Table Of Contents
Managing and Troubleshooting NAC
Overview of Operational Checks
Cisco Secure ACS Logs and Troubleshooting
Cisco Secure ACS Passed Authentication Log
Cisco Secure ACS Failed Authentication Log
Cisco IOS Software Show Commands
Correcting a Blank or Incorrect Posture
Cisco IOS Software Clear Commands
Cisco IOS Software Debug Commands
Managing and Troubleshooting NAC
This chapter describes how to manage and troubleshoot NAC and includes the following sections:
Management and Reporting
The Cisco Security Information Management System (SIMS) is an integral part of a NAC deployment. SIMS is an important tool for monitoring the condition of the network where admission control is implemented. This section describes how to use SIMS for monitoring and reporting NAC activity, and includes the following topics:
SIMS Hardware Requirements
The recommended hardware requirements for a SIMS installation are a dual Xeon processor class machine with 2 GB of memory and 50 GB of disk space.
This machine requirement is for a system that receives 1,000 messages per second. If the load on the server is different, the characteristics of the system may be adjusted accordingly. To obtain installation procedures for the host operation system, RedHat Linux Enterprise v2.1, and the SIMS software, see the documentation provided with SIMS at the following website: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/rtrmgmt/cw2000/cw2000_b/sims/3_1_1/
Monitoring and Reporting
SIMS provides several features for monitoring and reporting NAC network activity. The NAC dashboard shown in Figure 3-1 provides a consolidated view of the state of the application software being monitored by the NAC system.
Figure 3-1 netForensics SIM Desktop
This window displays the percentage of compliant and non-compliant hosts, and average remediation times. Other available reports list the hosts subject to posture checking and summarize overall network compliance.
For information about using SIMS, see the netForensics User's Guide at the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/security_management/sims/3.1_appliance/install/guide/Implement.pdf.
Troubleshooting and Logging
NAC helps ensure that connected client machines are submitted to an access policy that specifies criteria for applications that must be met before the client machine is allowed network access.
By examining the various logs from CTA, the Cisco IOS software NAD, and Cisco Secure ACS, you can obtain a fairly accurate picture of the NAC activity on your network.
The SIMS server correlates the log messages from Cisco IOS software and from Cisco Secure ACS. The Cisco IOS software NAD also provides Cisco IOS software debug and show commands for monitoring and troubleshooting purposes.
Overview of Operational Checks
When a client in the healthy condition accesses the network, the posturing process takes place transparently. No user notification of the admission control process takes place unless a pop-up message has been configured in the Cisco Secure ACS database mapping section. If network access is not allowed but the client should have been assigned a Healthy condition, make sure that the client CTA services are currently in a started state in the Microsoft Services windows in the control panel, and that the CTA has successfully started a PEAP session with the Cisco Secure ACS. This can be determined by examining the CTA log file.
If PEAP does not start properly, check the certificate installation in both Cisco Secure ACS and CTA. If PEAP starts but an unexpected EAP type is shown in the CTA log file, make sure that the Allow CNAC check box has been checked under the Global Authentication Setup menu in Cisco Secure ACS System Configuration and that the Unknown user policy has been properly configured under the External User Database section of ACS. If a PEAP session is successfully started and the expected results are still not achieved, check the external user database policy configuration and rule sets. The received attribute values may be found in the logging and reporting section of the ACS Administrators screen.
CTA Logging
To start CTA logging, run the ctalogd enable command from the command-line interface (CLI) in the directory where CTA is installed. After running this command, ctalogd writes a trace of its current activity into the following directory:
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Cisco Systems\CiscoTrustAgent\Logs
For sample output from a CTA logging session, see CTA Logging Output, page A-4.
Cisco Secure ACS Logs and Troubleshooting
The passed and failed authentication .csv files log files, which are created by Cisco Secure ACS, are of particular interest to NAC administrators. If properly configured, these logs contain the attribute values that are present in the clients.
Cisco Secure ACS Passed Authentication Log
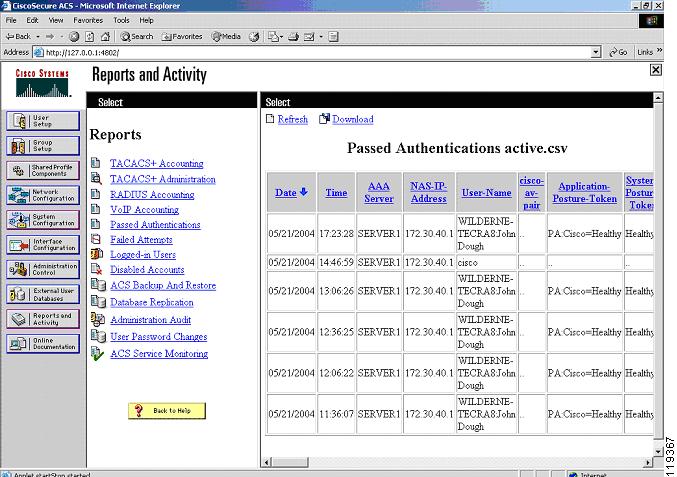
During the configuration process, Cisco Secure ACS is set up to log passed and failed authentications to comma-separated values (CSV) files. To access these files, use the Reports and Activity option from the Secure ACS main menu. During the rule configuration, view these files frequently to verify the attribute values being sent to Cisco Secure ACS in the received credentials.
To view the Reports and Activity window, complete the following steps:
Step 1
Click Reports and Activity from the Cisco Secure ACS main menu.
Step 2
Click CSV Passed Authentications in the window that is displayed.
The system displays the window shown in Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2 Reports and Activity
The current admission control session appears in the passed authentications file even if the client was posture checked into an unhealthy state. This is because the posturing process has completed successfully.
Pay special attention to the Reason field in the log file, because this shows the particular instance of the NAC external user database, the policy, and the specific rule in the policy that was matched to produce the SPT.
Cisco Secure ACS Failed Authentication Log
Some useful information may not be written to the failed log file because of the unknown state that a client may be in when the authentication for NAC fails. This information might include the credentials Cisco Secure ACS was expecting to receive as well as the attribute values contained in the credentials.
Some of the reasons a client admission control attempt appears in the failed attempts log include the following:
•
The set of NAC external user databases configured may not have a set of mandatory credentials that matches the set of received credentials from that client.
•
The NAD may not have been configured properly in Cisco Secure ACS.
Cisco IOS Software Commands
Cisco IOS software contains show, clear, and debug commands useful for verifying and troubleshooting NAC processes.
Cisco IOS Software Log Output
The following shows the console output from a router taking part in the admission control process with the eou logging command configured:
nac1751#May 13 13:05:16: %EOU-6-SESSION: IP=172.30.40.16| HOST=DETECTED| Interface=FastEthernet0/0May 13 13:05:16: %EOU-6-CTA: IP=172.30.40.16| CiscoTrustAgent=DETECTEDMay 13 13:05:18: %EOU-6-POLICY: IP=172.30.40.16| TOKEN=healthyMay 13 13:05:18: %EOU-6-POLICY: IP=172.30.40.16| ACLNAME=#Cisco Secure ACSACL#-IP-healthy-40a00ae9May 13 13:05:18: %EOU-6-POSTURE: IP=172.30.40.16| HOST=AUTHORIZED| Interface=FastEthernet0/0May 13 13:05:18: %EOU-6-AUTHTYPE: IP=172.30.40.16| AuthType=EAPMay 13 13:10:18: %EOU-6-SQ: IP=172.30.40.16| STATUSQUERY|VALIDATEDThe last line shows a single successful status query. These are informational level messages and are not normally seen by any logging device.
Cisco IOS Software Show Commands
The show eou all command displays a list of the currently detected hosts and their posture states if any.
nac1751#sh eou all------------------------------------------------------------------Address Interface AuthType Posture-Token Age(min)------------------------------------------------------------------172.30.40.16 FastEthernet0/0 EAP healthy 13This command may also be run with an IP address substituted for the all keyword to show the state of a single host.
show ip auth-proxy cache postureThe show ip access-list command displays the currently downloaded ACLs at the end of the output.
nac1751#sh ip access-listsStandard IP access list access10 deny 192.168.0.120 permit 192.168.0.0, wildcard bits 0.0.255.25530 permit 172.30.0.0, wildcard bits 0.0.255.25540 permit 172.31.0.0, wildcard bits 0.0.255.25550 deny anyExtended IP access list 101permit ip host 172.30.40.16 any (12 matches)10 permit ip any host 172.30.40.1 (1227 matches)Extended IP access list clientException10 permit ip any host 172.30.1.10Extended IP access list sl_def_acl10 deny tcp any any eq telnet log20 deny tcp any any eq www log30 deny tcp any any eq 22 log40 permit ip any any logExtended IP access list xCisco Secure ACSACLx-IP-healthy-40a00ae910 permit ip any anynac1751#In this example, the last access list is named xCisco Secure ACSACLx-IP-healthy-40a00ae9. This ACL has a single line, permit ip any any.
The first any in this ACL has been replaced by the IP address of the posture-checked client and the result has been placed over the top of the ACL (ACL 101 in this case) applied to the interface on the Cisco IOS software device taking part in the admission control process.
Correcting a Blank or Incorrect Posture
If the results of the show eou all or show eou ip address commands include postures that do not match the actual result of posture validation or display "-------" instead of a posture, the posture-token AV pair may be misconfigured in one or more groups in Cisco Secure ACS, or the group mapping may be misconfigured in the NAC database that processed the posture validation request.
If the posture displayed is "-------," the AAA client (the NAD) is not receiving the posture-token AV pair within a Cisco IOS/PIX RADIUS cisco-av-pair vendor-specific attribute (VSA). If the posture displayed does not correspond to the actual result of posture validation, the AAA client is receiving an incorrect value in the posture-token AV pair.
Check group mappings in the NAC database to verify that the correct user groups are associated with each system posture token (SPT). In the user groups configured for use with NAC, be sure that the Cisco IOS/PIX RADIUS cisco-av-pair VSA is configured correctly.
For example, in a group configured to authorize NAC clients receiving a Healthy SPT, be sure the [009\001] cisco-av-pair check box is checked and that the following string appears in the [009\001] cisco-av-pair text box:
posture-token=Healthy
EOU Commands
The following commands may be used to cause a re-initialization or a revalidation of any or all hosts on a network being subject to admission control:
eou initialize alleou initialize ip x.x.x.xeou revalidate alleou revalidate ip x.x.x.xThese commands are useful if a virus outbreak is detected and a new signature file is available. Client hosts that had already been successfully validated can be revalidated to immediately get the new signature file.
When a host is initialized, all previous state information about that host is deleted and the admission control process for that host starts with no state. When a host is revalidated, state information about that host is retained so that the host still has its current access during the revalidation process.
Cisco IOS Software Clear Commands
The Cisco IOS software clear eou command removes the state information regarding admission control about any or all hosts detected. This command can be used for specific IP addresses or for all the sessions on a specific router.
nac1751#clear eou allnac1751#May 13 13:18:47: %EOU-6-SESSION: IP=172.30.40.16| HOST=REMOVED| Interface=FastEthernet0/0Cisco IOS Software Debug Commands
The following debug commands are available for the various admission control components:
nac1751#debu eou ?all All EAPoUDP debugging messages turned oneap Debug EAP packetserrors Debug Errorsevents Debug Eventsobj-create Debug EAPoUDP Session Creationobj-destroy Debug EAPoUDP Session Destroyobj-link Debug EAPoUDP session addition to hash tableobj-unlink Debug EAPoUDP session removal from hash tablepackets Debug EAPoUDP packetsratelimit Debug Ratelimit Eventssm Debug EAPoUDP State Machine Eventsdebug eapFor sample debug output, see Admission Control Session Debug Output, page A-1.