Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Connecting the ASA CX Management Interface
ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X (Software Module)
Launching the Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) on the ASA
(ASA 5585-X) Changing the ASA CX Management IP Address
(ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X; May Be Required) Installing the Software Module
Configuring Basic ASA CX Settings at the ASA CX CLI
Redirecting Traffic to the ASA CX Module
Configuring the Security Policy on the ASA CX Module Using PRSM
Quick Start Guide
Cisco ASA CX Module
Revised: December 3, 20121 About the ASA CX Module
The ASA CX module might be a hardware module or a software module, depending on your ASA model. For ASA model software and hardware compatibility with the ASA CX module, see Cisco ASA Compatibility at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/asa/compatibility/asamatrx.html.
The ASA CX module lets you enforce security based on the complete context of a situation. This context includes the identity of the user (who), the application or website that the user is trying to access (what), the origin of the access attempt (where), the time of the attempted access (when), and the properties of the device used for the access (how). With the ASA CX module, you can extract the full context of a flow and enforce granular policies such as permitting access to Facebook but denying access to games on Facebook or permitting finance employees access to a sensitive enterprise database but denying the same to other employees.
The ASA CX module runs an application that is separate from the ASA. Configuring the ASA CX module requires two parts: the ASA CX policy configuration, using Cisco Prime Security Manager (PRSM); and the ASA policy for redirecting traffic to the ASA CX module, using ASDM.
The ASA CX module might include an external management interface (and console port) so you can connect to the ASA CX module directly; if it does not have a management interface, you can connect to the ASA CX module through the ASA interface. Any other interfaces on the ASA CX module, if available for your model, are used for ASA traffic only.
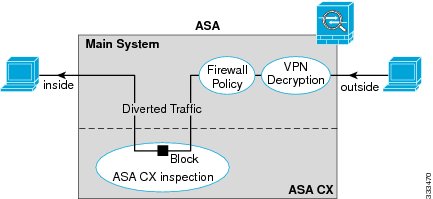
Traffic undergoes the firewall checks on the ASA before being forwarded to the ASA CX module. When you identify traffic for ASA CX inspection on the ASA, traffic flows through the ASA and the ASA CX module as described in the following steps:
1.
Traffic enters the ASA.
2.
Incoming VPN traffic is decrypted.
3.
Firewall policies are applied.
4.
Traffic is sent to the ASA CX module.
5.
The ASA CX module applies its security policy to the traffic, and takes appropriate actions.
6.
Valid traffic is sent back to the ASA; the ASA CX module might block some traffic according to its security policy, and that traffic is not passed on.
7.
Outgoing VPN traffic is encrypted.
8.
Traffic exits the ASA.
The following figure shows the traffic flow when using the ASA CX module. In this example, the ASA CX module automatically blocks traffic that is not allowed for a certain application. All other traffic is forwarded through the ASA.
2 Connecting the ASA CX Management Interface
In addition to providing management access to the ASA CX module, the ASA CX management interface needs access to an HTTP proxy server or a DNS server and the Internet for signature updates and more. This section describes recommended network configurations. Your network may differ.
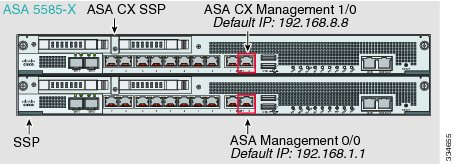
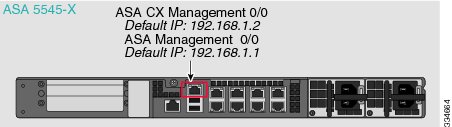
ASA 5585-X (Hardware Module)
The ASA CX module includes a separate management interface from the ASA.
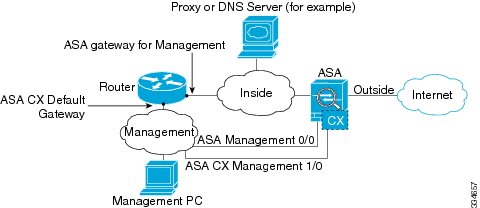
If you have an inside router
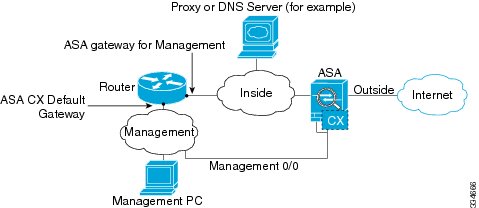
If you have an inside router, you can route between the management network, which can include both the ASA Management 0/0 and ASA CX Management 1/0 interfaces, and the ASA inside network for Internet access. Be sure to also add a route on the ASA to reach the Management network through the inside router.
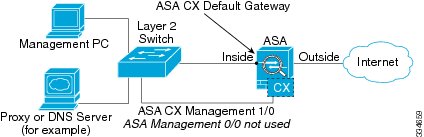
If you do not have an inside router
If you have only one inside network, then you cannot also have a separate management network, which would require an inside router to route between the networks. In this case, you can manage the ASA from the inside interface instead of the Management 0/0 interface. Because the ASA CX module is a separate device from the ASA, you can configure the ASA CX Management 1/0 address to be on the same network as the inside interface.
ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X (Software Module)
These models run the ASA CX module as a software module, and the ASA CX management interface shares the Management 0/0 interface with the ASA.
If you have an inside router
If you have an inside router, you can route between the Management 0/0 network, which includes both the ASA and ASA CX management IP addresses, and the inside network for Internet access. Be sure to also add a route on the ASA to reach the Management network through the inside router.
If you do not have an inside router
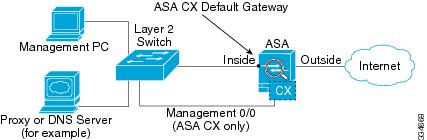
If you have only one inside network, then you cannot also have a separate management network. In this case, you can manage the ASA from the inside interface instead of the Management 0/0 interface. If you remove the ASA-configured name from the Management 0/0 interface, you can still configure the ASA CX IP address for that interface. Because the ASA CX module is essentially a separate device from the ASA, you can configure the ASA CX management address to be on the same network as the inside interface.
Note
You must remove the ASA-configured name for Management 0/0; if it is configured on the ASA, then the ASA CX address must be on the same network as the ASA, and that excludes any networks already configured on other ASA interfaces. If the name is not configured, then the ASA CX address can be on any network, for example, the ASA inside network.
3 Launching the Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) on the ASA
The default ASA configuration lets you connect to the default management IP address (192.168.1.1). Depending on your network, you might need to change the ASA management IP address, or even configure additional ASA interfaces for ASDM access (see the "Connecting the ASA CX Management Interface" section). For the ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X, if you do not have a separate management network (see the "If you do not have an inside router" section), you need to configure an inside interface for management, and you need to remove the name from the Management 0/0 interface. To change interface and management settings, see the ASA configuration guide.
Step 1
On the management PC, launch a web browser.
Step 2
In the Address field, enter the following URL: https://ASA_IP_address/admin. The default ASA management IP address is 192.168.1.1.
Step 3
Click Run ASDM to run the Java Web Start application. Alternatively, you can download the ASDM-IDM Launcher. See the ASA configuration guide for more information.
Step 4
Accept any certificates according to the dialog boxes that appear. The Cisco ASDM-IDM Launcher dialog box appears.
Step 5
Leave the username and password fields empty, and click OK. The main ASDM window appears.
4 (ASA 5585-X) Changing the ASA CX Management IP Address
If you cannot use the default management IP address, then you can set the management IP address from the ASA. After you set the management IP address, you can access the ASA CX module using SSH to perform initial setup.
Note
For a software module, you can access the ASA CX CLI to perform setup by sessioning from the ASA CLI; you can then set the ASA CX management IP address as part of setup. See the "Configuring Basic ASA CX Settings at the ASA CX CLI" section.
Step 1
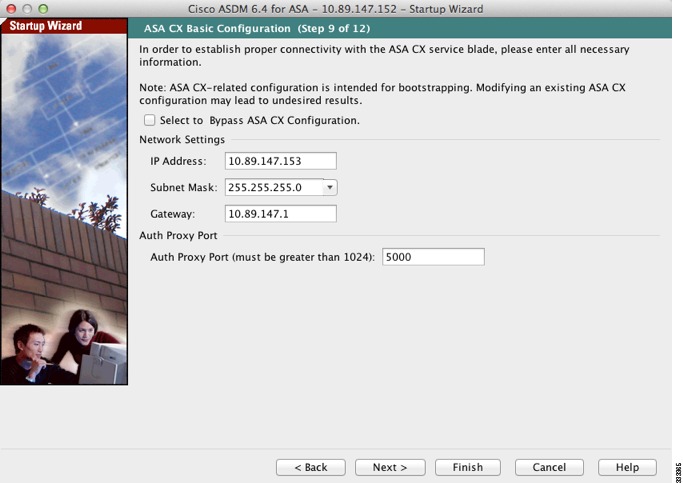
In ASDM, choose Wizards > Startup Wizard.
Step 2
Click Next to advance through the initial screens until you reach the ASA CX Basic Configuration screen.
Step 3
Enter the new management IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. See the "Connecting the ASA CX Management Interface" section to understand the requirements for your network.
Step 4
(Optional) Change the Auth Proxy Port.
Step 5
Click Finish to skip the remaining screens, or click Next to advance through the remaining screens and complete the wizard.
5 (ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X; May Be Required) Installing the Software Module
If you purchase the ASA with the ASA CX module, the module software and solid state drive(s) (SSDs) come pre-installed and ready to go. If you want to add the ASA CX to an existing ASA, or need to replace the SSD, you need to install the ASA CX boot software and partition the SSD according to this procedure. Only Cisco SSDs are supported. To physically install the SSD, see the ASA hardware guide.
Note
The free space on flash (disk0) should be at least 3GB plus the size of the boot software.
Step 1
Download the ASA CX boot software from Cisco.com to your computer. If you have a Cisco.com login, you can obtain the boot software from the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/software/release.html?mdfid=284325223&softwareid=284399946
The boot software lets you set basic ASA CX network configuration, partition the SSD, and download the larger system software from a server of your choice to the SSD.
Step 2
Download the ASA CX system software from Cisco.com to an HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP server accessible from the ASA CX management interface. If you have a Cisco.com login, you can obtain the system software from the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/software/release.html?mdfid=284325223&softwareid=284399944
Step 3
In ASDM, choose Tools > File Management, and then choose File Transfer > Between Local PC and Flash. Transfer the boot software to disk0 on the ASA. Do not transfer the system software; it is downloaded later to the SSD.
Step 4
Connect to the ASA CLI, and enter privileged EXEC mode. See the "Getting Started" chapter in the ASA configuration guide to access the ASA CLI.
Step 5
If you are replacing the IPS module with the ASA CX module, shut down and uninstall the IPS module, and then reload the ASA:
hostname# sw-module module ips shutdownhostname# sw-module module ips uninstallhostname# reloadAfter the ASA reloads, reconnect to the ASA CLI.
Step 6
Set the ASA CX module boot image location in ASA disk0 by entering the following command:
hostname# sw-module module cxsc recover configure image disk0:file_pathExample:
hostname# sw-module module cxsc recover configure image disk0:asacx-boot-9.1.1.imgStep 7
Load the ASA CX boot image by entering the following command:
hostname# sw-module module cxsc recover bootStep 8
Wait approximately 5 minutes for the ASA CX module to boot up, and then open a console session to the now-running ASA CX boot image. The default username is admin and the default password is Admin123.
hostname# session cxsc consoleEstablishing console session with slot 1Opening console session with module cxsc.Connected to module cxsc. Escape character sequence is 'CTRL-SHIFT-6 then x'.cxsc login: adminPassword: Admin123Step 9
Partition the SSD:
asacx-boot> partition....Partition Successfully CompletedStep 10
Perform the basic network setup using the setup command according to the "Configuring Basic ASA CX Settings at the ASA CX CLI" section (do not exit the ASA CX CLI), and then return to this procedure to install the software image.
Step 11
Install the system software from the HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP server where you copied the system software (see Step 2):
asacx-boot> system install urlExample:
The following command installs the asacx-sys-9.1.1.pkg system software from an HTTPS server.
asacx-boot> system install https://upgrades.example.com/packages/asacx-sys-9.1.1.pkgUsername: buffyPassword: angelforeverVerifyingDownloadingExtractingPackage DetailDescription:Requires reboot:Cisco ASA CX System UpgradeYesDo you want to continue with upgrade? [n]: YWarning: Please do not interrupt the process or turn off the system. Doing so might leave system in unusable state.UpgradingStopping all the services ...Starting upgrade process ...Reboot is required to complete the upgrade. Press Enter to reboot the system.Step 12
Press Enter to reboot the ASA CX module. Rebooting the module closes the console session. Allow 10 or more minutes for application component installation and for the ASA CX services to start.
6 Configuring Basic ASA CX Settings at the ASA CX CLI
You must configure basic network settings and other parameters on the ASA CX module before you can configure your security policy.
Step 1
Do one of the following:
•
(All models) Use SSH to connect to the ASA CX management IP address.
•
(ASA 5512-X through ASA 5555-X) Open a console session to the module from the ASA CLI (see the "Getting Started" chapter in the ASA configuration guide to access the ASA CLI):
hostname# session cxsc consoleStep 2
Log in with the username admin and the password Admin123. You will change the password as part of this procedure.
Step 3
Enter the following command:
asacx> setupExample:
asacx> setupWelcome to Cisco Prime Security Manager Setup[hit Ctrl-C to abort]Default values are inside [ ]The following example shows a typical path through the wizard. Note: You can configure IPv6 stateless auto configuration by answering N when asked if you want to configure a static IPv6 address.
Enter a hostname [asacx]: asa-cx-hostDo you want to configure IPv4 address on management interface?(y/n) [Y]: YDo you want to enable DHCP for IPv4 address assignment on management interface?(y/n)[N]: NEnter an IPv4 address [192.168.8.8]: 10.89.31.65Enter the netmask [255.255.255.0]: 255.255.255.0Enter the gateway [192.168.8.1]: 10.89.31.1Do you want to configure static IPv6 address on management interface?(y/n) [N]: YEnter an IPv6 address: 2001:DB8:0:CD30::1234/64Enter the gateway: 2001:DB8:0:CD30::1Enter the primary DNS server IP address [ ]: 10.89.47.11Do you want to configure Secondary DNS Server? (y/n) [N]: NDo you want to configure Local Domain Name? (y/n) [N] YEnter the local domain name: example.comDo you want to configure Search domains? (y/n) [N] YEnter the comma separated list for search domains: example.comDo you want to enable the NTP service?(y/n) [N]: YEnter the NTP servers separated by commas: 1.ntp.example.com, 2.ntp.example.comStep 4
After you complete the final prompt, you are presented with a summary of the settings. Look over the summary to verify that the values are correct, and enter Y to apply your changed configuration. Enter N to cancel your changes.
Example:
Apply the changes?(y,n) [Y]: YConfiguration saved successfully!Applying...Done.Generating self-signed certificate, the web server will be restarted after that...Done.Press ENTER to continue...asacx>Step 5
If you do not use NTP, configure the time settings. The default time zone is the UTC time zone. You can use the following commands to change time settings:
asacx> config timezoneasacx> config timeStep 6
Change the admin password by entering the following command:
asacx> config passwdExample:
asacx> config passwdThe password must be at least 8 characters long and must containat least one uppercase letter (A-Z), at least one lowercase letter(a-z) and at least one digit (0-9).Enter password: Farscape1Confirm password: Farscape1SUCCESS: Password changed for user adminStep 7
Enter the exit command to log out.
7 Redirecting Traffic to the ASA CX Module
This section identifies traffic to redirect from the ASA to the ASA CX module. Configure this policy on the ASA.
Note
When using PRSM in multiple device mode, you can configure the ASA policy for sending traffic to the ASA CX module within PRSM, instead of using ASDM. However, PRSM has some limitations when configuring the ASA service policy; see the ASA CX user guide for more information.
If you enable the authentication proxy on the ASA using this procedure, be sure to also configure a directory realm for authentication on the ASA CX module. See the ASA CX user guide for more information.
If you have an active service policy redirecting traffic to an IPS module (that you replaced with the ASA CX), you must remove that policy before you configure the ASA CX service policy.
Step 1
In ASDM, choose Configuration > Firewall > Service Policy Rules.
Step 2
Choose Add > Add Service Policy Rule. The Add Service Policy Rule Wizard - Service Policy dialog box appears.
Step 3
Complete the Service Policy dialog box as desired. See the ASDM online help for more information about these screens.
Step 4
Click Next. The Add Service Policy Rule Wizard - Traffic Classification Criteria dialog box appears.
Step 5
Complete the Traffic Classification Criteria dialog box as desired. See the ASDM online help for more information about these screens.
Step 6
Click Next to show the Add Service Policy Rule Wizard - Rule Actions dialog box.
Step 7
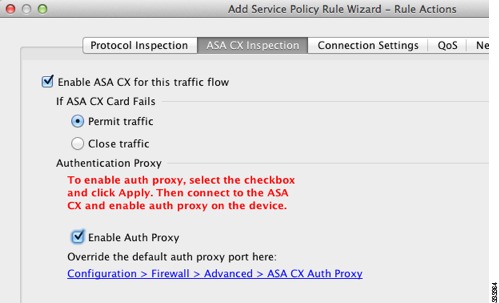
Click the ASA CX Inspection tab.
Step 8
Check the Enable ASA CX for this traffic flow check box.
Step 9
In the If ASA CX Card Fails area, click Permit traffic or Close traffic. The Close traffic option sets the ASA to block all traffic if the ASA CX module is unavailable. The Permit traffic option sets the ASA to allow all traffic through, uninspected, if the ASA CX module is unavailable.
Step 10
To enable the authentication proxy, which is required for active authentication, check the Enable Auth Proxy check box.
Step 11
Click OK and then click Apply.
Step 12
Repeat this procedure to configure additional traffic flows as desired.
8 Configuring the Security Policy on the ASA CX Module Using PRSM
This section describes how to launch PRSM to configure the ASA CX module application. For details on using PRSM to configure your ASA CX security policy, see the following ASA CX documentation roadmap: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/asacx/roadmap/asacxprsmroadmap.html.
Note
If you do not configure any policies on the ASA CX, all traffic redirected to the ASA CX will be allowed by default, and you can view the various reports in the ASA CX web interface to analyze the traffic.
You can launch PRSM from your web browser, or you can launch it from ASDM.
•
Launch PRSM from a web browser by enter the following URL:
https://ASA_CX_management_IPWhere the ASA CX management IP address is the one you set in the "Configuring Basic ASA CX Settings at the ASA CX CLI" section.
•
Launch PRSM from ASDM by choosing Home > ASA CX Status, and clicking the Connect to the ASA CX application link.
9 Where to Go Next
•
For more information about the ASA CX module, see the documentation roadmap:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/asacx/roadmap/asacxprsmroadmap.html.
•
See also the ASA CX home page: