Table Of Contents
Advanced Inter-VSAN Routing Configuration
Advanced IVR Configuration Task List
Configuring IVR Service Groups
Autonomous Fabric ID Guidelines
IVR Without IVR NAT or IVR Auto Topology Mode
IVR Without IVR NAT or IVR Auto Topology Guidelines
Manually Configuring and Activating an IVR Topology
Manual Configuration Guidelines
Manually Configuring an IVR Topology
Activating a Manually Configured IVR Topology
Working with Existing IVR Topologies
Clearing a Manually Configured IVR Topology Database
Migrating from IVR Auto Topology Mode to IVR Manual Topology Mode
Configuring Persistent FC IDs for IVR
Advanced IVR Zones and IVR Zone Sets
IVR Zone Configuration Guidelines
Configuring LUNs in IVR Zoning
Renaming IVR Zones and IVR Zone Sets
Configuring IVR Using Read-Only Zoning
Enabling Advanced Fabric Services on IVR Flows
Configuration Guidelines and Restrictions
Advanced Inter-VSAN Routing Configuration
This chapter provides advanced configuration information and instructions. Before setting up advanced IVR configurations, see Chapter 1, "Basic Inter-VSAN Routing Configuration," includes basic configuration instructions and descriptions of IVR features, limits, and terminology.
This chapter includes the following sections:
•
Advanced IVR Configuration Task List
•
IVR Without IVR NAT or IVR Auto Topology Mode
•
Manually Configuring and Activating an IVR Topology
•
Working with Existing IVR Topologies
•
Advanced IVR Zones and IVR Zone Sets
•
Enabling Advanced Fabric Services on IVR Flows
Advanced IVR Configuration Task List
To configure an advanced IVR topology in a SAN fabric, follow these steps:
Step 1
Determine whether or not to use IVR Network Address Translation (NAT).
See "IVR Network Address Translation" on page 1-4 and "IVR NAT Requirements and Guidelines" on page 1-10.
Step 2
If you do not plan to use IVR NAT, verify that unique domain IDs are configured in all switches and VSANs participating in IVR.
Step 3
Enable IVR in the border switches.
See "Configuring IVR and IVR Zones Using the IVR Zone Wizard" on page 1-6
Step 4
Configure the service group as required.
Step 5
Configure the IVR distribution as required.
Step 6
Configure the IVR topology, either manually or automatically.
See"Manually Configuring and Activating an IVR Topology" on page 2-8 and "Basic IVR Configuration" on page 1-6.
Step 7
Create and activate IVR zone sets in all of the IVR-enabled border switches, either manually or using fabric distribution.
Advanced IVR Configuration
This section includes instructions on advanced IVR configurations. It includes the following topics:
IVR Service Groups
In a complex network topology, you might only have a few IVR-enabled VSANs. To reduce the amount of traffic to non-IVR-enabled VSANs, you can configure service groups that restrict the traffic to the IVR-enabled VSANs. A maximum of 16 IVR service groups are allowed in a network. When a new IVR-enabled switch is added to the network, you must update the service groups to include the new VSANs.
This section includes the following information on service groups:
•
Configuring IVR Service Groups
Service Group Guidelines
When configuring IVR service groups, consider these guidelines:
•
If you use service groups with IVR auto topology mode, you should enable IVR and configure your service groups first, then distribute them with CFS before setting the IVR auto topology mode.
•
The CFS distribution is restricted within the service group only when the IVR VSAN topology is in IVR auto topology mode. See "IVR VSAN Topology" on page 1-5.
•
You can configure as many as 16 service groups in a network.
•
When a new IVR-enabled switch is added to the network, you must update the service group to include the new VSANs.
•
The same VSAN and AFID combination cannot be a member of more than one service group, otherwise, a CFS merge will fail.
•
The total number of AFID and VSAN combinations in all the service groups combined cannot exceed 128. The maximum number of AFID and VSAN combinations in a single service group is 128.
•
The IVR service group configuration is distributed in all IVR-enabled switches. IVR data traffic between two end devices belonging to a service group stays within that service group. For example, two members (for example, pWWN 1 and pWWN 2) cannot communicate if they belong to the same IVR zone and they belong to different service groups.
•
During a CFS merge, service groups with the same name would be merged, as long as there are no conflicts with other service groups.
•
If the total number of service groups exceeds 16 during a CFS merge, the CFS merge fails.
•
CFS distributes service group configuration information to all reachable SANs. If you do not enable CFS distribution, you must ensure that the service group configuration is the same on all IVR-enabled switches in all VSANs.
•
IVR end devices belonging to an IVR service group are not exported to any AFID or VSAN outside of its service group.
•
When at least one service group is defined and an IVR zone member does not belong to the service group, that IVR zone member is not able to communicate with any other device.
•
The default service group ID is zero (0).
Default Service Group
All AFID and VSAN combinations that are part of an IVR VSAN topology but are not part of any user-defined service group are members of the default service group. The identifier of the default service group is 0.
By default, IVR communication is permitted between members of the default service group. You can change the default policy to deny. To change the default policy, see "Configuring IVR Service Groups" on page 2-3. The default policy is not part of ASCII configuration.
Service Group Activation
A configured service group must be activated. Like zone set activation or VSAN topology activation, the activation of a configured service group replaces the currently active service group, if any, with the configured one. There is only one configured service group database and one active service group database. Each of these databases can have up to 16 service groups.
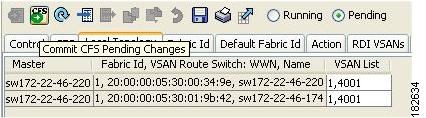
Configuring IVR Service Groups
To configure an IVR service group using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand All VSANs and then select IVR in the Logical Domains pane.
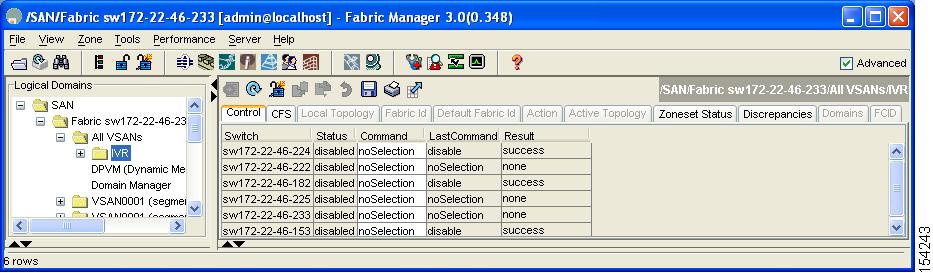
You see the IVR configuration in the Information pane (see Figure 2-1).
Figure 2-1 IVR Routing Configuration Control Tab
Step 2
Click the Service Group tab to display the existing service groups.
Step 3
Click the Create Row icon to make a new service group.
You see the service group dialog box.
Step 4
Check the switch check box for each switch involved in IVR.
Step 5
Complete the Name field for the service group and fill in the Fabric ID field for this entry.
Step 6
Enter a comma-separated list of VSAN IDs in the VSAN List text box.
Step 7
Click Create to create this entry or click Cancel to discard all changes.
Step 8
Repeat Step 1 through Step 7 for all switches and AFIDs associated with your IVR topology.
Autonomous Fabric IDs
The autonomous fabric ID (AFID) distinguishes segmented VSANS (for example, two VSANs that are logically and physically separate but have the same VSAN number). Cisco Fabric Manager Release 4.2(1) supports AFIDs 1 through 64. AFIDs are used in conjunction with IVR auto topology mode to allow segmented VSANs in the IVR VSAN topology database.
This section includes the following information about AFIDs:
•
Autonomous Fabric ID Guidelines
Autonomous Fabric ID Guidelines
You can configure AFIDs individually for VSANs, or you can set the default AFIDs for all VSANs on a switch. If you configure an individual AFID for a subset of the VSANs on a switch that has a default AFID, that subset uses the configured AFID while all other VSANs on that switch use the default AFID.
You can only use an AFID configuration when the VSAN topology is in IVR auto topology mode. In IVR manual topology mode, the AFIDs are specified in the VSAN topology configuration itself and a separate AFID configuration is not needed.
Note
Two VSANs with the same VSAN number but different AFIDs are counted as two VSANs out of the total 128 VSANs allowed in the fabric.
When devices attached to multiple switches belong to one VSAN, they cannot communicate with each other by configuring the regular zone set because the AFIDs are different. You can consider that the different AFIDs are different fabrics; therefore, the three switches represent three separate fabrics.
Configuring Default AFIDs
To configure default AFIDs using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand All VSANs and then select IVR in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the IVR configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the Default Fabric ID tab to display the existing default AFIDs.
Step 3
Click the Create Row icon to create a default AFID.
Step 4
Check the check boxes next to each switch involved in IVR that you want to use this default AFID.
Step 5
Provide a name for each SwitchWWN and set the default Fabric ID.
Step 6
Click Create to create this entry.
Step 7
Repeat Step 1 through Step 6 for all default AFIDs that you want to configure in your IVR topology.
Configuring Individual AFIDs
To configure individual AFIDs using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand All VSANs and then select IVR in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the IVR configuration in the Information pane.
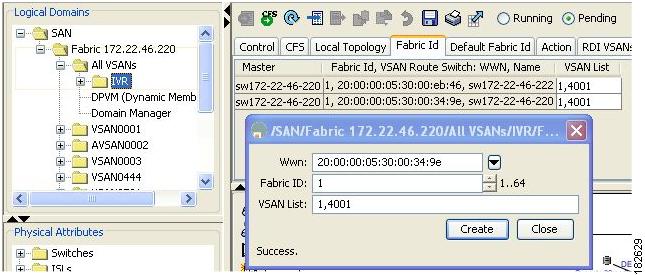
Figure 2-2 Fabric ID Tab
Step 2
Click the Fabric ID tab to display the existing AFIDs (see Figure 2-2).
Step 3
Click the Create Row icon to create an AFID.
Step 4
Check the check box next to each switch involved in IVR that you want to use this default AFID.
Step 5
Provide a name for each SwitchWWN and set the Fabric ID.
Step 6
Enter a comma-separated list of VSAN IDs in the VSAN List text box.
Step 7
Click Create to create this entry.
Step 8
Repeat Step 1 through Step 6 for all switches and AFIDs you want to configure in your IVR topology.
IVR Without IVR NAT or IVR Auto Topology Mode
This section includes the following sections on IVR without IVR NAT or IVR auto topology mode:
•
IVR Without IVR NAT or IVR Auto Topology Guidelines
•
Manually Configuring an IVR Topology
IVR Without IVR NAT or IVR Auto Topology Guidelines
Before configuring an IVR SAN fabric without IVR in NAT mode or IVR auto topology mode, consider the following general guidelines:
•
Acquire a mandatory Enterprise License Package or SAN-EXTENSION license package and one active IPS card for this feature.
•
If you change an FSPF link cost, ensure that the FSPF path distance (the sum of the link costs on the path) of any IVR path is less than 30,000.
•
IVR-enabled VSANs can be configured when an interop mode is enabled or disabled.
This section also includes the following:
Domain ID Guidelines
Before configuring domain IDs, consider the following guidelines:
•
Configure unique domain IDs across all VSANs and switches participating in IVR operations if you are not using IVR NAT. The following switches participate in IVR operations:
–
All edge switches in the edge VSANs (source and destination)
–
All switches in transit VSANs
•
Minimize the number of switches that require a domain ID assignment. This ensures minimum traffic disruption.
•
Minimize the coordination between interconnected VSANs when configuring the SAN for the first time as well as when you add each new switch.
You can configure domain IDs using one of two options:
•
Configure the allowed-domains list so that the domains in different VSANs are non-overlapping on all participating switches and VSANs.
•
Configure static, non-overlapping domains for each participating switch and VSAN.
Note
In a configuration involving IVR without NAT, if one VSAN in the IVR topology is configured with static domain IDs, then the other VSANs (edge or transit) in the topology must be configured with static domain IDs.
Transit VSAN Guidelines
Before configuring transit VSANS, consider the following guidelines:
•
Besides defining the IVR zone membership, you can choose to specify a set of transit VSANs to provide connectivity between two edge VSANs:
–
If two edge VSANs in an IVR zone overlap, then a transit VSAN is not required (though, not prohibited) to provide connectivity.
–
If two edge VSANs in an IVR zone do not overlap, you may need one or more transit VSANs to provide connectivity. Two edge VSANs in an IVR zone will not overlap if IVR is not enabled on a switch that is a member of both the source and destination edge VSANs.
•
Traffic between the edge VSANs only traverses through the shortest IVR path.
•
Transit VSAN information is common to all IVR zone sets. Sometimes, a transit VSAN can also act as an edge VSAN in another IVR zone.
Border Switch Guidelines
Before configuring border switches, consider the following guidelines:
•
Configure IVR only in the relevant border switches.
•
Border switches require Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 1.3(1) or later.
•
A border switch must be a member of two or more VSANs.
•
A border switch that facilitates IVR communications must be IVR enabled.
•
IVR can also be enabled on additional border switches to provide redundant paths between active IVR zone members.
•
The VSAN topology configuration must be updated before a border switch is added or removed.
Configuring IVR Without NAT
To enable IVR without NAT using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand All VSANs and then select IVR in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the IVR configuration in the Information pane.
Figure 2-3 Action Tab
Step 2
Click the Action tab.
Step 3
Uncheck the Enable IVR NAT check box (see Figure 2-3).
Step 4
Click the Apply Changes icon to distribute this change to all switches in the fabric.
Manually Configuring and Activating an IVR Topology
You must create the IVR topology on every IVR-enabled switch in the fabric if you have not enabled IVR auto topology mode. To use IVR manual topology mode, follow the instructions in this section.
This section includes the following:
•
Manual Configuration Guidelines
•
Manually Configuring an IVR Topology
•
Activating a Manually Configured IVR Topology
Manual Configuration Guidelines
Consider the following guidelines when using IVR manual topology mode:
•
You can configure a maximum of 128 IVR-enabled switches and 128 distinct VSANs in an IVR topology (see "Database Merge Guidelines" on page 1-23).
•
You will need to specify the IVR topology using the following information:
–
The switch WWNs of the IVR-enabled switches.
–
A minimum of two VSANs to which the IVR-enabled switch belongs.
–
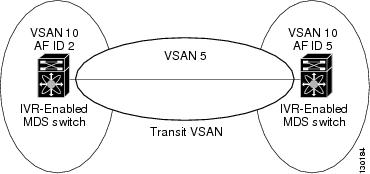
The AFID, which distinguishes two VSANs that are logically and physically separate, but have the same VSAN number. You can specify up to 64 AFIDs. See Figure 2-4.
Figure 2-4 Example IVR Topology with Non-Unique VSAN IDs Using AFIDs
•
If two VSANs in an IVR topology have the same VSAN ID and different AFIDs, they count as two VSANs for the 128-VSAN limit for IVR.
•
The use of a single AFID does not allow for segmented VSANs in an inter-VSAN routing topology.
Manually Configuring an IVR Topology
You can configure IVR using the IVR tables in the Information pane in Fabric Manager. Use these tables only if you are familiar with all IVR concepts. We recommend you configure IVR using the IVR Wizard. See "Configuring IVR and IVR Zones Using the IVR Zone Wizard" on page 1-6.
Note
Most tabs in the Information pane for features using CFS are dimmed until you click the CFS tab. The CFS tab shows which switches have CFS enabled and shows the master switch for this feature. Once the CFS tab is clicked, the other tabs in the Information pane are activated.
To manually configure an IVR topology using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand All VSANs and then select IVR in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the IVR configuration in the Information pane.
Figure 2-5 Local Topology Tab
Step 2
Click the Local Topology tab to display the existing IVR topology.
Step 3
Click the Create Row icon to create rows in the IVR topology (see Figure 2-5).
Step 4
Select the switch, switch WWN, and a comma-separated list of VSAN IDs for this topology.
Step 5
Click Create to create this new row.
Step 6
Click the Apply Changes icon to create the IVR topology.
Repeat this configuration on all IVR-enabled switches or distribute the IVR configuration using CFS.
Tip
Transit VSANs are deduced based on your configuration. The IVR feature does not have an explicit transit-VSAN configuration.
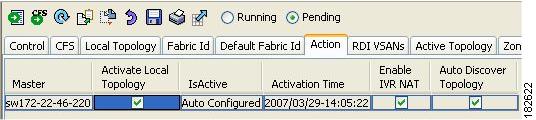
Activating a Manually Configured IVR Topology
After manually configuring the IVR topology, you must activate it.
CautionActive IVR topologies cannot be deactivated. You can only switch to IVR auto topology mode.
To activate a manually configured IVR topology using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand All VSANs and then select IVR in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the IVR configuration in the Information pane.
Figure 2-6 Action Tab
Step 2
Click the Action tab to display the existing IVR topology.
Step 3
Check the Activate Local Topology check box (see Figure 2-6).
Step 4
Click the Apply Changes icon to activate the IVR topology.
Working with Existing IVR Topologies
This section includes advanced IVR configurations for existing IVR topologies:
•
Clearing a Manually Configured IVR Topology Database
•
Migrating from IVR Auto Topology Mode to IVR Manual Topology Mode
Clearing a Manually Configured IVR Topology Database
To clear a manually created IVR topology database using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand All VSANs and then select IVR in the Logical Domains pane.
Step 2
Click the Control tab if it is not already displayed.
Step 3
Highlight the rows you want to delete from the IVR topology.
Step 4
Click the Delete Row icon to delete these rows from the IVR topology.
Step 5
Click the Apply Changes icon to delete the IVR topology.
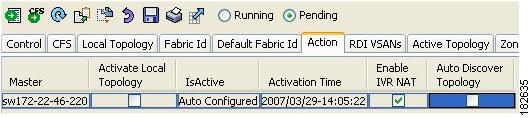
Migrating from IVR Auto Topology Mode to IVR Manual Topology Mode
If you want to migrate from IVR auto topology mode to IVR manual topology mode, copy the active IVR VSAN topology database to the user-configured IVR VSAN topology database before switching modes.
To migrate from IVR auto topology mode to IVR manual topology mode using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand All VSANs and then select IVR in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the IVR configuration in the Information pane.
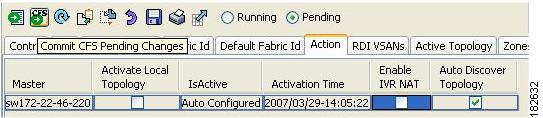
Figure 2-7 Action Tab
Step 2
Click the Action tab.
Step 3
Highlight the switch on which you want to disable IVR auto topology mode.
Step 4
Uncheck the Auto Discover Topology check box (see Figure 2-7).
Step 5
Click the Apply Changes icon.
Persistent FC IDs for IVR
This section includes the following information:
•
Configuring Persistent FC IDs for IVR
FC ID Features and Benefits
FC ID persistence improves IVR management by providing the following features:
•
Allows you to control and assign a specific virtual domain to use in a native VSAN.
•
Allows you to control and assign a specific virtual FC ID for a device.
The benefits of persistent FC IDs for IVR are as follows:
•
Host devices always see the same FC ID for targets.
•
FC IDs help you plan your SAN layout better by assigning virtual domains for IVR to use.
•
FC IDs can make SAN monitoring and management easier. When you see the same domain or FC ID consistently assigned, you can readily determine the native VSAN or device to which it refers.
FC ID Guidelines
Before configuring persistent FC IDs, consider the following:
•
You can configure two types of database entries for persistent IVR FC IDs:
–
Virtual domain entries—Contain the virtual domain that should be used to represent a native VSAN in a specific VSAN (current VSAN). Virtual domain entries contain the following information:
Native AFID
Native VSAN
Current AFID
Current VSAN
Virtual domain to be used for the native AFID and VSAN in current AFID and VSAN
–
Virtual FC ID entries—Contain the virtual FC ID that should be used to represent a device in a specific VSAN (current VSAN). Virtual FC ID entries contain the following information:
Port WWN
Current AFID
Current VSAN
Virtual FC ID to be used to represent a device for the given pWWN in the current AFID and VSAN
•
If you use persistent FC IDs for IVR, we recommend that you use them for all the devices in the IVR zone set. We do not recommend using persistent FC IDs for some of the IVR devices while using automatic allocation for other devices.
•
IVR NAT must be enabled to use IVR persistent FC IDs.
•
In an IVR NAT configuration, if one VSAN in the IVR topology is configured with static domain IDs, then the IVR domains that can be exported to that VSAN must also be assigned static domains.
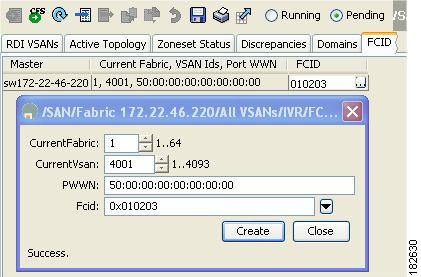
Configuring Persistent FC IDs for IVR
To configure persistent FC IDs for IVR using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand All VSANs and then select IVR in the Logical Domains pane.
You see the IVR configuration in the Information pane.
Figure 2-8 FCID Tab
Step 2
Click the FCID tab.
Step 3
Click the Create Row icon to create an FC ID (see Figure 2-8).
Step 4
Select the switch for which you are configuring the virtual FC ID to be used to represent a device in a specific VSAN (current VSAN).
Step 5
Enter the current fabric in the Current Fabric ID field for the fcdomain database.
Step 6
Enter the current VSAN in the Current VSAN ID field for the fcdomain database.
Step 7
Enter the pWWN.
Step 8
Click the drop-down menu to select the FC ID to map to the pWWN you selected.
Step 9
Click Create to create this new row.
Advanced IVR Zones and IVR Zone Sets
This section describes advanced configuration information for IVR zones and IVR zone sets. For basic information on configuring IVR zones and zone sets, see "IVR Zones and IVR Zone Sets" on page 1-14.
As part of the IVR configuration, you need to configure one or more IVR zone to enable cross-VSAN communication. To achieve this, you must specify each IVR zone as a set of (pWWN, VSAN) entries. Different IVR zone sets can contain the same IVR zone, because IVR zones can be members of one or more IVR zone sets.
Note
The same IVR zone set must be activated on all of the IVR-enabled switches.
CautionPrior to Cisco SAN-OS Release 3.0(3) you can only configure a total of 10,000 zone members on all switches in a network. As of Cisco SAN-OS Release 3.0(3) you can only configure a total of 20,000 zone members on all switches in a network. A zone member is counted twice if it exists in two zones. See "Database Merge Guidelines" on page 1-23.
This section includes the following topics:
•
IVR Zone Configuration Guidelines
•
Configuring LUNs in IVR Zoning
•
Configuring QoS for IVR Zones
•
Renaming IVR Zones and IVR Zone Sets
•
Configuring IVR Using Read-Only Zoning
IVR Zone Configuration Guidelines
When interop mode is enabled, consider the following IVR configuration guidelines:
•
When a member's native VSAN is in interop mode (for example, when the interop mode is 2, 3, or 4), then ReadOnly, the QoS attribute, and LUN zoning are not permitted.
•
When a member's VSAN is already in interop mode and an attempt is made to configure ReadOnly, the QoS attribute, or LUN zoning, a warning message is displayed to indicate that the configuration is not permitted.
•
When you configure ReadOnly, the QoS attribute, or LUN zoning first, and then change the member's VSAN interop mode, a warning message is displayed to indicate the configuration is not permitted. You are then prompted to change the configuration.
Configuring LUNs in IVR Zoning
LUN zoning can be used between members of active IVR zones.You can configure the service by creating and activating LUN zones between the desired IVR zone members in all relevant edge VSANs using the zoning interface or you can use LUN zoning directly supported by IVR. For more details on the advantages of LUN zoning, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family NX-OS Fabric Configuration Guide or the Cisco Fabric Manager Fabric Configuration Guide.
Note
You can configure LUN zoning in an IVR zone set setup.
Configuring QoS for IVR Zones
To configure QoS for an IVR zone using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Note
The default QoS attribute setting is low.
Step 1
Choose Zone > Edit Local Full Zone Database.
You see the Edit IVR Local Full Zone Database dialog box for the VSAN you selected.
Step 2
Select Zones or a zone set.
Step 3
Check the QoS check box and set the QoS priority.
Step 4
Click Activate to make the changes.
Renaming IVR Zones and IVR Zone Sets
To rename an IVR zone or IVR zone set, using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Choose Zone > Edit Local Full Zone Database.
You see the Edit IVR Local Full Zone Database dialog box for the VSAN you selected.
Step 2
Click a zone or zone set in the left pane.
Step 3
Choose Edit > Rename.
An edit box appears around the zone or zone set name.
Step 4
Enter a new name.
Step 5
Click Activate or Commit Changes.
Configuring IVR Using Read-Only Zoning
Read-only zoning (with or without LUNs) can be used between members of active IVR zones. To configure this service, you must create and activate read-only zones between the desired IVR zone members in all relevant edge VSANs using the zoning interface.
Note
Read-only zoning cannot be configured in an IVR zone set setup.
Enabling Advanced Fabric Services on IVR Flows
Advanced fabric services (such as SME and IOA) use fabric-wide FC-Redirect infrastructure to redirect the traffic flows. These services can now be enabled on IVR flows using an internal feature, Abstract ACL Manager (AAM).
The steps to enable this functionality is listed in the following sub-sections:
•
Configuration Guidelines and Restrictions
Configuration Guidelines and Restrictions
The following prerequisites must be considered before enabling AAM for IVR:
•
CFS distribution must be enabled for IVR.
•
AAM is supported only in IVR-NAT mode.
•
The switches where the fabric services (such as SME and IOA) are enabled must be running the AAM supported NX-OS release 5.0(1) or later.
•
FC-Redirect can be running in version 1 or version 2 mode.
•
AAM support for IVR must be enabled before enabling IVR support for FCR.
•
Generation 1 modules are not supported when IVR support is enabled for FCR. Specifically, ISLs should not be configured on Generation 1 modules, and the devices that support IVR for FCR should not be connected to Generation 1 modules.
•
LUN zoning is not supported when AAM is enabled for IVR.
•
IVR merge is supported only when both the fabrics have AAM enabled or both the fabrics have AAM disabled. The IVR merge will fail if one of the fabric has AAM enabled and the other fabric has AAM disabled.
•
You must delete all the advanced fabric service (SME and IOA) configurations for IVR devices and then disable IVR support for FCR before disabling AAM support for IVR.
•
Before downgrading to an earlier release to MDS NX-OS Release 5.0(1), you must delete all the advanced fabric service (SME and IOA) configurations for IVR devices, disable IVR support for FCR, and then disable AAM support for IVR.

 Feedback
Feedback