Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Release Notes for Cisco Secure Desktop 3.5.1077
Downloading the Latest Version of CSD
Standalone Installation Packages
Windows Mobile Device Management
Additional Operating System Support
CSD Integration with AnyConnect
Host Scan Support for Antivirus, Antispyware, and Personal Firewall Software
System and Environment Requirements
Operating System Interoperability
Secure Desktop (Vault), Keystroke Logger Detection, and Host Emulation Detection
Advanced Endpoint Assessment License
Enabling the Taskbar to Display the Yellow Lock Icon when Cache Cleaner is Running
CSD Loads Slowly or Appears to Stop
Specifying Windows 7 in a Dynamic Access Policy
Specifying Windows 7 as an Endpoint Attribute in the ASDM GUI
Specifying Windows 7 as an Operating System Attribute Using a Lua expression
Server Certificate Length Consideration
Guidelines Relating to User Account Control
Users With Administrator Privileges Receive UAC Pop Up Messages
Application Compatibility Layer and User Account Control
Responding to Java Warning Dialog Boxes
User Interface Privilege Isolation
Internet Explorer, Microsoft Office, and Adobe Acrobat Interaction with Cisco Secure Desktop
User Guidelines Related to Cache Cleaner
History Not Erased With Multiple Explorer Windows
Cache Cleaner Installation Behavior
Cache Cleaner Interface Change
Cisco Security Agent with Secure Desktop and Cache Cleaner
CSD Installation through a Proxy
Starting Applications from within Folders Created inside Secure Desktop
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Release Notes for Cisco Secure Desktop 3.5.1077
Last Updated: February 10, 2011This document contains release information for Cisco Secure Desktop 3.5.1077 and Cisco Secure Desktop 3.5.841. Read the following sections carefully prior to installing, upgrading, and configuring Cisco Secure Desktop.
•
Downloading the Latest Version of CSD
•
System and Environment Requirements
•
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Note
This document identifies the latest enhancement and guidelines. After reading about them, use the Cisco Secure Desktop Configuration Guide for Cisco ASA 5500 Series Administrators, Version 3.5 for more information about the features; and for installation, upgrade, and configuration instructions.
Introduction
Cisco Secure Desktop (CSD) is a multifunctional component of the Cisco SSL VPN solution. The main features of CSD include:
•
Host Scan checks for watermarks on a remote endpoint device attempting to establish a Cisco AnyConnect client or browser-based (clientless) session. These watermarks can signify whether the computer is corporate-owned. The watermarks include registry entries, process names, and filenames. You can also use Host Scan to configure a check for antivirus and antispyware applications, associated definitions updates, and firewalls. CSD supports hundreds of versions of these applications. Host Scan reports results to the adaptive security appliance, which integrates them with the dynamic access policies (DAPs).
•
Secure Desktop (Vault) encrypts the data and files associated with, or downloaded during a remote session into, a secure partition and presents a graphical representation of a desktop that includes an image of a lock to signify a safe environment for the remote user to work in. When the remote session ends, a sanitization algorithm wipes the encrypted partition. Typically used during clientless SSL VPN sessions, Secure Desktop attempts to reduce the possibility that cookies, browser history, temporary files, and downloaded content remain after a remote user logs out, the session times out, or after an abrupt termination occurs.
•
Cache Cleaner, an alternative to Secure Desktop, attempts to eliminate information in the browser cache at the end of a session. This information includes entered passwords, auto-completed text, files cached by the browser, and browser configuration changes.
•
Keystroke logger detection and host emulation detection let you deny access based on the presence of a suspected keystroke logging application or a host emulator. You can use Secure Desktop Manager to specify the keystroke logging applications that are safe or let the remote user interactively approve the applications and host emulator the scan identifies. Both keystroke logger detection and host emulation detection are available with Cache Cleaner, Secure Desktop, and Host Scan.
No technology that interoperates with an operating system can ensure the total removal of all data, especially from an untrusted system with potentially malicious third party software installed. However, deployments of Cisco SSL VPN using CSD, when combined with other security controls and mechanisms within the context of an effective risk management strategy and policy, can help reduce risks associated with using such technologies.
Downloading the Latest Version of CSD
To download the latest version of CSD you must be a registered user of Cisco.com.
Step 1
Follow this link to the CSD Product/Technology Support page:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6742/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Step 2
Click Download Software
Step 3
Log on to Cisco.com if you are not already.
Step 4
Expand the Latest Releases folder and click the link for 3.5.1077.
Step 5
There are different CSD packages for Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. If you would like to simply download the CSD 3.5.1077 package that contains versions for all operating systems, scroll down to find csd_3.5.1077-k9.pkg and click Download Now.
Step 6
Click Proceed with Download.
Step 7
Select a download manager option and proceed with the download.
New Features in CSD 3.5.1077
CSD 3.5.1077 is a maintenance release that resolves the caveats listed in Table 2 and adds support for additional antivirus, antispyware and personal firewall applications. This release does not introduce any new features.
New Features in CSD 3.5.841
Standalone Installation Packages
We provide CSD standalone installation packages. These installation packages do not need to be distributed to the endpoint by the ASA; they can be deployed by enterprise wide software distribution tools. The packages require administrative privileges to install CSD but upgrade installations do not.
These changes provide you with these benefits:
•
You can now deploy CSD out of band, thus decreasing the initial connection time and the additional time required to perform software updates.
•
The ability to fully assess the posture of the endpoint even when invoked by an unprivileged user.
•
The ability to perform software updates without requiring administrative privileges.
See Chapter 2, "Installing and Enabling CSD" in the Cisco Secure Desktop Configuration Guide for Cisco ASA 5500 Series Administrators, Release 3.5 for CSD installation instructions for Windows Desktops, Windows Mobile Devices, Mac OS X desktops, and Linux Desktops.
Windows Mobile Device Management
CSD 3.5.841 introduces Mobile Device Management which, in addition to the basic posture assessment that CSD Host Scan already performs, performs posture assessments that are specific to mobile devices. This allows VPN administrators to enforce Dynamic Access Policies (DAPs). The Windows Mobile Device Management feature requires AnyConnect client to be installed on the mobile device and the Advanced Endpoint Assessment license to be installed on the ASA.
Note
•
This feature supports the Windows Mobile 6.x Professional operating system for touch screen devices. It does not support Windows Mobile Smartphone or Windows Mobile Standard devices.
•
For Windows Mobile Devices, Host Scan does not gather posture information of antivirus, antispyware, and personal firewall applications.
DAPs are written in the Lua language and are most easily configured using the ASDM interface for the ASA. See the Configuring Dynamic Access Policies chapter of the Cisco Security Appliance Configuration Guide Using ASDM to learn more about configuring DAP.
See the "Using Match Criteria to Configure Dynamic Access Policies" chapter of Cisco Secure Desktop Configuration Guide for Cisco ASA 5500 Series Administrators, Release 3.5 for examples of these new Lua expressions:
•
Device Operating System Checks
•
Device Architecture Checks
•
Device Lock Status
•
Secondary Storage Status
•
Password Checks
•
SIM Policy
•
GPS Hardware and Location Checks
•
Application Checks
•
Bluetooth® Hardware and Status Checks
Improved Web Launch Usability
CSD 3.5.841 improves the usability of the web launch mechanism of CSD by adding the following functionality:
•
Improved error handling and recovery.
•
Notification of error state to the end-user with actionable messages.
•
Notification of state and progress through the several stages of the web-launch process.
•
Improved visual appearance and presentation.
Additional Operating System Support
CSD 3.5.841 supports these additional operating systems:
•
x86 (32-bit) and x64 (64-bit) Windows 7
Note
Secure Vault, Keystroke Logger Detection and Emulation Detection are not supported on Windows 7.
•
Windows Mobile Professional: 6.0, 6.1, 6.1.4, and 6.5
•
Mac OS X: 10.6, 10.6.1, and 10.6.2 for both 32-bit and 64-bit versions
CSD Integration with AnyConnect
CSD 3.5.841 is tightly integrated with AnyConnect 2.4. With this enhancement, the user prompts are displayed as soon as the pre-login scan completes. Typically, this is faster than waiting for the entire Host Scan process to run its course.
If your site uses AnyConnect 2.4 with CSD 3.4 or earlier, or if your site uses AnyConnect 2.3 with CSD 3.5.841, you will not receive the benefits of this integration. However, CSD 3.5.841 still runs with earlier versions of AnyConnect and AnyConnect 2.4 still runs with earlier versions of CSD. If an AnyConnect user is configured to use CSD, AnyConnect 2.4 will deploy the version of CSD installed on the ASA, even if a later version of CSD is already installed on the host.
AnyConnect 2.4 will display and log descriptive posture assessment messages and installation messages passed to it from CSD 3.5.841. Other than these messages, AnyConnect users will have no interaction with this enhancement in AnyConnect 2.4.
Host Scan Support for Antivirus, Antispyware, and Personal Firewall Software
With an Advanced Endpoint Assessment license, on Windows desktops, Host Scan 3.5.841 updates the list of antivirus, antispyware, and personal firewall applications it supports. The Cisco Secure Desktop Compatibility site lists the antivirus, antispyware, and firewall applications that Host Scan checks for on the endpoint.
CSD Manual Launch
This feature allows users to create a Clientless SSL VPN connection to their ASA by manually launching CSD from their computer. This benefits users who do not have permission to run Active X or Java, or do not have Active X or Java installed.
This feature can be used by Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X desktops. This feature is not available for Windows Mobile Device users.
See the "CSD Manual Launch" section of Chapter 2: Installing and Enabling CSD in the Cisco Secure Desktop Configuration Guide for Cisco ASA 5500 Series Administrators, Release 3.5 for more information.
System and Environment Requirements
The following sections identify the adaptive security appliance platform and end-user interoperability that CSD requires or supports.
Cisco 5500 Series
CSD 3.5.841 requires installation on a Cisco ASA 5500 Series running Release 8.0(4) or later and ASDM 6.1(3) or later.
Operating System Interoperability
The following section lists the CSD endpoint functions and identifies the endpoint OSs they support.
Note
•
Starting with release 3.5.841, CSD no longer supports Windows 2000 or Mac OS X 10.4.
•
Starting with release 3.5.841, Cache Cleaner no longer supports Internet Explorer 5.0.
Host Scan
Host Scan supports the following operating systems:
Windows
•
x86 (32-bit) and x64 (64-bit) Windows 7
•
x86 (32-bit) and x64 (64-bit) Windows Vista, Vista SP1, Vista SP2
•
x64 (64-bit) Windows XP SP2
•
x86 (32-bit) Windows XP SP2 and SP3
•
Windows Mobile versions 6.0, 6.1, 6.1.4, and 6.5 for touch screen devices only (Windows Mobile Professional).
Mac OS X
•
32-bit and 64-bit Mac OS X 10.6, 10.6.1, 10.6.2
•
32-bit and 64-bit Mac OS X 10.5.x
Linux
•
32-bit and 64-bit biarch Redhat Enterprise Linux 3
•
32-bit and 64-bit biarch Redhat Enterprise Linux 4
•
32-bit and 64-bit biarch Fedora Core 4 and later
•
Ubuntu
32-bit and 64-bit biarch Linux operating systems (that is, 64-bit operating systems that can run 32-bit code) require the 32-bit versions of these libraries to run Host Scan: libxml2, libcurl (with openssl support), openssl, glibc 2.3.2 or later, and libz.
Cache Cleaner
Cache Cleaner supports the following operating systems for 32-bit browsers only:
Windows
•
x86 (32-bit) and x64 (64-bit) Windows 7
•
x86 (32-bit) and x64 (64-bit) Windows Vista, Vista SP1, Vista SP2
•
x64 (64-bit) Windows XP SP2
•
x86 (32-bit) Windows XP SP2 and SP3
Mac OS X
•
32-bit and 64-bit Mac OS X 10.6, 10.6.1, and 10.6.2
•
32-bit and 64-bit Mac OS X 10.5.x
Linux
•
32-bit and 64-bit Redhat Enterprise Linux 3
•
32-bit and 64-bit Redhat Enterprise Linux 4
•
32-bit and 64-bit Fedora Core 4 and later
•
Ubuntu
32-bit and 64-bit biarch Linux operating systems (that is, 64-bit operating systems that can run 32-bit code) require the 32-bit versions of these libraries to run Cache Cleaner: libxml2, libcurl (with openssl support), openssl, glibc 2.3.2 or later, and libz.
Note
Cache Cleaner does not support the standalone startup of AnyConnect Client from any computer.
Secure Desktop (Vault), Keystroke Logger Detection, and Host Emulation Detection
Secure Desktop, Keystroke Logger Detection, and Host Emulation Detection run over the following operating systems:
•
x86 (32-bit) Windows Vista, SP1, and SP2
KB935855 must be installed.
•
x86 (32-bit) Windows XP SP2 and SP3
Note
Secure Desktop, Keystroke Logger Detection and Host Emulation Detection are not supported on Windows 7.
Browser Interoperability
These are the minimum versions of browsers Host Scan, Cache Cleaner, Secure Desktop (Vault), and Web Launch support:
•
Internet Explorer 6.0
•
Safari 3.2.1
•
Firefox 3.0.x
Host Scan, Cache Cleaner, Secure Desktop (Vault), and Web Launch also require Sun Java 1.5 or later. These browsers must also have JavaScript capabilities enabled and the browsers must support XML parsing operations.
Host Scan and Cache Cleaner do not support 64-bit versions of Internet Explorer. Please instruct users of x64 (64-bit) Windows OSs to use the 32-bit version of Internet Explorer or Firefox to avoid VPN connection issues. (At this time, Firefox is available only in a 32-bit version.) If one uses a 64-bit version of Internet Explorer to try to establish a VPN session with a security appliance configured to install Host Scan or Cache Cleaner on the endpoint, a "Platform Detection" message states, "Web-based launch of Cisco Secure Desktop is not supported with 64-bit versions of IE. Please retry with the 32-bit version of IE."
License Types
Cisco Secure Desktop requires a Premium SSL VPN license or Shared Premium SSL VPN license. Some new features in CSD 3.5.841 require the purchase of an Advanced Endpoint Assessment license.
Advanced Endpoint Assessment License
With the purchase of an Advanced Endpoint Assessment license installed on the ASA, you can use these advanced features of CSD:
•
Remediation - On Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux desktops, Advanced Endpoint Assessment can attempt to initiate remediation of various aspects of antivirus, antispyware and personal firewall protection if that software allows a separate application to initiate remediation.
•
Windows Mobile Device Lua Expressions - For Windows Mobile Devices, administrators will be able to write Lua expressions in Dynamic Access Policies (DAPs) to perform posture checks on those attributes unique to mobile devices. You can read examples of these Lua expressions in the Cisco Secure Desktop Configuration Guide for ASA 5500 Administrators, Release 3.5.
Administrator Guidelines
Refer to the following sections for information you should know before installing and configuring CSD. These sections supplement the information provided in the Cisco Secure Desktop Configuration Guide for Cisco ASA 5500 Series Administrators, Release 3.5.
Enabling the Taskbar to Display the Yellow Lock Icon when Cache Cleaner is Running
By default, the taskbar no longer displays the yellow lock icon while Cache Cleaner is running. Releases of Cisco Secure Desktop earlier than 3.5 displayed this icon with Cache Cleaner. To display the icon, enable keystroke logger detection, host emulation detection, or both.
CautionEnabling keystroke logger detection, host emulation detection, or both turns on the Cisco Secure Desktop 3.4.2048 behavior of Cache Cleaner. It also replaces the Cisco Secure Desktop 3.5 version of Host Scan with that provided in Cisco Secure Desktop 3.4.2048 for both Cache Cleaner and AnyConnect sessions.
To be inserted into the "End User Guidelines" section:
Cache Cleaner Delay
When an SSL VPN session ends, Cache Cleaner may take about a minute to clean the cache and close the browser. Differences in endpoints and the size of the cache can affect the length of the delay.
CSD Loads Slowly or Appears to Stop
If CSD is taking too long to load, it may be that the SSL client (your browser) cannot access the certificate revocation list (CRL) server. In this case, your browser will attempt to reconnect. Eventually, the connection will time-out. These extra attempts delay CSD from launching.
Ensure that your CRL server is properly configured so that your browser can reach it and access the certificate revocation list. This will help CSD launch more quickly.
Here is an example of when the SSL server and SSL client attempt to reach the certificate revocation list:
During the initial SSL handshake between the ASA and the client, the ASA (the SSL server) sends down a certificate, that has its name on it, to the SSL client (your browser). Your browser then attempts to validate the certificate. For example, it could check that the certificate's name corresponds to the host and domain name the browser is pointing to. After that, the client may also contact the certificate revocation list server to determine if the certificate has been revoked.
The ASA may also request a certificate from the client, in which case, the client, if it has one, submits its client certificate. The ASA will then attempt to validate the certificate similarly to the way the client did.
Specifying Windows 7 in a Dynamic Access Policy
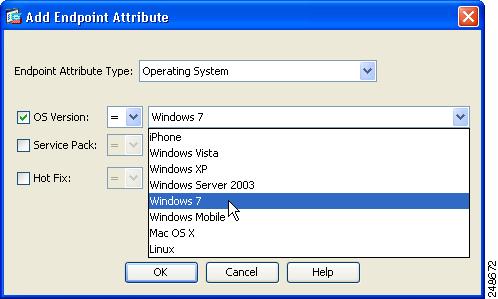
Specifying Windows 7 as an Endpoint Attribute in the ASDM GUI
You will be able to specify Windows 7 as an endpoint attribute, using the ASDM GUI, if you are using ASDM version 6.2.(5) on an ASA running version 8.2.2 or earlier.
Figure 1 Windows 7 specified as an endpoint attribute using ASDM GUI
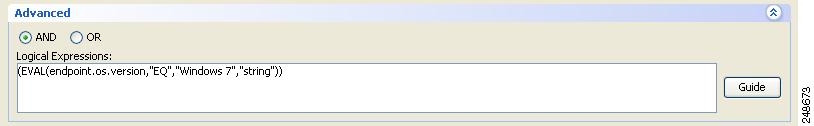
Specifying Windows 7 as an Operating System Attribute Using a Lua expression
If you are running a version of ASDM, which is earlier that 6.2(5), on your ASA, you can still use a DAP to check for the Windows 7 OS but you will need to do this using a Lua expression.
To learn more about Lua expressions in Dynamic Access Policies, see the section on "Configuring Dynamic Access Policies" in Cisco Security Appliance Configuration Guide Using ASDM.
This Lua expression is true if the operating system on the endpoint is Windows 7:
(EVAL(endpoint.os.version,"EQ","Windows 7","string"))Figure 1-2 Windows 7 specified in a Lua expression
Hostscan and GPS Interaction
Host Scan does not wait for the GPS device to activate in order to retrieve location information. It reports the latest GPS location if the GPS device is active and has a GPS fix.
If the GPS hardware is off, hostscan does not switch it on. It uses the cached location information at the timestamp noted. If the mobile device has erased or invalidated latitude and longitude information, it will not be reported to hostscan.
Reset All
This description of the Reset All button in the "Adaptive Security Appliance" help topic in the CSD help is incorrect:
"If you click Reset All in any Secure Desktop Manager panel other than Setup, all unapplied changes from this session are removed and Secure Desktop Manager replaces all data in the data.xml file with the factory default settings."
The Reset All button is correctly described in the Cisco Secure Desktop Configuration Guide for Cisco ASA 5500 Series Administrators, Release 3.5. The Configuration Guide is available on Cisco.com. This is the correct description:
"If you click Reset All in any Secure Desktop Manager panel other than Setup, all unapplied changes from your session are removed."
Server Certificate Length Consideration
Many SSL connections using identity certificates with RSA key pairs that exceed 1024 bits can cause a high CPU usage on the adaptive security appliance and rejected VPN log-ins.
Guidelines Relating to User Account Control
These guidelines relate to Windows operating systems that run user account control (UAC). Windows Vista and Windows 7 are examples of Windows operating systems that use UAC.
Users With Administrator Privileges Receive UAC Pop Up Messages
CSD users receive User Account Control (UAC) requests to elevate their user privileges when all these conditions are true:
•
CSD performs a function that requires elevated user privileges.
•
The user has administrative privileges.
•
CSD is running on Windows Vista or Windows 7.
Some of the functions that require elevated privileges are keystroke logger detection, host scanning for system files, and advanced endpoint assessment.
CSD only issues a UAC prompt to users with administrative privileges because after responding to the UAC prompt, CSD will be able to perform the function that requires the elevated privileges.
CSD does not issue a UAC prompt to users with standard privileges because they most likely do not have an additional administrative user name and password with which to respond to the prompt. As a result, even if CSD did issue a UAC prompt, the attempt to elevate privileges would most likely fail, CSD could not perform the function that requires elevated privileges, and the user would have been interrupted for no reason. In circumstances where CSD is not running with elevated privileges, it makes its best effort to perform its functions with standard user privileges.
Application Compatibility Layer and User Account Control
Windows Vista uses virtualization to provide application compatibility. CSD turns off user account control (UAC) from within Secure Desktop to avoid collisions with the CSD file system virtualization. Consequently, applications running over Secure Desktop (Vault) do not always share the same resources, such as mapped drives, as non-secure desktop applications.
Downgrade Support
CSD supports upgrades and downgrades between 3.5.841 and 3.4.2 on the adaptive security appliance. Users can establish remote sessions with one or the other, but cannot connect to adaptive security appliances running CSD versions earlier than 3.2.1.
End User Guidelines
Be sure to communicate these guidelines to end users.
Responding to Java Warning Dialog Boxes
If a user who has not added the URL of the VPN as a trusted site initiates a Firefox connection to the adaptive security appliance, Firefox displays the following warning message in a dialog box: "The web site's certificate cannot be verified. Do you want to continue?" Please instruct users to do the following:
Step 1
Click Always trust content from this publisher, then click Yes.
A second dialog box indicates "The application's digital signature has been verified. Do you want to run the application?"
Step 2
Click Always trust content from this publisher, then click Run.
Following these two steps prevents the associated dialog boxes from appearing during subsequent connection attempts originating from that user profile on that computer.
ActiveX or Java Settings
CSD tries different methods to install itself on Microsoft Windows client computers until it finds a method that works. The installation is automatic and transparent to the user, however, one of the methods must be available on the remote computer and the user must have privileges to use that method. Table 1 shows the installation methods and associated user requirements.
Note
Starting in this release, CSD no longer supports Microsoft Java VM.
The following Internet Explorer security settings are required. Use these settings as a guideline for other browsers:
To access and launch the executable page:
•
Scripting > Active scripting > Enable
•
Downloads > File download > Enable
To launch ActiveX:
•
Scripting > Active scripting > Enable
•
ActiveX controls and plug-ins > Download signed ActiveX controls > Enable
•
ActiveX controls and plug-ins > Run ActiveX controls and plug-ins > Enable
User Interface Privilege Isolation
Because tasks such as Host Scan and idle mouse detection require monitoring of other processes, CSD cannot run at a low integrity level. This means that starting CSD sometimes requires privilege elevation. Users experience prompting for privilege elevation and have to consent to use CSD.
Internet Explorer (7 or later) on Vista runs at a low integrity level by default to avoid installation of software that monitors the system. This creates a conflict with CSD. Users who have limited privileges must add the URL of the adaptive security appliance to the trusted zone list before proceeding.
Home Directory Requirement
The home directory on the remote computer must not contain any folder or file named .cachedlg.zip.
Windows Mail
CSD does not support Windows Mail, the e-mail client that comes with Windows Vista.
Internet Explorer, Microsoft Office, and Adobe Acrobat Interaction with Cisco Secure Desktop
CSD closes all instances of Internet Explorer, Microsoft Office applications, and Adobe Acrobat running on Windows operating systems before Secure Desktop installs or before users switch to the Secure Desktop.
If Desktop Switching is enabled, you cannot switch from a Secure Desktop session to the host desktop and then open Internet Explorer, Microsoft Office applications, or Adobe Acrobat. This Windows limitation might cause some applications running on the host desktop to fail.
User Guidelines Related to Cache Cleaner
Do Not Change Cache Locations
Cache sessions may not get cleaned if a user changes cache locations during Secure Desktop and Cache Cleaner sessions.
History Not Erased With Multiple Explorer Windows
Windows Explorer does not erase browser history because other Explorer windows could share it. Before users start Cache Cleaner, they should uncheck "Launch folder windows in a separate process" in the Windows Explorer Tools > Folder Options > View > Launch folder.
Cache Cleaner Installation Behavior
Cisco Secure Desktop's Cache Cleaner has a configurable option in the Cache Cleaner panel of Secure Desktop Manager called, Show success message at the end of successful installation. (Windows only). When this option was selected in CSD 3.4 and earlier releases, a message informed users when Cache Cleaner was successfully installed. Cache Cleaner no longer displays this message.
Cache Cleaner Interface Change
In CSD 3.4 and earlier releases, when Cache Cleaner was running, a yellow lock icon displayed in the system tray as a visual reminder to the user. Cache Cleaner no longer displays this icon.
Cisco Security Agent with Secure Desktop and Cache Cleaner
Because Secure Desktop and Cache Cleaner connect tightly with the OS, the Cisco Security Agent often prompts the user to confirm that the CSD components can be trusted. It is important that the user confirms that they can be trusted when prompted by a dialog.
CSA Versions before V4.5 often prompt the user on the local desktop instead of Secure Desktop; for this reason we encourage that the user upgrade to CSA V4.5 or later, or contact the administrator to check the "Enable switching between Secure Desktop and Local Desktop" configuration option.
CSD Installation through a Proxy
To specify CSD installation through a proxy server, regardless of the browser, go to the Internet Options control panel under Microsoft Windows, click the Connections tab, and click the LAN Settings button.
To use the ActiveX installation of CSD, go to the "Internet Options" control panel under Windows, click the Advanced tab, and enable the "Use HTTP 1.1" option.
To use the Java installation of CSD, go to the "Java" control panel under Windows, click the General tab, click the Network Settings button, and configure the proxy.
Starting Applications from within Folders Created inside Secure Desktop
Microsoft Windows treats folders created within Secure Desktop differently from other folders. An application cannot always determine the default folder location for files if you start it from within these folders. For example, if you create a folder within a Secure Desktop session, open the command prompt, change the directory to that folder without specifying the full path, and run FTP, it does not download files to that folder. We recommend that you specify the full path or explicitly change the working directory (for example, using the lcd command in the case of FTP) from within the applications. This problem occurs only for applications launched from within a shell. Otherwise, the problem does not occur.
Caveats
For your convenience in locating caveats in the Cisco Bug Toolkit, the caveat titles listed in this section are drawn directly from the Bug Toolkit database. These caveat titles are not intended to be read as complete sentences because the title field length is limited. In the caveat titles, some truncation of wording or punctuation may be necessary to provide the most complete and concise description.
Note
If you are a registered cisco.com user, view Bug Toolkit on cisco.com at the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/support/bugtools
To become a registered cisco.com user, go to the following website:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.doThe following sections lists the caveats this release resolves and the open caveats.
Resolved Caveats
These tables list the caveats resolved by recent releases of CSD:
Open Caveats
Table 4 lists the severity 1-3 caveats that are open in this release:
Related Documentation
•
Cisco Secure Desktop Configuration Guide for Cisco ASA 5500 Series Administrators, Release 3.5
•
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Release Notes
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What's New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service and Cisco currently supports RSS Version 2.0.
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.