Contents
Migration Overview
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Prerequisites
- Existing FabricPath Topology
- Cisco Dynamic Fabric Automation Topology
- Traffic Flow Before and After Migration
Prerequisites
To prepare for migration to the Cisco Dynamic Fabric Automation (DFA) solution, you must meet the following prerequisites.
- Install and configure Cisco Data Center Network Manager 7.0
- Perform tasks specified in the DCNM 7.0 OVA Installation Guide
- Perform tasks specified in the DCNM 7.0 Fundamentals Guide
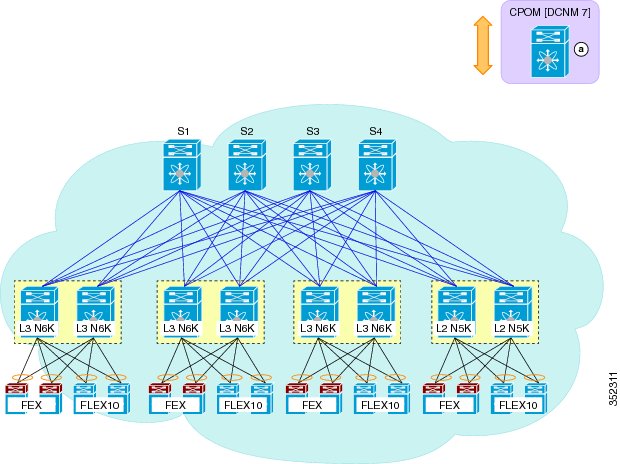
- FabricPath on Spine-Leaf Topology
- Nexus 7000 spine switches with NX-OS 6.2.(2) images
- Nexus 6000 border leaf switches with NX-OS 6.02.N2 images
- Nexus 6000 leaf switches with NX-OS 6.02.N2 images
NoteAll non-Nexus 6000 boxes must be physically replaced with Nexus 6000 boxes with NX-OS 7.0(0)N1(1).
- Nexus 1000v Series virtual switches at the virtual machine access layer
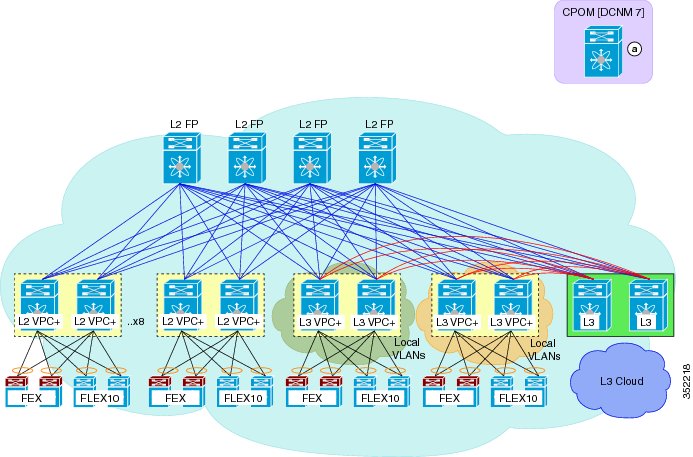
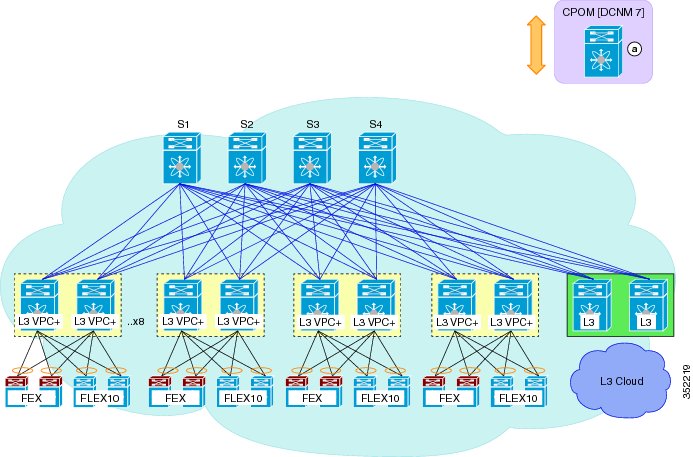
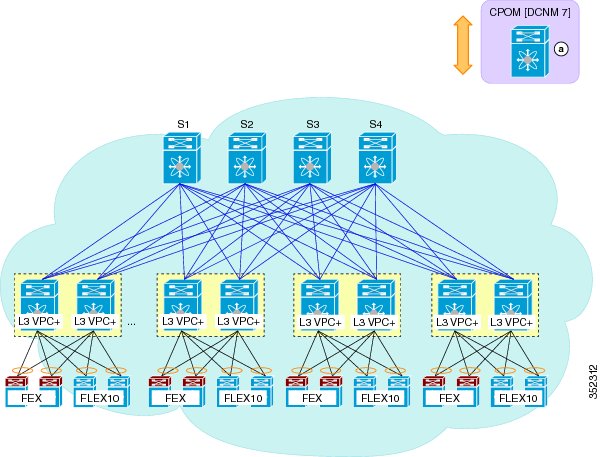
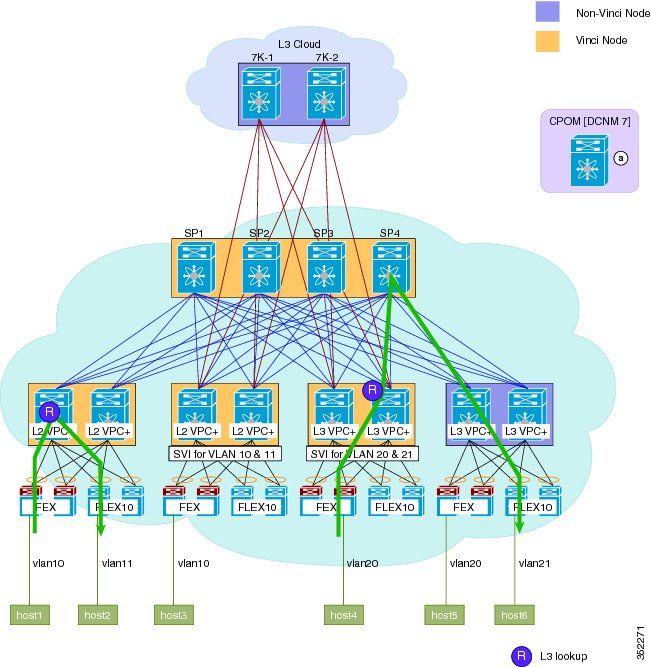
Cisco Dynamic Fabric Automation Topology
An illustration of the Cisco Dynamic Fabric Automation (DFA) topology is shown in the following figure.
You can structure your Cisco Dynamic Fabric Automation (DFA) topology with two distinct fabrics:The Cisco DFA fabric with both Nexus 5000 and 6000 leaves includes the following:
- Nexus 5000 remains as Layer 2
- Spine switches that can forward both 1q and 2q traffic, encapsulated in a FabricPath header
- On a Nexus 5000, the VLAN/SVI is non-Segment ID-enabled across all Cisco DFA leaves running anycast gateway mode on Nexus 6000 leaves. Border leaf runs HSRP/VRRP as well as anycast gateway
- On a Nexus 6000, the VLAN/SVI is Segment ID-enabled. The forwarding mode can be either proxy or anycast gateway.
- Multicast will continue to run in the legacy multicast mode. Cisco DFA multicast should not be turned on.
The DFA fabric with only Nexus 6000 leaves includes the following:
Traffic Flow Before and After Migration
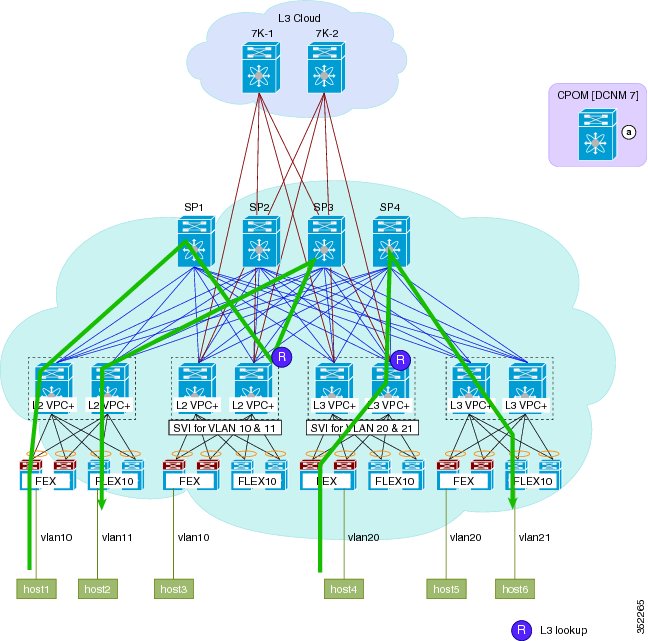
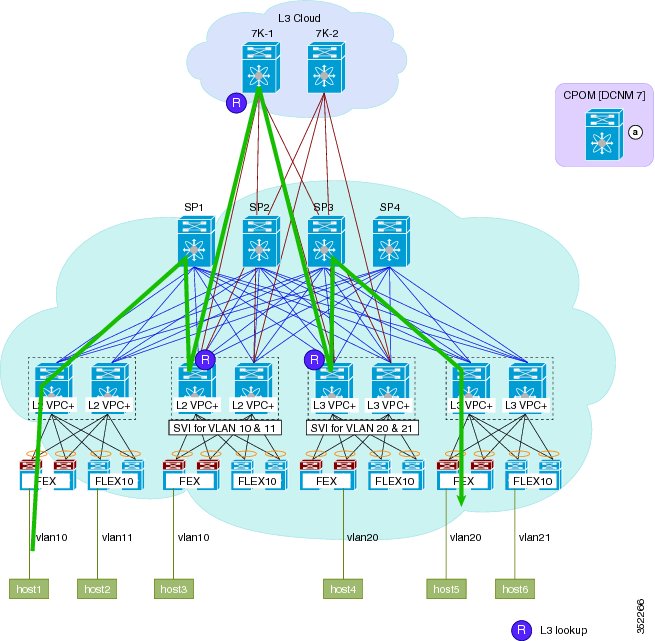
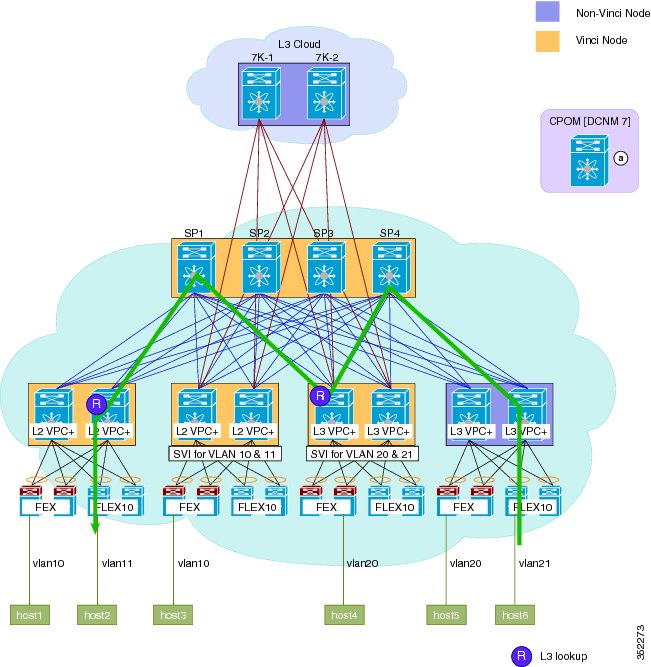
As a result of changes to the topology and configuration of switches, traffic flow is optimized after the migration. Differences in traffic flow are shown in the following set of figures:
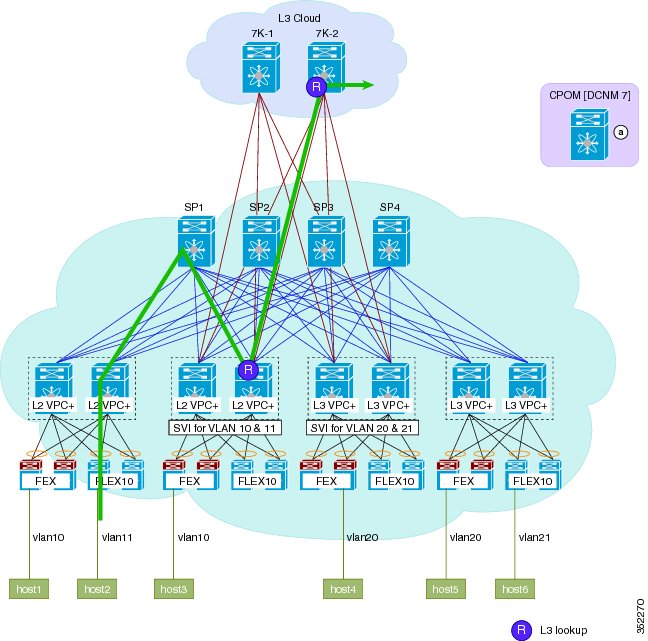
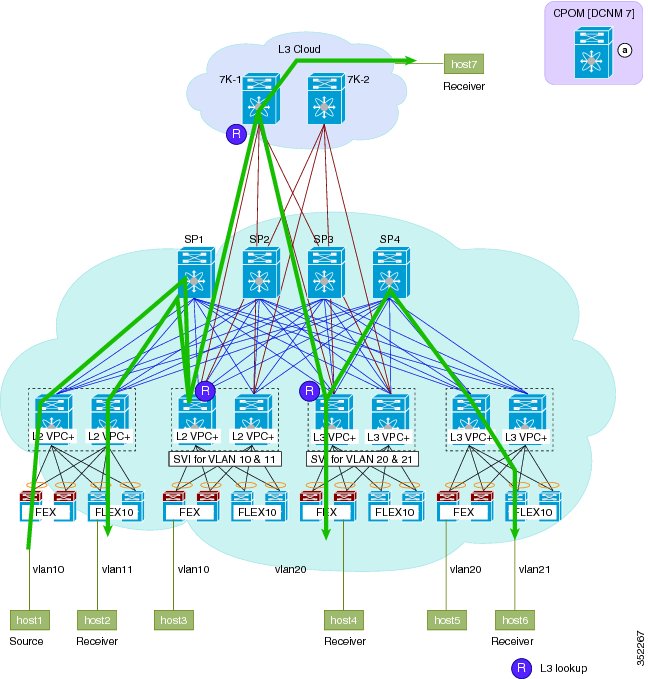
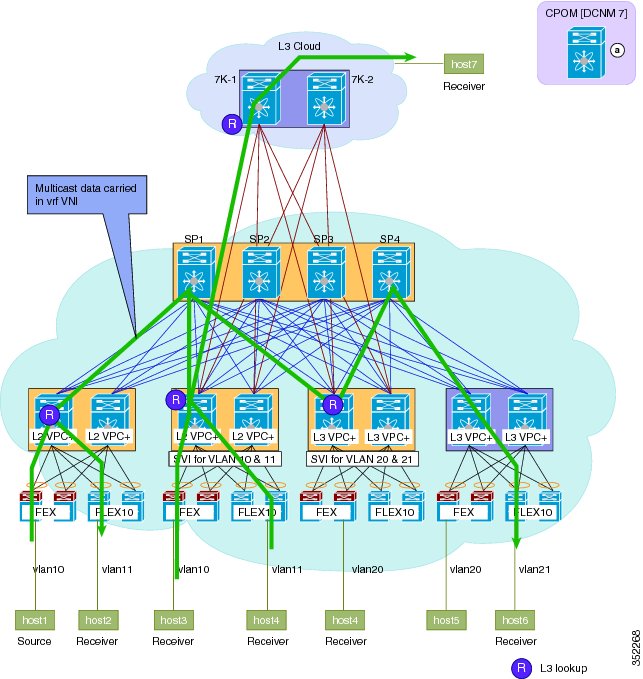
Figure 6. Figure: post-migration inter-vlan single hop . After migration to the Cisco DFA fabric, inter-Vlan traffic from Host 1 on Vlan 10 takes a single hop through a single leaf node, where a Layer 3 lookup is performed and traffic is routed to host 2 on Vlan 11. Border Leafs start to respond to address resolution protocol (ARP) with anycast gateway media access control (MAC).Figure 11. Figure: Pre-migration Multicast Traffic Flow. PIM-SM and multicast replication behavior is the same as a non-FabricPath topology. Layer 2 multicast forwarding follows a pruned FabricPath tree. Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is propagated to all FabricPath nodes via Intermediate-system to intermediate-system (ISIS).

 Feedback
Feedback