Table Of Contents
Release Notes for NAC/NAP Interoperability Architecture 1.0
NAC/NAP Interoperability Architecture
SoH in Host Credentials Authorization Protocol, version 2 Support
Posture Optional Configuration Support
Authenticated In-Band PAC Provisioning Support
EAP Type in NAC/NAP Environment
EAP-FAST Enhancement for Anonymous TLS Renegotiation
EAP-FAST Module on Windows Vista with Service Pack 1 Platform
Supported Cisco Component Versions
Supported Cisco Wireless Access Points
Supported Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers
Supported Cisco Wireless LAN Service Module
Supported Cisco Secure Access Control Server Release
External Software Requirements
After authentication fails, the next authentication attempt starts in about 20 minutes
User authentication is not performed when Remote Desktop is used
Known Defects in NAC Components
Known Defects in Cisco Secure Access Control Server 4.2
Release Notes for NAC/NAP Interoperability Architecture 1.0
These release notes pertain to the Network Admission Control (NAC)/Network Access Protection (NAP) interoperability architecture, Release 1.0 by Cisco Systems, Inc., and Microsoft Corporation.
Contents
This document contains:
•
Supported Cisco Component Versions
•
External Software Requirements
•
Known Defects in NAC Components
NAC/NAP Overview
The NAC/NAP solution components include Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS) version 4.2, Cisco 802.1x-capable Catalyst switches, Microsoft Network Policy Server (NPS), and Microsoft NAP-enabled Vista desktops.
The Cisco NAC appliance does not support NAP at this time and is not part of the solution.
The NAC/NAP interoperability architecture:
•
Gathers identity and posture information from an endpoint.
•
Determines the security policy compliance of the endpoint.
•
Provides remediation services.
•
Enforces network access policies based on the compliance of the endpoint.
NAC/NAP verifies the identity and health status of a Windows Vista client, provides remediation capabilities, and dynamically enforces access policies on the network infrastructure.
For additional information about the Cisco NAC solution, go to:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/netsol/ns466/networking_solutions_package.html
For additional information about the Microsoft NAP solution, go to:
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/itsolutions/network/nap/default.mspx
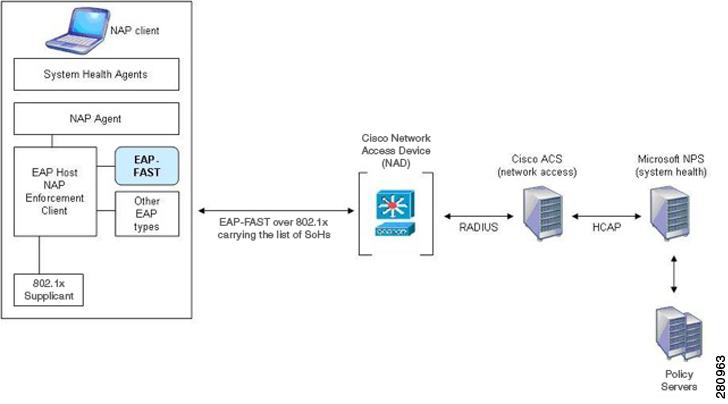
NAC/NAP Interoperability Architecture
Figure 1 shows the components of the NAC/NAP Interoperability Architecture.
Figure 1 NAC/NAP Interoperability Architecture
The EAP-FAST module on Windows Vista, NAD (Cisco switches and access points), and ACS components belong to Cisco.The NAP Client, NAP agent, and NPS components belong to Microsoft.Table 1 describes the components in NAC/NAP Interoperability Architecture.
Features of NAC/NAP
This section describes the new features that Cisco components support in the NAC/NAP environment:
•
SoH in Host Credentials Authorization Protocol, version 2 Support
•
Posture Optional Configuration Support
•
Authenticated In-Band PAC Provisioning Support
•
EAP Type in NAC/NAP Environment
•
EAP-FAST Enhancement for Anonymous TLS Renegotiation
•
EAP-FAST Module on Windows Vista with Service Pack 1 Platform
SoH in Host Credentials Authorization Protocol, version 2 Support
NPS supports the Host Credentials Authorization Protocol (HCAP), version 2, to receive a list of SOHs from ACS and return a list of SOH Response (SOHRs) back to ACS.
Posture Optional Configuration Support
NAC/NAP deployment requires posture optional configuration in ACS. A posture optional setting prevents a machine or user from failing authentication during computer bootup process, if the NAP agent service has not yet started. If the authentication fails, the NAP agent does not send SOH information to ACS.
Authenticated In-Band PAC Provisioning Support
NAC/NAP 1.0 supports authenticated in-band Protected Access Credential (PAC) provisioning.
PACs are strong shared secrets that enable ACS and an EAP-FAST end-user client to authenticate each other, and establish a Transport Layer Security (TLS) tunnel for use in EAP-FAST phase <2>.
The in-band provisioning mode operates inside an authenticated tunnel before the client authenticates the server. This method minimizes the risk of exposing the user's credentials.
For a description of the in-band PAC provisioning method, see the "About PACs" section in Chapter 9, System Configuration: Authentication and Certificates of the User Guide for Cisco Secure Access Control Server 4.2.
EAP Type in NAC/NAP Environment
EAP-FAST is the only EAP type that NAC/NAP supports. EAP-FAST is enhanced to support SoH information. You can use any of the following EAP inner methods:
•
EAP-GTC
•
EAP-MSCHAPv2
•
EAP-TLS
EAP-FAST Enhancement for Anonymous TLS Renegotiation
EAP-FAST is a tunneling protocol that works in two phases:
•
Provisioning
•
Authentication
In the Server-Unauthenticated provisioning phase, an anonymous TLS handshake occurs between the client and ACS to establish a protected tunnel. ACS provisions a PAC and sends an access-reject message (failure) to the client.
In the authentication phase, the client again starts a new authentication with ACS using the PAC received in the provisioning phase.
This EAP-FAST enhancement combines the provisioning and authentication phases into a single phase, bypassing the failure state. After the provisioning phase, the authentication does not fail. Instead, the client initiates a TLS renegotiation, followed by a new authentication. Upon successful authentication, ACS grants the client network access.
For a description of the EAP-FAST enhancement for anonymous TLS renegotiation, see the "EAP-FAST for Anonymous TLS Renegotiation" section in Chapter 9, System Configuration: Authentication and Certificates of the User Guide for Cisco Secure Access Control Server 4.2.
EAP-FAST Module on Windows Vista with Service Pack 1 Platform
The EAP-FAST module is installed through Microsoft Windows Vista Update. For information on EAP-FAST installation, refer to Microsoft's NAP Design Guide and NAP Deployment Guide.
Supported Cisco Component Versions
The following sections list the hardware and software that you can use in the NAC/NAP environment:
•
Supported Cisco Wireless Access Points
•
Supported Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers
•
Supported Cisco Wireless LAN Service Module
•
Supported Cisco Secure Access Control Server Release
Supported Cisco Switches
Table 2 lists the devices that support the NAC L2 802.1x (EAP over IEEE 802.1x) method:
Supported Cisco Wireless Access Points
Table 3 lists the Cisco Wireless Access Points that support the NAC L2 802.1x method:
Supported Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers
Table 4 lists the Cisco Wireless LAN Controllers that support the NAC L2 802.1x method:
Supported Cisco Wireless LAN Service Module
Table 5 lists the Cisco Wireless Service Module that supports the NAC L2 802.1x method:
Table 5 Supported Cisco Wireless LAN Service Module
Wireless LAN Services Module (WLSM)
Release 1.4.1 or later
Supported EAP-FAST Module
Cisco EAP-FAST module, version 2.2.8, supports NAC/NAP 1.0. The EAP-FAST 2.2.8 is available for 32-bit and 64-bit platforms.
You must install the EAP-FAST 2.2.8 on Windows Vista with Service Pack 1 applied. The following editions of Windows Vista support the EAP-FAST module:
•
Windows Vista Enterprise
•
Windows Vista Business
•
Windows Vista Ultimate
Note
The EAP-FAST module is only available through the Microsoft Windows Vista Update Service in the form of an optional driver package installation.
Supported Cisco Secure Access Control Server Release
ACS 4.2 (124), supports NAC/NAP 1.0.
External Software Requirements
To deploy NAC/NAP, you need:
•
Client operating system—Windows Vista (Enterprise, Business, or Ultimate edition) with Service Pack 1 applied.
•
Server—Windows Server 2008.
•
EAP-FAST Module for Windows Vista. See Supported EAP-FAST Module for more information.
Obtaining NAC/NAP
This initial NAC/NAP release is a limited offering from Cisco and Microsoft.
If your organization has an immediate need to evaluate or deploy the NAC/NAP solution in your environment, contact your Cisco sales representative.
Important Notes
This section contains:
•
Important Notes for Cisco IOS
Important Notes for Cisco IOS
The following information applies to Cisco IOS, Release 12.2(35)SE2, which runs on Catalyst switches 2960, 3560, and 3570:
A device attached to Multi-Domain Authentication-enabled port with Guest VLAN, but no MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB), shows up as a dot1x authenticated device
When MAB is not enabled and the switch obtains the MAC address from the port, the port status indicates a device authenticated by dot1x.
To prevent this behavior, enable MAB, or set the tx-period to one second.
Important Notes for EAP-FAST
The following information applies to EAP-FAST, version 2.2.8:
After authentication fails, the next authentication attempt starts in about 20 minutes
If your authentication fails because of identity failure, explicit EAP failure, or UI failure, you must wait for 20 minutes before you can log in again.
This condition occurs because the Vista supplicant goes into a 20-minute wait period (block) when your authentication fails.
When the Vista supplicant receives an explicit EAP-Failure message from the AAA server, it starts the blocking timer (the default value is set to 20 minutes). During this blocking-timer period, the Vista supplicant does not initiate EAPOL-Start, or respond to EAP-ID Request from NAD.
This condition also exists on a wireless supplicant in Windows Vista.
To get around this wait period:
•
For wired interfaces, physically disconnect and reconnect the cable; or, disable and re-enable the affected adapter.
•
For wireless interfaces, you can manually change the EAP-FAST profile. Add the maxAuthFailures element and set its value to 3.
User authentication is not performed when Remote Desktop is used
When you use Remote Desktop, profiles that are configured for automatic connection undergo machine authentication instead of user authentication.
If you start authentication manually, user authentication occurs as expected.
Known Defects in NAC Components
This section contains the Known Defects in Cisco Secure Access Control Server 4.2.
For a complete list of bugs on individual components of the NAC security solution, refer to that component's release notes on Cisco.com.
Known Defects in Cisco Secure Access Control Server 4.2
Table 6 lists the known defects in Cisco Secure Access Control Server for Windows and Solution Engine 4.2. These defects in ACS can affect a NAC implementation:
.
Related Documentation
•
Cisco Network Admission Control and Microsoft Network Access Protection Integration Deployment Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/solutions/collateral/ns340/ns394/ns171/ns466/ns812/
guide_c07-491729.html•
Cisco Network Admission Control and Microsoft Network Access Protection Troubleshotting Guide
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/solutions/collateral/ns340/ns394/ns171/ns466/ns812/
guide_c07-491725.html•
Cisco Secure Access Control Server Configuration Guide for NAC/NAP Interoperability
http://cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/nac-nap/1.0/config/guide/acsconfnacnap10.html
•
EAP-FAST for Windows Vista Administrator Guide
http://cisco.com/en/US/docs/wireless/wlan_adapter/eap_types/fast/admin/guide/FAST_admin.html
•
Release Notes for Cisco Secure ACS 4.2
•
Supported Interoperable Devices and Software Tables for Cisco Secure ACS Release 4.2
•
Documentation Guide for Cisco Secure ACS 4.2
•
Installation Guide for Cisco Secure ACS for Windows 4.2
•
User Guide for Cisco Secure Access Control Server 4.2
•
Cisco Secure ACS Online Troubleshooting Guide, 4.2
•
Microsoft NAP Documentation
Obtaining Documentation
For information on obtaining documentation and gathering additional information, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What's New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service and Cisco currently supports RSS version 2.0.
CCDE, CCSI, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco HealthPresence, the Cisco logo, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco Nurse Connect, Cisco Stackpower, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, Cisco WebEx, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn and Cisco Store are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0903R)
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.