Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Site Preparation and Unpacking
Prepare for Workbench or Tabletop Installation
Prepare for Rack-Mount Installation
Install the GBIC or SFP Module
Attach the Rack-Mount Brackets—Chassis Front-Mounted
Attach the Cable-Management Brackets
Chassis Ground Connection Installation
Connect the Router to the Network
Console and Auxiliary Port Cable Connections
Gigabit Ethernet and Fast Ethernet Port Connections
Fast Ethernet Management Port on the NSE-100 or NSE-150
Gigabit Ethernet RJ-45 Ports on the NPE-G100
Intra-Building Lightning Protection
GBIC and SFP Module Cabling and Connection Equipment
Connect the Optical Fiber Cables to the GBIC in the NSE-100
Connect the Optical Fiber Cables to an SFP Module in the NPE-G100 or NSE-150
Attach the Mode-Conditioning Patch Cord
Observe System Startup and Perform a Basic Configuration
Perform a Basic Configuration Using the Setup Facility
Save the Running Configuration to NVRAM
Check the Running Configuration Settings
View Your System Configuration
Perform Complex Configurations
Replace or Recover a Lost Password
Which prompt do you see on the console?
Router in Boot Mode: Router (boot)>
Cisco Technical Support & Documentation Website
Quick Start Guide
Cisco 7304 Quick Start Guide
1 Documentation and Resources
Documentation for the Cisco 7304 router is online and orderable. For detailed hardware installation instructions, refer to the online Cisco 7304 Installation and Configuration Guide. Refer to the following online documents for titles and links to related documentation for installation and replacement of parts (including line cards and port adapters), regulatory compliance information, and troubleshooting information and tools.
•
All Cisco 7304 documentation—See the Cisco 7304 Internet Router Documentation Roadmap at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/core/cis7300/3515.htm.
•
Line card, carrier card, port adapter, modular services card, and shared port adapter documentation—See the Cisco 7304 Router Line Card, Carrier Card, Port Adapter, Modular Services Card, and Shared Port Adapter Documentation Roadmap at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/core/cis7300/3531.htm.
•
Troubleshooting documentation and tools—See the Cisco 7304 Internet Router Troubleshooting Documentation Roadmap at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/core/cis7300/3516.htm.
Documentation Survey
Is Cisco documentation helpful? Click here or go to http://forums.cisco.com/eforum/servlet/viewsflash?cmd=showform&pollid=rtgdoc01!rtgdoc to give us your feedback
Obtaining Documentation
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available on Cisco.com. Cisco also provides several ways to obtain technical assistance and other technical resources. These sections explain how to obtain technical information from Cisco Systems.
Cisco.com
You can access the most current Cisco documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
You can access the Cisco website at this URL:
You can access international Cisco websites at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Product Documentation DVD
The Product Documentation DVD is a comprehensive library of technical product documentation on a portable medium. The DVD enables you to access multiple versions of installation, configuration, and command guides for Cisco hardware and software products. With the DVD, you have access to the same HTML documentation that is found on the Cisco website without being connected to the Internet. Certain products also have .PDF versions of the documentation available.
The Product Documentation DVD is available as a single unit or as a subscription. Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order a Product Documentation DVD (product number DOC-DOCDVD= or DOC-DOCDVD=SUB) from Cisco Marketplace at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Ordering Documentation
Registered Cisco.com users may order Cisco documentation at the Product Documentation Store in the Cisco Marketplace at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order technical documentation from 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. (0800 to 1700) PDT by calling 1 866 463-3487 in the United States and Canada, or elsewhere by calling 011 408 519-5055. You can also order documentation by e-mail at tech-doc-store-mkpl@external.cisco.com or by fax at 1 408 519-5001 in the United States and Canada, or elsewhere at 011 408 519-5001.
Documentation Feedback
You can rate and provide feedback about Cisco technical documents by completing the online feedback form that appears with the technical documents on Cisco.com.
You can submit comments about Cisco documentation by using the response card (if present) behind the front cover of your document or by writing to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Customer Document Ordering
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883We appreciate your comments.
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Information about Cisco products, technologies, and network solutions is available from various online and printed sources.
The Cisco Product Quick Reference Guide is a handy, compact reference tool that includes brief product overviews, key features, sample part numbers, and abbreviated technical specifications for many Cisco products that are sold through channel partners. It is updated twice a year and includes the latest Cisco offerings. To order and find out more about the Cisco Product Quick Reference Guide, go to this URL:
Cisco Marketplace provides a variety of Cisco books, reference guides, documentation, and logo merchandise. Visit Cisco Marketplace, the company store, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Cisco Press publishes a wide range of general networking, training and certification titles. Both new and experienced users will benefit from these publications. For current Cisco Press titles and other information, go to Cisco Press at this URL:
Packet magazine is the Cisco Systems technical user magazine for maximizing Internet and networking investments. Each quarter, Packet delivers coverage of the latest industry trends, technology breakthroughs, and Cisco products and solutions, as well as network deployment and troubleshooting tips, configuration examples, customer case studies, certification and training information, and links to scores of in-depth online resources. You can access Packet magazine at this URL:
Internet Protocol Journal is a quarterly journal published by Cisco Systems for engineering professionals involved in designing, developing, and operating public and private internets and intranets. You can access the Internet Protocol Journal at this URL:
Networking products offered by Cisco Systems, as well as customer support services, can be obtained at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/index.html
Networking Professionals Connection is an interactive website for networking professionals to share questions, suggestions, and information about networking products and technologies with Cisco experts and other networking professionals. Join a discussion at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/discuss/networking
World-class networking training is available from Cisco. You can view current offerings at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/learning/index.html
2 Prepare for Installation
This section contains warnings, information about tools and parts, site preparation information, and information for workbench or tabletop installation and rack-mount installation.
Warning
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing accidents. To see translations of the warnings that appear in this publication, refer to the translated safety warnings that accompanied this device.
Warning
Only trained and qualified personnel should install, replace, or service this equipment.
Warning
Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source.
Warning
This unit is intended for installation in restricted access areas. A restricted access area is where access can only be gained by service personnel through the use of a special tool, lock and key, or other means of security, and is controlled by the authority responsible for the location.
Warning
Class 1 (21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11) and Class 1M (IEC 60825-1 2001-01) laser products.
Warning
Voltage is present on the backplane when the system is operating. To reduce risk of an electric shock, keep hands and fingers out of the power supply bays and backplane areas.
Warning
Blank faceplates and cover panels serve three important functions: they prevent exposure to hazardous voltages and currents inside the chassis; they contain electromagnetic interference (EMI) that might disrupt other equipment; and they direct the flow of cooling air through the chassis. Do not operate the system unless all cards, faceplates, front covers, and rear covers are in place.
Warning
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity.
Before beginning this router installation, read the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco 7304 Internet Router document.
Site Preparation and Unpacking
•
Lift the router safely out of the packing container.
•
Ensure the power service at the site is suitable for the router you are installing.
•
Check the packing slip to ensure that all the proper components are present.
•
Locate and have accessible the Site Log for recording information about this installation.
Tools and Parts
Use the following list of tools and parts as a checklist for preparing for installing the Cisco 7304 router:
•
ESD-preventative wrist strap
•
Power cord
•
12-AWG or 2.5-mm copper installation wire for DC power leads
•
Appropriate cables to connect the router to the network and console terminal
•
Data service unit (DSU) to connect each serial port to an external network
•
Tape measure
•
Level
•
Number 2 Phillips screwdriver
•
1/8-inch flat-blade screwdriver
•
3/16-inch flat-blade screwdriver
•
Grounding lug and wires:
–
A grounding lug with two number-10 screw holes with a 0.63-inch (16.002-mm) spacing between them
–
A wire receptacle large enough to accept a 6-AWG multistrand, copper wire
–
Two Phillips machine screws with locking washers—M5 (metric), 0.031-inch (.08-mm) pitch, 0.315-inch (8-mm) length
–
A crimping tool to fit the grounding lug wire receptacle
–
One grounding wire—6-AWG, 0.162-inch (4.115-mm) diameter, with approximately 0.108-inch (2.743-mm) insulation, for a total wire diameter of approximately 0.27 inches (6.858 mm). The wire length depends on your router location and site environment.
•
Rack-mounting kit (shipped installed on chassis)
–
Spare screws for changing bracket position
•
Cable-management kit:
–
Two cable-management brackets
–
Four M4 x 20-mm screws
Prepare for Workbench or Tabletop Installation
For a workbench or tabletop installation, verify the following before installing the router:
•
The router is off the floor and has adequate ventilation.
•
An adequate chassis ground (earth) connection exists for the router.
•
The router has at last 3 inches (7.62 cm) of clearance at the inlet and exhaust vents (front and rear of router).
•
The router has 19 inches (48.3 cm) clearance at the front and rear to allow for CompactFlash Disk, Gigabit Ethernet GBIC module or Gigabit Ethernet SFP module, and line card replacement or installation, or to access cables or equipment.
•
The line card filler panel is installed if a line card is not installed. The slot must not be empty.
For cable-management bracket installation instructions, see the "Attach the Cable-Management Brackets" section.
Prepare for Rack-Mount Installation
Make these decisions before you begin the rack-mounting tasks:
•
Decide whether or not you want to front- or rear-mount the chassis.
•
Decide whether or not you want to attach the cable-management brackets.
•
Determine the type of rack—four-post or two-post—that you will be using.
3 Install the External Options
This section provides installation instructions for the CompactFlash Disk and the GBIC and SFP module.
Install the CompactFlash Disk
Figure 1 Inserting and Removing the CompactFlash Disk
Insert the CompactFlash Disk into the CompactFlash Disk slot with the label with the vendor name and memory size facing up. The CompactFlash Disk protrudes when completely inserted.
To eject a CompactFlash Disk, press the ejector button—located on the right side of the slot—until the CompactFlash Disk is free of the connector at the rear of the PC Card slot. Remove the CompactFlash Disk from the slot and place it in an antistatic bag.
About the CompactFlash Disk
The CompactFlash Disk supports online insertion and removal (OIR). For more information on CompactFlash Disks, see Appendix C of the Cisco 7304 Installation and Configuration Guide at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/core/cis7300/install/13279fd.htm
Install the GBIC or SFP Module
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no fiber cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures.
Warning
Class 1 laser product.
Warning
Class 1 LED product.
About the GBIC and SFP Module
The Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) and small form-factor pluggable (SFP) module support online insertion and removal (OIR). For more information on the GBIC or SFP type, technologies, and models, see the Cisco 7304 Installation and Configuration Guide.
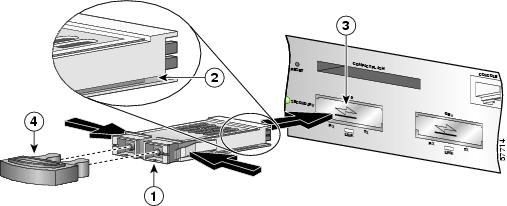
Figure 2 Installing a Gigabit Interface Converter in the NSE-100
Step 1
Turn the Gigabit Interface Convertor (GBIC) (1) so the label side is up and the alignment groove (2) is down.
Note
The GBIC is keyed so that it cannot be inserted incorrectly.
Step 2
Insert the GBIC into GBIC slot 0 or 1 (3). Repeat Step 2 if you are inserting a second GBIC.
Note
Do not remove the GBIC plug until you are ready to install the cables.
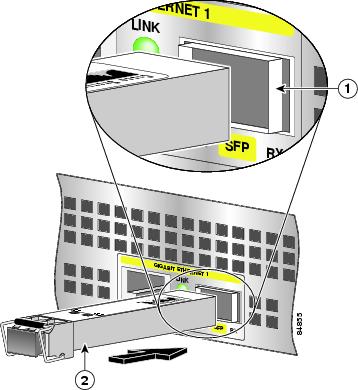
Figure 3 Inserting an SFP Module in the NPE-G100 or the NSE-150
The NSE-150 and NPE-G100 use only Gigabit Ethernet SFP modules. A variety of latch types are available. Figure 3 shows one type. For more information about SFP types, technologies, models, and cabling specifications, see the Cisco 7304 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Step 1
Attach an ESD-preventative wrist strap between you and an unpainted chassis surface.
Step 2
Locate the label on the Gigabit Ethernet SFP module and turn the SFP module so the label is on top and the alignment groove is down.
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no fiber cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures.
Note
The SFP module is keyed so that it cannot be inserted incorrectly.
Step 3
Insert the Gigabit Ethernet SFP module into an SFP slot. The SFP module snaps into place after you have completely and properly inserted it.
Step 4
Repeat Step 3 if you have a second, third, or fourth SFP module.
Note
Do not remove the plug from the SFP optical bores until you are ready to install the network interface optical fiber cable. Save the plug for future use.
4 Rack-Mount the Router
This section provides information for rack-mounting the router.
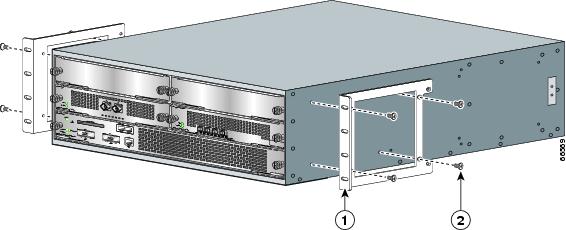
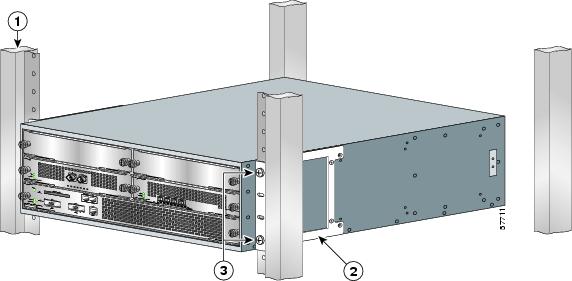
Attach the Rack-Mount Brackets—Chassis Front-Mounted
Figure 4 Attaching the Rack-Mount Brackets to the Front of the Chassis
Rack-mount bracket
Eight 8-18 x .37-inch screws—19-inch rack
Eight 8 x .755-inch screws—21-23-inch rack
The rack-mount brackets ship installed on the router. These instructions are provided if you want to change the position of the brackets or reattach them. Depending on how the rack-mount brackets are attached to the chassis, the chassis either protrudes from the rack or is recessed in the rack.
Step 1
Locate the rack-mount and cable-management brackets and screws and a Number 2 Phillips screwdriver.
Step 2
Align the rack-mount bracket to the side of the router. Depending on which set of rack-mount bracket holes you choose to use to attach the rack-mount bracket to the router, the chassis will either be recessed in the rack or protrude from the rack.
Step 3
Insert and tighten the two screws. Repeat Step 1 and Step 2 on the other side of the router.
Step 4
To install the cable-management brackets, see the "Attach the Cable-Management Brackets" section. If you are not installing the cable-management brackets, skip to the "Four-Post Rack Installation" section or the "Two-Post Rack Installation" section for rack-mount instructions.
Attach the Cable-Management Brackets
Figure 5 Attaching the Cable-Management Brackets
Step 1
Align a cable-management bracket to the rack-mount bracket on the left side of the Cisco 7304 router.
Step 2
Using a Phillips screwdriver and the M4 x 20-mm screws, thread and tighten the screws to the cable-management bracket.
Step 3
Repeat Step 1 and Step 2 for the other side of the router.
Go to the "Four-Post Rack Installation" section or the "Two-Post Rack Installation" section.
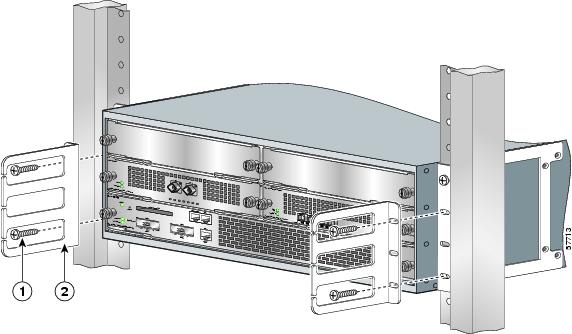
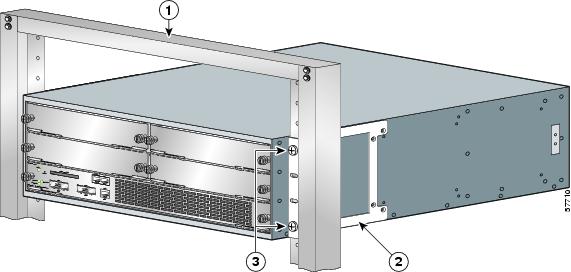
Four-Post Rack Installation
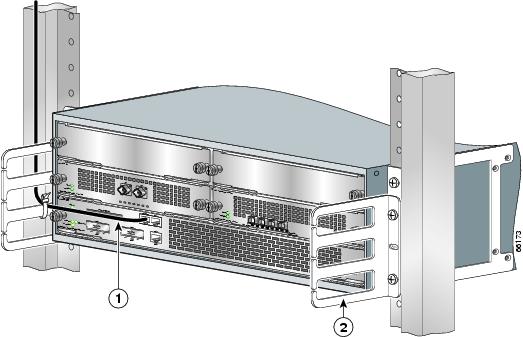
Figure 6 Installing the Cisco 7304 Router in a Four-Post Rack
Note
Inner clearance (the width between the inner sides of the two posts or rails) must be at least 17.6 inches (44.70 cm). The height of the chassis is 6.94 inches (17.63 cm). Airflow through the chassis is from front to back.
Step 1
Make sure that the line card levers are in the locked position and the locking thumbscrews are tightened.
Step 2
Make sure the rack brakes are locked or the rack is stabilized.
Step 3
Position the router so the front is closest to you and lift it carefully into the rack. To prevent injury, avoid any sudden twists or moves.
Step 4
Slide the chassis into the rack, pushing it back until the brackets meet the mounting strips or posts on both sides of the rack.
Step 5
Keeping the brackets flush against the posts or mounting strips, align the holes in the brackets with the holes on the rack or mounting strip.
Step 6
For each bracket, insert and tighten two 12-24 x 0.5-inch screws to the rack.
Two-Post Rack Installation
Figure 7 Installing the Cisco 7304 Router in a Two-Post or Telco Rack
Note
Inner clearance (the width between the inner sides of the two posts or rails) must be at least 17.6 inches (44.70 cm). The height of the chassis is 6.94 inches (17.63 cm). Airflow through the chassis is from front to back.
Step 1
Make sure that the line card levers are in the locked position and the locking thumbscrews are tightened.
Step 2
Make sure the rack brakes are locked or the rack is stabilized.
Step 3
Position the router so the front is closest to you and lift it carefully into the rack. To prevent injury, avoid any sudden twists or moves.
Step 4
Slide the chassis into the rack, pushing it back until the brackets meet the mounting strips or posts on both sides of the rack.
Step 5
Keeping the brackets flush against the posts or mounting strips, align the holes in the brackets with the holes on the rack or mounting strip.
Step 6
For each bracket, insert and tighten two 12-24 x 0.5-inch screws to the rack.
Chassis Ground Connection Installation
Warning
This equipment is intended to be grounded. Ensure that the host is connected to earth ground during normal use.
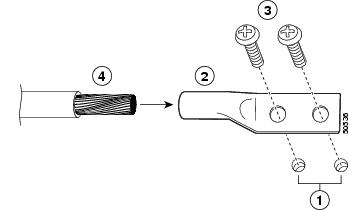
Figure 8 Attaching the Grounding Lug and Wire to the Chassis
Note
The grounding lug and Phillips screws are not available from Cisco Systems. Get the grounding lug from an electrical-connector vendor and the screws from a hardware vendor. See the "Tools and Parts" section for the parts needed.
Step 1
Use the wire stripper to strip one end of the 6-AWG wire approximately 0.75 inches (19.05 mm).
Step 2
Insert the 6-AWG wire (4) into the wire receptacle on the grounding lug.
Step 3
Use the crimping tool, approved for use with the lug, to carefully crimp the wire receptacle around the wire; this step is required to ensure a proper mechanical connection.
Step 4
Locate the chassis ground connectors (1) on the side of the router.
Step 5
Insert the two screws (3) through the holes in the grounding lug (2).
Step 6
Use a Number 2 Phillips screwdriver to carefully tighten the screws until the grounding lug is held firmly to the chassis. Do not overtighten the screws.
Step 7
Connect the opposite end of the grounding wire to the appropriate grounding point at your site to ensure an adequate chassis ground.
5 Connect the Router to the Network
The NSE-100, NSE-150, and NPE-G100 are the processing engines available for the Cisco 7304 router. Each processing engine has a different number of Gigabit Ethernet interfaces and different Gigabit Ethernet Gigabit Interface Converter port types (GBIC or SFP). In addition, the NSE-100 and NSE-150 have a Fast Ethernet management port; the NPE-G100 does not. The console port and auxiliary port are the same on all three processing engines.
This section provides information about processing engine cables and ports and attaching the router to the network. Use the information about the NPE-G100, NSE-100, or the NSE-150, whichever is appropriate for your installation.
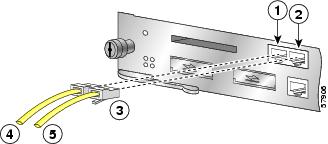
Figure 9 Attaching the Console and Auxiliary Port Cables
Console port
Cable to console terminal or DTE
Auxiliary port
Cable to modem or DCE
RJ-45 connector
Console and Auxiliary Port Cable Connections
Note
Both the console and auxiliary ports are asynchronous serial ports; any devices connected to these ports must be capable of asynchronous transmission. The DCE-mode console port is for connecting a console terminal and the DTE-mode auxiliary port is for connecting a modem or other DCE device (such as a CSU/DSU or other router) to your router.
Step 1
Before connecting a terminal to the console port, configure the terminal to match the router console port as follows: 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, 2 stop bits (9600 8N2).
Step 2
Use an auxiliary and console port cable. Use the console cable to connect the terminal to the console port. After you establish normal router operation, you can disconnect the terminal.
Note
You must supply your own interface cables between the auxiliary and console ports and the equipment you are connecting. For console and auxiliary port pinouts, see the online Cisco 7304 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Gigabit Ethernet and Fast Ethernet Port Connections
Your Cisco 7304 router has either one or two NSE-100s, one or two NSE-150s, or one or two NPE-G100s installed. Use this section to connect the appropriate cables to the appropriate processing engine.
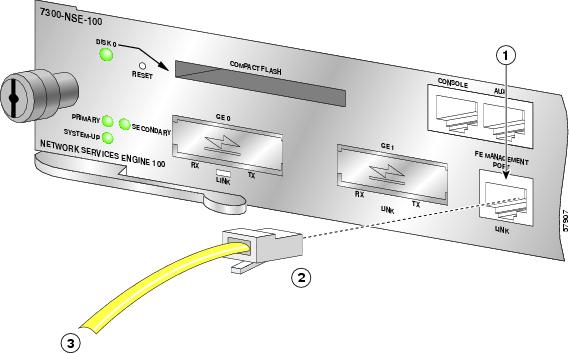
Fast Ethernet Management Port on the NSE-100 or NSE-150
The NSE-100 has one two-port Gigabit Ethernet interface and one Fast Ethernet Management port. The NPE-G100 has three Gigabit Ethernet interfaces, with three RJ-45 10/100/1000 ports and three SFP ports; any three are available at any time. The NSE-150 has four SFP ports that are all available at any time and a Fast Ethernet Management port.
For more information, see the online Cisco 7304 Installation and Configuration Guide.
Figure 10 Attaching the Fast Ethernet Cable (NSE-100 Example)
Warning
To avoid electric shock, do not connect safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits to telephone-network voltage (TNV) circuits. LAN ports contain SELV circuits, and WAN ports contain TNV circuits. Some LAN and WAN ports both use RJ-45 connectors. Use caution when connecting cables.
To identify the cable type, hold the two ends of the cable next to each other so you can see the colored wires inside the ends. The straight-through wire type has colored wires in the same sequence at both ends. In the crossover wire type, the first colored wire at the far left is the third colored wire at the other end. The second colored wire at the far left is the sixth colored wire at the other end.
Attach RJ-45 Fast Ethernet cables to the appropriate connector.
Note
The Fast Ethernet management port is a management port only; it is not intended for normal router traffic.
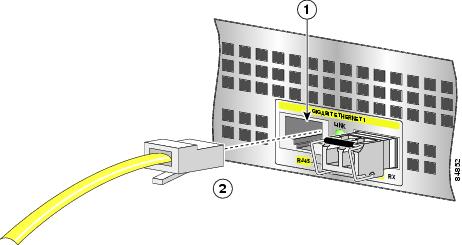
Gigabit Ethernet RJ-45 Ports on the NPE-G100
Intra-Building Lightning Protection
Shielded cables, which are grounded at both ends, are required to be used on the 10/100/1000 Ethernet/Fast Ethernet /Gigabit Ethernet (RJ-45) port in order to be in compliance with requirement R4-11 in GR-1089-Core for a Central Office environment. This is not a requirement for customer premise installations.
Figure 11 Attaching the RJ-45 Port Gigabit Ethernet Cables
Attach one, two, or three Gigabit Ethernet 10/100/1000 cables to the Gigabit Ethernet RJ-45 port 0, port 1, or port 2.
Warning
To avoid electric shock, do not connect safety extra-low voltage (SELV) circuits to telephone-network voltage (TNV) circuits. LAN ports contain SELV circuits, and WAN ports contain TNV circuits. Some LAN and WAN ports both use RJ-45 connectors. Use caution when connecting cables.
GBIC and SFP Module Cabling and Connection Equipment
The Cisco 7304 has three processing engines, the NSE-100, the NSE-150, and the NPE-G100. The NSE-100 uses GBICs GBIC-SX or WS-G5484, GBIC-LX/LH or WS-G5486, GBIC-ZX or WS-G5487, the CWDM GBICs, and WS-G5483= . The NPE-G100 uses SFPs GLC-SX-MM, GLC-LH-SM, GLC-ZX-SM, and the CWDM SFPs. The NSE-150 uses the CWDM SFPs, GLC-BX-D, GLC-BX-U, GLC-LH-SM, GLC-SX-MM, GLC-T, GLC-ZX-SM, SFP-GE-L, SFP-GE-S, and SFP-GE-Z.
The Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC) port is a 1000-Mbps optical interface in the form of an SC-type duplex port that supports IEEE 802.3z interfaces compliant with the 1000BASEX standard.
The Gigabit Ethernet SFP port is a 1000-Mbps optical interface in the form of an LC-type duplex port that supports IEEE 802.3z interfaces compliant with the 1000BASEX standard.
For cabling distances, specifications, and other information, see the online Cisco 7304 Router Installation and Configuration Guide at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/core/cis7300/install/index.htm.
Note
Note that all GBIC ports have SC-type connectors and that all SFP ports have LC-type connectors.
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no fiber cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures.
Warning
Class 1 laser product.
Warning
Class 1 LED product.
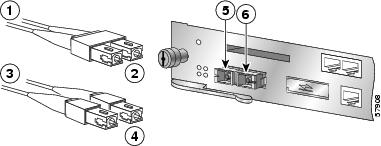
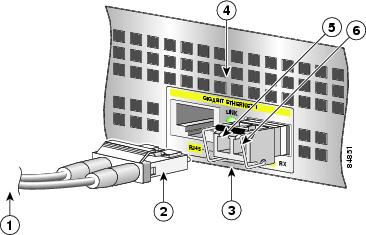
Connect the Optical Fiber Cables to the GBIC in the NSE-100
Figure 12 Inserting the Gigabit Ethernet Optical Fiber Cables into the NSE-100 GBIC
To external 1000BASEX network
2 simplex connectors
1 duplex connector (TX and RX)
RX
To external 1000BASEX network
TX
Note
There is no support for copper-based GBICs (1000BASET) as these do not conform to the GBIC standard and have not been validated by Cisco.
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no fiber cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures.
Step 1
Remove the GBIC plug.
Step 2
Attach the appropriate optical fiber cable directly to the SC-type receptacle on the GBIC. You can use either simplex or duplex connectors for most devices.
Two cables are required for simplex connectors, one cable for transmit (TX) and one for receive (RX).
One cable that has both TX and RX connectors is required for duplex connectors.
CautionIf you plan to use a GBIC-LX/LH or WS-G5486 at distances greater than 984.25 feet (300 meters) over 50/125-micron or 62.5/125-micron multimode fiber, to prevent data transmission problems you must use the mode-conditioning patch cord.
Connect the Optical Fiber Cables to an SFP Module in the NPE-G100 or NSE-150
Figure 13 Inserting the Gigabit Ethernet Optical Fiber Cable in the SFP Module (NPE-G100 Example)
To external 1000BASEX network
Gigabit Ethernet SFP slot 1
Duplex connector (TX and RX)
TX (Gigabit Ethernet SFP slot 1)
Gigabit Ethernet SFP module
RX (Gigabit Ethernet SFP slot 1)
Step 1
Remove the plug from the SFP so that you can insert the cables. Keep the plug for use should you ever disconnect the optical fiber cables.
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port when no fiber cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare into open apertures.
Step 2
Attach the appropriate optical fiber cable directly to the SFP. You can use either simplex or duplex connectors for most devices.
•
For simplex connectors, two cables are required, one cable for transmit (TX) and a second cable for receive (RX).
•
For duplex connectors, only one cable that has both TX and RX connectors is required.
Attach the Mode-Conditioning Patch Cord
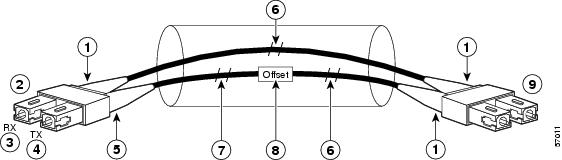
Figure 14 Attaching the Mode-Conditioning Patch Cord (LC-Type Connectors Shown)
Beige color identifier
Multimode bar
To GE interface
Single-mode bar
RX
Offset
TX
To cable plant
Blue color identifier
Step 1
Attach the patch cord to the SC-type receptacle on the GBIC (2) or SFP module.
Step 2
Attach the network ends of your patch cord to the appropriate 1000BASEX equipment in your building cable plant (9).
Note
Ensure that you connect the TX and RX ports on one end of the patch cord to the RX and TX ports (respectively) on the other end. Connect TX to RX and RX to TX.
A mode-conditioning patch cord can be used with the GBIC-LX/LH or WS-G5486, or GLC-LH-SM to allow reliable laser transmission between the single-mode laser source on the GBIC or SFP module and a multimode optical fiber cable.
Line Card Cable Connections
The instructions for connecting the cables for each line card, port adapter, or SPA installed in the Cisco 7304 router are in the respective online notes for each line card. Refer to the documents at http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/core/cis7300/3531.htm
Cable Management
Figure 15 Inserting the Cables Through the Cable-Management Brackets
If you have not already done so, run the line card cables, port adapter cables, SPA cables, and input/output cables through the cable-management brackets.
6 Start the System
Warning
Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source.
This section provides instructions for attaching the power cables to the router and powering on the router.
The Cisco 7304 router comes with either an AC or DC power supply. A redundant AC or DC power supply option is available. Using an AC and DC power supply in the same chassis simultaneously is not supported.
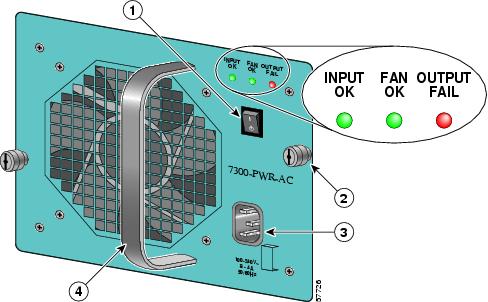
Connect AC-Input Power
Figure 16 Attaching the AC Power Cable
Step 1
Plug the power cable into the AC-input power receptacle on the AC-input power supply.
Step 2
Plug the AC power supply cable into the AC power source.
Connect DC-Input Power
Warning
Before completing any of the following steps, and to prevent short-circuit or shock hazards, ensure that power is removed from the DC circuit. To ensure that all power is OFF, locate the circuit breaker on the panel board that services the DC circuit, switch the circuit breaker to the OFF position, and tape the switch handle of the circuit breaker in the OFF position.
Warning
When installing the unit, the ground connection must always be made first and disconnected last.
Note
The color coding of the DC-input power supply leads depends on the color coding of the DC power source at your site. Typically, green or green/yellow is used for ground. Make certain the lead color coding you choose for the DC-input power supply matches lead color coding used at the DC power source.
Note
Install a 20A maximum, 60 VDC listed breaker at the power source.
Step 1
Ensure that the power switch is in the standby (off) position.
Step 2
Ensure that the -V and +V leads are disconnected from the power source.
Note
Use only 12-AWG or 2.5-mm copper installation wire.
Step 3
Using a wire stripper, strip approximately 0.55 inch (14 mm) from the -V and +V leads.
Note
Do not use soft-soldering to consolidate the strands.
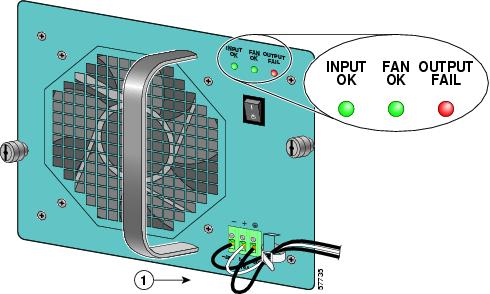
Figure 17 Attaching the Wires to the DC Power Receptacles
Step 4
Insert the stripped end of the ground lead all the way into the ground lead receptacle on the DC-input power supply and tighten the receptacle screw using a 1/8-inch flat-blade screwdriver. (See Figure 17.)
Step 5
Insert the stripped end of the + DC power line input lead all the way into the + lead receptacle and tighten the receptacle screw using the same 1/8-inch flat-blade screwdriver. Repeat Step 5 for the - DC power line input lead.
Note
Make sure the entire stripped end of each lead is inserted all the way into its receptacle. If any exposed wire at the stripped end of a lead is visible after inserting the lead into its receptacle, remove the lead from the receptacle, use the wire stripper to cut the stripped end of the lead, and repeat Step 3 through Step 5.
Step 6
After tightening the receptacle screw for the ground and DC power line input leads, use a cable tie to secure the three leads to the power supply faceplate.
Note
When securing the ground and DC power line input leads to the power supply faceplate, leave a small service loop in the ground lead to ensure that it is the last lead to disconnect from the power supply if a great deal of strain is placed on all three leads (refer to Figure 17).
Step 7
Connect the ground and DC power line input leads to the power source.
Note
After powering off the router, wait a minimum of 30 seconds before powering it on again.
Observe System Startup and Perform a Basic Configuration
Check conditions prior to system startup:
Step 1
Check that all hardware parts and cables are securely attached to the chassis.
Step 2
Check that line card configuration information is available, if needed.
Step 3
Check that a CompactFlash Disk is installed.
Step 4
Check that the console terminal is turned on.
Start the Router
Step 1
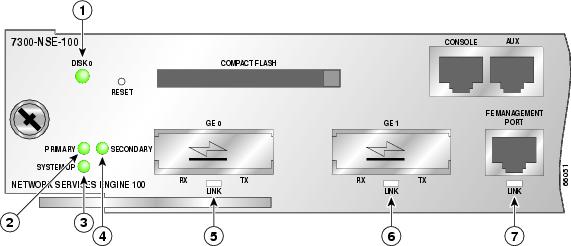
Plug the power supply cable into the power source. Switch power on. Verify that the INPUT OK LED is on and green.
Step 2
Listen for the fans; they should be operating as soon as power is turned on. Verify that the FAN OK LED is on and green.
Step 3
During the boot process, observe the system LEDs. The SYSTEM-UP LED comes on immediately as yellow, then turns to green when IOS is booted. When the SYSTEM-UP LED turns off, ROMmon has completed the boot up process and the system either is in the autoboot stage or displays a Router> prompt.
Step 4
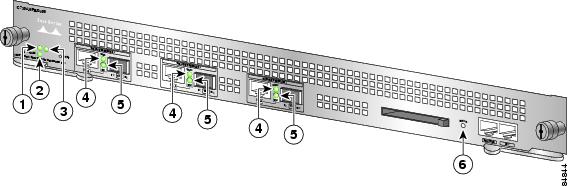
Observe the initialization process. The LEDs on the line card behave differently (most flash on and off).
The following illustrations and tables provide information about the NSE-100, NSE-150, and NPE-G100 LEDs as the system starts.
Figure 18 Identifying LEDs and LED Status on the NSE-100
Figure 19 Identifying LEDs and LED Status on the NPE-G100
Figure 0-20 Identifying LEDs and LED Status on the NSE-150 LEDs
7 Configure the Router
Perform a Basic Configuration Using the Setup Facility
You can run the setup facility any time you are at the enable prompt (#) by entering the setup command.
The router may take several minutes to determine that AutoInstall is not set up to a remote TCP/IP host. Once the router determines that AutoInstall is not configured, it defaults to the setup facility.
Configure Global Parameters
When you first start the setup program, you must configure the global parameters. These parameters are used for controlling system-wide settings. Complete the following steps to enter the global parameters:
Step 1
Connect a console terminal to the console port, and then boot the router.
The system boots from Flash memory. The following information appears after about 30 seconds. When you see this information, you have successfully booted your router:
Restricted Rights LegendUse, duplication, or disclosure by the Government issubject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph(c) of the Commercial Computer Software - RestrictedRights clause at FAR sec. 52.227-19 and subparagraph(c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and ComputerSoftware clause at DFARS sec. 252.227-7013.cisco Systems, Inc.170 West Tasman DriveSan Jose, California 95134-1706Cisco Internetwork Operating System SoftwareIOS (tm) 7300 Software (C7300-JS-M), Version 12.1(9), CISCO RELEASED VERSIONTEST VERSIONCopyright (c) 1986-2001 by cisco Systems, Inc.Compiled Tue 17-Jul-01 01:51 by biffImage text-base:0x40008970, data-base:0x40BF8000Downloading default microcode:system:pxf/ucode1Successfully downloaded the production microcode.updating timeout values directlyCurrently running ROMMON from OTP ROMcisco 7300 (NSE100) processor (revision B) with 114688K/16384K bytes of memory.Processor board IDR7000 CPU at 350Mhz, Implementation 39, Rev 3.2, 256KB L2, 1024KB L3 Cache4 slot midplane, Version 65.48Last reset from watchdog nmiX.25 software, Version 3.0.0.PXF processor tmc0 is running.PXF processor tmc1 is running.1 FastEthernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)2 Gigabit Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)9 Packet over SONET network interface(s)509K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.16064K bytes of ATA compact flash disk at bootdisk (Sector size 512 bytes).64000K bytes of ATA compact flash disk at disk 0 (Sector size 512 bytes).Press RETURN to get started!The first two sections of the configuration script (the banner and the installed hardware) appear only at initial system startup. On subsequent uses of the setup facility, the script begins with a System Configuration Dialog as shown in the following example.
--- System Configuration Dialog ---At any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help.Use ctrl-c to abort configuration dialog at any prompt.Default settings are in square brackets '[]'.Step 2
When asked if you want to enter the initial configuration dialog and see the current interface summary, enter yes or press Return:
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes]:First, would you like to see the current interface summary? [yes]:In the following example, the summary shows a Cisco 7304 router at first-time startup; that is, nothing is configured.
Any interface listed with OK? value "NO" does not have a valid configuration
Step 3
Choose which protocols to support on your interfaces. For Internet Protocol (IP)-only installations, you can accept the default values for most of the questions. A typical configuration using IP, IPX, and AppleTalk follows and continues through Step 8:
Configuring global parameters:Enter host name [Router]:Step 4
Enter enable secret, enable, and virtual terminal passwords:
The enable secret password is a one-way cryptographic secret password used instead of the enable password when it exists.Enter enable secret: barneyThe enable password is used when there is no enable secret password and when using older software and some boot images.Enter enable password: bettyEnter virtual terminal password: fredStep 5
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is the most widely supported open standard for network management. It provides a means to access and set configuration and run-time parameters of routers and communication servers. SNMP defines a set of functions that can be used to monitor and control network elements.
Enter yes or press Return to accept SNMP management; enter no to refuse it:
Configure SNMP Network Management? [yes]:Community string [public]:Step 6
For the following queries, do not enable VINES, LAT, DECnet, CLNS, bridging, XNS, or Apollo:
Configure Vines? [no]:Configure LAT? [no]:Configure DECnet? [no]:Configure CLNS? [no]:Configure bridging? [no]:Configure XNS? [no]:Configure Apollo? [no]:Step 7
For the following queries, enable routing on AppleTalk and IPX:
Configure AppleTalk? [no]: yesMultizone networks? [no]: yesConfigure IPX? [no]: yesStep 8
In most cases you use IP routing. If you are using IP routing, you must also select an interior routing protocol. You can specify only one of two interior routing protocols to operate on your system using the setup facility: Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) or Routing Information Protocol (RIP). To configure IP routing, enter yes (the default) or press Return, and then select an interior routing protocol:
Configure IP? [yes]:Configure IGRP routing? [yes]:Your IGRP autonomous system number [1]: 15The following sample display includes a continuous listing of all configuration parameters selected in Step 3 through Step 8. Only IP, IPX, and AppleTalk are the selected protocols for this example.
Configuring global parameters:Enter host name [Router]: routerThe enable secret is a one-way cryptographic secret usedinstead of the enable password when it exists.Enter enable secret: barneyThe enable password is used when there is no enable secret and when using older software and some boot images.Enter enable password: bettyEnter virtual terminal password: fredConfigure SNMP Network Management? [yes]:Community string [public]:Configure Vines? [no]:Configure LAT? [no]:Configure AppleTalk? [no]: yesMultizone networks? [no]: yesConfigure DECnet? [no]:Configure IP? [yes]:Configure IGRP routing? [yes]:Your IGRP autonomous system number [1]: 15Configure RIP routing? [no]:Configure CLNS? [no]: noConfigure bridging? [no]:Configure IPX? [no]: yesConfigure XNS? [no]:Configure Apollo? [no]:Step 9
Save your settings to NVRAM. See the "Save the Running Configuration to NVRAM" section. If you do not save the configuration settings that you created in the router using configuration mode and the setup facility, your configuration will be lost the next time you reload the router.
Debug
Cisco IOS provides two commands to provide information on your interfaces: show interface GigabitEthernet 0/X (where X is either 0 or 1) and show controllers GigabitEthernet 0/X (where X is either 0 or 1).
The output of the show interface command is useful for determining the current operating mode of the interface (speed/duplex/media-type) and the current interface statistics.
The output of the show controller command displays more information specific to the Cisco 7304 router Gigabit Ethernet interface. For example, it shows the detected link status, speed, and duplex, and also determines the current status of autonegotiation and the link partners' abilities (if it is an autonegotiation-capable interface). (Speed and duplex are always full duplex, 1000-Mbps.)
The show controller command also displays the current operating state of the driver and the Ethernet controller hardware. The show controller command is a very powerful debugging aid, especially for Cisco engineers should you need help in debugging a problem. If you have any problems with your Gigabit Ethernet interfaces, you will need to provide this information to Cisco for analysis.
Reset the Interface
Should you have a problem with your interface and wish to try and reset it, use the command:
clear interface GigabitEthernet 0/X (where X is either 0 or 1)
Clear Counters
Interface counters may be cleared (reset) by using the command:
clear counters GigabitEthernet 0/X (where X is either 0 or 1)
Using this command will not reset the interface.
Save the Running Configuration to NVRAM
To store the configuration or changes to your startup configuration in NVRAM, enter the copy running-config startup-config command at the Router# prompt:
Router# copy running-config startup-configUsing this command saves the configuration settings that you created in the router using configuration mode and the setup facility. If you fail to do this, your configuration will be lost the next time you reload the router.
Check the Running Configuration Settings
To check the value of the settings you have entered, enter the show running-config command at the Router# prompt:
Router# show running-configTo review changes you make to the configuration, use the EXEC mode show startup-config command to display the information stored in NVRAM.
View Your System Configuration
You can use the show version (or show hardware) and the show c7300 commands to display the system hardware, the software version, the names and sources of configuration files, and the boot images. Use the show c7300 command to determine what type of line card is installed.
For specific information on the show version, show c7300, and other commands, refer to the modular configuration and modular command reference publications in the Cisco IOS software configuration documentation set that corresponds to the software release installed on your Cisco hardware.
Perform Complex Configurations
After you have installed your Cisco 7304 router hardware and minimally configured the system, you might need to perform more complex configurations, which are beyond the scope of this publication.
For specific information on system and interface configuration, refer to the modular configuration and modular command reference publications in the Cisco IOS software configuration documentation set that corresponds to the software release installed on your Cisco hardware. These publications contain additional information on using the configure command.
Replace or Recover a Lost Password
See the Cisco 7304 Installation and Configuration Guide, Chapter 3, "Starting and Configuring," for instructions. It is possible to recover the enable or console login password. The enable secret password is encrypted and must be replaced with a new enable secret password.
8 Troubleshoot Startup Problems
Which prompt do you see on the console?
•
None: See the "Check the LEDs" section.
•
Garbled: See the "Check Terminal Settings" section.
•
ROMmon prompt: See the "ROMmon prompt: rommon # >" section.
•
Router in Boot Mode: See the "Router in Boot Mode: Router (boot)>" section.
Check the LEDs
If you get no response from the console after pressing Return a couple times, check the NSE and power supply LEDs. Refer to the "Start the Router" section for LED information.
Check Terminal Settings
Terminal Settings
•
9600 baud rate
•
8 data bits
•
No parity
•
2 stop bits
•
No flow control
ROMmon prompt: rommon # >
Use this procedure to recover a router stuck in ROMmon mode (rommon # > prompt).
Step 1
Using the dev command, see which devices are available on your router.
rommon 1 > devDevices in device table:id namebootdisk: boot diskdisk0: PCMCIA slot 0eprom: epromrommon 2 >Step 2
Using the dir [device-ID] command, look for a valid Cisco IOS image. The device ID is bootdisk: or disk0:, corresponding to the CompactFlash Disks inserted in their respective slots.
rommon 3 > dir disk0:Directory of disk0:3 4965400 -rw- c7300-js-mz.121-99.WS_DAILY_BUILD_200107061216 1867 -rw- running-configrommon 4 >Step 3
Try to boot from the valid Cisco IOS image.
rommon 5 > boot disk0:c7300-js-mz.121-99.WS_DAILY_BUILD_20010706Self decompressing the image : ############################################################### ################################################################################################## ################################################################################################## ################################################################################################## [OK]Step 4
If the image is valid, this brings you back to normal operation mode. Confirm that the boot variable and configuration register contain values to point to this image.
Router# show bootvariableBOOT variable = disk0:c7300-js-mz.121-99.WS_DAILY_BUILD_20010706,12CONFIG_FILE variable does not existBOOTLDR variable =Configuration register is 0x2101Router# conf tEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.Step 5
Enter no boot system to erase all previously defined boot variables.
Router(config)# no boot systemRouter(config)# boot system disk0:c7304-js-mz.121.99Router(config)#^ZRouter#22:51:40: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by consoleA newly defined variable does not go into effect yet, as seen from show bootvariable.
Router# show bootvariableBOOT variable = disk0:c7300-js-mz.121-99.WS_DAILY_BUILD_20010706,12CONFIG_FILE variable does not existBOOTLDR variable =Configuration register is 0x2102The newly defined variable only takes effect after using the copy running-config startup-config command or after a save of system configuration during the reload command.
Router# copy running-config startup-configBuilding configuration...[OK]Router#sh bootvBOOT variable = disk0:c7304-js-mz.121.99,12CONFIG_FILE variable does not existBOOTLDR variable =Configuration register is 0x2102Step 6
If none of the images are valid, use the boot image to download a valid Cisco IOS software image using a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server.
a.
Change the configuration register to boot the boot image by setting the configuration register as follows, depending on the prompt you have:
rommon 1 > confreg 0x2101b.
Boot the boot image by resetting the router. (You must reset or power cycle the router for the new configuration to take effect.)
rommon 2 > resetor> iThe System Bootstrap message appears and the router loads an image from bootdisk. On the screen, you should see something similar to the following:
System Bootstrap, Version 12.1(9) [biff-ws28 124], RELEASED SOFTWARECopyright (c) 1994-2001 by cisco Systems, Inc.C7300 platform with 131072 Kbytes of main memoryCurrently running ROMMON from OTP ROMSelf decompressing the image : ######################################################################################## ######################################################################################## ######################################################################################### [OK]Restricted Rights LegendYou should now have a prompt similar to Router (boot)>. Upgrade the Cisco IOS software by following the procedure in the "Router in Boot Mode: Router (boot)>" section.
Note
Another option is to boot from an image copied from another router.
rommon 3 > boot disk0:c7300-js-mz (where disk0:is the flash disk with the image c7300-js-mz copied from another Cisco 7304 router)Step 7
If you are still in ROMmon mode, that means your boot image is either missing or corrupted. If your router has no valid image in disk0: or bootdisk:, and no other ROMmon upgrade procedure, the only way to recover is to use the CompactFlash Disk on another 7304 router, download the image on that router, and then move the CompactFlash Disk to the one with a corrupt or missing boot image.
If you do not have another Cisco 7304 router, call TAC to request a CompactFlash Disk with a valid boot image.
Using the bootldr Command
Use the bootldr command to specify an image to boot the system in the case of a system crash. You can use the bootldr command in IOS or in ROMmon mode.
You can use the bootldr command in IOS:
Router> enableRouter#> configRouter(config)# boot bootldr bootdisk:c7300-boot-mz-my-imageRouter# copy running-config startup-configThe show bootvar command can be used in ROMmon mode to verify that parameter settings are correct.
In cases where the system will not boot up, you can also use the bootldr command in ROMmon mode. First check to see if bootldr is set correctly:
ROMMON> setIf bootldr is not set correctly, set it with the correct image:
ROMMON> BOOTLDR="bootdisk:c7300-boot-mz-my-image"
CautionBe careful of typographical errors in ROMmon mode as there is no error checking.
You can use the ROMmon command sync to save the current parameters that remain after a power cycle to NVRAM.
Use the set command to check your configuration.
Router in Boot Mode: Router (boot)>
If the router is in boot mode, it means the router has a corrupt or missing Cisco IOS image. Use this procedure to upgrade the Cisco IOS software.
Step 1
Set the configuration register value to 0x0 for the next reload.
Note
Do not save anything while you are in boot mode. Do not use the saving commands (write mem or copy run start) and answer no to any prompt suggesting that you save your current configuration. If you save while you are in this mode, your configuration can be partially or completely erased.
Router(boot)>Router(boot)>enablePassword: passwordRouter(boot)# conf tEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.Router(boot)(config)# conRouter(boot)(config)# config-register 0x0Router(boot)(config)# ^ZStep 2
Verify the TFTP server has IP connectivity to the router by confirming that the router IP address and default gateway (if necessary) are set. Ping the router to verify that a network connection exists between it and the TFTP server.
Step 3
Copy the new software image from the TFTP server to the router. (Keep a copy of the router configuration before upgrading the router software.)
Router> enablePassword: passwordRouter#Router# copy tftp disk0:Step 4
Specify the IP address of the TFTP server.
Address or name of remote host [255.255.255.255]? 172.17.247.195Step 5
Specify the filename of the new Cisco IOS software image.
Source file name? c7300-js-mz.121-9.E
Note
The image name varies depending on the filename of the image on the TFTP server.
Step 6
Specify the destination image filename. This is the name the new software image will have when it is loaded onto the router. The image can be named anything, but common practice is to enter the UNIX image filename.
Destination file name c7300-js-mz.121-9.EPThe copying process takes several minutes; the time differs from network to network. During the copy process, messages are displayed to indicate which files have been accessed.
The exclamation point (!) indicates that the copy process is taking place. Each exclamation point (!) indicates that ten packets were transferred successfully. A checksum verification of the image occurs after the image is written to Flash memory. The router reloads itself with the new image when the software upgrade is complete.
Step 7
Reload the router.
Router(boot)# reload*Mar 1 00:30:49.972: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by consoleSystem configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: NOProceed with reload? [confirm] YESBecause the configuration register is set to 0x0, the router will go into ROMmon when you reload and you will load the image you just copied. Follow the instructions in the "ROMmon prompt: rommon # >" section.
Step 8
Change the boot variable and configuration register to contain values to point to the image you copied.
rommon 1 > confreg 0x2101Step 9
Use the show version command to verify that the router is running with the proper image.
Router# show versionCisco Internetwork Operating System SoftwareIOS (tm) 7300 Software (C7300-js-M), Version 12.1(9), CISCO RELEASED VERSIONCopyright (c) 1986-2001 by cisco Systems, Inc.Compiled Fri 06-Jul-01 02:01 by biffImage text-base: 0x40008970, data-base: 0x40BF6000ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 12.1(20010705:000010) [biff-ws28 124], RELEASED SOFTWAREROM: 7300 Software (C7300-BOOT-M), Version 12.1(9), CISCO RELEASED VERSIONRouter uptime is 18 minutesSystem returned to ROM by power-onSystem image file is "disk0:c7300-js-mz.121-99.WS_DAILY_BUILD_20010706"cisco 7300 (NSE100) processor (revision A) with 114688K/16384K bytes of memory.Processor board IDR7000 CPU at 350Mhz, Implementation 39, Rev 3.2, 256KB L2, 1024KB L3 Cache4 slot midplane, Version 65.48Last reset from watchdog nmiX.25 software, Version 3.0.0.PXF processor tmc0 is running.PXF processor tmc1 is running.1 FastEthernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)2 Gigabit Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)509K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.16064K bytes of ATA compact flash disk at bootdisk (Sector size 512 bytes).64000K bytes of ATA compact flash disk at disk 0 (Sector size 512 bytes).Configuration register is 0x2102
9 After Installation
For installation and configuration information and specifications for field-replaceable units (FRUs) such as the network processing engine or network services engine, power supply, SODIMMs, GBICs and SFP modules, CompactFlash Disks, see the online Cisco 7304 Installation and Configuration Guide, the Cisco 7304 Network Services Engine Installation and Configuration, and the Cisco 7304 Network Processing Engine Installation and Configuration documentation.
For information on line cards, carrier card, port adapter, modular services card, and shared port adapters, see the Cisco 7304 Router Line Card, Carrier Card, Port Adapter, Modular Services Card, and Shared Port Adapter Documentation Roadmap document.
Note
If you have difficulty installing a processing engine in the lowest slot of a Cisco 7304 router that is rack-mounted, remove the line cards, port adapter carrier cards, modular services cards, and processing engines from the chassis and reinstall them. Install a processing engine in the lowest slot first, then populate the slots above it, in a bottom-to-top order.
10 Obtain Technical Assistance
Cisco Technical Support provides 24-hour-a-day award-winning technical assistance. The Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website on Cisco.com features extensive online support resources. In addition, if you have a valid Cisco service contract, Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) engineers provide telephone support. If you do not have a valid Cisco service contract, contact your reseller.
Cisco Technical Support & Documentation Website
The Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website provides online documents and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. The website is available 24 hours a day, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Access to all tools on the Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. If you have a valid service contract but do not have a user ID or password, you can register at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Note
Use the Cisco Product Identification (CPI) tool to locate your product serial number before submitting a web or phone request for service. You can access the CPI tool from the Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website by clicking the Tools & Resources link under Documentation & Tools. Choose Cisco Product Identification Tool from the Alphabetical Index drop-down list, or click the Cisco Product Identification Tool link under Alerts & RMAs. The CPI tool offers three search options: by product ID or model name; by tree view; or for certain products, by copying and pasting show command output. Search results show an illustration of your product with the serial number label location highlighted. Locate the serial number label on your product and record the information before placing a service call.
Submitting a Service Request
Using the online TAC Service Request Tool is the fastest way to open S3 and S4 service requests. (S3 and S4 service requests are those in which your network is minimally impaired or for which you require product information.) After you describe your situation, the TAC Service Request Tool provides recommended solutions. If your issue is not resolved using the recommended resources, your service request is assigned to a Cisco engineer. The TAC Service Request Tool is located at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/servicerequest
For S1 or S2 service requests, or if you do not have Internet access, contact the Cisco TAC by telephone. (S1 or S2 service requests are those in which your production network is down or severely degraded.) Cisco engineers are assigned immediately to S1 and S2 service requests to help keep your business operations running smoothly.
To open a service request by telephone, use one of the following numbers:
Asia-Pacific: +61 2 8446 7411 (Australia: 1 800 805 227)
EMEA: +32 2 704 55 55
USA: 1 800 553-2447For a complete list of Cisco TAC contacts, go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/contacts