Finish. Wait for the migration process to complete.
8.
In the vSphere Client window, choose Home > Hosts and Clusters.
9.
Choose the first ESXi host and click the Configuration tab. In the Hardware field, choose Networking.
10.
Make sure that vSphere Standard Switch is selected at the top next to View. vSwitch0 should not have any active VMkernel or VM Network ports on it. On the upper right of vSwitch0, click Remove.
11.
Click Yes.
12.
After vSwitch0 has disappeared from the screen, click vSphere Distributed Switch at the top next to View.
13.
Click Manage Physical Adapters.
14.
In the uplink-pg-DVS-FEX field click Add NIC.
15.
Choose vmnic0 and click OK.
16.
Click OK to close the Manage Physical Adapters window. Two uplinks should now be present.
17.
Choose the second ESXi host and click the Configuration tab. In the Hardware field, choose Networking.
18.
Make sure vSphere Standard Switch is selected at the top next to View. vSwitch0 should have no active VMkernel or VM Network ports on it. On the upper right of vSwitch0, click Remove.
19.
Click Yes.
20.
After vSwitch0 has disappeared from the screen, click vSphere Distributed Switch.
21.
Click Manage Physical Adapters.
22.
In the uplink-pg-DVS-FEX field click Add NIC.
23.
Choose vmnic0 and click OK.
24.
Click OK to close the Manage Physical Adapters window. Two uplinks should now be present.
VM-FEX Virtual Interfaces
In a blade server environment, the number of vNICs and vHBAs configurable for a service profile is determined by adapter capability and the amount of virtual interface (VIF) namespace available in the adapter. In Cisco UCS, portions of VIF namespace are allotted in chunks called VIFs. Depending on your hardware, the maximum number of VIFs is allocated on a predefined, per-port basis.
The maximum number of VIFs varies based on hardware capability and port connectivity. For each configured vNIC or vHBA, one or two VIFs are allocated. Standalone vNICs and vHBAs use one VIF, and failover vNICs and vHBAs use two.
The following variables affect the number of VIFs available to a blade server, and therefore, the number of vNICs and vHBAs you can configure for a service profile.
•
The maximum number of VIFs supported on your fabric interconnect
•
How the fabric interconnects are cabled
•
If the fabric interconnect and IOM are configured in fabric port channel mode
For more information about the maximum number of VIFs supported by your hardware configuration, refer to the Cisco UCS 6100 and 6200 Series Configuration Limits for Cisco UCS Manager for your software release. Table 23 and Table 24 reference these limits.
Note
•
For a non-VIC adapter the maximum number of vNICs is two and the maximum number of vHBAs is two.
•
If the server in single-wire mode has two VIC adapters, the maximum number of VIFs (vNICs + vHBAs) available for the second adapter would be same as for an adapter in a dual-wire mode server.
•
For more information on Cisco UCS C-Series Server integration into UCSM, see: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/unified_computing/ucs/c-series_integration/ucsm2.1/b_UCSM2-1_C-Integration.pdf
Cisco Nexus 5548 Example Configurations
Cisco Nexus 5548 A
!Command: show running-config!Time: Mon Feb 25 18:52:54 2013version 5.2(1)N1(3)feature fcoeswitchname icef1-sw1feature npivno feature telnetcfs eth distributefeature lacpfeature vpcfeature lldpusername admin password 5 $1$bzvqy03B$xPzr5b6TKfwPE2vWVj25A/ role network-adminbanner motd #Nexus 5000 Switch#ip domain-lookupclass-map type qos class-fcoeclass-map type queuing class-fcoematch qos-group 1class-map type queuing class-all-floodmatch qos-group 2class-map type queuing class-ip-multicastmatch qos-group 2class-map type network-qos class-fcoematch qos-group 1class-map type network-qos class-all-floodmatch qos-group 2class-map type network-qos class-ip-multicastmatch qos-group 2policy-map type network-qos jumboclass type network-qos class-fcoepause no-dropmtu 2158class type network-qos class-defaultmtu 9216multicast-optimizesystem qosservice-policy type queuing input fcoe-default-in-policyservice-policy type queuing output fcoe-default-out-policyservice-policy type qos input fcoe-default-in-policyservice-policy type network-qos jumbosnmp-server user admin network-admin auth md5 0x9f7f45ac8ee14ff3cf5e72e22bb95942 priv 0x9f7f45ac8ee14ff3cf5e72e22bb95942 localizedkeyntp server 192.168.171.4 use-vrf managementvrf context managementip route 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.171.1vlan 1vlan 2name Native-VLANvlan 101fcoe vsan 101name FCoE_Fabric_Avlan 3170name NFS-VLANvlan 3173name vMotion-VLANvlan 3174name VM-Traffic-VLANvlan 3175name IB-MGMT-VLANvlan 3176name Packet-Control-VLANspanning-tree port type edge bpduguard defaultspanning-tree port type network defaultport-channel load-balance ethernet source-dest-portvpc domain 23role priority 10peer-keepalive destination 192.168.171.70 source 192.168.171.69auto-recoveryport-profile default max-ports 512vsan databasevsan 101 name "Fabric_A"device-alias databasedevice-alias name icef1-st1a_1a pwwn 50:0a:09:81:9d:02:4c:1adevice-alias name icef1-st1a_1a pwwn 50:0a:09:81:8d:02:4c:1adevice-alias name VM-Host-Infra-01_A pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:01:0a:0fdevice-alias name VM-Host-Infra-02_A pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:01:0a:1fdevice-alias commitfcdomain fcid databasevsan 101 wwn 50:0a:09:81:88:12:85:b3 fcid 0x550000 dynamicvsan 101 wwn 50:0a:09:81:9d:02:4c:1a fcid 0x550001 dynamic! [icef1-st1a_1a]vsan 101 wwn 50:0a:09:81:88:22:87:76 fcid 0x550020 dynamicvsan 101 wwn 50:0a:09:81:8d:02:4c:1a fcid 0x550021 dynamic! [icef1-st1b:1a]vsan 101 wwn 22:ca:54:7f:ee:23:52:7f fcid 0x550040 dynamicvsan 101 wwn 20:00:00:25:b5:01:0a:0f fcid 0x550041 dynamic! [VM-Host-Infra-01_A]vsan 101 wwn 20:00:00:25:b5:01:0a:1f fcid 0x550042 dynamic! [VM-Host-Infra-02_A]interface port-channel10description vPC peer-linkswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3176spanning-tree port type networkvpc peer-linkinterface port-channel11description icef1-st1aswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,3170spanning-tree port type edge trunkvpc 11interface port-channel12description icef1-st1bswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,3170spanning-tree port type edge trunkvpc 12interface port-channel13description icef1-uc1-Aswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3175spanning-tree port type edge trunkvpc 13interface port-channel14description icef1-uc1-Bswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3175spanning-tree port type edge trunkvpc 14interface port-channel15description icef1-uc1-A:FCoEswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 101spanning-tree port type edge trunkinterface port-channel20description icecore Uplinkswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3175spanning-tree port type networkvpc 20interface vfc11bind interface Ethernet1/1switchport trunk allowed vsan 101switchport description icef1-st1a:1ano shutdowninterface vfc12bind interface Ethernet1/2switchport trunk allowed vsan 101switchport description icef1-st1b:1ano shutdowninterface vfc15bind interface port-channel15switchport trunk allowed vsan 101switchport description icef1-uc1-A:FCoEno shutdownvsan databasevsan 101 interface vfc11vsan 101 interface vfc12vsan 101 interface vfc15interface Ethernet1/1description icef1-st1a:e1aswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,3170channel-group 11 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/2description icef1-st1b:e1bswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 101,3170channel-group 12 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/3interface Ethernet1/4interface Ethernet1/5interface Ethernet1/6interface Ethernet1/7interface Ethernet1/8interface Ethernet1/9interface Ethernet1/10interface Ethernet1/11description icef1-uc1-A:1/19switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3175channel-group 13 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/12description icef1-uc1-B:1/19switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3175channel-group 14 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/13description icef1-sw2:1/13switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3176channel-group 10 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/14description icef1-sw2:1/14switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3176channel-group 10 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/15description icef1-1110x-1:Eth1switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk allowed vlan 3175-3176spanning-tree port type edge trunkspeed 1000interface Ethernet1/16description icef1-1110x-2:Eth1switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk allowed vlan 3175-3176spanning-tree port type edge trunkspeed 1000interface Ethernet1/17interface Ethernet1/18interface Ethernet1/19interface Ethernet1/20description icecore:Eth1/7 Uplinkswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3175spanning-tree port type networkchannel-group 20 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/21interface Ethernet1/22interface Ethernet1/23interface Ethernet1/24interface Ethernet1/25interface Ethernet1/26interface Ethernet1/27interface Ethernet1/28interface Ethernet1/29interface Ethernet1/30interface Ethernet1/31description icef1-uc1-A:1/31switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 101channel-group 15 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/32description icef1-uc1-A:1/32switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 101channel-group 15 mode activeinterface mgmt0ip address 192.168.171.69/24line consoleline vtyboot kickstart bootflash:/n5000-uk9-kickstart.5.2.1.N1.3.binboot system bootflash:/n5000-uk9.5.2.1.N1.3.bin!Full Zone Database Section for vsan 101zone name VM-Host-Infra-01_A vsan 101member pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:01:0a:0f! [VM-Host-Infra-01_A]member pwwn 50:0a:09:81:9d:02:4c:1a! [icef1-st1a_1a]member pwwn 50:0a:09:81:8d:02:4c:1a! [icef1-st1b_1a]zone name VM-Host-Infra-02_A vsan 101member pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:01:0a:1f! [VM-Host-Infra-02_A]member pwwn 50:0a:09:81:9d:02:4c:1a! [icef1-st1a_1a]member pwwn 50:0a:09:81:8d:02:4c:1a! [icef1-st1b_1a]zoneset name FlexPod vsan 101member VM-Host-Infra-01_Amember VM-Host-Infra-02_Azoneset activate name FlexPod vsan 101Cisco Nexus 5548 B
!Command: show running-config!Time: Mon Feb 25 18:54:02 2013version 5.2(1)N1(3)feature fcoeswitchname icef1-sw2feature npivno feature telnetcfs eth distributefeature lacpfeature vpcfeature lldpusername admin password 5 $1$uCGfL31v$UuLHg53DEK3VvDGkbjUGb1 role network-adminbanner motd #Nexus 5000 Switch#ip domain-lookupclass-map type qos class-fcoeclass-map type queuing class-fcoematch qos-group 1class-map type queuing class-all-floodmatch qos-group 2class-map type queuing class-ip-multicastmatch qos-group 2class-map type network-qos class-fcoematch qos-group 1class-map type network-qos class-all-floodmatch qos-group 2class-map type network-qos class-ip-multicastmatch qos-group 2policy-map type network-qos jumboclass type network-qos class-fcoepause no-dropmtu 2158class type network-qos class-defaultmtu 9216multicast-optimizesystem qosservice-policy type queuing input fcoe-default-in-policyservice-policy type queuing output fcoe-default-out-policyservice-policy type qos input fcoe-default-in-policyservice-policy type network-qos jumbosnmp-server user admin network-admin auth md5 0x2bd90b73090e2a5ffe4b35ead5f6e070 priv 0x2bd90b73090e2a5ffe4b35ead5f6e070 localizedkeyntp server 192.168.171.4 use-vrf managementvrf context managementip route 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.171.1vlan 1vlan 2name Native-VLANvlan 102fcoe vsan 102name FCoE_Fabric_Bvlan 3170name NFS-VLANvlan 3173name vMotion-VLANvlan 3174name VM-Traffic-VLANvlan 3175name IB-MGMT-VLANvlan 3176name Packet-Control-VLANspanning-tree port type edge bpduguard defaultspanning-tree port type network defaultport-channel load-balance ethernet source-dest-portvpc domain 23role priority 20peer-keepalive destination 192.168.171.69 source 192.168.171.70auto-recoveryport-profile default max-ports 512vsan databasevsan 102 name "Fabric_B"device-alias databasedevice-alias name icef1-st1a_1b pwwn 50:0a:09:82:9d:02:4c:1adevice-alias name icef1-st1b_1b pwwn 50:0a:09:82:8d:02:4c:1adevice-alias name VM-Host-Infra-01_B pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:01:0b:0fdevice-alias name VM-Host-Infra-02_B pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:01:0b:1fdevice-alias commitfcdomain fcid databasevsan 102 wwn 50:0a:09:83:88:22:87:76 fcid 0x3f0000 dynamicvsan 102 wwn 50:0a:09:82:9d:02:4c:1a fcid 0x3f0001 dynamic! [icef1-st1a_1b]vsan 102 wwn 50:0a:09:83:88:12:85:b3 fcid 0x3f0020 dynamicvsan 102 wwn 50:0a:09:82:8d:02:4c:1a fcid 0x3f0021 dynamic! [icef1-st1b_1b]vsan 102 wwn 22:cb:54:7f:ee:23:8b:3f fcid 0x3f0040 dynamicvsan 102 wwn 20:00:00:25:b5:01:0b:1f fcid 0x3f0041 dynamic! [VM-Host-Infra-02_B]vsan 102 wwn 20:00:00:25:b5:01:0b:0f fcid 0x3f0042 dynamic! [VM-Host-Infra-01_B]interface port-channel10description vPC peer-linkswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3176spanning-tree port type networkvpc peer-linkinterface port-channel11description icef1-st1aswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 102,3170spanning-tree port type edge trunkvpc 11interface port-channel12description icef1-st1bswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 102,3170spanning-tree port type edge trunkvpc 12interface port-channel13description icef1-uc1-Aswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3175spanning-tree port type edge trunkvpc 13interface port-channel14description icef1-uc1-Bswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3175spanning-tree port type edge trunkvpc 14interface port-channel15description icef1-uc1-B:FCoEswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 102spanning-tree port type edge trunkinterface port-channel20description icecore Uplinkswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3175spanning-tree port type networkvpc 20interface vfc11bind interface Ethernet1/1switchport trunk allowed vsan 102switchport description icef1-st1a:1bno shutdowninterface vfc12bind interface Ethernet1/2switchport trunk allowed vsan 102switchport description icef1-st1b:1bno shutdowninterface vfc15bind interface port-channel15switchport trunk allowed vsan 102switchport description icef1-uc1-B:FCoEno shutdownvsan databasevsan 102 interface vfc11vsan 102 interface vfc12vsan 102 interface vfc15interface Ethernet1/1description icef1-st1a:e1bswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 102,3170channel-group 11 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/2description icef1-st1b:e1bswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 102,3170channel-group 12 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/3interface Ethernet1/4interface Ethernet1/5interface Ethernet1/6interface Ethernet1/7interface Ethernet1/8interface Ethernet1/9interface Ethernet1/10interface Ethernet1/11description icef1-uc1-A:1/20switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3175channel-group 13 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/12description icef1-uc1-B:1/20switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3175channel-group 14 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/13description icef1-sw1:1/13switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3176channel-group 10 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/14description icef1-sw1:1/14switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3170,3173-3176channel-group 10 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/15description icef1-1110x-1:Eth2switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk allowed vlan 3175-3176spanning-tree port type edge trunkspeed 1000interface Ethernet1/16description icef1-1110x-2:Eth2switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk allowed vlan 3175-3176spanning-tree port type edge trunkspeed 1000interface Ethernet1/17interface Ethernet1/18interface Ethernet1/19interface Ethernet1/20description icecore:Eth1/8 Uplinkswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 3175spanning-tree port type networkchannel-group 20 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/21interface Ethernet1/22interface Ethernet1/23interface Ethernet1/24interface Ethernet1/25interface Ethernet1/26interface Ethernet1/27interface Ethernet1/28interface Ethernet1/29interface Ethernet1/30interface Ethernet1/31description icef1-uc1-B:1/31switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 102channel-group 15 mode activeinterface Ethernet1/32description icef1-uc1-B:1/32switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk native vlan 2switchport trunk allowed vlan 102channel-group 15 mode activeinterface mgmt0ip address 192.168.171.70/24line consoleline vtyboot kickstart bootflash:/n5000-uk9-kickstart.5.2.1.N1.3.binboot system bootflash:/n5000-uk9.5.2.1.N1.3.bin!Full Zone Database Section for vsan 102zone name VM-Host-Infra-01_B vsan 102member pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:01:0b:0f! [VM-Host-Infra-01_B]member pwwn 50:0a:09:82:9d:02:4c:1a! [icef1-st1a_1b]member pwwn 50:0a:09:82:8d:02:4c:1a! [icef1-st1b_1b]zone name VM-Host-Infra-02_B vsan 102member pwwn 20:00:00:25:b5:01:0b:1f! [VM-Host-Infra-02_B]member pwwn 50:0a:09:82:9d:02:4c:1a! [icef1-st1a_1b]member pwwn 50:0a:09:82:8d:02:4c:1a! [icef1-st1b_1b]zoneset name FlexPod vsan 102member VM-Host-Infra-01_Bmember VM-Host-Infra-02_Bzoneset activate name FlexPod vsan 102