Table Of Contents
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
Configuring the Virtual N Port
Generating SCSI Disk Read/Write IO
Generating SCSI Tape Read/Write IO
Verifying the SAN Extension Tuner Configuration
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
The SAN Extension Tuner (SET) feature is unique to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family of switches. This feature helps you optimize FCIP performance by generating either direct access (magnetic disk) or sequential access (magnetic tape) SCSI I/O commands and directing such traffic to a specific virtual target. You can specify the size of the test I/O transfers and how many concurrent or serial I/Os to generate while testing. The SET reports the resulting I/Os per second (IOPS) and I/O latency, which helps you determine the number of concurrent I/Os needed to maximize FCIP throughput.
This chapter includes the following sections:
•
About the SAN Extension Tuner
•
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
•
Verifying the SAN Extension Tuner Configuration
About the SAN Extension Tuner
Note
SAN Extension Tuner is not supported on the Cisco Fabric Switch for HP c-Class BladeSystem, the Cisco Fabric Switch for IBM BladeCenter, and 16-Port Storage Services Node (SSN-16).
Note
As of Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 3.3(1a), SAN Extension Tuner is supported on the Multiservice Module (MSM) and the Multiservice Modular Switch.
Applications such as remote copy and data backup use FCIP over an IP network to connect across geographically distributed SANs. To achieve maximum throughput performance across the fabric, you can tune the following configuration parameters:
•
The TCP parameters for the FCIP profile (see "Window Management" section for more information).
•
The number of concurrent SCSI I/Os generated by the application.
•
The transfer size used by the application over an FCIP link.
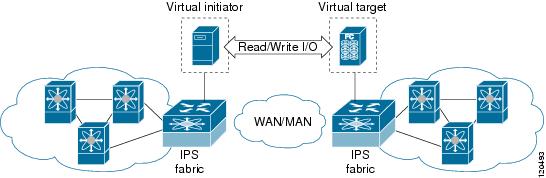
SET is implemented in IPS ports. When enabled, this feature can be used to generate SCSI I/O commands (read and write) to the virtual target based on your configured options (see Figure 3-1).
Figure 3-1 SCSI Command Generation to the Virtual Target
The SET feature assists with tuning by generating varying SCSI traffic workloads. It also measures throughput and response time per I/ O over an FCIP link.
Before tuning the SAN fabric, be aware of the following guidelines:
•
Following these implementation details:
–
The tuned configuration is not persistent.
–
The virtual N ports created do not register FC4 features supported with the name server. This is to avoid the hosts in the SAN from discovering these N ports as regular initiators or targets.
–
Login requests from other initiators in the SAN are rejected.
–
The virtual N ports do not implement the entire SCSI suite; it only implements the SCSI read and write commands.
–
Tuner initiators can only communicate with tuner targets.
•
Verify that the Gigabit Ethernet interface is up at the physical layer (GBIC and Cable connected—an IP address is not required).
•
Enable iSCSI on the switch (no other iSCSI configuration is required).
•
Create an iSCSI interface on the Gigabit Ethernet interface and enable the interface (no other iSCSI interface configuration is required)
See "Creating iSCSI Interfaces" section for more information.
•
Configure the virtual N ports in a separate VSAN or zone as required by your network.
•
Be aware that a separate VSAN with only virtual N ports is not required, but is recommended as some legacy HBAs may fail if logins to targets are rejected.
•
Do not use same Gigabit Ethernet interface to configure virtual N ports and FCIP links—use different Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. While this is not a requirement, it is recommended as the traffic generated by the virtual N ports may interfere with the performance of the FCIP link.
SAN Extension Tuner Setup
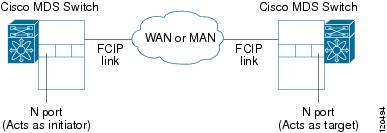
Figure 3-2 provides a sample physical setup in which the virtual N ports are created on ports that are not a part of the FCIP link for which the throughput and latency is measured.
Figure 3-2 N Port Tuning Configuration Physical Example
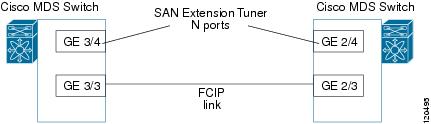
Figure 3-3 provides a sample logical setup in which the virtual N ports are created on ports that are not a part of the FCIP link for which the throughput and latency is measured.
Figure 3-3 Logical Example of N Port Tuning for a FCIP Link
Data Pattern
By default, an all-zero pattern is used as the pattern for data generated by the virtual N ports. You can optionally specify a file as the data pattern to be generated by selecting a data pattern file from one of three locations: the bootflash: directory, the volatile: directory, or the slot0: directory. This option is especially useful when testing compression over FCIP links. You can also use Canterbury corpus or artificial corpus files for benchmarking purposes.
License Prerequisites
To use the SET, you need to obtain the SAN_EXTN_OVER_IP license (see the Cisco Family NX-OS Licensing Guide).
Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner
This section includes the following topics:
•
Configuring the Virtual N Port
•
Generating SCSI Disk Read/Write IO
•
Generating SCSI Tape Read/Write IO
Tuning the FCIP Link
To tune the required FCIP link, follow these steps:
Step 1
Configure the nWWN for the virtual N ports on the switch.
Step 2
Enable iSCSI on the interfaces on which you want to create the N ports.
Step 3
Configure the virtual N ports on either side of the FCIP link.
Step 4
Ensure that the virtual N ports are not visible to real initiators in the SAN. You can use zoning (see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family NX-OS Fabric Configuration Guide) to segregate the real initiators. Ensure that the zoning configuration is set up to allow the virtual N ports to communicate with each other.
Step 5
Start the SCSI read and write I/Os.
Step 6
Add more N ports (as required) to other Gigabit Ethernet ports in the switch to obtain maximum throughput. One scenario that may require additional N ports is if you use FCIP PortChannels.
Enabling the Tuner
The tuning feature is disabled by default in all switches in the Cisco 9000 Family. When you enable this feature, tuning is globally enabled for the entire switch.
To enable the tuning feature, follow these steps:
Configuring nWWN
To configure the nWWNs for the tuner in this switch, follow these steps:
Configuring the Virtual N Port
To configure the virtual N port for tuning, follow these steps:
Generating SCSI Disk Read/Write IO
You can assign SCSI read and write commands on a one-time basis or on a continuous basis.
To generate SCSI read or write commands on a one-time basis, follow these steps:
To generate SCSI read or write commands continuously, follow these steps:
To specify a transfer ready size for a SCSI write command, follow these steps:
Generating SCSI Tape Read/Write IO
Note
Ensure that the zoning configuration is set up to allow the virtual N-ports to communicate with each other.
You can assign SCSI tape read and write commands on a one-time basis or on a continuous basis.
Note
There is only one outstanding I/O at a time to the virtual N-port that emulates the tape behavior.
To generate SCSI tape read and or write commands on a one-time basis, follow these steps:
To generate SCSI tape read or write commands continuously, follow these steps:
Configuring a Data Pattern
To optionally configure a data pattern for SCSI commands, follow these steps:
Verifying the SAN Extension Tuner Configuration
The show commands display the current SAN extension tuner settings for the Cisco MDS switch (see Examples 3-1 to 3-6).
Example 3-1 Displays Entries in the FLOGI Database
switch# show flogi database ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ INTERFACE VSAN FCID PORT NAME NODE NAME ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ iscsi1/1 200 0x050000 12:00:00:00:00:00:00:56 10:00:00:00:00:00:00:00Example 3-2 Displays Details for a VSAN Entry in the FLOGI Database
switch# show fcns database vsan 200VSAN 200-------------------------------------------------------------------------- FCID TYPE PWWN (VENDOR) FC4-TYPE:FEATURE -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0x020000 N 22:22:22:22:22:22:22:22 scsi-fcp0x050000 N 12:00:00:00:00:00:00:56 scsi-fcpExample 3-3 Displays All Virtual N Ports Configured on the Specified Interface
switch# show san-ext-tuner interface gigabitethernet 3/4 nport pWWN 12:00:00:00:00:00:00:56 vsan 200 countersStatistics for nportNode name 10:00:00:00:00:00:00:00 Port name 12:00:00:00:00:00:00:56I/Os per second : 148Read : 0%Write : 100%Ingress MB per second : 0.02 MBs/sec (Max -0.02 MBs/sec)Egress MB per second : 73.97 MBs/sec (Max -75.47 MBs/sec))Average Response time per I/O : Read - 0 us, Write - 13432 usMaximum Response time per I/O : Read - 0 us, Write - 6953 usMinimum Response time per I/O : Read - 0 us, Write - 19752 usErrors : 0Example 3-4 Displays N Ports Configured on a Specified Gigabit Ethernet Interface
switch# show san-ext-tuner interface gigabitethernet 3/1----------------------------------------------------------------------------Interface NODE NAME PORT NAME VSAN----------------------------------------------------------------------------GigabitEthernet3/1 10:00:00:00:00:00:00:00 10:00:00:00:00:00:00:01 91Example 3-5 Displays the Transfer Ready Size Configured for a Specified N Port
switch# show san-ext-tuner interface gigabitethernet 3/1 nport pWWN 10:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 vsan 91Node name : 10:00:00:00:00:00:00:00Port name : 10:00:00:00:00:00:00:01Transfer ready size : allExample 3-6 Displays All Virtual N Ports Configured in This Switch
switch# show san-ext-tuner nports----------------------------------------------------------------------------Interface NODE NAME PORT NAME VSAN----------------------------------------------------------------------------GigabitEthernet3/1 10:00:00:00:00:00:00:00 10:00:00:00:00:00:00:01 91Default Settings
Table 3-1 lists the default settings for tuning parameters.

 Feedback
Feedback