-
Cisco IP Solution Center Infrastructure Reference, 4.1
-
Index
-
About This Guide
-
Getting Started
-
WatchDog Commands
-
Service Inventory - Inventory and Connection Manager
-
Service Inventory - Discovery
-
Service Inventory - Device Console
-
Service Design
-
Monitoring
-
Diagnostics
-
Administration
-
ISC XML Reference
-
Cisco CNS IE2100 Appliances
-
Property Settings
-
Glossary
-
Table Of Contents
View Templates Tree and Data Pane
Summary of Repository Variables
Service Design
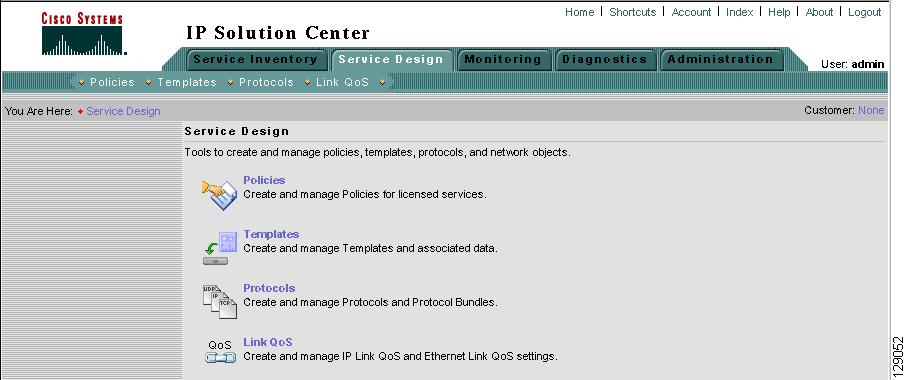
From the Home window of Cisco IP Solution Center (ISC), you receive upon logging in, click the Service Design tab and you receive a window as shown in Figure 6-1, "Service Design Selections."
Figure 6-1 Service Design Selections
Next you can navigate to the following selections:
•
Policies Create and manage Policies for licensed services.
•
Templates Create and manage Templates and associated data.
•
Link QoS Create and manage IP Link QoS and Ethernet Link QoS settings.
Policies
Policies is explained in each of the User Guides for each of the licensed services.
Templates
Templates supports the browsing, creation, and deletion of Template Folders, Templates, and Data Files and it supports the viewing of Template-generated configurations. The configuration created from the template and data file can be downloaded to devices. When creating a Service Request, you can select from the list of templates and data files and associate them with the Service Request. At Deploy time, the template and data file are instantiated and the configuration is appended or prepended to the configlet generated by ISC.
ISC provides a way to integrate a template with ISC configlets.
For a given customer edge router and/or provider edge router, you specify the following:
•
template name
•
template data file name
•
whether the template configuration file should be appended or prepended to the ISC configlet
•
whether the template configuration file is active or inactive for downloading to the edge device
The template data files are tightly linked with the corresponding template. You can use a data file and its associated template to create a template configuration file. The template configuration file is merged with (either appended or prepended to) the ISC configlet. ISC downloads the combined ISC configlet and template configuration file to the edge device router.
•
You can download a template configuration file to a router.
•
You can apply the same template to multiple edge routers, assigning the appropriate template data file for each device. Each template data file includes the specific data for a particular device (for example, the management IP address or host name of each device).
To use Templates, follow these steps:
Step 1
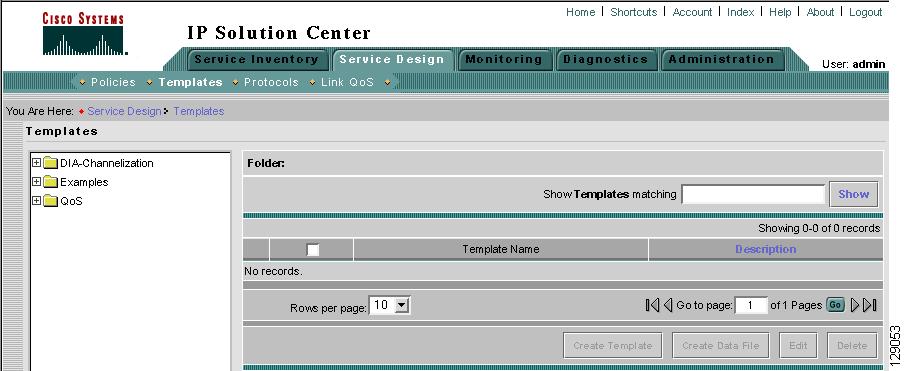
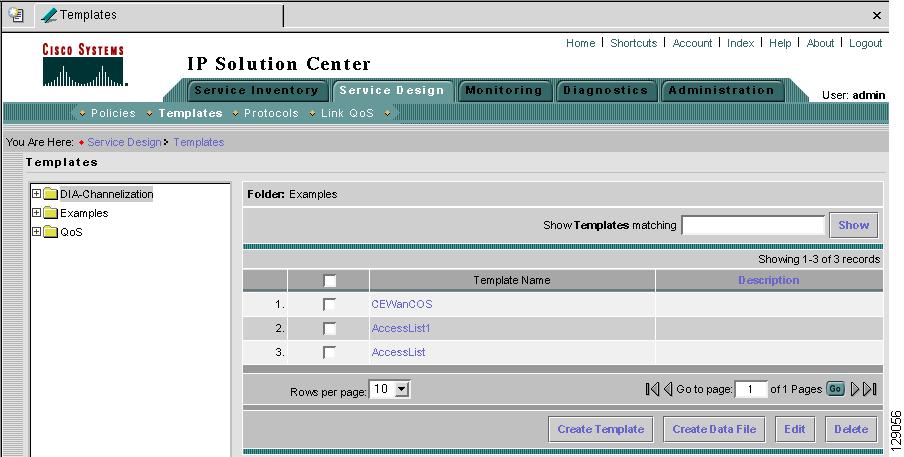
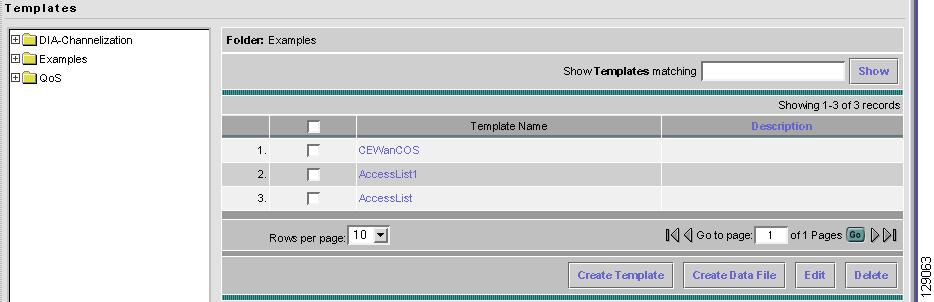
Navigate to Service Design > Templates and you receive a window as shown in Figure 6-2, "Templates."
Figure 6-2 Templates
Template examples are shown in the left column. A complete list of template examples is specified in the "Template Examples" section. A complete list of Repository variables is shown in the "Summary of Repository Variables" section.
Step 2
Then you can do any of the following:
•
View Templates Tree and Data Pane
•
Create Folders and Subfolders
•
Edit
View Templates Tree and Data Pane
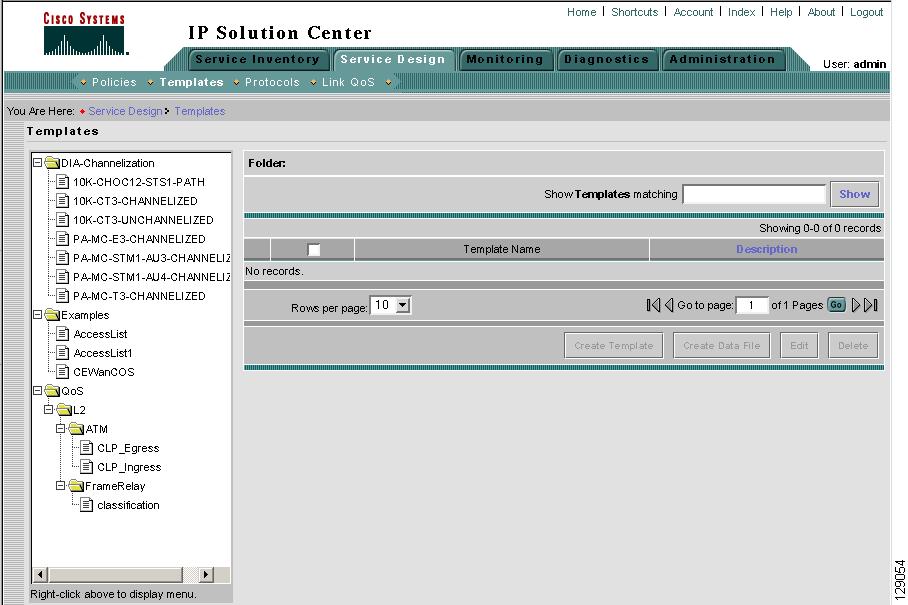
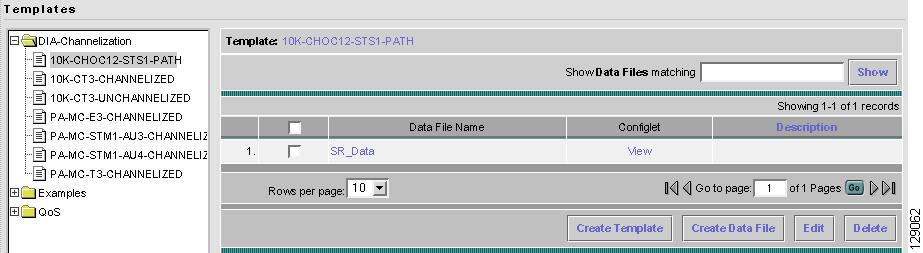
When you navigate to Service Design > Templates, you receive a window as shown in Figure 6-3, "Tree and Data Pane Structure."
The Templates tree is in the left column. You can continue clicking the + sign next to each created folder and subfolder until you get to the last level of information. The last possible level is the template name. Data file information is not kept in the tree.
The right section of the window is the data pane. The name of the folder or template is in the upper-left corner. When you select the check box next to the template or data file information, the Create Template, Create Data File, Edit, or Delete buttons are enabled as described in the following sections.
When there are many templates in a folder or many data files in a template, the Show Template Matching or Show Data File Matching filter in the upper right-hand corner of the data pane can be very useful. For example, you might just want to work with templates or data files that start with abc. In this case, enter abc* in the field and then click the Show button. Only the templates or data files that start with abc appear.
You can also View configurations when the table displays data files.
Figure 6-3 Tree and Data Pane Structure
Create Folders and Subfolders
To create a new folder or subfolder, follow these steps:
Step 1
Navigate to Service Design > Templates.
Step 2
In the Templates tree, right-click in the white area and select New > Folder to create a new folder or right-click on an existing folder or subfolder and select New > Folder to create a subfolder.
Note
There is no limit to the number of levels of folders and subfolders you can create.
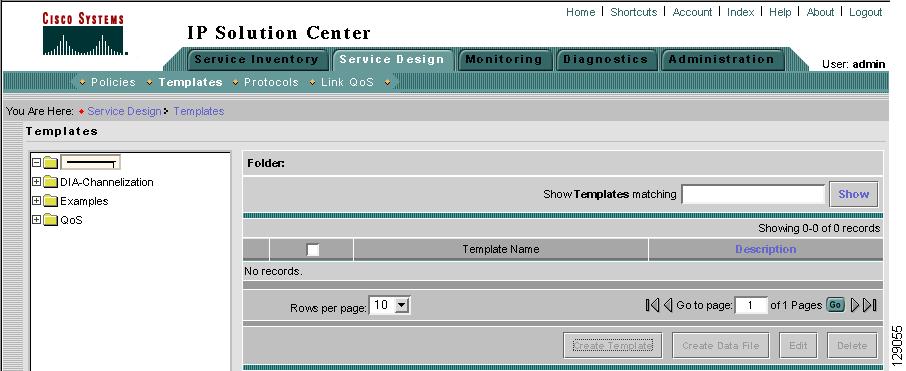
Step 3
In the new text field that appears in the Templates tree, type the new folder or subfolder name, as shown in the first entry of the Templates tree in Figure 6-4, "Folder Naming."
Figure 6-4 Folder Naming
Copying Folders or Subfolders
To copy a folder or subfolder and paste it into another folder or subfolder, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select a folder or subfolder and then right-click and you receive the opportunity to copy. Click Copy.
Step 2
Right-click on the folder or subfolder into which you want to paste the copied folder or subfolder and all its content and click Paste.
Step 3
You will see the new folder or subfolder and all its content in the selected location. You can edit and rename from there.
Note
This function works with Internet Explorer but not with Netscape.
Create Template
You can either create a new template in an existing folder or you can create a new folder first and then create the template. To create a new folder, see the section "Create Folders and Subfolders".
To create a new template, follow these steps:
Step 1
Navigate to Service Design > Templates.
Step 2
In the Templates tree, click on the folder in which you want to create a new template.
Step 3
A window appears as shown in Figure 6-5, "Folder with Existing Templates."
Figure 6-5 Folder with Existing Templates
Step 4
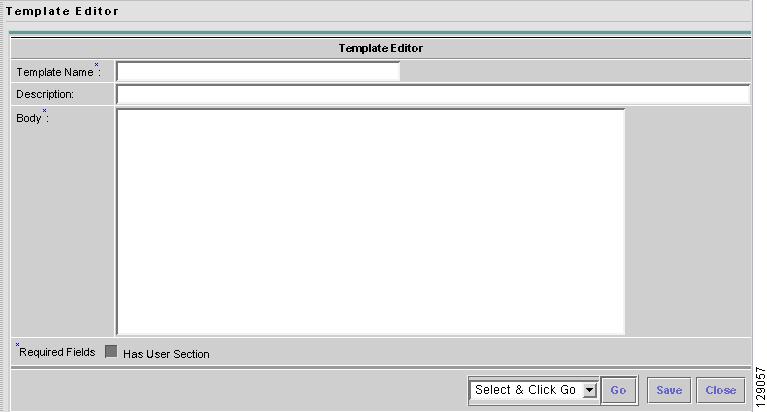
Click the Create Template button and you receive a window as shown in Figure 6-6, "Template Editor."
Figure 6-6 Template Editor
Step 5
Enter the following:
•
Template Name (required) This must be a unique name within a folder. This name must begin with an alphabetic character and can only contain alphanumeric characters, underscores, and hyphens.
•
Description (optional) You can enter any description here.
•
Body (required) Enter the configuration text, Velocity template language directives, and variables that you want included.
Note
The Velocity template language is explained at http://jakarta.apache.org/velocity/user-guide.html.
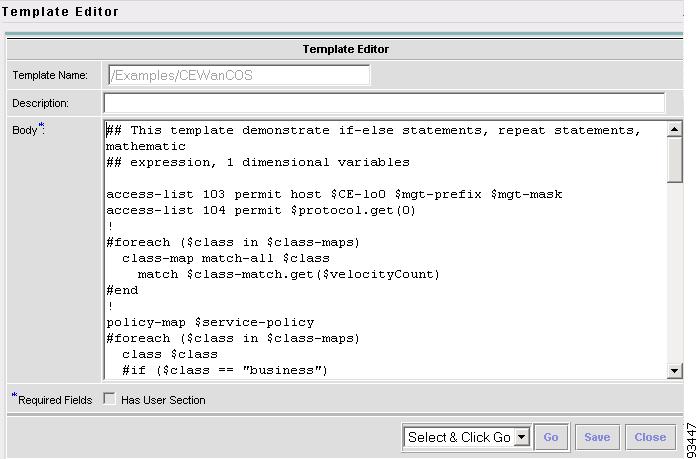
An example template is shown in Figure 6-7, "Example Template."
Figure 6-7 Example Template
ISC has the template system predefined variable $TMSystem that can be used within the template body text to access template system functions. The syntax is as follows, where, $ipAddrMask is a string that contains an IP address and its mask in the format of: 10.33.4.5/30:
$TMSystem.getAddr ($ipAddrMask) returns: 10.33.4.5
$TMSystem.getMask ($ipAddrMask) returns: 255.255.255.252
$TMSystem.getReverseMask ($ipAddrMask) returns: 0.0.0.3
$TMSystem.getNetworkAddr ($ipAddrMask) returns: 10.33.4.4
$TMSystem.getClassfulNetworkAddr ($ipAddrMask) returns: 10.0.0.0
Step 6
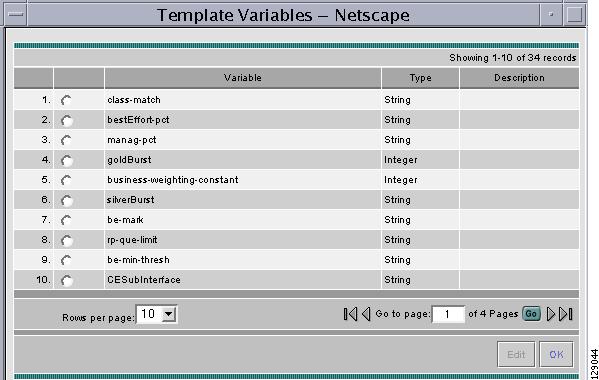
Click the Select & Click Go drop-down list. If you want to validate the information you entered in Step 5, select Validate and then click the Go button. Otherwise, select Variables and then click the Go button and you receive a window as in Figure 6-8, Template Variables".
Figure 6-8 Template Variables
Step 7
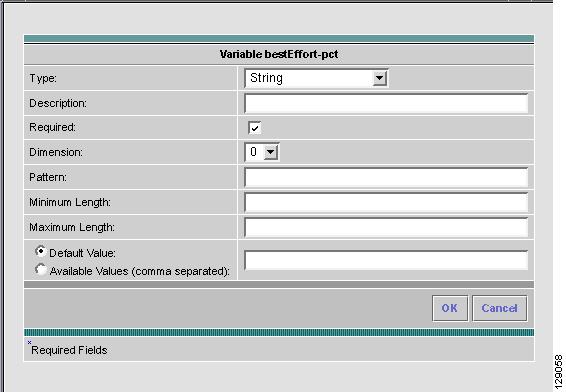
Click the radio button for the Variable you want to edit and click Edit. You receive a window as in Figure 6-9, "Variable Definition—Type String."
Figure 6-9 Variable Definition—Type String
Step 8
In Figure 6-9, click the drop-down list for Type to receive the following choices:
•
String Proceed to Step 9.
•
Integer Proceed to Step 10.
•
Float Proceed to Step 11.
•
IPv4 Address Proceed to Step 12.
•
Sub-Template Proceed to Step 13.
•
Dynamic Java Class Proceed to Step 14.
•
Dynamic URL Proceed to Step 15.
Step 9
The default Type to appear is String, a combination of ASCII characters considered as a group. The resulting Variable window is shown in Figure 6-9 and its attributes are as follows:
•
Description (optional) You can enter any descriptive statement about this variable here.
•
Required Leave the default of the selected check box if this variable is required. Otherwise, deselect it.
•
Dimension Choose 0 (default), which indicates a scalar or enum variable; choose 1, in which case the variable becomes a one-dimensional array; or choose 2, in which case the variable becomes a two-dimensional array.
•
Pattern (optional) Specify a regular expression pattern of the string. For example, a pattern of isc[0-9]+ defines a string that starts with isc followed by one or more digits from 0 to 9.
•
Minimum Length (optional) If you specify a minimum length, the string cannot be less than the length specified here.
•
Maximum Length (optional) If you specify a maximum length, the string cannot exceed the length specified here.
•
Radio Button: Default (optional) If there is a default value for the specified variable, specify it here.
•
Radio Button: Available Values (optional) Enter string values for this variable. Separate the values by commas.
After you enter all the data, click OK to accept this information for the specified variable; continue editing all variables you want to change in this same way, then click OK in a window such as Figure 6-8, which now includes these updated variables; click Save and then Close or click Close and when asked, agree to Save for a window such as Figure 6-6. Create a Data File is shown in the "Create Data File" section, Edit is shown in the "Edit" section, and Delete is shown in the "Delete" section.
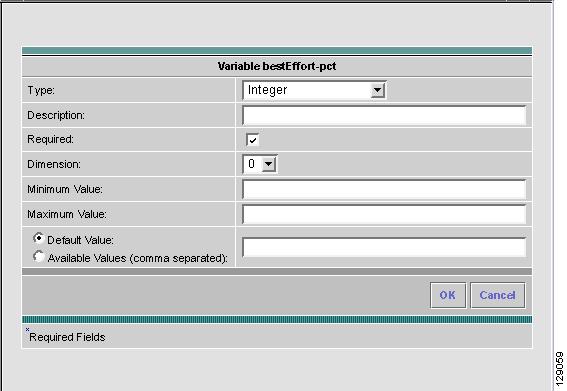
Step 10
When you choose the Type Integer, a whole number, the resulting Variable window is shown in Figure 6-10 and its attributes are as follows:
•
Description (optional) You can enter any descriptive statement about this variable here.
•
Required Leave the default of the selected check box if this variable is required. Otherwise, deselect it.
•
Dimension Choose 0 (default), which indicates a scalar or enum variable; choose 1, in which case the variable becomes a one-dimensional array; or choose 2, in which case the variable becomes a two-dimensional array.
•
Minimum Value (optional) If you specify a minimum value, the integer cannot be less than the value specified here.
•
Maximum Value (optional) If you specify a maximum value, the integer cannot exceed the value specified here.
•
Radio Button: Default (optional) If there is a default value for the specified variable, specify it here.
•
Radio Button: Available Values (optional) Enter string values for this variable. Separate the values by commas.
After you enter all the data, click OK to accept this information for the specified variable; continue editing all variables you want to change in this same way, then click OK in a window such as Figure 6-8, which now includes these updated variables; click Save and then Close or click Close and when asked, agree to Save for a window such as Figure 6-6. Create a Data File is shown in the "Create Data File" section, Edit is shown in the "Edit" section, and Delete is shown in the "Delete" section.
Figure 6-10 Variable Definition—Type Integer
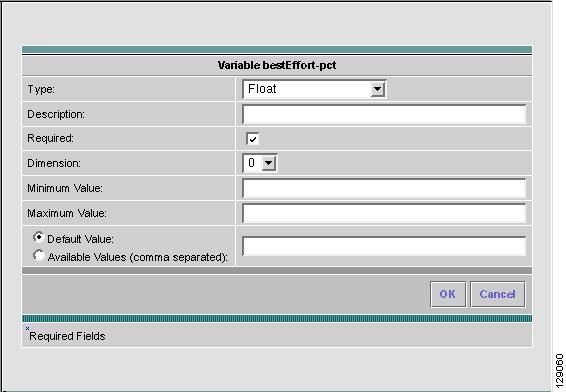
Step 11
When you choose the Type Float, a number that has no fixed number of digits before or after the decimal point, the resulting Variable window is shown in Figure 6-11 and its attributes are as follows:
•
Description (optional) You can enter any descriptive statement about this variable here.
•
Required Leave the default of the selected check box if this variable is required. Otherwise, deselect it.
•
Dimension Choose 0 (default), which indicates a scalar or enum variable; choose 1, in which case the variable becomes a one-dimensional array; or choose 2, in which case the variable becomes a two-dimensional array.
•
Minimum Value (optional) If you specify a minimum value, the floating point value cannot be less than the value specified here.
•
Maximum Value (optional) If you specify a maximum value, the floating point value cannot exceed the value specified here.
•
Radio Button: Default (optional) If there is a default value for the specified variable, specify it here.
•
Radio Button: Available Values (optional) Enter string values for this variable. Separate the values by commas.
After you enter all the data, click OK to accept this information for the specified variable; continue editing all variables you want to change in this same way, then click OK in a window such as Figure 6-8, which now includes these updated variables; click Save and then Close or click Close and when asked, agree to Save for a window such as Figure 6-6. Create a Data File is shown in the "Create Data File" section, Edit is shown in the "Edit" section, and Delete is shown in the "Delete" section.
Figure 6-11 Variable Definition—Type Float
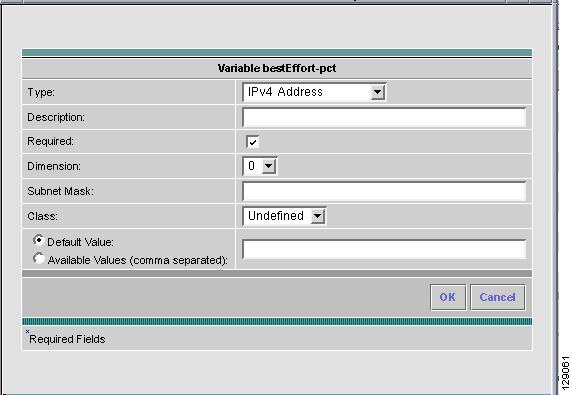
Step 12
When you choose the Type IPv4 Address, the resulting Variable window is shown in Figure 6-12 and its attributes are as follows:
•
Description (optional) You can enter any descriptive statement about this variable here.
•
Required Leave the default of the selected check box if this variable is required. Otherwise, deselect it.
•
Dimension Choose 0 (default), which indicates a scalar or enum variable; choose 1, in which case the variable becomes a one-dimensional array; or choose 2, in which case the variable becomes a two-dimensional array.
•
Subnet Mask (optional) Enter a valid subnet mask.
•
Class (optional) Enter the class of the IP address. The options are: Undefined, A, B, or C.
•
Radio Button: Default (optional) If there is a default value for the specified variable, specify it here.
•
Radio Button: Available Values (optional) Enter string values for this variable. Separate the values by commas.
After you enter all the data, click OK to accept this information for the specified variable; continue editing all variables you want to change in this same way, then click OK in a window such as Figure 6-8, which now includes these updated variables; click Save and then Close or click Close and when asked, agree to Save for a window such as Figure 6-6. Create a Data File is shown in the "Create Data File" section, Edit is shown in the "Edit" section, and Delete is shown in the "Delete" section.
Figure 6-12 Variable Definition—Type IPv4
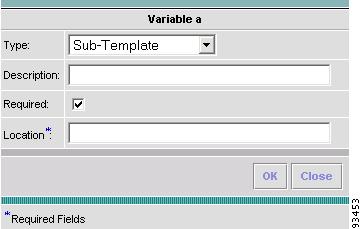
Step 13
When you choose the Type Sub-Template, you instantiate one subtemplate into the Main template. The resulting Variable window is shown in Figure 6-13 and its attributes are as follows:
•
Description (optional) You can enter any descriptive statement about this variable here.
•
Required Leave the default of the selected check box if this variable is required. Otherwise, deselect it.
•
Location (required) Enter the full path name of the parent template. For example /test2/testyy.
The variable varName is defined as the subtemplate type (by selecting Variables and clicking Go). The Sub-Template defined earlier is called and you must provide the subtemplate path. The syntax is as follows:
$<varName>.callWithDatafile (<DatafileName>)
After you enter all the data, click OK to accept this information for the specified variable; continue editing all variables you want to change in this same way, then click OK in a window such as Figure 6-8, which now includes these updated variables; click Save and then Close or click Close and when asked, agree to Save for a window such as Figure 6-6. Create a Data File is shown in the "Create Data File" section, Edit is shown in the "Edit" section, and Delete is shown in the "Delete" section.
Figure 6-13 Variable Definition—Type Sub-Template
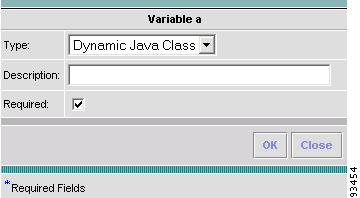
Step 14
When you choose the Type Dynamic Java Class, the resulting Variable window is shown in Figure 6-14 and its attributes are as follows:
•
Description (optional) You can enter any descriptive statement about this variable here.
•
Required Leave the default of the selected check box if this variable is required. Otherwise, deselect it.
The variable varName is defined as the Dynamic Java Class type (by selecting Variables and clicking Go). The syntax is as follows:
$<varName>.<method_name_in_Java_class> ([<parameters>])
After you enter all the data, click OK to accept this information for the specified variable; continue editing all variables you want to change in this same way, then click OK in a window such as Figure 6-8, which now includes these updated variables; click Save and then Close or click Close and when asked, agree to Save for a window such as Figure 6-6. Create a Data File is shown in the "Create Data File" section, Edit is shown in the "Edit" section, and Delete is shown in the "Delete" section.
Figure 6-14 Variable Definition—Type Dynamic Java Class
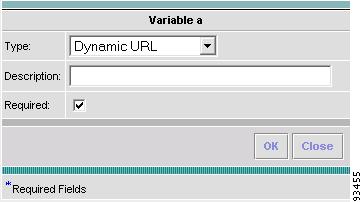
Step 15
When you choose the Type Dynamic URL, the resulting Variable window is shown in Figure 6-15 and its attributes are as follows:
•
Description (optional) You can enter any descriptive statement about this variable here.
•
Required Leave the default of the selected check box if this variable is required. Otherwise, deselect it.
The variable varName is defined as the Dynamic URL type (by selecting Variables and clicking Go). The syntax is as follows:
$<varName>.callURL (<url-address>)
After you enter all the data, click OK to accept this information for the specified variable; continue editing all variables you want to change in this same way, then click OK in a window such as Figure 6-8, which now includes these updated variables; click Save and then Close or click Close and when asked, agree to Save for a window such as Figure 6-6. Create a Data File is shown in the "Create Data File" section, Edit is shown in the "Edit" section, and Delete is shown in the "Delete" section.
Figure 6-15 Variable Definition—Type Dynamic URL
Copying Templates
To copy a template and paste it into another folder, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select a template and then right-click and you receive the opportunity to copy. Click Copy.
Step 2
Right-click on the folder into which you want to paste the copied template and all its data files and click Paste.
Step 3
You will see the new template and all its data files in the selected location. You can edit and rename from there.
Note
This function works with Internet Explorer but not with Netscape.
Create Data File
You can create a new data file from an existing template. If the template you want is not available, go to the "Create Template" section.
To create a data file, follow these steps:
Step 1
Navigate to Service Design > Templates.
Step 2
In the Templates tree in the left part of your window, do one of the following
1.
Left-click on the folder or subfolder in which the template for which you want to create a data file exists or
2.
Click on the + next to the folder of choice and then click on the template for which you want to create a data file.
Step 3
If you chose 1. in Step 2, a window appears as shown in Figure 6-16, "Choose Existing Template > Create Data File."
Figure 6-16 Choose Existing Template > Create Data File
Select the check box for the template for which you want to create a data file and click Create Data File. Then proceed to Step 5.
Otherwise, proceed to Step 4.
Step 4
If you chose 2. in Step 2, the buttons appear as shown in Figure 6-17, "Choose Existing Template > Create Data File."
Figure 6-17 Choose Existing Template > Create Data File
Click Create Data File and proceed to Step 5.
Step 5
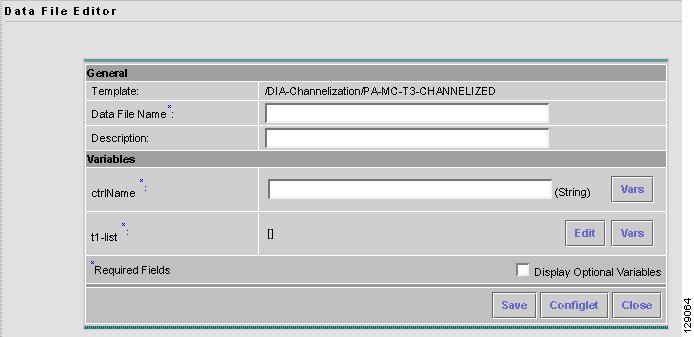
An example of a window that appears is shown in Figure 6-18, "Template Data File Editor."
Figure 6-18 Template Data File Editor
Step 6
In the General area, fill in the following:
•
Data File Name (required) This must be a unique name. This name must begin with an alphabetic character and can only contain alphanumeric characters and the underscore.
•
Description (optional) Enter any description that helps you identify this data file.
Step 7
In the example in Figure 6-18, in the Variables area, cntrlName is a string variable (Dimension defined when the template was created was 0); you can also create a one-dimensional array (Dimension defined when the template was created was 1); and t1-list is a two-dimensional array (Dimension defined when the template was created was 2).
If t1-list is a Dynamic Java Class variable, you must enter the entire Java Class package name. For example: com.cisco.isc.class_name.
Step 8
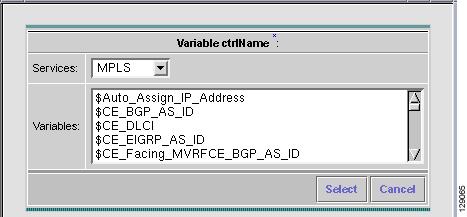
If you click Vars as shown in Figure 6-18, you receive a window as shown in Figure 6-19, "Template Data File Editor."
Figure 6-19 Template Data File Editor
Click the Services drop-down list to have access to variables for:
•
MPLS
•
L2VPN
•
QoS
•
VPLS
Then click the entry in Variables that you want to use and click Select.
If you have a 0 dimensional entry (set as Dimension 0 when creating a template), you can only enter variables in the provided field.
Step 9
When you click Edit., as shown in Figure 6-18, the resulting window depends on whether you are editing a 1 or 2 dimensional array.
Proceed to Step 10 for information about a 1 dimensional array.
Proceed to Step 13 for information about a 2 dimensional array.
Step 10
For a one-dimensional array (set as Dimension 1 when creating the template), when you click Edit, you receive a window as shown in Figure 6-20, "Editing a One-Dimensional Array."
Figure 6-20 Editing a One-Dimensional Array
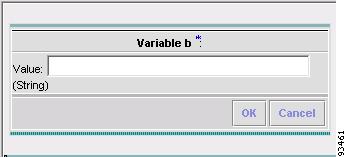
Step 11
To add a variable, click Add and a window, as shown in Figure 6-21, "Adding a Variable," appears in which you can add the variable. Then click OK.
Figure 6-21 Adding a Variable
Step 12
To edit or delete a variable, highlight the variable in Figure 6-20 and click Edit or Delete. For Edit you receive a figure as in Figure 6-21. Then click OK. For Delete, be sure you want to delete. After you click Delete, it automatically occurs and the window is updated. Proceed to Step 19.
Step 13
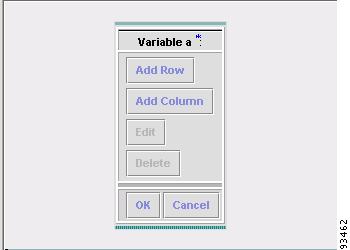
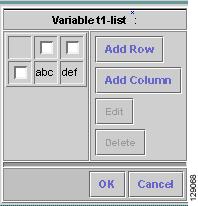
For a two-dimensional array (set as Dimension 2 when creating the template), when you click Edit, you receive a window as shown in Figure 6-22, "Editing a Two-Dimensional Array.
Figure 6-22 Editing a Two-Dimensional Array
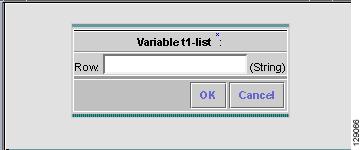
Step 14
Click Add Row in Figure 6-22 and a window, as shown in Figure 6-23, "Enter Row Information," appears. Enter a value and click OK.
Figure 6-23 Enter Row Information
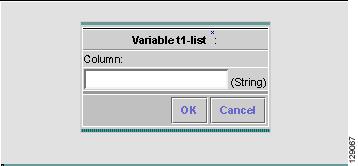
Step 15
Click Add Column in Figure 6-22 and a window as shown in Figure 6-24, "Enter Column Information," appears. Enter a value and click OK.
Figure 6-24 Enter Column Information
Step 16
A resulting window, as shown in Figure 6-25, "Two-Dimensional Array Results," appears.
Figure 6-25 Two-Dimensional Array Results
Step 17
You can select any of the check boxes (toggles) and you can then Edit or Delete that row or column. You can also continue to Add Row and Add Column as shown in Step 15 and Step 16, respectively.
Step 18
When you complete setting up your two-dimensional array, click OK in Figure 6-25.
Step 19
A window as shown in Figure 6-18 is updated to reflect the new data file information.
Step 20
You can then click Save and then Close to save this information and close this file; click Configure to show the configuration file; or click Close and then be sure to click OK, if you want to save the information you have created. If you do not want to save this information, click Close and then click Cancel.
Edit
To edit a Template or Data File, follow these steps:
Step 1
Navigate to Service Design > Templates.
Step 2
In the Templates tree, left-click on the folder or subfolder in which the template you want to edit exists or the template in which the data file you want to edit exists. Alternatively, when the name in the upper left corner of the data pane is a template, you can click on the template name to edit the template.
Step 3
To edit a template, a window appears as shown in Figure 6-26, "Choose Existing Template > Edit." To edit a data file, a window appears as shown in Figure 6-27, "Choose Existing Data File > Edit."
Figure 6-26 Choose Existing Template > Edit
Figure 6-27 Choose Existing Data File > Edit
Step 4
Select the check box for the template or data file you want to edit.
Note
For a data file, there is a Configlet column in which you can click View to view the configuration file.
Step 5
Click Edit.
Step 6
When editing a template, you receive a window as shown in Figure 6-6, "Template Editor." Then proceed as in in the "Create Template" section. When editing a data file, you receive a window as shown in Figure 6-17, "Choose Existing Template > Create Data File." Then proceed as in Step 5 in the "Create Data File" section.
Delete
To delete a Template or Data File, follow these steps:
Step 1
Navigate to Service Design > Templates.
Step 2
In the Templates tree, left-click on the folder or subfolder in which the template you want to delete exists or the template in which the data file you want to delete exists.
Step 3
To delete a template, a window appears as shown in Figure 6-28, "Choose Existing Template > Delete." To delete a data file, a window appears as shown in Figure 6-29, "Choose Existing Data File > Delete."
Figure 6-28 Choose Existing Template > Delete
Figure 6-29 Choose Existing Data File > Delete
Step 4
Select the check box for the template or data file you want to delete.
Note
For a data file, there is a Configlet column in which you can click View to view the configuration file.
Step 5
Click Delete.
Step 6
You receive an updated window as shown in Figure 6-28, "Choose Existing Template > Delete" or Figure 6-29, "Choose Existing Data File > Delete" with the deleted template or data file no longer available.
Template Examples
In the left column, the hierarchy pane, of Service Design > Templates, as shown in Figure 6-2, "Templates," template examples appear. See Table 6-1, "Template Examples and Their Descriptions."
Summary of Repository Variables
This section contains the following tables:
•
Table 6-2, "L2VPN Repository Variables"
•
Table 6-3, "MPLS Repository Variables"
•
Table 6-4, "QoS Repository Variables"
•
Table 6-5, "VPLS Repository Variables"
Table 6-2 provides a summary of the L2VPN Repository variables available from ISC Templates.
Table 6-3 provides a summary of the MPLS Repository variables available from ISC Templates.
Table 6-4 provides a summary of the QoS Repository variables available from ISC Templates.
Table 6-5 provides a summary of the VPLS Repository variables available from ISC Templates.
Link QoS
The Link QoS feature provides separate settings for IP QoS and Ethernet QoS.
IP QoS deals with link-level QoS settings that depend on Layer2 encapsulation and link bandwidth, such as Aggregate Shapers (FRTS; ATM Shapers, parent-level cb-shaper), Link Efficiency Mechanisms (FRF.12, LFIoMLPPP, and cRTP), and Interface-based Aggregated Rate Limiter.
Ethernet QoS allows you to configure Shape, Bandwidth, and Trust (CoS or DSCP) settings.
You can create a link QoS setting for a network independent of a VPN service. To manage IP Link QoS Settings for an MPLS service or Ethernet Link QoS Settings for an L2VPN service, see Cisco IP Solution Center Quality of Service User Guide, 4.1.

 Feedback
Feedback