Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Release Notes for Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client,
Release 2.3.nnnNew Features in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.2016
Using PPP Exclusion to Support AnyConnect over L2TP or PPTP
New Features in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.254
Allow AnyConnect Session from an RDP Session for Windows Users
New Syslog Message for Older or Non-Cisco Clients
Translation Templates and Upgrading the AnyConnect Client
New Features in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.185
Security Appliances and Software Supported
Interoperability Considerations
AnyConnect Client and Cisco Secure Desktop
Upgrading to AnyConnect Release 2.3
AnyConnect Client Disconnect Behavior
Where to Find the AnyConnect Client Files for Installation
Suggested Practice for the Position of the Windows Mobile Package on the Security Appliance
Before You Install the AnyConnect Client
Ensuring Automatic Installation of AnyConnect Clients
AnyConnect Client and New Windows 2000 Installations
Adding a Security Appliance to the List of Trusted Sites (IE)
Adding a Security Certificate in Response to Browser Alert Windows
Installing the AnyConnect Client on a System Running Windows
Installing Start Before Logon Components (Windows Only)
Differences Between Windows-Vista and Pre-Vista Start Before Logon
Fulfilling Requirements for Biarch Linux
Installing the AnyConnect Client on Linux
Installing the AnyConnect Client on Mac OS
Using the Standalone Install Procedure on Mac OS
Using the Manual Install Option on Mac OS if the Java Installer Fails during WebLaunch
Installing the AnyConnect Client on a Windows Mobile Device
Pushing the User Profile to the Client PC
Using the AnyConnect CLI Commands
Loading the AnyConnect Client and Configuring the Security Appliance with ASDM
Loading the AnyConnect Client and Configuring the Security Appliance with CLI
Disabling Permanent Client Installation
Enabling AnyConnect Client Profile Downloads
Enabling Start Before Logon for the AnyConnect Client
CSA Interoperability with the AnyConnect Client and Cisco Secure Desktop
Uninstalling the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client
Vista Routing and Remote Access Service Incompatibility
PC with Faulty Driver Blue-screens after AnyConnect Authentication
vpncli Process Exits During an Upgrade and Is Not Relaunched
XML Profile Enhancement for Selecting Windows Certificate Store
Certificate Enrollment Prompts Can Occur Twice
Using the AT&T Aircard with Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client
Usage Notes for AnyConnect VPN Client Release 2.3
Split-Exclude Tunneling Requires Enabling AllowLocalLanAccess in the AnyConnect Client
AutoReconnectBehavior Preference Defaults to DisconnectOnSuspend
Using Virtualization Software over a Tunnel with AnyConnect.
Microsoft Java is Not Supported from the AnyConnect WebLaunch
AnyConnect 2.3 Supports DEP Option
Avoiding Installation of an ActiveX Control in Pre-deployment Scenarios
Usage Notes From Earlier Releases
Network Connections Control Panel Might Show Generic Adapter Name
QoS Policing Does Not Apply to AnyConnect Connections
AnyConnect Client over Proxies
SSL VPN Clients Do Not Support DNS Fallback for Split Tunneling
Setting the Secure Connection (Lock) Icon
Cisco Security Agent Version Requirements
PC Wireless Client Configurations
Certificate Revocation List Processing
Dynamic Install Fails on Windows Vista When Running Low-rights Internet Explorer
AnyConnect Fails to Establish a DTLS Tunnel When Using RC4-MD5 Encryption
msvcp60.dll Must Be Available for Installation of the AnyConnect Client
Secure VPN Via Windows Remote Desktop Is Supported
AnyConnect Start Before Logon GINA Might Not Appear on Login Screen after Reboot
When Using a Client-Side Proxy and Full Tunneling, the Proxy Should Be Reset
Linux-Specific AnyConnect Client Issue
Setting the AnyConnect Pre-Login Banner
AnyConnect Requires That the ASA Be Configured to Accept TLSv1 Traffic
IPv6 AnyConnect Failover is Not Supported for the Security Appliance
RADIUS Interim Accounting Update Feature
AnyConnect Split-tunneling Works on Windows Vista
Selecting Crypto Toolkits for AnyConnect on Windows Platforms
First User Message for Double-byte Languages Does Not Translate Correctly
Ensuring Reliable DTLS (UDP) Connections Through Third-Party Firewalls
No AnyConnect Confirmation Dialog for Cisco Secure Desktop Users
AnyConnect Client Uses Custom-built OpenSSL Libraries Based on 0.9.8f
Optionally Disable Tearing Down Tunnel Upon Smartcard Removal
Upgrading Standalone AnyConnect Client for Windows Vista Shows Activity Indication
AnyConnect SBL Does Not Support Dialer and Third-Party Application Launchers
Start Before Logon and PLAP Require a Network Connection
Windows Machine Cannot Be Named localhost
Synchronizing a Mobile Device to a PC While a Tunnel Is Active
Obtaining a DHCP Ethernet IP If Connected via Wireless-only First
Open Caveats in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.2016
Open Caveats in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.254
Open Caveats in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.185
Caveats Resolved in AnyConnect Release 2.3.2016
Caveats Resolved in AnyConnect Release 2.3.254
Caveats Resolved by AnyConnect Release 2.3.185
Release Notes for Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client,
Release 2.3.nnn
Revised: May 24, 2010, OL-18325-18Introduction
These release notes are for the following Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client releases:
•
2.3.2016
•
2.3.254
•
2.3.185
The AnyConnect client provides remote users with secure VPN connections to the Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance using the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol and the Datagram TLS (DTLS) protocol.
The AnyConnect client provides remote end users running Microsoft Windows, Windows Mobile, Linux, and Mac OS X, with the benefits of a Cisco SSL VPN client, and supports applications and functions unavailable to a clientless, browser-based SSL VPN connection. In addition, the AnyConnect client supports connecting to IPv6 resources over an IPv4 network tunnel. This release supports the SSL and DTLS protocol. This release does not include IPsec support.
The client can be loaded on the security appliance and automatically downloaded to remote users when they log in, or it can be manually installed as an application on PCs by a network administrator. After downloading, it can automatically uninstall itself after the connection terminates, or it can remain on the remote PC for future SSL VPN connections.
The client includes the ability to create user profiles that are displayed in the user interface and define the names and addresses of host computers.
These release notes describe new features, limitations and restrictions, open and resolved caveats, and related documentation. They also include procedures you should follow before loading this release. The section Usage Notes describes interoperability considerations and other issues you should be aware of when installing and using the AnyConnect client. Read these release notes carefully prior to installing this software.
Contents
This document includes the following sections:
•
Upgrading to AnyConnect Release 2.3
New Features
The following sections describe the new features in the 2.3 releases:
•
New Features in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.2016
•
New Features in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.254
•
New Features in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.185
New Features in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.2016
AnyConnect VPN Client Release 2.3.2016 is primarily a quality improvement release; however, it does include the following new features.
Ignore Proxy
This feature lets you specify a policy in the AnyConnect profile to bypass the Internet Explorer proxy configuration settings on the user's PC. It is useful when the proxy configuration prevents the user from establishing a tunnel from outside the corporate network.
To enable Ignore Proxy, insert the following line into the <ClientInitialization> section of the AnyConnect profile (anyfilename.xml):
<ProxySettings>IgnoreProxy</ProxySettings>
Note
AnyConnect currently supports only the IgnoreProxy setting; it does not support the Native and Override settings in the new ProxySettings section within the <ClientInitialization> section of the XML schema (AnyConnectProfile.xsd).
Using PPP Exclusion to Support AnyConnect over L2TP or PPTP
AnyConnect Release 2.3.2016 introduces support for the L2TP and PPTP tunneling protocols used by ISPs in some countries, including Israel.
To send traffic destined for the ASA over a PPP connection, AnyConnect uses the point-to-point adapter generated by the external tunnel. When establishing a VPN tunnel over a PPP connection, AnyConnect must exclude traffic destined for the ASA from the tunneled traffic intended for destinations beyond the ASA. To specify whether and how to determine the exclusion route, use the PPPExclusion configuration option.
The exclusion route appears as a non-secured route in the Route Details display of the AnyConnect GUI.
The following sections describe how to set up PPP exclusion:
•
Instructing Users to Override PPP Exclusion
Configuring PPP Exclusion
By default, PPP Exclusion is disabled. AnyConnect Release 2.3.2016 does not provide Profile Editor support for editing the PPP Exclusion settings. To enable PPP exclusion, insert the PPPExclusion line shown below in bold into the <ClientInitialization> section of the AnyConnect profile (anyfilename.xml):
<AnyConnectProfile xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/encoding/" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/encoding/ AnyConnectProfile.xsd"><ClientInitialization><PPPExclusion UserControllable="true">Automatic</PPPExclusion></ClientInitialization><ServerList><HostEntry><HostName>DomainNameofASA</HostName><HostAddress>IPaddressOfASA</HostAddress></HostEntry></ServerList></AnyConnectProfile>The PPPExclusion UserControllable value true lets users read and change the PPP exclusion settings. If you want to prevent users from viewing and changing the PPP exclusion settings, change it to false.
AnyConnect supports the following PPPExclusion values:
•
Automatic—Enables PPP exclusion. AnyConnect automatically uses the IP address of the PPP server. Instruct users to change the value only if automatic detection fails to get the IP address.
•
Override—Also enables PPP exclusion. If automatic detection fails to get the IP address of the PPP server, and the PPPExclusion UserControllable value is true, instruct users to follow the instructions in the next section to use this setting.
•
Disabled—Disables PPP exclusion by forwarding all client traffic through the VPN tunnel.
To let users view and change the IP address of the security appliance used for PPP exclusion, add the PPPExclusionServerIP tag with its UserControllable value set to true, as shown in bold below:
<AnyConnectProfile xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/encoding/" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/encoding/ AnyConnectProfile.xsd"><ClientInitialization><PPPExclusion UserControllable="true">Automatic</PPPExclusion><PPPExclusionServerIP UserControllable="true"></PPPExclusionServerIP></ClientInitialization><ServerList><HostEntry><HostName>DomainNameofASA</HostName><HostAddress>IPaddressOfASA</HostAddress></HostEntry></ServerList></AnyConnectProfile>Instructing Users to Override PPP Exclusion
AnyConnect does not currently provide UI support for PPP exclusion. If automatic detection does not work, and the PPPExclusion UserControllable value is true, instruct the user to manually override PPP exclusion, as follows:
Step 1
Use an editor such as Notepad to open the AnyConnect (anyfilename.xml) file.
This file is on one of the following paths on the user's computer:
•
Windows: %LOCAL_APPDATA%\Cisco\Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client\anyfilename.xml. For example,
–
Windows Vista—C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Cisco\Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client\anyfilename.xml
–
Windows XP—C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Cisco\Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client\Profile\anyfilename.xml
•
Mac OS X: /Users/username/.anyconnect
•
Linux: /home/username/.anyconnect
Step 2
Insert the PPPExclusion details under <ControllablePreferences>, while specifying the Override value and the IP address of the PPP server. The address must be a well-formed IPv4 address. For example:
<AnyConnectPreferences><ControllablePreferences><PPPExclusion>Override<PPPExclusionServerIP>192.168.22.44</PPPExclusionServerIP></PPPExclusion></ControllablePreferences></AnyConnectPreferences>Step 3
Save the file.
Step 4
Exit and restart AnyConnect.
New Features in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.254
The AnyConnect client Release 2.3.1 includes one new feature and improvements to some existing features, as well as resolving numerous open caveats:
•
Windows users can now establish an AnyConnect session from a single Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) session.
•
In addition, the security appliance now issues a syslog message when an older Cisco VPN client or a non-Cisco client attempts a connection to the security appliance. This syslog message is configurable and is disabled by default.
•
This release includes new translation templates and a procedure for upgrading the AnyConnect client.
•
You can use the Java-based utility, Cisco AnyConnect Profile Editor - Beta, as an alternative to using ASDM to create AnyConnect profiles. After using it to create a profile, you can import it to the ASA for pushing to clients. Click the AnyConnectProfileEditor.zip link adjacent to "2.3.0254" on the AnyConnect VPN Client Software Download page, download and extract the file, then see the AnyConnectProfileEditor\jar\profileEditorHelp.rtf document for instructions.
Allow AnyConnect Session from an RDP Session for Windows Users
Some customers require the ability to log on to a client PC using Windows Remote Desktop and create a VPN connection to a secure gateway from within the Remote Desktop (RDP) session. This new feature allows a VPN session to be established from an RDP session. A split tunneling VPN configuration is required for this to function correctly. For information about split tunneling, see Cisco ASDM User Guide or Cisco ASA 5500 Series Command Line Configuration Guide Using the CLI.
The default settings for this feature retain the existing functionality: namely, a locally logged-on user can establish a VPN connection only when no other local user is logged in. The VPN connection is terminated when the user logs out, and additional local logons during a VPN connection result in the connection being torn down. Remote logons and logoffs during a VPN connection are unrestricted.
Note
With this new feature, the AnyConnect client disconnects the VPN connection when the user who established the VPN connection logs off. If the connection is established by a remote user, and that remote user logs off, then the VPN connection is terminated.
New preference settings in the AnyConnect profile dictate how Windows logons are treated at connection establishment and during the connection. These preferences are configurable only by the network administrator. They let customers configure the client to allow VPN connection establishment from an RDP session. The end-user does not see any changes in the AnyConnect client GUI as a result of this feature. Table 1 shows the new preferences.
Table 1 Windows Logon Preferences
WindowsLogonEnforcement
SingleLocalLogon
SingleLogon
WindowsVPNEstablishment
LocalUsersOnly
AllowRemoteUsers
Windows Logon Enforcement
The WindowsLogonEnforcement preference setting determines the behavior of the AnyConnect client when a user logs on to the client PC. The possible values for this preference setting are as follows:
•
SingleLocalLogon—(Default) Allows only one local user to be logged on during the entire VPN connection. This behavior is similar to, but not exactly the same as, the behavior in earlier releases. If more than one local user is logged on when the VPN connection is being established, the connection is not allowed. If a second local user logs on during the VPN connection, then the VPN connection is terminated.
With this setting, a local user can establish a VPN connection while one or more remote users are logged on to the client PC, but if the VPN connection is configured for all-or-nothing tunneling, then the remote logon is disconnected because of the resulting modifications of the client PC routing table for the VPN connection. If the VPN connection is configured for split-tunneling, the remote logon might or might not be disconnected, depending on the routing configuration for the VPN connection. The SingleLocalLogin setting has no effect on remote user logons from the enterprise network over the VPN connection.
•
SingleLogon—Allows only one user to be logged on during the entire VPN connection. If more than one user is logged on, either locally or remotely, when the VPN connection is being established, the connection is not allowed. If a second user logs on, either locally or remotely, during the VPN connection, the VPN connection is terminated.
When you select the SingleLogon setting, no additional logons are allowed during the VPN connection, so a remote logon over the VPN connection is not possible.
Windows VPN Establishment
The WindowsVPNEstablishment preference setting determines the behavior of the AnyConnect client when a user who is remotely logged on to the client PC establishes a VPN connection. The possible values are:
•
LocalUsersOnly—(Default) Prevents a remotely logged-on user from establishing a VPN connection. This is the same functionality as in prior versions of the AnyConnect client.
•
AllowRemoteUsers—Allows remote users to establish a VPN connection. However, if the configured VPN connection routing causes the remote user to become disconnected, the VPN connection is terminated to allow the remote user to regain access to the client PC.
Remote users must wait 90 seconds after VPN establishment if they want to disconnect their remote login session without causing the VPN connection to be terminated.
On Vista, the WindowsVPNEstablishment profile setting is not currently enforced during Start Before Logon (SBL). The AnyConnect client does not determine whether the VPN connection is being established by a remote user before logon; therefore, a remote user can establish a VPN connection via SBL even when the WindowsVPNEstablishment setting is LocalUsersOnly. Previous versions of AnyConnect also did not prevent this behavior.
New Syslog Message for Older or Non-Cisco Clients
The AnyConnect client, Releases higher than 2.3.0185, identifies itself as an official, proprietary implementation of the Cisco SSL tunneling protocol. You can configure the security appliance to issue a system log message when an unknown implementation attempts to connect. The message also appears when a version of the AnyConnect prior to 2.3.0185 or the legacy Cisco SSL VPN client connects.
%hostname-6-722053: Group <g> User <u> IP <ip> Unknown client <user-agent> connectionWhere:
•
g is the group-policy the user logged in on.
•
u is the username of the user.
•
ip is the public (i.e. Internet) IP address of the user.
•
user-agent is the user agent string from the client, indicating the version of the client the user is using.
For example:
%hostname-6-722053: Group <webvpn> User <sales> IP <1.2.3.4> Unknown client <Cisco AnyConnect VPN Agent for Windows 2.3.0185> connectionThis syslog can occur when an older, or non-supported, SSL VPN client has connected to the security appliance. Such clients include:
•
Cisco SSL VPN Client (SVC).
•
Cisco AnyConnect Client, Release 2.3.185 or earlier.
This message has no effect on whether the connection succeeds.
Configuration
This syslog is disabled by default. To enable this syslog on the console, do the following:
hostname(config)# logging enablehostname(config)# logging class svc console warningTo change the severity of this syslog to notification (5), do the following:
hostname(config)# logging message 722053 level notificationTo enable just this syslog, do the following:
hostname(config)# logging enablehostname(config)# logging message 722053 level emergencieshostname(config)# logging class svc console emergenciesTranslation Templates and Upgrading the AnyConnect Client
Occasionally, we add new messages displayed to AnyConnect users that provide helpful information about the client connection. To enable translation of these new messages, we create new message strings and include them in the translation template packaged with the latest client image. Therefore, if you upgrade to the latest available client, you also receive the template with the new messages. However, if you have created translation tables based on the template included with the previous client, the new messages are not automatically displayed to remote users. You must merge the latest template with your translation table.
Convenient tools exist to help you merge the template and the translation table. The tools and procedure are covered in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Administrator Guide, Merging a Newer Translation Template with your Translation Table, page 5-23.
New Features in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.185
The AnyConnect client Release 2.3 focuses on providing an improved user experience. This release includes the following new features:
•
AnyConnect support for the Windows Mobile OS touch-screen devices listed in "System Requirements" section for VPN connections to Cisco Series 5500 Adaptive Security Appliances. Although AnyConnect 2.3 is designed for compatibility with Windows Mobile 6.1, 6.0 and 5.0 Professional and Classic, Cisco supports only the devices it has specifically qualified and listed in that section.
Note
Windows Mobile requires an AnyConnect for Mobile license and must have ASA Release 8.0.3 or later running on the security appliance.
•
Machine certificate access for authentication (standalone mode only). Any logged-in user on the system in standalone mode can have access to available machine certificates, as well as to user certificates, for VPN authentication.
•
The AnyConnect client for Windows Mobile requires that a security appliance mobile license be installed. If the correct license is not installed, end user receives an error message.
•
Dynamic Updating of the user interface when changing groups.
•
Enhancements to the management of user preferences, including a new profile template and more customizable attributes.
•
New profile template with all the possible preferences and comments about their use under the <ClientInitialization> tag.
–
UseStartBeforeLogon: existed in 2.2 but now it can be made user controllable (visible in the preferences dialog)
–
ShowPreConnectMessage: existed in 2.2
The rest are all new preferences under ClientInitialization:
–
CertificateStoreOverride
–
CertificateStore
–
AutoConnectOnStart
–
MinimizeOnConnect
–
LocalLanAccess
–
AutoReconnect and its child element AutoReconnectBehavior
–
AutoUpdate
–
RSASecurIDIntegration
Table 2 shows the default values for these elements (if not found in the profile) and their possible values.
Table 2 Default Values for Preferences Elements
CertificateStoreOverride
false
false
true, false
No
n/a
All
CertificateStore
false
All
All, Machine, User
No
n/a
All
ShowPreConnectMessage
false
false
true, false
No
n/a
All
AutoConnectOnStart7
true
true
true, false
Yes
True
All
MinimizeOnConnect
true
true
true, false
Yes
True
All
LocalLanAccess
true
false
true, false
Yes
True
All
AutoReconnect8
false
true
true, false
Yes
False
All
AutoReconnectBehavior
false
DisconnectOnSuspend
ReconnectAfterResumeDisconnectOnSuspend
Yes
False
Windows
Mac
UseStartBeforeLogon
false
True
true, false
Yes
True
Windows except mobile
AutoUpdate
false
True
true, false
Yes
False
All
RSASecurIDIntegration9
false
Automatic
Automatic, SoftwareToken, HardwareToken
Yes
False
Windows
1 Preferences available by default are visible to the user and configurable even if there is no profile in the head end.
2 The default value of a preference is used when its value is not defined in the profile.
3 The value of a preference is defined in between the preference tags; for example, <AutoUpdate>true</AutoUpdate>.
4 Preferences that don't allow user control cannot be made UserControllable; that is, even if they are defined as UserControllable="true" in the profile, this is ignored, and the default values are used.
5 The user controllable attribute is defined inside the preference tags; for example, <AutoUpdate UserControllable="true">true</AutoUpdate>. Its possible values are "true" or "false", and these determine which preferences are overridden by the anyfilename.xml file. This is an optional attribute, and if not defined, the default value is used. Preferences made UserControllable="true" in the profile are visible in the Preferences dialog.
6 OS that supports these preferences.
7 If you disable AutoConnectOnStart, the user must select an option in the Connect to drop-down list to establish an AnyConnect session. After the user does so, AnyConnect applies the settings of the AnyConnect client profile provided by that host
8 See the note below to add the AutoReconnect preference.
9 The AnyConnect client is compatible with RSA SecurID software versions 1.1 and higher. At the time of this release, RSA SecurID Software Token client software does not support Windows Vista and 64-bit systems.
Note
AutoReconnect is a special type of preference, as it has a child preference. This is configured in the profile as:
<AutoReconnect UserControllable="true">true
<AutoReconnectBehavior UserControllable="true">ReconnectAfterResume</AutoReconnectBehavior>
</AutoReconnect>
Note
Where, if AutoReconnect is configured as Not UserControllable, then AutoReconnectBehavior is not UserControllable, even if the profile says it is. If AutoReconnect is UserControllable, then AutoReconnectBehavior can be either UserControllable or not.
•
Enhancements to Application Programming Interface (API), for customers who want to automate a VPN connection with the AnyConnect client from another application, including the following:
–
Preferences
–
Set tunnel-group method
The API package contains documentation, source files, and library files to support a C++ interface for the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client.There are libraries and example programs that can be used for building on Windows, Linux and MAC (10.4 or higher) platforms. The Makefiles (or project files) for the Windows platform are also included. For other platforms, there is a platform specific script showing how to compile the example code. Network administrators can link their application (GUI, CLI, or embedded application) with these files and libraries.
Feature Overview
In addition to the new features listed above, the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client provides remote users with secure VPN connections to the Cisco 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance.
Additional features of the AnyConnect client include:
•
Support for Start Before Logon for Windows Vista systems, in addition to other Windows operating systems.
•
Extended customization and localization features—This version of the AnyConnect client includes enhanced customization features and language translation features. In previous versions, you could customize client installations only on an individual PC basis. With this version, the security appliance can customize the client as it downloads and installs the client on the remote PC. You can also translate the client installer. These extended features include the following items:
–
Localized installs using localized MSI transforms (Windows only).
–
Custom MSI transforms (Windows only).
–
User-defined resource files.
–
Third-party GUI/CLI support.
–
Localization for Mac OS X 10.4 and 10.5.
•
System tray in Windows systems now shows an icon when the AnyConnect client is reconnecting after losing connectivity.
•
Enhanced Network Mobility—A user can lose connectivity for an extended period of time and still be able to have the client automatically resume the connection, as long as the security appliance has not logged the session off. In addition, a VPN session can now be retained during a hibernate/standby condition. This does not require any configuration changes; it is automatically enabled. The VPN tunnel might be dropped if the hibernation/sleep time exceeds the idle connection timeout or session timeout configured on the security appliance. You can also restrict this feature by setting the idle session timeout to a low value.
In earlier versions, the tunnel would be automatically torn down when a system entered suspend or hibernate. For Windows Vista, please see the usage note on this topic "Network Subsystem on Windows Vista Might Become Unresponsive During Sleep/Resume Cycles or Other High-load Conditions (KB-952876)" section.
•
Application Programming Interface (API), for customers who want to automate a VPN connection with the AnyConnect client from another application.
•
Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) with SSL connections—Avoids latency and bandwidth problems associated with some SSL-only connections and improves the performance of real-time applications that are sensitive to packet delays. DTLS is a standards-based SSL protocol that provides a low-latency data path using UDP. For detailed information about DTLS, see RFC 4347 (http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4347.txt).
•
Standalone Mode—Allows a Cisco AnyConnect VPN client to be established as a PC application without the need to use a web browser to establish a connection.
•
Command Line Interface (CLI)—Provides direct access to client commands at the command prompt.
•
Microsoft Installer (MSI)—Gives Windows users a pre-install package option that provides installation, maintenance, and removal of AnyConnect client software on Windows systems.
•
IPv6 VPN access—Allows access to IPv6 resources over a public IPv4 connection (Windows XP SP2, Windows Vista, Mac OSX, and Linux only). See the Usage Notes section for information about setting up IPv6 access.
•
Start Before Logon (SBL)—Allows for login scripts, password caching, drive mapping, and more, for Windows.
•
Certificate-only authentication—Allows users to connect with digital certificate and not provide a user ID and password.
•
Simultaneous AnyConnect client and clientless, browser-based connections.
•
Compression—Increases the communications performance between the security appliance and the client by reducing the size of the packets being transferred. Compression works only for TLS.
•
Fallback from DTLS to TLS—Provides a way of falling back from DTLS to TLS if DTLS is no longer working.
•
Language Translation (localization)—Provides a way of implementing translation for user messages that appear on the client user interface.
•
Dynamic Access Policies feature of the security appliance—Lets you configure authorization that addresses the variables of multiple group membership and endpoint security for VPN connections.
•
Cisco Secure Desktop (CSD) support—Validates the security of client computers requesting access to your SSL VPN, helps ensure they remain secure while they are connected, and attempts to remove traces of the session after they disconnect. AnyConnect supports the Host Scan component of Cisco Secure Desktop on Windows XP and Windows 2000. Cisco Secure Desktop does not support the AnyConnect client within the Secure Desktop (Vault) on Windows Vista systems.
•
Rekey—Provides the ability to renegotiate the key used to encrypt data packets throughout the life of the VPN connection.
System Requirements
If you are using Internet Explorer, use version 5.0, Service Pack 2 or later.
AnyConnect does not support virtualization software, such as VMWare for any platform or Parallels Desktop for Mac OS. Although initial testing suggests that AnyConnect 2.4 running over VMware or Microsoft Virtual PC on Windows 7 will generally work, it has never been fully tested and is not guaranteed to be 100% reliable.
AnyConnect does not support sessions with a security appliance running on the same subnet.
Microsoft Windows
If you are using Internet Explorer, use version 5.0, Service Pack 2 or later. For WebLaunch, use Internet Explorer 6.0+ or Firefox 2.0+, and enable ActiveX or install Sun JRE 1.4+.
Windows Versions
•
Windows Vista—32- and 64-bit Microsoft Windows Vista SP2 or Vista Service Pack 1 with KB952876.
•
Windows XP SP2 and SP3.
•
Windows 2000 SP4.
Windows Requirements
•
Pentium class processor or greater.
•
x64 or x86 processors on Windows XP and Windows Vista.
•
5 MB hard disk space.
•
RAM:
–
128 MB for Windows 2000.
–
256 MB for Windows XP.
–
512 MB for Windows Vista.
•
Microsoft Installer, version 3.1.
Linux
The following sections show the Linux distributions and requirements.
Linux Distributions
AnyConnect supports Linux Kernel releases 2.4 and 2.6 on 32-bit architectures, and 64-bit architectures that support biarch (that is, that run 32-bit code).
The following Linux distributions follow the requirements and work with the AnyConnect Client:
•
Ubuntu 7 and 8 (32-bit only).
•
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3 or 4. (As of publication, we have not tested AnyConnect with Red Hat Linux 5.
•
Fedora Core 4 through 9. To use Fedora 9 with the AnyConnect client, you must first install Sun Microsystems JRE, preferably JRE 6, Update 5 or higher.
•
Slackware 11 or 12.1.
•
openSuSE 10 or SuSE 10.1.
Linux Requirements
•
x86 instruction set.
•
32-bit or biarch 64-bit processor
•
32 MB RAM.
•
20 MB hard disk space.
•
Superuser privileges.
•
libstdc++ users must have libstdc++ version 3.3.2 (libstdc++.so.5) or higher, but below version 4.
•
Firefox 2.0 or later with libnss3.so installed in /usr/local/lib, /usr/local/firefox/lib, or /usr/lib. Firefox must be installed in /usr/lib or /usr/local, or there must be a symbolic link in /usr/lib or /usr/local called firefox that points to the Firefox installation directory.
•
libcurl 7.10 or later.
•
openssl 0.9.7a or later.
•
java 1.5 or later. The default Java package on Fedora is an open-source GNU version, called Iced Tea on Fedora 8. The only version that works for web installation is Sun Java. You must install Sun Java and configure your browser to use that instead of the default package.
•
zlib or later.
•
gtk 2.0.0,
gdk 2.0.0,
libpango 1.0.•
iptables 1.2.7a or later.
•
tun module supplied with kernel 2.4.21 or 2.6.
Mac OS
AnyConnect supports Mac OS X Versions 10.4 and 10.5. It requires 50 MB hard disk space.
Windows Mobile
Cisco designed AnyConnect 2.3 for compatibility with Windows Mobile 6.1, 6.0 and 5.0 Professional and Classic for touch-screens only, but has specifically qualified only the devices listed in Table 3 to ensure interoperability. While other devices might work, Cisco does not guarantee compatibility with other devices. Table 3 lists the supported devices with their corresponding service providers and supported operating system versions.
Security Appliances and Software Supported
The Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client supports all Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance models. It does not support PIX devices. See the Adaptive Security Appliance VPN Compatibility Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/asa/compatibility/asa-vpn-compatibility.html for a complete list of compatibility requirements.
Table 4 shows the minimum Cisco ASA 5500 Adaptive Security Appliance software images that support the AnyConnect client.
Table 4 Software Images that Support the AnyConnect Client, Release 2.3
ASA Boot image
8.0(3).1 or later
Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM)
6.1(3).1 or later
Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client
Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X: 2.3
Cisco Secure Desktop
3.2(2)1
Interoperability Considerations
This section describes how the AnyConnect VPN Client interoperates with other software. The AnyConnect client can be loaded on the security appliance and automatically deployed to remote users when they log in to the security appliance, or it can be installed as an application on PCs by a network administrator using standard software deployment mechanisms. You can use a text editor to create user profiles as XML files. These profiles drive the display in the user interface and define the names and addresses of host computers.
AnyConnect Client and Cisco Secure Desktop
See the Adaptive Security Appliance VPN Compatibility Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/asa/compatibility/asa-vpn-compatibility.html for a complete list of compatibility requirements.
There is no support of the AnyConnect client within Secure Desktop (Vault) on the Windows Vista platform in Release 3.3 of Cisco Secure Desktop. Do not configure the AnyConnect client and Secure Desktop (Vault) if your users use the Windows Vista platform. This limitation applies only to AnyConnect client users who are using the Windows Vista platform. Users who connect using a clientless connection can use the Secure Desktop (Vault).
ïIf you must configure the AnyConnect client and Cisco Secure Desktop secure desktop, but some of your users might be on the Windows Vista platform, consider using Cisco Secure Desktop, Release 3.2.1 to accomplish this. In this case, Secure Desktop (Vault) is started only on non-Vista platforms (otherwise, Cache Cleaner is invoked in its place for the clientless environment).
ïIf you want to enforce Cisco Secure Desktop secure desktop for certain users, and you expect that AnyConnect will also be used for those users who may use Windows Vista or Windows XP, you can, through prelogin policy, configure a policy that starts Cache Cleaner or Hostscan (in place of Secure Desktop) for users on Windows Vista platforms. For example, the policy can key off the registry value:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\CurrentVersion
Note
Cisco Secure Desktop does not support AnyConnect Windows Mobile, and AnyConnect Windows Mobile does not connect to a host that has Cisco Secure Desktop enabled. If the device is a Windows Mobile device or the iPhone, it bypasses Cisco Secure Desktop, even if Cisco Secure Desktop is enabled.
AnyConnect and Citrix
There exists a conflict between AnyConnect and Citrix Advanced Gateway client 2.2.1.
When disconnecting AnyConnect, users can receive this Microsoft Windows error: "VPN Agent Service has encountered a problem and needs to close. We are sorry for the inconvenience." After clicking close on the Microsoft Windows error, users receive this next message from AnyConnect: "Unable to Proceed. Cannot contact the VPN service." Finally, at the bottom of the AnyConnect client window, users receive the message: "The VPN Service has failed. Please restart the application" This indicates the AnyConnect Agent service has crashed.
The Citrix client installs a Layered Service Provider DLL (CtxLsp.dll) that it loads into every process using Windows Sockets (WinSock). As such, this DLL is loaded into the AnyConnect Agent Service. The crash occurs as a result of this DLL being part of the Agent process. The crashes always occur during freeing of memory because of memory heap corruptions caused by this DLL. These same operations work correctly when the DLL is not part of the process. The crashes have been seen to occur in the downloader application as well, and even in the FileZilla FTP Server.
While the crashes occur very frequently, they do not always occur. Also, the crashes occur in different places in the process, but they are always the result of a memory heap corruption. The bug is in the Citrix DLL. Others have reported this issue to Citrix: http://support.citrix.com/forums/thread.jspa?forumID=60&threadID=80923&tstart=15
The current workaround for this problem is to disable the Citrix client.
AnyConnect and IOS
Several features of the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client are supported in conjunction with various IOS routers with SSL VPN support. Please see the system requirements listed in the Cisco IOS SSL VPN Data Sheet for specific details about supported features for IOS devices and the IOS SSL VPN feature guide for configuration details. If you are a remote user, see the IOS SSL VPN Remote User Guide for configuration information.
AnyConnect and PIX
PIX does not support SSL VPN connections, either clientless or AnyConnect.
Upgrading to AnyConnect Release 2.3
This section contains information about upgrading from the Cisco SSL VPN Client to Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.
Before you begin, be aware of the considerations listed in the Usage Notes, section of these Release Notes before you upgrade. These are known product behaviors, and knowing about them at the beginning of the process should expedite the upgrade. Where appropriate, the number of the caveat documenting the issue appears at the end of the item. See the "Caveats" section for a list of open and resolved caveats.
End User Interface
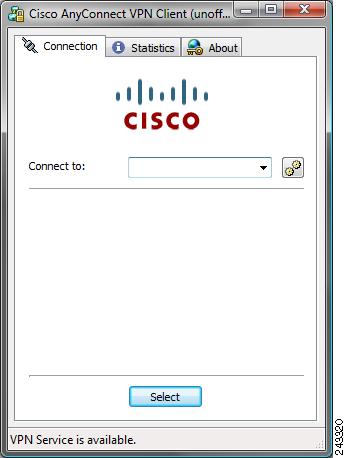
Figure 1 shows the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client user interface. The Connection tab provides a drop-down list of profiles for connecting to remote systems.
Figure 1 Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client User Interface, Connection Tab
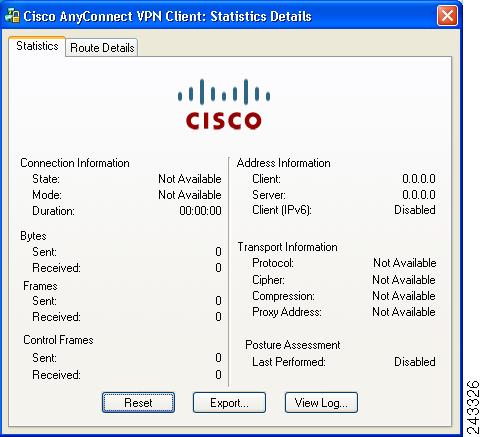
Figure 2 shows the Statistics tab, including current connection information.
Figure 2 Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client User Interface, Statistics Tab
AnyConnect Client Disconnect Behavior
If you click Disconnect, the AnyConnect client, starting with Release 2.3, terminates the connection, as shown in the status bar at the bottom of the dialog box, and the AnyConnect GUI displays a login dialog box with a "Connect to" combo box and a Select button. To reconnect, the remote user must select a new host server to connect to or click Select. At that point, the appropriate authentication prompts are displayed.
Installation Notes
This section contains procedures for installing the AnyConnect client software on the ASA5500 using the Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) or the CLI command interface.
WebLaunch Mode
Without a previously-installed client, remote users enter the IP address or DNS name in their browser of an interface configured to accept clientless SSL VPN connections. Local system admin privileges are required if the client is not already installed. Unless the security appliance is configured to redirect http:// requests to https://, users must enter the URL in the form https://<address>. Weblaunch mode can also be used even when the client is already installed.
Note
A user with a clientless SSL VPN connection can switch to an AnyConnect client vpn connection by clicking the Network Access drawer on the portal and following the instructions on that page.
After the user enters the URL, the browser connects to that interface and displays the login screen. If the user satisfies the login and authentication, and the security appliance identifies the user as requiring the client, it loads the client that matches the operating system of the remote computer. After loading, the client installs and configures itself, establishes a secure SSL connection and either remains or uninstalls itself (depending on the security appliance configuration) when the connection terminates.
Standalone Mode
In the case of a previously-installed client, when the user authenticates, the security appliance examines the revision of the client, and upgrades the client as necessary.
When the client negotiates an SSL VPN connection with the security appliance, it connects using Transport Layer Security (TLS). The client can also negotiate a simultaneous Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) connection. DTLS avoids latency and bandwidth problems associated with some SSL connections and improves the performance of real-time applications that are sensitive to packet delays.
The AnyConnect client can be downloaded from the security appliance, or it can be installed manually on the remote PC by the system administrator. For more information about configuring the AnyConnect client, see the Cisco 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance CLI Configuration Guide. For more detailed information about configuring the AnyConnect client and other SSL VPN connections on the security appliance, see "Configuring SSL VPN Connections" in Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide. For detailed descriptions of the commands referred to in this administrator's guide, see the Cisco ASA 5500 Command Reference Guide for version 8.0 or later.
The security appliance loads the client based on the group policy or username attributes of the user establishing the connection. You can configure the security appliance to automatically load the client, or you can configure it to prompt the remote user about whether to download the client. In the latter case, if the user does not respond, you can configure the security appliance either to load the client after a timeout period or to present the login page.
The installation and configuration consists of two parts: what you have to do on the security appliance, and what you have to do on the remote PC. The AnyConnect client software is built into the ASA Release 8.0(1) and later. You can decide whether to make the AnyConnect client software permanently resident on the remote PC, or whether to have it resident only for the duration of the connection. We recommend keeping the client resident on the system, as doing so can speed up subsequent connection attempts.
Note
When using Start Before Logon, the VPN Gina (VPN Graphical Identification and Authentication) can not be installed dynamically if the AnyConnect client is installed manually. The VPN Gina can be installed either before or after the AnyConnect client, but they must either be both installed manually or both installed dynamically.
This section describes installation-specific issues and procedures for AnyConnect client Release 2.3, and contains the following sections:
•
Where to Find the AnyConnect Client Files for Installation
•
Suggested Practice for the Position of the Windows Mobile Package on the Security Appliance
•
Before You Install the AnyConnect Client
•
Installing the AnyConnect Client on a System Running Windows
•
Installing the AnyConnect Client on Linux
•
Installing the AnyConnect Client on Mac OS
•
Installing the AnyConnect Client on a Windows Mobile Device
•
Loading the AnyConnect Client and Configuring the Security Appliance with ASDM
•
Loading the AnyConnect Client and Configuring the Security Appliance with CLI
Where to Find the AnyConnect Client Files for Installation
All of the AnyConnect clients are located in the same place: http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/anyconnect
The AnyConnect client packages are as follows:
•
anyconnect-win-2.3.0254-k9.pkg—Contains AnyConnect, vpngina, and DART.
•
anyconnect-no-dart-win-2.3.0254-k9.pkg—Contains AnyConnect, vpngina, but not DART.
In addition, you can download and load the following AnyConnect files from the same location:
•
AnyConnect translation file —anyconnect.po_2.3.0254.zip
•
AnyConnect API—anyconnect_API_2.3.0254.zip
•
DART (Diagnostic AnyConnect Reporting Tool)— The downloads containing DART are as follows:
–
anyconnect-win-2.3.00254-k9.pkg—Contains AnyConnect, vpngina, and DART.
–
anyconnect-dart-win.msi—Contains only the DART installation package, not the AnyConnect or vpngina software.
Note
The download anyconnect-no-dart-win-2.3.0254-k9.pkg contains AnyConnect and vpngina software, but not DART.
Within the DART zip file is an msi that can be extracted and installed like other MS msi. DART creates a program group under Start -> All Programs -> Cisco -> Cisco DART. By default, the output file is available via a Desktop icon named "DARTBundle.zip".
Suggested Practice for the Position of the Windows Mobile Package on the Security Appliance
You must store the AnyConnect image on the security appliance to support AnyConnect for remote users even if the AnyConnect image is already deployed. You can improve the connection times by storing the Windows Mobile package in the first package slot. For example:
Recommended:
•
svc image disk0:/AC-WINCE-23061.pkg 1
•
svc image disk0:/AC-MACPPC-220139.pkg 2
•
svc image disk0:/AC-LINUX-220139.pkg 3
•
svc image disk0:/AC-WIN-220144.pkg 4
•
svc image disk0:/AC-MAC386-220139.pkg 5
Not recommended:
•
svc image disk0:/AC-MACPPC-220139.pkg 1
•
svc image disk0:/AC-LINUX-220139.pkg 2
•
svc image disk0:/AC-WIN-220144.pkg 3
•
svc image disk0:/AC-MAC386-220139.pkg 4
•
svc image disk0:/AC-WINCE-23061.pkg 5
Before You Install the AnyConnect Client
The following sections contain recommendations to ensure successful AnyConnect client installation, as well as tips about certificates, Cisco Security Agent (CSA), adding trusted sites, and responding to browser alerts:
•
Ensuring Automatic Installation of AnyConnect Clients
•
AnyConnect Client and New Windows 2000 Installations
•
Adding a Security Appliance to the List of Trusted Sites (IE)
•
Adding a Security Certificate in Response to Browser Alert Windows
Ensuring Automatic Installation of AnyConnect Clients
The following recommendations and caveats apply to the automatic installation of AnyConnect client software on client PCs:
•
To minimize user prompts during AnyConnect client setup, make sure certificate data on client PCs and on the security appliance match:
–
If you are using a Certificate Authority (CA) for certificates on the security appliance, choose one that is already configured as a trusted CA on client machines.
–
If you are using a self-signed certificate on the security appliance, be sure to install it as a trusted root certificate on clients.
The procedure varies by browser. See the procedures that follow this section.
–
Make sure the Common Name (CN) in security appliance certificates matches the name clients use to connect to it. By default, the security appliance certificate CN field is its IP address. If clients use a DNS name, change the CN field on the security appliance certificate to that name.
If the certificate has a SAN (Subject Alternate Name) then the browser will ignore the CN value in the Subject field and look for a DNS Name entry in the SAN field.
If users connect to the ASA using its hostname, the SAN should contain the hostname and domain name of the ASA. For example, the SAN field would contain
DNS Name=hostname.domain.com.If users connect to the ASA using its IP address, the SAN should contain the IP address of the ASA. For example, the SAN field would contain DNS Name=209.165.200.254.
•
The Cisco Security Agent (CSA) might display warnings during the AnyConnect client installation.
Current shipping versions of CSA do not have a built-in rule that is compatible with the AnyConnect client. You can create the following rule using CSA version 5.0 or later by following these steps:
Step 1
In Rule Module: "Cisco Secure Tunneling Client Module", add a FACL:
Priority Allow, no Log, Description: "Cisco Secure Tunneling Browsers, read/write vpnweb.ocx"Applications in the following class: "Cisco Secure Tunneling Client - Controlled Web Browsers"Attempt: Read file, Write FileOn any of these files: @SYSTEM\vpnweb.ocx
Step 2
Application Class: "Cisco Secure Tunneling Client - Installation Applications" add the following process names:
**\vpndownloader.exe@program_files\**\Cisco\Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client\vpndownloader.exeThis rule will be built into a future version of CSA.
We recommend that Microsoft Internet Explorer (MSIE) users add the security appliance to the list of trusted sites, or install Java. The latter enables the ActiveX control to install with minimal interaction from the user. This is particularly important for users of Windows XP SP2 with enhanced security. Windows Vista users must add the security appliance to the list of trusted sites in order to use the dynamic deployment feature. For information about adding a security appliance to the list of trusted sites, see the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Administrator Guide. For information about how to use Microsoft Active Directory to add the security appliance to the list of trusted sites for Internet Explorer, see Appendix B of Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Administrator Guide.
AnyConnect Client and New Windows 2000 Installations
In rare circumstances, if you install the AnyConnect client on a computer that has a new or clean Windows 2000 installation, the AnyConnect client might fail to connect, and your computer might display the following message:
The required system DLL (filename) is not present on the system.This could occur if the computer does not have the file MSVCP60.dll or MSVCRT.dll located in the winnt\system32 directory. For more information about this problem, see the Microsoft Knowledge Base, article 259403, at http://support.microsoft.com/kb/259403.
Adding a Security Appliance to the List of Trusted Sites (IE)
To add a security appliance to the list of trusted sites, use Microsoft Internet Explorer and do the following steps.
Note
This is required on Windows Vista to use WebLaunch.
Step 1
Go to Tools | Internet Options | Trusted Sites.
The Internet Options window opens.
Step 2
Click the Security tab.
Step 3
Click the Trusted Sites icon.
Step 4
Click Sites.
The Trusted Sites window opens.
Step 5
Type the host name or IP address of the security appliance. Use a wildcard such as https://*.yourcompany.com to allow all ASA 5500s within the yourcompany.com domain to be used to support multiple sites.
Step 6
Click Add.
Step 7
Click OK.
The Trusted Sites window closes.
Step 8
Click OK in the Internet Options window.
Adding a Security Certificate in Response to Browser Alert Windows
This section explains how to install a self-signed certificate as a trusted root certificate on a client in response to the browser alert windows.
In Response to a Microsoft Internet Explorer "Security Alert" Window
The following procedure explains how to install a self-signed certificate as a trusted root certificate on a client in response to a Microsoft Internet Explorer Security Alert window. This window opens when you establish a Microsoft Internet Explorer connection to a security appliance that is not recognized as a trusted site. The upper half of the Security Alert window shows the following text:
Information you exchange with this site cannot be viewed or changed by others. However, there is a problem with the site's security certificate. The security certificate was issued by a company you have not chosen to trust. View the certificate to determine whether you want to trust the certifying authority.Install the certificate as a trusted root certificate as follows:
Step 1
Click View Certificate in the Security Alert window.
The Certificate window opens.
Step 2
Click Install Certificate.
The Certificate Import Wizard Welcome opens.
Step 3
Click Next.
The Certificate Import Wizard - Certificate Store window opens.
Step 4
Select "Automatically select the certificate store based on the type of certificate."
Step 5
Click Next.
The Certificate Import Wizard - Completing window opens.
Step 6
Click Finish.
Step 7
Another Security Warning window prompts "Do you want to install this certificate?" Click Yes.
The Certificate Import Wizard window indicates the import is successful.
Step 8
Click OK to close this window.
Step 9
Click OK to close the Certificate window.
Step 10
Click Yes to close the Security Alert window.
The security appliance window opens, signifying the certificate is trusted.
In Response to a Netscape, Mozilla, or Firefox "Certified by an Unknown Authority" Window
The following procedure explains how to install a self-signed certificate as a trusted root certificate on a client in response to a "Web Site Certified by an Unknown Authority" window. This window opens when you establish a Netscape, Mozilla, or Firefox connection to a security appliance that is not recognized as a trusted site. This window shows the following text:
Unable to verify the identity of <Hostname_or_IP_address> as a trusted site.Install the certificate as a trusted root certificate as follows:
Step 1
Click the Examine Certificate button in the "Web Site Certified by an Unknown Authority" window.
The Certificate Viewer window opens.
Step 2
Click the "Accept this certificate permanently" option.
Step 3
Click OK.
The security appliance window opens, signifying the certificate is trusted.
Installing the AnyConnect Client on a System Running Windows
To install the AnyConnect client on a PC running Windows, follow these steps. We suggest you accept the defaults unless your system administrator has instructed otherwise.
Note
Vista users must add the security appliance to the trusted zone for automatic installation by the security appliance to work.
Step 1
Exit all Windows programs, and disable any antivirus software.
Step 2
Download the AnyConnect client package file from the Cisco site.
Step 3
Double-click the package file. The welcome screen for the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Setup Wizard displays.
Step 4
Click Next. The End-User License Agreement displays. Accept the license agreement and click OK. The Select Installation Folder screen displays.
Step 5
Accept the default folder or enter a new folder and click Next. The Ready to Install screen displays.
Step 6
Click Install. The client installs and displays the status bar during installation. After installing, the Completing the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Setup Wizard screen displays.
Step 7
Click Next. The wizard disappears and the installation is complete.
Installing Start Before Logon Components (Windows Only)
The Start Before Logon components must be installed after the core client has been installed. Additionally, the AnyConnect 2.3 Start Before Logon components require that version 2.3, or later, of the core AnyConnect client software be installed. If you are pre-deploying the AnyConnect client and the Start Before Logon components using the MSI files (for example, you are at a big company that has its own software deployment—Altiris or Active Directory or SMS.) then you must get the order right. The order of the installation is handled automatically when the administrator loads AnyConnect if it is web deployed and/or web updated.
Both the AnyConnect client and the Start Before Login components must be installed same way, either both manually or both via weblaunch. Therefore:
•
If you pre-deploy AnyConnect, you must also pre-deploy the Start Before Logon components.
•
If you web-update AnyConnect, you must web-update the Start Before Logon components.
•
If you web-deploy AnyConnect, you must web-deploy the Start Before Logon components.
•
You cannot pre-deploy AnyConnect, and then web-deploy the Start Before Logon components.
If you manually uninstall either the pre-Vista Start Before Logon component GINA or the Windows Vista Start Before Logon component PLAP, you must manually reinstall it.
You can, for example, pre-deploy both of them... put a new version of both on the head end and web-update them both. The two are joined together in whatever action you perform.
For example, a customer sends out laptops with the software pre-installed. Six months later, Cisco ships a new version of the software and the network administrators want all their users to get the latest version. To do this, the network administrators can put the new software on the security appliance, and all users get the web update.
They could not pre-image with just core AnyConnect software and then decide to update via the security appliance both the client and the Start Before Logon software components, since they never pre-installed the Start Before Logon software to begin with.
Differences Between Windows-Vista and Pre-Vista Start Before Logon
The procedures for enabling SBL differ slightly on Windows Vista systems. Pre-Vista systems use a component called VPNGINA (which stands for virtual private network graphical identification and authentication) to implement SBL. Vista systems use a component called PLAP to implement SBL.
In the AnyConnect client, the Windows Vista Start Before Logon feature is known as the Pre-Login Access Provider (PLAP), which is a connectable credential provider. This feature lets network administrators perform specific tasks, such as collecting credentials or connecting to network resources, prior to login. PLAP provides start Before Logon functions on Windows Vista. PLAP supports 32-bit and 64-bit versions of the operating system with vpnplap.dll and vpnplap64.dll, respectively. The PLAP function supports Windows Vista x86 and x64 versions.
Note
In this section, VPNGINA refers to the Start Before Logon feature for pre-Vista platforms, and PLAP refers to the Start Before Logon feature for Windows Vista systems.
In pre-Vista systems, Start Before Logon uses a component known as the VPN Graphical Identification and Authentication Dynamic Link Library (vpngina.dll) to provide Start Before Logon capabilities. The Windows PLAP component, which is part of Windows Vista, replaces the Windows GINA component.
A GINA is activated when a user presses the Ctrl+Alt+Del key combination. With PLAP, the Ctrl+Alt+Del key combination opens a window where the user can choose either to log in to the system or to activate any Network Connections (PLAP components) using the Network Connect button in the lower-right corner of the window.
For a complete description of enabling, configuring, and using the Start Before Logon feature (VPNGINA or PLAP) on a Windows platform, see Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Administrator Guide, Chapter 4.
Fulfilling Requirements for Biarch Linux
If you are running 64-bit Linux, prepare it to run 32-bit AnyConnect binary files, as follows:
Step 1
Install the following packages:
•
ia32-libs
•
lib32nss-mdns.
Step 2
Install 32-bit Firefox into the /usr/local/firefox directory.
Step 3
Copy or link the following files from /usr/local/firefox to either /usr/lib32 or /opt/cisco/vpn/lib:
•
libnssutil3.so
•
libplc4.so
•
libplds4.so
•
libnspr4.so
•
libsqlite3.so
•
libnssdbm3.so
•
libfreebl3.so
Installing the AnyConnect Client on Linux
To install the AnyConnect client on Linux, follow these steps:
Step 1
For Linux, the client files are contained in a tar/gz file. Unpack the archive with a tar command. For example:
tar xvzf AnyConnect-Linux-Release-2.3.xxxx.tar.gzThe files necessary for installation are placed in the folder ciscovpn.
Step 2
Change to the ciscovpn folder. As a root user, run the script named vpn_install.sh. For example:
[root@linuxhost]# cd ciscovpn[root@linuxhost] /vpn_install.shThe client installs in the directory /opt/cisco/vpn. This script also installs the daemon vpnagentd and sets it up as a service that is automatically started when the system boots.
After installing the client, you can start the client manually with the Linux command /opt/cisco/vpn/bin/vpnui or with the client CLI command /opt/cisco/vpn/bin/vpn.
Installing the AnyConnect Client on Mac OS
You can use the WebLaunch procedure to start AnyConnect from the clientless portal page, or you can install AnyConnect using the following standalone procedure. The section that follows describes what to do if the Java installer fails during an attempt to use WebLaunch to install AnyConnect.
Using the Standalone Install Procedure on Mac OS
The AnyConnect client image for Mac OS is a DMG disk image installation package. To install the AnyConnect client on a system running Mac OS, follow these steps:
Step 1
Transfer the installation package file to the desktop and double-click the file. A window opens showing an icon representing the installation package file.
Step 2
Double-click the icon to initiate the installation. A dialog window appears asking you to select the device on which to install the client.
Step 3
Select a device and click Next. A dialog to accept the licensing agreement (EULA) appears.
Step 4
Accept the license agreement and click Next.
The installation is complete.
Using the Manual Install Option on Mac OS if the Java Installer Fails during WebLaunch
If you use WebLaunch to start AnyConnect on a Mac and the Java installer fails, a dialog box presents a Manual Install link. Proceed as follows:
Step 1
Click Manual Install.
A dialog box presents the option to save the vpnsetup.sh file.
Step 2
Save the vpnsetup.sh file on the Mac.
Step 3
Open a Terminal window and use the CD command to navigate to the directory containing the file saved.
Step 4
Enter the following command:
sudo /bin/sh vpnsetup.shThe vpnsetup script starts the AnyConnect installation.
Step 5
Following the installation, choose Applications > Cisco > Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client to initiate an AnyConnect VPN session.
Installing the AnyConnect Client on a Windows Mobile Device
The security appliance does not support WebLaunch of AnyConnect on a mobile device; therefore, mobile users must download and install AnyConnect Client for Windows Mobile. Just as you can do so with corporate computers, you can pre-deploy AnyConnect on Windows Mobile devices issued to employees.
Perform the following steps to download and install AnyConnect Client for Windows Mobile.
Step 1
Download any of the following files from the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Download Software site to get the Windows Mobile Client:
•
File containing all client installation packages: anyconnect-all-packages—AnyConnectRelease_Number-k9.zip
•
CAB package signed by Cisco for Windows Mobile devices: anyconnect-wince-ARMv4I-AnyConnectRelease_Number-k9.cab
•
ActiveSync MSI package for Windows Mobile platforms: anyconnect-wince-ARMv4I-activesync-AnyConnectRelease_Number-k9.msi
Step 2
Unzip the anyconnect-all-packages—AnyConnectRelease_Number-k9.zip file if you chose to download that file.
Step 3
Transfer the file to a corporate server if you want to provide users with a link to the client.
Step 4
Make sure the Windows Mobile device meets the system requirements in the latest AnyConnect Release Notes.
Step 5
Use your preferred method to transfer the .cab or .msi file from your intranet server or local computer to the mobile device. Some examples include:
•
Microsoft ActiveSync over radio
•
HTTP, FTP, SSH, or shared files over the LAN or radio
•
Bluetooth
•
(USB) Cable
•
Media card transfer
Step 6
Use the mobile device to open the file you transferred, and proceed with the installation wizard.s
Pushing the User Profile to the Client PC
After AnyConnect 2.3 is installed, you should have the file "AnyConnectProfile.tmpl" in the folder C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Cisco\Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client\Profile. That is a template file you can rename with an .XML extension and then copy it to the FLASH on the ASA.
You can push the profile from security appliance to the client PC by specifying the CLI group-policy-webvpn-svc-profiles <anyfilename.xml> command. In ASDM, select Configuration > Remote Access VPN > Network (Client) Access > Group Policies > Advanced > SSL VPN Client > Client Profile to Download.
Connect to the security appliance using the Client; the profile is pushed down to the client. Then disconnect, exit and restart the client. You see the checkbox "Auto reconnect" in the client preferences.
Using the AnyConnect CLI Commands
The Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client provides a command line interface (CLI) for users who prefer to issue commands instead of using the graphical user interface. The following sections describe how to launch the CLI command prompt.
For Windows
To launch the CLI command prompt and issue commands on a Windows system, locate the file vpncli.exe in the Windows folder C:\Program Files\Cisco\Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client. Double-click the file vpncli.exe.
For Linux
To launch the CLI command prompt and issue commands on a Linux system, locate the file vpn in the folder /opt/cisco/vpn/bin/. Execute the file vpn.
You can run the CLI in interactive mode, in which it provides its own prompt, or you can run it with the commands on the command line. Table 5 shows the CLI commands.
Note
You cannot adjust preferences using the CLI interface of the AnyConnect client.
The following examples shows the user establishing and terminating a connection from the command line:
/opt/cisco/vpn/bin/vpn connect 1.2.3.4Establishes a connection to a security appliance with the address 1.2.3.4.
/opt/cisco/vpn/bin/vpn connect some_asa_aliasEstablishes a connection to a security appliance by reading the profile and looking up the alias some_asa_alias in order to find its address.
/opt/cisco/vpn/bin/vpn statsDisplays statistics about the vpn connection.
/opt/cisco/vpn/bin/vpn disconnectDisconnect the vpn session if it exists.
Loading the AnyConnect Client and Configuring the Security Appliance with ASDM
Loading the client on the security appliance consists of copying a client image to the security appliance and identifying the file to the security appliance as a client image. With multiple clients, you must also assign the order that the security appliance loads the clients to the remote PC. Perform the following steps to install the client:
Step 1
Load the AnyConnect client images to the security appliance. On the ASDM toolbar, click Configuration. The navigation pane displays features to configure.
Step 2
In the navigation pane, click Remote Access VPN. The navigation pane displays VPN features.
Step 3
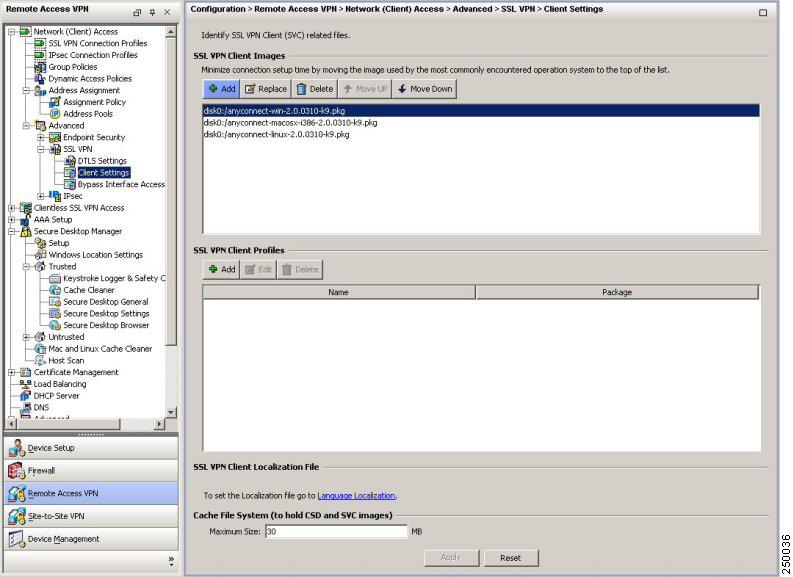
Choose Network Access > Advanced > SSL VPN > Client Settings. The SSL VPN Client Settings panel displays. (Figure 3).
This panel lists any AnyConnect client files that have been identified as AnyConnect client images. The order in which they appear in the table reflects the order that they download to the remote computer.
Figure 3 SSL VPN Client Settings Panel
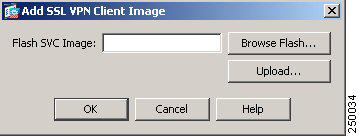
To add an AnyConnect client image, Click Add in the SSL VPN Client Images area. The Add SSL VPN Client Image dialog appears (Figure 4).
Figure 4 Add SSL VPN Client Image Dialog
If you already have an image located in the flash memory of the security appliance, you can enter the name of the image in the Flash SVC Image field, and click OK. The SSL VPN Client Images panel now shows the AnyConnect client images you identified (Figure 5).
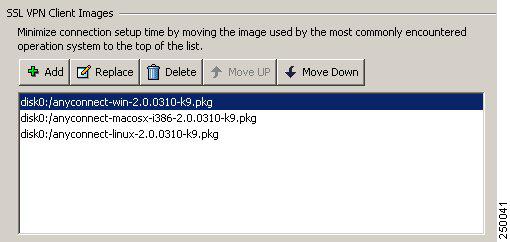
Figure 5 SSL VPN Client Panel with AnyConnect Client Images
Step 4
Click on an image name, and use the Move Down button to change the position of the image within the list.
This establishes the order in which the security appliance loads them to the remote computer. It loads the AnyConnect client image at the top of the list of images first. Therefore, you should move the image used by the most commonly-encountered operating system to the top of the list.
Step 5
Enable the security appliance to download the AnyConnect client to remote users. Go to Network Access > SSL VPN Connections. The SSL VPN Connections panel appears (Figure 6). Check Enable SSL VPN client access for an interface.
Figure 6 Enable SSL VPN Client Check Box
Step 6
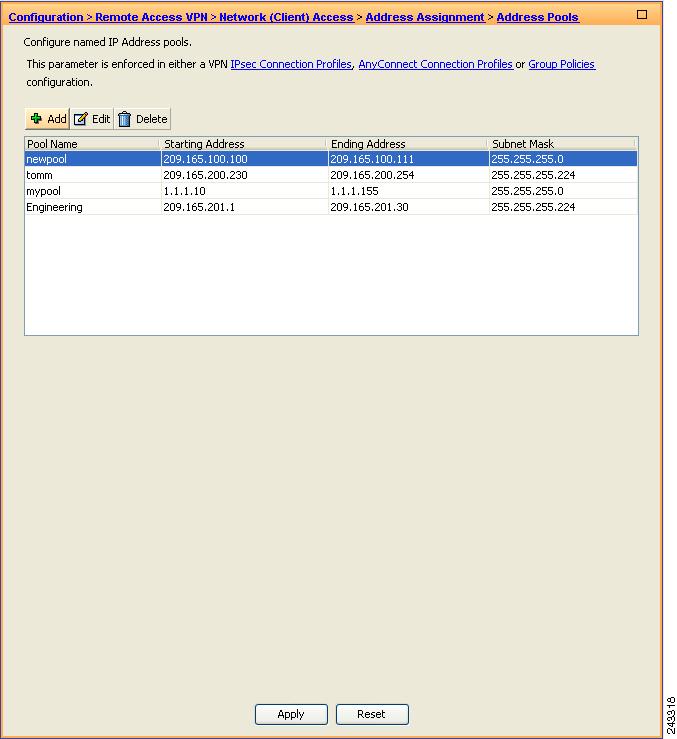
Configure a method of address assignment. You can use DHCP, and/or user-assigned addressing. You can also create a local IP address pool and assign the pool to a tunnel group.
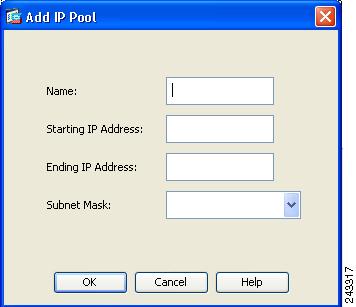
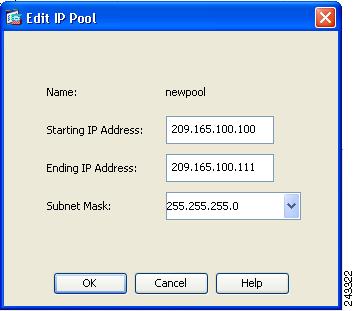
To create an IP address pool, choose Network Access > Address Assignment > Address Pools. Click Add. The Add IP Pool dialog appears (Figure 7).
Figure 7 Add IP Pool Dialog
Step 7
Enter the name of the new IP address pool. Enter the starting and ending IP addresses, and enter the subnet mask and click OK.
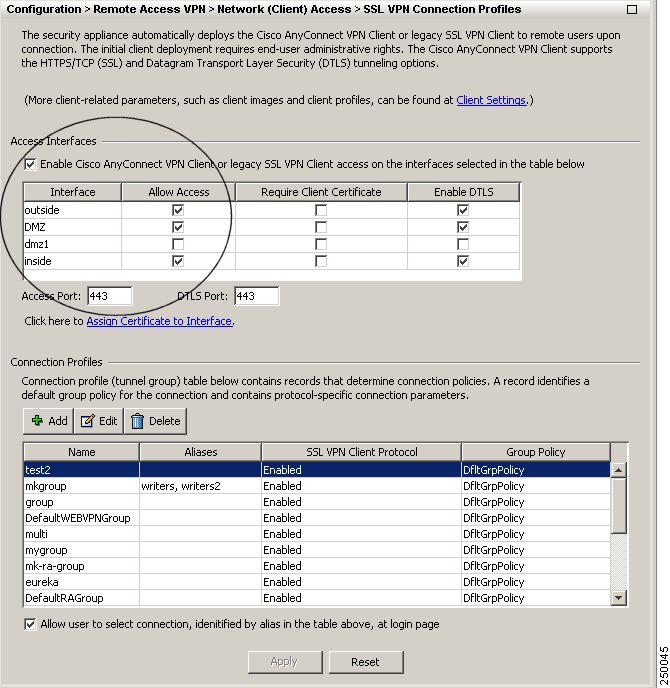
Step 8
Assign the IP address pool to a Connection (tunnel group). To do this, choose Network (Client) Access > AnyConnect Connection Profiles. The AnyConnect Connection Profiles panel appears (Figure 8):
Figure 8 AnyConnect Connection Profiles Dialog Box
Highlight a connection in the table, and click Edit. The Edit SSL VPN Connection dialog appears.
Click Select in the Client Address Assignment area. The Select Address Pool dialog appears (Figure 9), containing available address pools. Select a pool and click OK.
Figure 9 Select Address Pool Dialog
Step 9
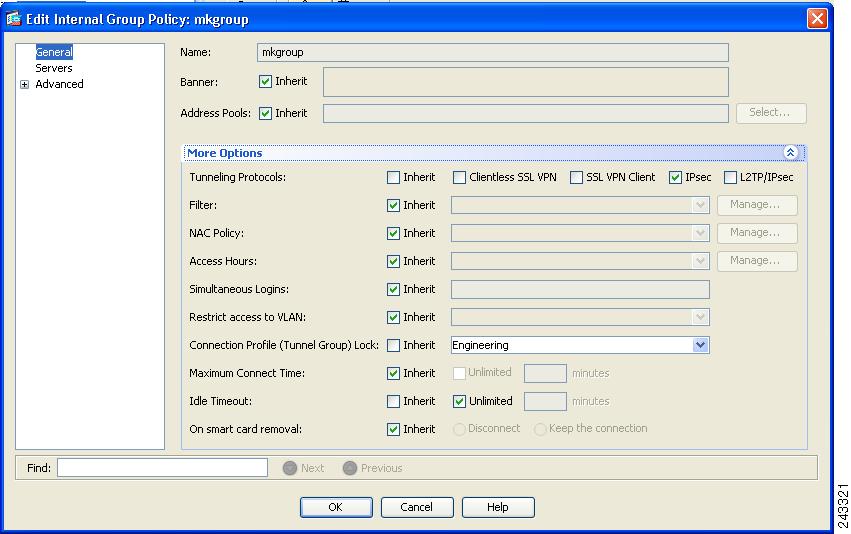
Identify SSL VPN as a permitted VPN tunneling protocol for the group or user.
Choose Network (Client) Access > Group Policies from the navigation pane. Highlight the group policy in the Group Policy table, and click Edit.
The Edit Internal Group Policy dialog appears (Figure 10):
Figure 10 Edit Internal Group Policy > General
Step 10
Check the SSL VPN Client check box to include SSL VPN as a tunneling protocol.
Step 11
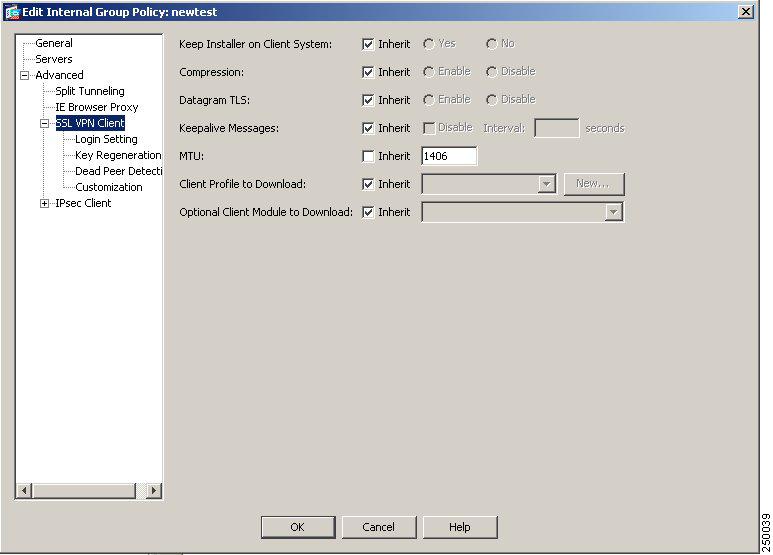
Configure SSL VPN features for a user or group. To display SSL VPN features for groups, In the navigation pane of the Internal Group Policy dialog, choose Advanced > SSL VPN Client. The SSL VPN Client features display Figure 11.
Figure 11 SSL VPN Client Features
Step 12
Configure the following features on the SSL VPN Client panel:
Keep Installer on Client System—Enable to allow permanent client installation on the remote computer. Enabling disables the automatic uninstalling feature of the client. The client remains installed on the remote computer for subsequent connections, reducing the connection time for the remote user.
Compression—Compression increases the communications performance between the security appliance and the client by reducing the size of the packets being transferred.
Datagram TLS—Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) allows the AnyConnect client establishing an SSL VPN connection to use two simultaneous tunnels—an SSL tunnel and a DTLS tunnel. Using DTLS avoids latency and bandwidth problems associated with some SSL connections and improves the performance of real-time applications that are sensitive to packet delays.
Keepalive Messages—Enter an number, from 15 to 600 seconds, in the Interval field to enable and adjust the interval of keepalive messages to ensure that an connection through a proxy, firewall, or NAT device remains open, even if the device limits the time that the connection can be idle. Adjusting the interval also ensures that the client does not disconnect and reconnect when the remote user is not actively running a socket-based application, such as Microsoft Outlook or Microsoft Internet Explorer.
MTU—Adjust the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) in bytes, from 256 to 1406 bytes. This setting affects only the AnyConnect client connections established in SSL, with or without DTLS. By default, the MTU size adjusts automatically based on the MTU of the interface that the connection uses, minus the IP/UDP/DTLS overhead.
Client Profile to Download—Specify a file on flash as a client profile. A profile is a group of configuration parameters that the CVC uses to configure the connection entries that appear in the client user interface, including the names and addresses of host computers.
Optional Client Module to Download—Specify any modules that the AnyConnect client needs to download to enable more features, such as Start Before Logon (SBL). To minimize download time, the CVC only requests downloads (from the security appliance) of core modules that it needs for each feature that it supports.
Loading the AnyConnect Client and Configuring the Security Appliance with CLI
This section covers the following topics:
•
Loading the AnyConnect Client
•
Disabling Permanent Client Installation
•
Enabling AnyConnect Client Profile Downloads
•
Enabling Start Before Logon for the AnyConnect Client
Loading the AnyConnect Client
Loading the client on the security appliance consists of copying a client image to the security appliance and identifying the file to the security appliance as a client image. With multiple clients, you must also assign the order that the security appliance loads the clients to the remote PC. Perform the following steps to install the client:
Step 1
Copy the client image package to the security appliance using the copy command from privileged EXEC mode, or using another method. In this example, the images are copied from a tftp server using the copy tftp command:
hostname# copy tftp flashAddress or name of remote host []? 209.165.200.226Source filename []? anyconnect-win-2.3.xxx-k9.pkgDestination filename []? anyconnect-win-2.3.xxx-k9.pkgAccessing tftp://209.165.200.226/anyconnect-win-2.3.xxx-k9.pkg...!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Writing file disk0:/cdisk71...!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!319662 bytes copied in 3.695 secs (86511 bytes/sec)Step 2
Identify a file on flash as a client package file using the svc image command from webvpn configuration mode:
svc image filename order
The security appliance expands the file in cache memory for downloading to remote PCs. If you have multiple clients, assign an order to the client images with the order argument.
The security appliance loads portions of each client in the order you specify until it matches the operating system of the remote PC. Therefore, assign the lowest number to the image used by the most commonly-encountered operating system. For example:
hostname(config-webvpn)# svc image windows.pkg 1hostname(config-webvpn)# svc image linux.pkg 2
Note
The security appliance expands SSL VPN client and the Cisco Secure Desktop images in cache memory. If you receive the error message ERROR: Unable to load SVC image - extraction failed, use the cache-fs limit command to adjust the size of cache memory:
Step 3
Check the status of the clients using the show webvpn svc command:
hostname(config-webvpn)# show webvpn svc1. disk0:/windows.pkg 1CISCO STC win2k+ 1.0.01,0,2,132Thu 06/22/2008 21:51:30.432. disk0:/linux.pkg 2CISCO STC linux 1.0.01,0,0,164Thu 06/15/2008 20:09:22.432 SSL VPN Client(s) installed
Enabling SSL VPN Connections
After installing the client, enable the security appliance to allow SSL VPN client connections by performing the following steps:
Step 1
Enable clientless, browser-based connections on an interface using the enable command from webvpn configuration mode:
enable interface
For example:
hostname(config)# webvpnhostname(config-webvpn)# enable outsideThe following is an example for an IPv6 connection that enables IPv6 on the outside interface:
hostname(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0hostname(config-if)# ipv6 enableStep 2
Enable SSL VPN connections globally using the svc enable command from webvpn configuration mode.
For example:
hostname(config-webvpn)# svc enableStep 3
Configure a method of address assignment. You can use DHCP, and/or user-assigned addressing. You can also create a local IP address pool using the ip local pool command from global configuration mode:
ip local pool poolname startaddr-endaddr mask mask
The following example assumes the authentication server group is LOCAL. The example creates the local IP address pool vpn_users:
hostname(config)# ip local pool vpn_users 209.165.200.225-209.165.200.254 mask 255.255.255.224Step 4
Assign IP addresses to a tunnel group. One method you can use to do this is to assign a local IP address pool with the address-pool command from general-attributes mode:
address-pool poolname
To do this, first enter the tunnel-group name general-attributes command to enter general-attributes mode. Then specify the local IP address pool using the address-pool command.
In the following example, the user configures the existing tunnel group telecommuters to use the address pool vpn_users created in step 3:
hostname(config)# tunnel-group telecommuters general-attributeshostname(config-tunnel-general)# address-pool vpn_usersStep 5
Assign a default group policy to the tunnel group with the default-group-policy command from tunnel group general attributes mode:
default-group-policy name
In the following example, the user assigns the group policy sales to the tunnel group telecommuters:
hostname(config-tunnel-general)# default-group-policy salesStep 6
Create and enable a group alias that displays in the group list on the login page using the group-alias command from tunnel group webvpn attributes mode:
group-alias name enable
First exit to global configuration mode, and then enter the tunnel-group name webvpn-attributes command to enter tunnel group webvpn attributes mode.
In the following example, the user enters webvpn attributes configuration mode for the tunnel group telecommuters, and creates the group alias sales_department:
hostname(config)# tunnel-group telecommuters webvpn-attributeshostname(config-tunnel-webvpn)# group-alias sales_department enableStep 7
Enable the display of the tunnel-group list on the login page from webvpn mode:
tunnel-group-list enable
First exit to global configuration mode, and then enter webvpn mode.
In the following example, the user enters webvpn mode, and then enables the tunnel group list:
hostname(config)# webvpnhostname(config-webvpn)# tunnel-group-list enableStep 8
Specify SSL as a permitted VPN tunneling protocol for the group or user with the vpn-tunnel-protocol svc command in group-policy mode or username mode:
vpn-tunnel-protocol svc
To do this, first exit to global configuration mode, enter the group-policy name attributes command to enter group-policy mode, or the username name attributes command to enter username mode, and then enter the webvpn command to enter webvpn mode and change the settings for the group or user.
The following example identifies SSL as the only permitted tunneling protocol for the group-policy sales:
hostname(config)# group-policy sales attributeshostname(config-group-policy)# webvpnhostname(config-group-webvpn)# vpn-tunnel-protocol svcFor more information about assigning users to group policies, see Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide, Chapter 30, "Configuring Tunnel Groups, Group Policies, and Users."
Enabling IPv6 Connections
The AnyConnect client allows access to IPv6 resources over a public IPv4 connection (only for Windows XP SP2, Windows Vista, Mac OS X, and Linux). You must use the command line interface to configure IPv6 access. ASDM does not support IPv6.
You enable IPv6 access using the ipv6 enable command as part of enabling SSL VPN connections. The following is an example for an IPv6 connection that enables IPv6 on the outside interface:
hostname (config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0hostname (config-if)# ipv6 enableTo enable IPv6 SSL VPN, do the following general actions:
1.
Enable IPv6 on the outside interface.
2.
Enable IPv6 and an IPv6 address on the inside interface.
3.
Configure an IPv6 address local pool for client-assigned IP addresses.
4.
Configure an IPv6 tunnel default gateway.
To implement this procedure, do the following steps:
Step 1
Configure Interfaces:
interface GigabitEthernet0/0nameif outsidesecurity-level 0ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0ipv6 enable ; Needed for IPv6.!interface GigabitEthernet0/1nameif insidesecurity-level 100ip address 10.10.0.1 255.255.0.0ipv6 address 2001:DB8::1/32 ; Needed for IPv6.ipv6 enable ; Needed for IPv6.Step 2
Configure an 'ipv6 local pool' (used for AnyConnect Client IPv6 address assignment):
ipv6 local pool ipv6pool 2001:DB8:1:1::5/32 100 ; Use your IPv6 prefix here
Note
You still need to configure an IPv4 address pool when using IPv6 (using the ip local pool command)
Step 3
Add the ipv6 address pool to your Tunnel group policy (or group-policy):
tunnel-group YourTunGrp1 general-attributes ipv6-address-pool ipv6pool
Note
Again, you must also configure an IPv4 address pool here as well (using the 'address-pool' command).
Step 4
Configure an IPv6 Tunnel Default Gateway:
ipv6 route inside ::/0 X:X:X:X::X tunneled
Disabling Permanent Client Installation
Disabling permanent AnyConnect client installation disables the automatic uninstalling feature of the client. The client remains installed on the remote computer for subsequent connections, reducing the connection time for the remote user.
To disable permanent AnyConnect client installation for a specific group or user, use the svc keep-installer command from group-policy or username webvpn modes:
svc keep-installer none
The default is that permanent installation of the client is enabled. The client on the remote computer stays installed at the end of every session. The following example configures the existing group-policy sales to not keep the client installed on the remote computer:
hostname(config)# group-policy sales attributeshostname(config-group-policy)# webvpnhostname(config-group-policy)# svc keep-installer nonePrompting Remote Users
You can enable the security appliance to prompt remote SSL VPN client users to download the client with the svc ask command from group policy webvpn or username webvpn configuration modes:
[no] svc ask {none | enable [default {webvpn | svc} timeout value]}
svc ask enable prompts the remote user to download the client or go to the portal page for a clientless connection and waits indefinitely for user response.
svc ask enable default svc immediately loads the client.
svc ask enable default webvpn immediately goes to the portal page.
svc ask enable default svc timeout value prompts the remote user to download the client or go to the portal page and waits the duration of value before taking the default action—downloading the client.
svc ask enable default webvpn timeout value prompts the remote user to download the client or go to the portal page, and waits the duration of value before taking the default action—displaying the portal page.
Figure 12 shows the prompt displayed to remote users when either default svc timeout value or default webvpn timeout value is configured:
Figure 12 Prompt Displayed to Remote Users for SSL VPN Client Download
The following example configures the security appliance to prompt the remote user to download the client or go to the portal page and to wait 10 seconds for user response before downloading the client:
hostname(config-group-webvpn)# svc ask enable default svc timeout 10Enabling AnyConnect Client Profile Downloads
An AnyConnect client profile is a group of configuration parameters, stored in an XML file, that the client uses to configure the connection entries that appear in the client user interface. The client parameters (XML tags) include the names and addresses of host computers and settings to enable additional client features.
You can create and save XML profile files using a text editor. The client installation contains one profile template (AnyConnectProfile.tmpl) that you can edit and use as a basis to create other profile files.
The profile file is downloaded from the security appliance to the remote user's PC, so you must first import the profile(s) into the security appliance in preparation for downloading to the remote PC. You can import a profile using either ASDM or the command-line interface. See Appendix A of the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Administrator Guide for a sample AnyConnect profile.
When the AnyConnect client starts, it reads the anyfilename.xml file in the following directory:
C:\Documents and Settings\<your_username>\Application Data\Cisco\Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client.
The AnyConnect client stores data that the user previously entered, such as the username and the security appliance IP address/hostname from the last successful connection. The client then establishes an initial connection to the security appliance to get the list of tunnel groups to display in the GUI. during this initial connection, if the security appliance is no longer accessible or if the hostname cannot be resolved, the user sees the message, "Connection attempt has failed" or "Connection attempt has failed due to unresolvable host entry."
You can place a copy of your profile (for example, CiscoAnyConnectProfile.xml) in the directory: C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\Cisco\Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client\Profile The location for Windows Vista is slightly different: C:\ProgramData\Cisco\Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client\Profile. The host that appears in the Connect to combo box is the first one listed in the profile or the last host you successfully connected with. This is a way to test a potential client profile.
For more information about editing AnyConnect client profiles, see the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Administrator Guide.
After you create an AnyConnect client profile, follow these steps to enable the security appliance to download them to remote AnyConnect client users:
Step 1
Identify to the security appliance an AnyConnect client profiles file to load into cache memory using the svc profile command from webvpn configuration mode:
[no] svc profiles {value profile | none}
This command makes profiles available to group policies and username attributes of AnyConnect client users.
In the following example, the user previously created two new profile files (sales_hosts.xml and engineering_hosts.xml) from the cvcprofile.xml file and loaded them to the flash memory.
Now the user specifies these files as AnyConnect client profiles for use by group policies, specifying the names sales_hosts and engineering_hosts:
asa1(config-webvpn)# svc profiles sales disk0:/sales_hosts.xmlasa1(config-webvpn)# svc profiles engineering disk0:/engineering_hosts.xmlEntering the dir cache:stc/profiles command shows the profiles loaded in cache memory:
asa1(config-webvpn)# dir cache:/stc/profilesDirectory of cache:stc/profiles/0 ---- 774 11:54:41 Oct 22 2008 engineering.xml0 ---- 774 11:54:29 Oct 22 2008 sales.xml2428928 bytes total (18219008 bytes free)asa1(config-webvpn)#Step 2
Enter group policy webvpn or username attributes webvpn configuration mode and specify a profile for the group or user with the svc profiles command:
[no] svc profiles {value profile | none}
In the following example, the user follows the svc profiles value command with a question mark (?) to query the security appliance so see the available profiles. Then the user configures the group policy to use the AnyConnect client profile sales:
asa1(config-group-webvpn)# svc profiles value ?config-group-webvpn mode commands/options:Available configured profile packages:engineeringsalesasa1(config-group-webvpn)# svc profiles sales
Enabling Rekey
When the security appliance and the AnyConnect client perform a rekey, they renegotiate the crypto keys and initialization vectors, increasing the security of the connection.
To enable the client to perform a rekey on an SSL VPN connection for a specific group or user, use the svc rekey command from group-policy and username webvpn modes.
[no] svc rekey {method {new-tunnel | none | ssl} | time minutes}
method new-tunnel specifies that the client establishes a new tunnel during rekey.
method none disables rekey.
method ssl specifies that SSL renegotiation takes place during rekey.
time minutes specifies the number of minutes from the start of the session until the rekey takes place, from 1 to 10080 (1 week).
In the following example, the client is configured to renegotiate with SSL during rekey, which takes place 30 minutes after the session begins, for the existing group-policy sales:
hostname(config)# group-policy sales attributeshostname(config-group-policy)# webvpnhostname(config-group-policy)# svc rekey method sslhostname(config-group-policy)# svc rekey time 30Enabling or Disabling DTLS
Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) allows the AnyConnect client establishing an SSL VPN connection to use two simultaneous tunnels—an SSL (TLS) tunnel and a DTLS tunnel. DTLS requires the TLS tunnel for a number of reasons, including protocol negotiation and fallback technologies. Using DTLS avoids latency and bandwidth problems associated with some SSL connections and improves the performance of real-time applications that are sensitive to packet delays.
DTLS is enabled implicitly when you enable the interface. If you decide to disable DTLS, SSL VPN connections connect with an SSL VPN tunnel only.
Use the following command options to enable an interface with DTLS or just with TLS:
You can enable DTLS for all AnyConnect client users with the dtls enable command in webvpn configuration mode:
[no] enable interface | tls-only}
For example, to enable the outside interface with DTLS, enter the following:
hostname(config-webvpn)# enable outside
To disable DTLS and allow only TLS, enter the following command instead:
hostname(config-webvpn)# enable outside tls-onlyYou can enable DTLS or TLS on a per-user or per-group basis.
Note
When using the AnyConnect VPN client with DTLS on an ASA device Dead Peer Detection (DPD) must be enabled in the group policy on the ASA to allow the AnyConnect client to fall back to TLS, if necessary. Fallback to TLS occurs if the AnyConnect client cannot send data over the UDP/DTLS session, and DPD is the mechanism necessary for fallback to occur.
Enabling Start Before Logon for the AnyConnect Client
To minimize download time, the AnyConnect client requests downloads (from the security appliance) only of core modules that it needs for each feature that it supports. To enable new features, such as Start Before Logon (SBL), you must specify the module name using the svc modules command from group policy webvpn or username webvpn configuration mode:
[no] svc modules {none | value string}
The string for SBL is vpngina
In the following example, the user enters group-policy attributes mode for the group policy telecommuters, enters webvpn configuration mode for the group policy, and specifies the string vpngina to enable SBL:
hostname(config)# group-policy telecommuters attributeshostname(config-group-policy)# webvpnhostame(config-group-webvpn)# svc modules value vpnginaIn addition, the administrator must ensure that the AnyConnect <anyfilename.xml> profile has the <UseStartBeforeLogon> statement set to true. For example:
<UseStartBeforeLogon UserControllable="false">true</UseStartBeforeLogon>The system must be rebooted before Start Before Logon takes effect.
For more information about editing AnyConnect client profiles, see the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Administrator Guide.
Note
On Systems prior to Windows Vista, Start Before Logon works only for PCs that are part of a domain and not part of a workgroup or working standalone.
CSA Interoperability with the AnyConnect Client and Cisco Secure Desktop
If your remote users have Cisco Security Agent (CSA) installed, you must import new CSA policies to the remote users to enable the AnyConnect VPN Client and Cisco Secure Desktop to interoperate with the security appliance.
To do this, follow these steps:
Step 1
Retrieve the CSA policies for the AnyConnect client and Cisco Secure Desktop. You can get the files from:
•
The CD shipped with the security appliance.
•
The software download page for the ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance at http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/asa.
The filenames are AnyConnect-CSA.zip and CSD-for-CSA-updates.zip
Step 2
Extract the .export files from the .zip package files.
Step 3
Choose the correct version of the .export file to import. The Version 5.2 export files work for CSA Versions 5.2 and higher. The 5.x export files are for CSA Versions 5.0 and 5.1.
Step 4
Import the file using the Maintenance > Export/Import tab on the CSA Management Center.
Step 5
Attach the new rule module to your VPN policy and generate rules.
For more information, see the CSA document Using Management Center for Cisco Security Agents 5.2. Specific information about exporting policies is located in the section Exporting and Importing Configurations.
Uninstalling the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client
To manually uninstall the AnyConnect client from a Windows system, use the standard "Add or Remove Programs" Control Panel available from the Start menu.
The procedure for manually uninstalling the AnyConnect client from a Linux or Mac OS X system is the same for both systems. As root, run the following shell script:
/opt/cisco/vpn/bin/vpn_uninstall.shTypically, you would do this via sudo, as follows:
$ sudo /opt/cisco/vpn/bin/vpn_uninstall.shIf you do not use sudo, use a root shell:
# /opt/cisco/vpn/bin/vpn_uninstall.shUsage Notes
This section lists known interoperability considerations and other issues to consider before installing and using the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.2016 and earlier releases.
Vista Routing and Remote Access Service Incompatibility
The Routing and Remote Access Service on a client PC running Vista prevents AnyConnect from updating the Windows IP Forwarding (routing) table to direct network traffic to the VPN connection. A Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client window displays the following message:
The Windows Routing and Remote Access service is not compatible with the VPN client. The VPN client cannot operate correctly when this service is running.
To open the window required to disable this service, choose Start > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services > Routing and Remote Access Service.
PC with Faulty Driver Blue-screens after AnyConnect Authentication
PCs sometimes crash after AnyConnect authentication if they are running Microsoft Windows XP with SP2 and the faulty Microsoft driver usbhub.sys (Default Hub Driver for USB, v5.1.2600.3020). To prevent the problem, users may do either of the following:
•
Upgrade to XP SP3.
•
Go to Stop error when you resume a computer that is running Windows XP or a 64-bit version of Windows Server 2003 from hibernation: "STOP 0x1000007E" to install the Microsoft hotfix.
vpncli Process Exits During an Upgrade and Is Not Relaunched
By design, any process that needs to be upgraded is terminated so that the upgrade can complete. If the process is the CLI (vpncli), then the process is not relaunched. The command shell might also exit, depending on the configuration of the default behavior of the command shell on a particular OS.
XML Profile Enhancement for Selecting Windows Certificate Store
In Release 2.3.185 and later releases, administrators can control which certificate store AnyConnect uses for locating certificates. This applies only to the AnyConnect client on Windows.
Windows provides separate certificate stores for the local machine and for the current user. Users with administrative privileges on the computer will have access to both stores. The original AnyConnect behavior was to load certificates from all available certificate stores. An ASA administrator may want to configure AnyConnect via XML profile to restrict certificate lookups to only the user store or only the machine store.
To this end, a new setting called CertificateStore has been added to the ClientInitialization element in the XML profile. It has three possible (case-sensitive) values: All (default), Machine, or User.
Note
The default setting (All) is appropriate for the majority of cases. Do not change this setting unless you have a specific reason or scenario requirement to do so.
If the CertificateStore setting is not in the profile, AnyConnect uses all available certificate stores. This setting has no effect on non-Windows platforms.
Within the ClientInitialization section of the XML template, you can specify the certificate store that you want to use. Possible values are as follows:
•
All—(default) All certificates are acceptable.
•
Machine—Use the machine certificate.
•
User—Use a user-generated certificate.
Note
These attributes are case-sensitive.
Certificate Enrollment Prompts Can Occur Twice
Internet Explorer (IE) attempts to access the user certificate store when one establishes a browser-based VPN connection. With Start Before Logon, AnyConnect attempts to access the machine certificate store because user login credentials are not yet present. Because Internet Explorer cannot access the machine certificate store, users who use WebLaunch to start AnyConnect, or use Start Before Logon may be prompted to enroll first by Internet Explorer for a user certificate and later by AnyConnect for a machine certificate; however, the prompts do not specify the type of certificate store accessed.
AnyConnect Client Setup Flow
The following section is an example of the AnyConnect client setup flow. In this example, there is one tunnel session.
•
There can be up to two channels associated with the one tunnel session (TLS and DTLS).
•
TLS is always established as the first channel and this channel remains active for the entire tunnel session.
TLS is established in two phases:
1.
Authentication phase—The authentication phase uses core components of the OS, for example WinInet on Windows. This phase uses the cryptographic protocols available to the OS; for example, AES is only available on Vista or later, therefore, you must configure the Secure Gateway to use the protocols that allow the authentication phase to succeed.
2.
Tunneling phase—When the authentication phase is complete, the tunneling phase begins. This phase uses the strongest possible cryptography offered by the Secure Gateway configuration; therefore, if the Secure Gateway has configured:
AES-256-SHA1; 3DES-MD5, RC4-MD5The tunneled data uses AES-256-SHA1.
Note
Because platforms such as Windows XP do not support AES in WinInet, the addition of 3DES-MD5 as an alternative cryptographic suite is needed to complete the initial authentication phase.
When the TLS channel is active, tunneled data immediate flows over the TLS channel.
AnyConnect then attempts to fall-forward to the preferable DTLS channel if the headend allows this configuration.
AnyConnect also falls back from DTLS to TLS at any time if the DTLS channel DPD indicates a loss of communication.
Control data always flows down the TLS channel (there are also separate DPDs and svc-keepalives for both channels).
Note
There is some degree of TLS traffic that is compressed for all tunnel types, whether doing DTLS or solely TLS.
Using the AT&T Aircard with Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client
When using the AT&T Aircard with Cisco AnyConnect VPN client, if you encounter problems, use the AT&T Communications Manager to uncheck Use Rules Engine in version 6.7 of the AT&T client or Use Connection Maintenance in the 6.2 version.
Usage Notes for AnyConnect VPN Client Release 2.3
The following usage notes are specifically for Release 2.3.
Split-Exclude Tunneling Requires Enabling AllowLocalLanAccess in the AnyConnect Client
Split-Exclude Tunneling Requires Enabling AllowLocalLanAccess in the AnyConnect Client. All split-exclude tunneling is regarded as local LAN access. To use the exclude feature of split-tunneling, you must enable the AllowLocalLanAccess preference in the AnyConnect VPN Client preferences. By default, local LAN access is disabled. This behavior is different from that of AnyConnect Client Release 2.2.
To allow local LAN access, and therefore split-exclude tunneling, a network administrator can enable it in the profile, or users can enable it in their preferences settings. To allow local LAN access, a user selects the "Allow Local LAN access" check box if split-tunneling is enabled on the secure gateway and is configured with the "split-tunnel-policy exclude specified" policy.
AutoReconnectBehavior Preference Defaults to DisconnectOnSuspend
The AutoReconnectBehavior preference defaults to DisconnectOnSuspend, This behavior is different from that of AnyConnect Client Release 2.2. For reconnect after resume, the network administrator must either set ReconnectAfterResume in the profile or make the AutoReconnect and AutoReconnectBehavior preferences user controllable in the profile to allow users to set it.
Using Virtualization Software over a Tunnel with AnyConnect.
To connect to resources on the private side of the secure gateway using virtualization technologies, configure the virtual machine on your PC to use NAT for the networking configuration. This allows tunneling of the Virtual Machine traffic over the AnyConnect tunnel.
Microsoft Java is Not Supported from the AnyConnect WebLaunch
The AnyConnect client no longer supports Microsoft Java from the AnyConnect WebLaunch. To use WebLaunch, Windows end-systems must have either ActiveX enabled or Sun Java version 1.4 or higher installed.
AnyConnect 2.3 Supports DEP Option
On Windows Vista, on any hardware, DEP is on by default for all AnyConnect processes. For Windows 2003 and Windows XP, this is true if the hardware processor supports DEP. See http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;875352 for more details.
Avoiding Installation of an ActiveX Control in Pre-deployment Scenarios
In pre-deploy scenarios, if you intend to use only standalone mode and/or you do not want the ActiveX control to be installed on a system, you can do one of the following operations:
•
Create an MSI transform to set the ActiveX property to disabled (NOINSTALLACTIVEX=1)
•
Invoke the installer as follows: MSIExec /i anyconnect-win-n.n.n-pre-deploy-k9.msi NOINSTALLACTIVEX=1
where n.n.n is the actual version that is being installed.
Usage Notes From Earlier Releases
The following usage notes from earlier releases also apply to the AnyConnect client Release 2.3.
Network Connections Control Panel Might Show Generic Adapter Name
The name of the adapter that AnyConnect adds to Windows (as shown in the Network Connections control panel) might be marked with the generic name "Local Area Connection n", where n is a number (for example, Local Area Connection 6). The Windows operating system sets this generic name when the adapter is installed. The AnyConnect client code attempts to update this name to "Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client Connection" each time a VPN session starts. If an upgrade occurs during Start Before Login (SBL), then the attempt to change the name of the AnyConnect adapter might fail. In this case, the generic name appears in the operating system's Network Connections control panel. The next time a VPN is established (after the SBL-initiated session disconnects), the name should be properly updated. This is a cosmetic issue (due to a limitation in the operating system) that affects only the name displayed in the Windows Network Connections control panel. An upgrade during SBL is the only known cause for this issue.
QoS Policing Does Not Apply to AnyConnect Connections
Quality of Service policing does not apply to AnyConnect client connections. Attempting to do this results in an error message.
Network Subsystem on Windows Vista Might Become Unresponsive During Sleep/Resume Cycles or Other High-load Conditions (KB-952876)
If you use sleep and resume on Vista, you might find that the tunnel cannot be established due to the AnyConnect driver not being enabled. A reboot is typically required to recover from this condition.
The problem is caused by an issue in the Vista Kernel component as described in KB-952876 (http://support.microsoft.com/kb/952876). When this issue occurs, another core Vista component, TCPIPREG.sys, fails to function. The Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client relies on this service to set the IP address of the Virtual Adapter. If you see an error stating that the Virtual Adapter could not be set up, you might have encountered this issue. We recommend that you apply the patch if you are experiencing issues on Vista where the AnyConnect adapter fails to enable. After applying the patch, you might still see an occasional failure due to a timing issue in the TCPIPREG.sys service. This is rare and should be recoverable by simply trying the tunnel a second time. Cisco is working with Microsoft to correct this remaining issue.
AnyConnect Client over Proxies
AnyConnect supports connections to the security appliance via a proxy server that uses Basic and NTLM authentication. Socks proxies are not supported. DTLS (using UDP) is not supported if the proxy server runs only TCP.
Additionally, on Windows only, you can also use authenticating proxies that use Basic or NTLM for authorization. If you have Internet Explorer configured with a proxy, you must activate the "Use HTTP 1.1 through proxy connections" setting in the advanced Internet Explorer settings to use the AnyConnect client. If this option is not set, the AnyConnect client connection does not come up.
In Internet Explorer, choose Internet Options from the Tools menu. Click the Advanced tab, and under the HTTP 1.1 Settings, check "Use HTTP 1.1 through proxy connections."
WINS and DNS
The AnyConnect client supports group-policy configured primary and secondary Windows Internet Naming Services (WINS) or Domain Naming Services (DNS).
SSL VPN Clients Do Not Support DNS Fallback for Split Tunneling
The AnyConnect 2.3 client does not support DNS Fallback for Split Tunneling (also called Split DNS). Regardless of whether split DNS is enabled on the security appliance, VPN3000 Concentrator, or IOS, all DNS queries are sent through the tunnel.
Setting the Secure Connection (Lock) Icon
The Lock icon indicates a secure connection. XP automatically hides this icon among those that have not been recently used. The end user can prevent XP from hiding this icon as follows:
Step 1
Go to the taskbar where the tray icons are displayed and right click the left angle bracket ( < ).
Step 2
Select "Customize Notifications..."
Step 3
Select "Cisco Systems AnyConnect VPN Client" and set to "Always Show."
Cisco Security Agent Version Requirements
Cisco Security Agent (CSA) Version 4.5 and higher is the only version compatible with the AnyConnect client. The appropriate CSA policy ships with CSA and is attached to the group "Remote desktops and laptops." These policies are not enabled by default; you must select them to prevent the AnyConnect client from failing with CSA version 4.5.
PC Wireless Client Configurations
If a client wireless adapter profile supports scanning for a better access point, and you use the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client or Cisco VPN Client (IPsec) with that profile, disable such scanning. These scans can cause disconnections or stall traffic on the tunnel. To support scanning for non-SSL/IPsec connections, create another profile.
Certificate Revocation List Processing
A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) contains a number of certificate serial numbers that have been revoked. The client downloads this list from a CRL server and looks up the certificate of the security appliance in the list.
The Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client requires a Certificate Revocation key with a value of 1 to enable the checking of the certificate revocation list. The following path shows the Certificate Revocation key and value on the remote PC:
My Computer | HKEY_USERS | <Secure ID_of_Logged_User> | Software | Microsoft | Windows | CurrentVersion | CertificateRevocation REG_DWORD 0x00000001
The client attempts to read the value of the flag CertificateRevocations shown above to determine whether the client checks for revocation of the security appliance certificate.
To set the Revocation flag, select Control Panel > Internet Options. Click the Advanced tab, and click the Restore Defaults button near the bottom of the window. This option restores all of the options under the Advanced tab to the original settings.
Alternatively, to avoid restoring original settings, you can perform the following:
Step 1
Check the check-box Check for server certificate revocation (requires restart).
Step 2
Click Apply.
Step 3
Click OK.
Step 4
Restart Windows.
If Revocation is enabled, a dialog window prompts the remote user to accept or deny the certificate that has a revocation error.
Dynamic Install Fails on Windows Vista When Running Low-rights Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer 7 on Windows Vista has a new security feature called Low Rights Internet Explorer. This feature changes the rights of the sandbox that the browser operates from to the lowest level possible. Because Windows Installer service has the ability to elevate all the way to Local System, the Windows Installer refuses to accept calls from Low Rights processes (as IE7 now is).
When using low-rights Internet Explorer to attempt a first-time web installation of the AnyConnect client, the MSI install fails immediately. The MSI log contains the following entry:
Failed to connect to server. Error: 0x80070005To avoid this, users on Vista must add the Secure Gateway to the Trusted Zone.
AnyConnect Fails to Establish a DTLS Tunnel When Using RC4-MD5 Encryption
When the ASA to which the AnyConnect client is attempting to connect is configured to only do RC4-MD5 encryption, the client is unable to establish a DTLS tunnel.
msvcp60.dll Must Be Available for Installation of the AnyConnect Client
To use the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, you must have the file msvcp60.dll — c++ runtime located in the winnt\system32 directory on your system. This dll is likely already to be present on most images, since installing other products (such as Office 2000) results in this file being placed on the system.
Because of this common practice, this dll file is excluded to reduce the image size for AnyConnect client dynamic installations. For more information about this problem, see the Microsoft Knowledge Base, article 259403, at http://support.microsoft.com/kb/259403.
Secure VPN Via Windows Remote Desktop Is Supported
The AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.2 and higher, supports VPN connection establishment via a Windows Remote Desktop session. If you connect to the PC via Remote Desktop, your VPN connection will be allowed.
AnyConnect Start Before Logon GINA Might Not Appear on Login Screen after Reboot
When the AnyConnect Start Before Logon GINA is installed on a user's PC using the standalone installer (WinGinaSetup-xxxx.msi), the GINA does not appear on the login screen after a reboot. This occurs because the AnyConnect GINA requires that the following be installed:
•
AnyConnect Client
•
An AnyConnect profile (anyfilename.xml file) in Documents and Settings/All Users/Application Data/Disco/CiscnyConnect VPN Client/Profile/ with the following line in it:
<UseStartBeforeLogon UserControllable="false">true</UseStartBeforeLogon>Network administrators must push out a profile using their SMS or other software deployment engine along with the MSI files if they want to perform a preinstall of the profile.
When Using a Client-Side Proxy and Full Tunneling, the Proxy Should Be Reset
When a client side proxy is used to connect to the Internet, full tunneling cannot not be enforced on the client since users can still connect to the proxy server even when in full tunneling mode. This behavior inherent in the nature of SSL VPN solutions.
To work around this issue, set the VPN connection MSIE configuration settings on the secure gateway to "no proxy" rather than "do not change proxy settings." This will cause the client to remove the "public side" proxy settings from MSIE, while the VPN connection is established. Then, browser and other Windows Internet traffic goes over the tunnel.
Linux-Specific AnyConnect Client Issue
The AnyConnect client might not establish DTLS tunnel in Linux and might revert to TLS.
In addition, the AnyConnect client reports that statistics in the Linux user interface are not available. Closing the user interface without disconnecting and launching another (while the tunnel is still active) seems to fix the problem.
Setting the AnyConnect Pre-Login Banner
The pre-login banner is the optional banner message that appears in line with the end-user AnyConnect client interface. You can use either of the following methods to configure the banner on the security appliance:
•
Import/export the DfltCustomization file <custom> <auth-page>.
<copyright-panel><mode>enable</mode><text>Copyright...</text><copyright-panel>The <text> element value is the pre-banner text.
•
Select ASDM.Remote Access VPN > Clientless SSL VPN Access > Portal > Customization. On the resulting window, select DfltCustomization, and then Edit. A GUI appears, and you can edit the Copyright text.
AnyConnect Requires That the ASA Be Configured to Accept TLSv1 Traffic
The AnyConnect client cannot establish a connection with the following ASA settings for "ssl server-version":
•
ssl server-version sslv3.
•
ssl server-version sslv3-only.
Smartcards Supported
The AnyConnect client supports Aladdin eTokenPro32k and Axalto Smartcards and readers on Windows Vista Ultimate, Windows XP Professional with SP2 and Windows 2000 Professional with SP4, as well as for Mac OS X Versions 10.4 and 10.5. In Release 2.3, there is no Smartcard support for Linux.
IPv6 AnyConnect Failover is Not Supported for the Security Appliance
ASA Releases 8.0 and 8.1 do not support IPv6 failover, so failover of IPv6 AnyConnect (as well as failover of clientless SSL VPN) sessions is also not supported.
RADIUS Interim Accounting Update Feature
In conjunction with ASA Release 8.0.3.1 and higher, the AnyConnect client now supports interim accounting for a VPN connection running simultaneous SSL VPN Clientless and AnyConnect sessions.
This is especially important for SSO integration with the NAC appliance, where NAC requires the Accounting Start request to contain the Frame-IP-Address.
Previously, if an AnyConnect session was launched from a browser and not the standalone AnyConnect GUI, the Clientless session (with no concept of Frame-IP) would send the Accounting Start request without it, and NAC-SSO would fail as a result.
To enable this feature, enable the new CLI command interim-accounting-update under aaa-server on the security appliance.
AnyConnect Split-tunneling Works on Windows Vista
In the AnyConnect client, Release 2.1 and higher, split-tunneling works correctly with Windows XP, Windows 2000, and Windows Vista.
Selecting Crypto Toolkits for AnyConnect on Windows Platforms
To use Windows certificates and proxy support, the AnyConnect client uses the cryptography support present on the operating system to establish an authentication session. The cryptographic cipher used for authentication is bounded by what the host operating system supports and is distinct from the cipher used to encrypt the AnyConnect tunnel data.
This is commonly encountered when an administrator configures "ssl encryption aes128-sha1" on the security appliance. Because older versions of Windows (pre-Vista) do not support AES, neither Internet Explorer nor the AnyConnect client in stand-alone mode can establish clientless or AnyConnect sessions on these platforms when only AES is configured.
Since the AnyConnect client always attempts to use the strongest tunnel encryption possible, it is possible to work around this by using "ssl encryption aes128-sha1 3des-sha1". This causes the initial authentication session to use triple DES, but causes all tunneled data to be encrypted with AES.
First User Message for Double-byte Languages Does Not Translate Correctly
With the Unicode version of the AnyConnect VPN Client—which allows for double-byte languages such as Japanese, Chinese, and so on—the first user message to appear does not correctly translate, because that message is missing from the AnyConnect translation table.
To work around this problem, add the following lines to the translation table file that you are using for translations:
msgid "Please enter your username and password."
msgstr ""
The message string (msgstr) value should be your translation of the English string in msgid.Ensuring Reliable DTLS (UDP) Connections Through Third-Party Firewalls
A third-party network firewall blocks DTLS (UDP) traffic if traffic is idle for 40 seconds and if DTLS keepalive is not enabled.
When a third-party network firewall is located between the client PC and the security appliance, the firewall inspects each DTLS packet and makes a decision whether to pass the packet along to the destination. If there has been an idle period of DTLS traffic, the firewall might stop sending data to the client or security appliance.
A customer has observed that the default behavior of a third-party firewall in their network results in the DTLS (UDP) traffic being dropped after an idle period of 40 seconds. This occurs when the DTLS keepalive is not configured, or is configured with a value that is greater than the timeout interval of the third-party firewall.
By default, the DTLS keepalive is disabled.
When the firewall stops DTLS traffic, applications such as Microsoft Outlook stop responding while the DTLS tunnel remains active. The time of inactivity is directly related to the interval set for client DTLS DPD. By default, DPD is set to an optimal value of 30 seconds which should work in most cases.
If the client DTLS DPD is too high, failover does not occur quickly enough, and a user notices applications being unresponsive. Once the client DTLS DPD is set correctly, the customer then notices excessive loss and re-establishment of the DTLS channel. This might also be perceived as poor performance of the tunnel.
To correct this problem, do the following steps:
Step 1
Enable the client DTLS DPD and configure it to be twice the interval of the firewall idle timer.
For example, set this value to 2 minutes when using the default setting with the third-party firewall (40 seconds). The client DTLS DPD value should be no greater than 10 minutes to ensure that TLS fallback occurs in a timely manner.
Step 2
Enable the client DTLS keepalive and configure it to be at least 10 seconds less than the firewall idle timer default interval.
For example, set this value to 30 seconds if using the default configuration (40 seconds) of the third-party firewall.
If there has been an idle period of DTLS traffic, the firewall might stop sending data to the client or security appliance. The client attempts to re-establish DTLS each time this occurs up to the limit of the retry counter. The tunnel falls back to TLS during this period if the DTLS DPD is set to a sufficient value. For example, a typical setting for DPD from both the client and security appliance might be 120 seconds. If the DTLS session is blocked by the firewall, a user experiences an outage and then eventually the session falls back to TLS. This outage is directly proportional to the value set for DTLS DPD.
DTLS is a UDP based protocol and is connectionless. There is a flow associated with the DTLS session that is based on the source and destination addresses and ports. Firewalls build a session table based on these values and track this as a unique session. By default, DTLS is enabled when SSL VPN access is enabled on an interface.
No AnyConnect Confirmation Dialog for Cisco Secure Desktop Users
When contacting a central-site security appliance that enforces a Cisco Secure Desktop policy, the AnyConnect client no longer lets the user terminate the connection attempt prior to starting the download and execution of Cisco Secure Desktop. In AnyConnect Release 2.0, the dialog appears for each connection attempt. The AnyConnect client, Release 2.1 and higher, however, removes this dialog for Cisco Secure Desktop users, and Cisco Secure Desktop processing continues without further input from the user.
AnyConnect Client Uses Custom-built OpenSSL Libraries Based on 0.9.8f
The AnyConnect client uses the OpenSSL cryptography libraries to perform encryption and security protocol encapsulation. A new version of OpenSSL has been released that fixes several issues in older versions of OpenSSL. The OpenSSL libraries used by the AnyConnect client have been updated by merging in 0.9.8f changes with custom Cisco changes.
AnyConnect is not exposed to the flaws found between 0.9.8f and 0.9.8j because it does not include the vulnerable code.
For more information see the following URLs:
http://www.cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2007-4995
http://www.cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2007-5135
Optionally Disable Tearing Down Tunnel Upon Smartcard Removal
A network administrator can optionally disable tearing down a tunnel when the remote user removes the Smartcard. Some companies impose a requirement that a user must remove his/her Smartcard when the laptop is unattended. If the remote user in such a situation is downloading an application or replicating data to the central site and needs to step away from the laptop, the transfer fails and must be restarted because the tunnel has been dropped.
Upgrading Standalone AnyConnect Client for Windows Vista Shows Activity Indication
When Windows Vista users upgrade via standalone AnyConnect client, the client briefly displays a message "Exiting. Update in progress." and then the client exits. There is no AnyConnect or Installer windows or dialogs visible on the user's desktop for the duration of the upgrade. When the upgrade completes, the AnyConnect icon appears in the system tray.
When Windows Vista users upgrade via the browser launch of AnyConnect, the AnyConnect Downloader window is visible for the duration of the upgrade, but the Installer window is not visible. When the upgrade completes, the Downloader exits and the AnyConnect icon appears in the system tray.
AnyConnect SBL Does Not Support Dialer and Third-Party Application Launchers
Due to the security implications, the dialer and third-party application launchers are not supported in AnyConnect Start Before Login.
Start Before Logon and PLAP Require a Network Connection
Start Before Logon and PLAP require a network connection to be present at the time it is invoked. In some cases, this might not be possible, because a wireless connection might depend on credentials of the user to connect to the wireless infrastructure. Since SBL mode precedes the credential phase of a login, a connection would not be available in this scenario. In this case, for SBL/PLAP to work, the wireless connection must be configured to cache the credentials across login, or another wireless authentication must be configured.
Windows Machine Cannot Be Named localhost
Microsoft allows a user to configure the machine name as "localhost" without any warnings. When a machine has the name of localhost, connections made with the SSL VPN Client or IPSec VPN Client fail.
AnyConnect Client connections fail without logs clearly outlining the issue. The AnyConnect message is "Unable to establish VPN." IPSec VPN Client connections fail with Reason 442. To work around this issue, rename the PC to something other than localhost.
Synchronizing a Mobile Device to a PC While a Tunnel Is Active
If you use ActiveSync or Windows Mobile Device Center to synchronize a mobile device to your PC while the tunnel is active, you must either enable Local LAN in the security appliance configuration or configure your device to use a serial port instead of Remote Network Driver Interface Specification (RNDIS).
When RNDIS is enabled, mobile devices are assigned a link-local address when they are connected to the PC. When Tunnel All is configured on the security appliance, all network traffic, including link-local traffic, is sent to the tunnel interface.
If Tunnel All is a requirement for your deployment, you can try to configure the mobile device to synchronize using a serial port interface, you can synchronize your device while Tunnel All is configured. On the Mobile Device, under Start > Settings > Connections > USB-to-PC, deselect the "Enable advanced network functionality" check box to disable RNDIS.
Obtaining a DHCP Ethernet IP If Connected via Wireless-only First
When roaming between different network interfaces with the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, you might be unable to obtain an IP address via DHCP on a new interface, causing an inability to move to the new network without first tearing down the VPN session.
To work around this issue, ensure that Split Tunneling or Local LAN access is enabled. With one of these features enabled, the new local network interface can obtain a DHCP assigned IP address and the user can successfully roam.
AnyConnect Support Policy
We support all AnyConnect software versions available on the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Software Download site; however, we provide fixes and enhancements only in maintenance or feature releases based on the most recently released version.
Caveats
Caveats describe unexpected behavior or defects in Cisco software releases. The following sections, prioritized with the latest 2.3 release first, identifies caveats with Severities 2 and 3.
Note
If you have an account with CCO, you can use Bug Navigator II to find caveats of any severity for any release. To reach Bug Navigator II on CCO, select Software & Support: Online Technical Support: Software Bug Toolkit or navigate to http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/Support/Bugtool/launch_bugtool.pl.
Open Caveats in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.2016
Table 6 lists the caveats that are unresolved in the Cisco AnyConnect VPN client, Release 2.3.2016.
Open Caveats in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.254
Table 7 lists the caveats that are unresolved in the Cisco AnyConnect VPN client, Release 2.3.254.
Open Caveats in Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.185
Table 8 lists the caveats that are unresolved in the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.185.
Resolved Caveats
The following sections identify the caveats that each Release 2.3 build resolves.
Caveats Resolved in AnyConnect Release 2.3.2016
Table 9 shows the caveats that AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.2016 resolves.
Caveats Resolved in AnyConnect Release 2.3.254
Table 10 shows the caveats that AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.254 resolves.
Caveats Resolved by AnyConnect Release 2.3.185
Table 11 shows the caveats that AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.3.185 resolves.
Notices/Licensing
See the following sections for Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client license information.
License Options
For brief descriptions and example product numbers (SKUs) of the AnyConnect user license options, see Cisco Secure Remote Access: VPN Licensing Overview.
For the latest detailed information about the AnyConnect user license options, see Managing Feature Licenses in the Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using the CLI, 8.2.
End-User License Agreement
For information on the end-user license agreement, see: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/es_inpck/eu1jen__.pdf
OpenSSL/Open SSL Project
This product includes software developed by the OpenSSL Project for use in the OpenSSL Toolkit (http://www.openssl.org/).
This product includes cryptographic software written by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com).
This product includes software written by Tim Hudson (tjh@cryptsoft.com).
For Open Source License information for this product, please see the following link: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/asa/asa80/license/opensrce.html#wp50053.
Related Documentation
For more information, refer to the following documentation:
•
For additional information about the security appliance or ASDM or its platforms, see Navigating the Cisco ASA 5500 Series Documentation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/asa/roadmap/asaroadmap.html
•
Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client, Release 2.2, Administrator Guide
•
Cisco Secure Desktop Configuration Guide for Cisco ASA 5500 Series Administrators
CCDE, CCENT, CCSI, Cisco Eos, Cisco HealthPresence, Cisco IronPort, the Cisco logo, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco Nurse Connect, Cisco Pulse, Cisco StackPower, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, Cisco Unified Computing System, Cisco WebEx, DCE, Flip Channels, Flip for Good, Flip Mino, Flipshare (Design), Flip Ultra, Flip Video, Flip Video (Design), Instant Broadband, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Cisco Capital, Cisco Capital (Design), Cisco:Financed (Stylized), Cisco Store, and Flip Gift Card are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AllTouch, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, Continuum, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Explorer, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GainMaker, GigaDrive, HomeLink, iLYNX, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, Laser Link, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerKEY, PowerPanels, PowerTV, PowerTV (Design), PowerVu, Prisma, ProConnect, ROSA, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0908R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2009-2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.