-
User Guide for Cisco Prime Access Registrar 6.0
-
Preface
-
Chapter 1 Overview
-
Chapter 2 Using the aregcmd Commands
-
Chapter 3 Using the Graphical User Interface
-
Chapter 4 Cisco Prime Access Registrar Server Objects
-
Chapter 5 Using the radclient Command
-
Chapter 6 Configuring Local Authentication and Authorization
-
Chapter 7 RADIUS Accounting
-
Chapter 8 Diameter
-
Chapter 9 Extensible Authentication Protocols
-
Chapter 10 Using WiMAX in Cisco Prime Access Registrar
-
Chapter 11 Using Extension Points
-
Chapter 12 Using Replication
-
Chapter 13 Using On-Demand Address Pools
-
Chapter 14 Using Identity Caching
-
Chapter 15 Using Trusted ID Authorization with SESM
-
Chapter 16 Using Prepaid Billing
-
Chapter 17 Using Cisco Prime Access Registrar Server Features
-
Chapter 18 Directing RADIUS Requests
-
Chapter 19 Wireless Support
-
Chapter 20 Using LDAP
-
Chapter 21 Using Open Database Connectivity
-
Chapter 22 SIGTRAN-M3UA
-
Chapter 23 Using SNMP
-
Chapter 24 Enforcement of Licensing Models
-
Chapter 25 Backing Up the Database
-
Chapter 26 Using the REX Accounting Script
-
Chapter 27 Logging Syslog Messages
-
Chapter 28 Troubleshooting Cisco Prime Access Registrar
-
Appendix A: Cisco Prime Access Registrar Tcl, REX and Java Dictionaries
-
Appendix B: Environment Dictionary
-
Appendix C: RADIUS Attributes
-
Glossary
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring EAP-AKA/EAP-SIM with SIGTRAN-M3UA
SIGTRAN-M3UA
SIGTRAN, a working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), has defined a protocol for the transport of real-time signaling data over IP networks. Cisco Prime AR supports SS7 messaging over IP (SS7oIP) via SIGTRAN-M3UA, a new transport layer which leverages Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP). Cisco Prime AR supports SIGTRAN-M3UA to fetch the authentication vectors from HLR, which is required for EAP-AKA/EAP-SIM authentication.
Note
You have SIGTRAN-M3UA interface support in addition to the existing SUA interface support.
The EAP-AKA and EAP-SIM authentication service is extended to use M3UA. When using M3UA service for authentication, the subscriber identity (IMSI) is used to send a request to HLR and receives information from HLR containing the authentication information for authenticating an user. The authentication service initiates a request to the SIGTRAN server using IMSI, which retrieves the configured number of authentication vectors from HLR, i.e Triplets or Quintets.
Note
When you install SIGTRAN-M3UA remote server for the first time or update the existing installation, you need to update the ip address of Cisco Prime AR where it is been installed in network.data and cli_client.conf files. Also, you must restart Cisco Prime AR to have the changes reflected.
If the LocalSubSystemNumber is not set as SGSN(149), you need to make the same change in the default.xml file, located at /cisco-ar/m3ua-cfg/.
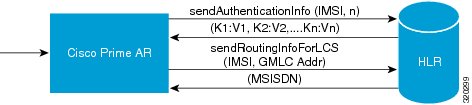
Figure 22-1 MAP Service
The Cisco Prime AR server initiates the MAP service. After enabling the MAP service, the Cisco Prime AR server sends a sendAuthenticationInfo request that contains IMSI and the number of requested authentication vectors to HLR. The HLR sends a response containing the requested vectors information to Cisco Prime AR. Next, the Cisco Prime AR server sends a sendRoutinginfoForLCS request that contains IMSI and the GMLC address to HLR. The HLR sends a response containing the MSISDN information for authenticating the mobile subscribers.
Note
Cisco Prime AR 6.0 supports only one remote server with the protocol type, SIGTRAN-M3UA.
This section describes the following:
•
Prerequisites to SIGTRAN-M3UA
•
Configuring EAP-AKA/EAP-SIM with SIGTRAN-M3UA
Prerequisites to SIGTRAN-M3UA
Before enabling the SIGTRAN-M3UA remote server, you must do the following:
•
ensure that LKSCTP is not available in the Cisco Prime AR server.
•
ensure to restart the Cisco Prime AR server whenever you make any configuration changes.
•
ensure that the following rpm files are not installed while installing the Cisco Prime AR in RHEL 6.2:
–
nss-softokn-freebl-3.12.9-11.el6.i686.rpm
–
glibc-2.12-1.47.el6.i686.rpm
–
ncurses-libs-5.7-3.20090208.el6.i686.rpm
–
ncurses-devel-5.7-3.20090208.el6.i686.rpm
–
ncurses-5.7-3.20090208.el6.i686.rpm
–
nspr-4.8.8-3.el6.i686.rpm
–
nss-util-3.12.10-2.el6.i686.rpm
•
ensure that the following rpm files are installed while installing the Cisco Prime AR in RHEL 6.2:
–
nss-softokn-freebl-3.12.9-11.el6.i686.rpm
–
glibc-2.12-1.47.el6.i686.rpm
–
ncurses-libs-5.7-3.20090208.el6.i686.rpm
–
ncurses-devel-5.7-3.20090208.el6.i686.rpm
–
ncurses-5.7-3.20090208.el6.i686.rpm
–
nspr-4.8.8-3.el6.i686.rpm
–
nss-util-3.12.10-2.el6.i686.rpm
–
gamin-0.1.10-9.el6.i686.rpm
–
libselinux-2.0.94-5.2.el6.i686.rpm
–
glib2-2.22.5-6.el6.i686.rpm
–
zlib-1.2.3-27.el6.i686.rpm
–
libxml2-2.7.6-4.el6.i686.rpm
–
gdome2-0.8.1-1.i386.rpm
–
glib-1.2.10-33.el6.i686.rpm
–
libgcc-4.4.6-3.el6.i686.rpm
–
libstdc++-4.4.6-3.el6.i686.rpm
Note
You must install the rpm verions relevant to the RHEL OS versions while installing the Cisco Prime AR.
Configuring EAP-AKA/EAP-SIM with SIGTRAN-M3UA
You can use aregcmd to create and configure the service of type eap-aka or eap-sim, see EAP-AKA or EAP-SIM for more information.
To configure EAP-AKA service with SIGTRAN-M3UA remote server:
Step 1
Launch aregcmd.
Step 2
Create an EAP-AKA service.
cd /Radius/Services
add eap-aka-service
Step 3
Set type as eap-aka.
set eap-aka
Step 4
Add m3ua remote server in the remoteServers
cd remoteServers/
Set 1 m3ua
The following shows an example configuration for EAP-AKA service with SIGTRAN-M3UA remote server support, see Table 9-1 to know more about EAP-AKA service properties.
[ //localhost/Radius/Services ]Entries 1 to 2 from 2 total entriesCurrent filter: <all>eap-aka/Name = eap-akaDescription =Type = eap-akaAlwaysRequestIdentity = FalseEnableIdentityPrivacy = FalsePseudonymSecret = <encrypted>PseudonymRenewtime = "24 Hours"PseudonymLifetime = ForeverGenerate3GPPCompliantPseudonym = FalseEnableReauthentication = FalseMaximumReauthentications = 16ReauthenticationTimeout = 3600ReauthenticationRealm =AuthenticationTimeout = 120QuintetGenerationScript~ =UseProtectedResults = FalseSendReAuthIDInAccept = FalseSubscriber_DBLookup = siGTRAN-m3UAFetchAuthorizationInfo = FALSEMultipleServersPolicy = FailoverIncomingScript~ =OutgoingScript~ =OutageScript~ =RemoteServers/To configure EAP-SIM service with SIGTRAN-M3UA remote server:
Step 1
Launch aregcmd.
Step 2
Create an EAP-SIM service.
cd /Radius/Services
add eap-sim-service
Step 3
Set type as eap-sim.
set eap-sim
Step 4
Add m3ua remote server in the remoteServers
cd remoteServers
Set 1 m3ua
The following shows an example configuration for EAP-SIM service with SIGTRAN-M3UA remote server support, see Table 9-6 to know more about EAP-SIM service properties.
eap-sim/Name = eap-simDescription =Type = eap-simNumberOfTriplets = 2UseSimDemoTriplets = FalseAlwaysRequestIdentity = FalseEnableIdentityPrivacy = FalsePseudonymSecret = <encrypted>PseudonymRenewtime = "24 Hours"PseudonymLifetime = ForeverGenerate3GPPCompliantPseudonym = FalseEnableReauthentication = FalseMaximumReauthentications = 16ReauthenticationTimeout = 3600ReauthenticationRealm =TripletCacheTimeout = 0AuthenticationTimeout = 120UseProtectedResults = FalseSendReAuthIDInAccept = FalseSubscriberDBLookup = SiGTRAN-M3UAFetchAuthorizationInfo = FALSEMultipleServersPolicy = FailoverIncomingScript~ =OutgoingScript~ =OutageScript~ =RemoteServers/
Note
Before enabling the SIGTRAN-M3UA remote server, you must ensure to restart the Cisco Prime AR server whenever you make any configuration changes.
Note
If you set FetchAuthorizationInfo as TRUE for EAP-AKA or EAP-SIM service for SIGTRAN-M3UA in Cisco Prime AR, it fetches the MSISDN information from HLR in response. The following is an example script for reading the MSISDN information from the response,
proc MapMSISDN {request response environ} {
$environ get AuthorizationInfo
}
You can configure the SIGTRAN-M3UA remoteserver under /Radius/RemoteServers.
To configure the SIGTRAN-M3UA remote server:
Step 1
Launch aregcmd.
Step 2
Create sigtran-m3ua remote server.
cd /r/remoteServers/
add M3UA
cd M3UA
set protocol sigtran-m3ua
Step 3
Set the Subscriber_DBLookup.
set Subscriber_DBLookup SIGTRAN-M3UA
Step 4
Set the hostname and port of the HLR.
set hostName 10.81.78.140
set DestinationPort 2905
Step 5
Set the IP address and port for the source.
set SourceIPAddress 10.81.78.142
set SourcePort 2905
Step 6
Set the reactivatetimerinterval.
Step 7
Set the subsystem number for the local.
set LocalSubSystemNumber 149
Step 8
Set routingindicator.
Set routingindicator rte_gt
Step 9
Set mlcnumber.
Set mlcnumber
Step 10
Set routingparameters.
cd routingparameters/
set OriginPointCode 2
set DestinationPointCode 4
set RemoteSubSystemNumber 6
set OPCMask 16383
set DPCMask 16383
set RoutingContext 11
Step 11
Set the source and destination gt parameters.
Step 12
Set the numbering plan, encoding scheme, format, and digits for source.
Step 13
Set the numbering plan, encoding scheme, format, and digits for destination.
The following shows an example configuration of SIGTRAN-M3UA remote server support:
[ //localhost/Radius/RemoteServers/m3ua ]Name = m3uaDescription =Protocol = sigtran-m3ua)HostName = 10.81.78.138SourceIPAddress = 10.81.78.139SourcePort = 2905LocalSubSystemNumber = 149DestinationPort = 2905IMSITranslationScript~ =GlobalTitleTranslationScript~ = setGTTimeout = 15ReactivateTimerInterval = 2000LimitOutstandingRequests = FALSEMaxOutstandingRequests = 0MaxRetries = 3MAPVersion = 2NetworkVariant = ITUSubServiceField = NATTCAPVariant = ITU96NetworkAppearance = 1NetworkIndicator = NATMLCNumber = 123456789012345TrafficMode = LOADSHARELoadShareMode = SLSRoutingIndicator = RTE_GTRoutingParameters/OriginPointCode = 2DestinationPointCode = 4RemoteSubSystemNumber = 6OPCMask = 16383DPCMask = 16383ServiceIndicatorOctet = 0RoutingContext = 11SourceGTAddress/SourceGTDigits = 919845071842SourceGTFormat = GTFRMT_4SourceNatureofAddress = INTNUMSourceTranslationType = 0SourceNumberingPlan = ISDNSourceEncodingScheme = BCDEVENDestinationGTAddress/DestGTDigits = 919845071842DestGTFormat = GTFRMT_4DestNatureofAddress = INTNUMDestTranslationType = 0DestNumberingPlan = ISDNDestEncodingScheme = BCDEVENTable 22-1 describes SIGTRAN-M3UA remote server properties.
Configuring M3UA Service
Cisco Prime AR supports the M3UA service, which is used to fetch MSISDN from IMSI through RADIUS Packets, see Chapter 4 "Cisco Prime Access Registrar Server Objects," for more information.
To configure the M3UA service with SIGTRAN-M3UA remote server:
Step 1
Launch aregcmd.
Step 2
Create an M3UA service.
cd /Radius/Services
add FetchMSISDN
Step 3
Set the type as M3UA.
set type M3UA
Step 4
Add M3UA remote server in the remoteServers.
cd remoteServers
Set 1 m3ua

 Feedback
Feedback