-
User Guide for the Cisco Application Networking Manager 2.1
-
Preface
-
Overview
-
Adding and Managing Devices
-
Configuring Virtual Contexts
-
Managing Virtual Servers
-
Configuring Real Servers and Server Farms
-
Configuring Sticky Groups
-
Configuring Parameter Maps
-
Configuring SSL
-
Configuring Network Access
-
Configuring ANM High Availability
-
Configuring Traffic Policies
-
Configuring Application Acceleration and Optimization
-
Using Configuration Building Blocks
-
Monitoring Your Network
-
Administering the Cisco Application Networking Manager
-
Troubleshooting
-
Ports Reference
-
Glossary
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Cisco Application Networking Manager Overview
Logging Into the Cisco Application Networking Manager
Changing Your Account Password
Understanding ANM Screens and Menus
Using the Advanced Editing Option
Understanding Cisco Application Networking Manager Terminology
Cisco Application Networking Manager Overview
Date: 4/9/09The Cisco Application Networking Manager (ANM) is a networking management application that manages Cisco Application Control Engine (ACE) modules or appliances in your networking environment.
The following topics introduce you to ANM:
•
Logging Into the Cisco Application Networking Manager
•
Changing Your Account Password
•
Understanding Cisco Application Networking Manager Terminology
Logging Into the Cisco Application Networking Manager
You access ANM features and functions through a web-based interface. The following sections describe logging in, the interface, and terms used in ANM.
The ANM login screen allows you to:
•
Log into the ANM server
•
Change the password for your account (See the "Changing Your Account Password" section.)
•
Obtain online help by clicking Help
Use this procedure to log into ANM.
Procedure
Step 1
Choose one the following:
•
To log in after a new install (which uses the default web ports of 443 and 80 and therefore it is unnecessary to explicitly enter them), enter: https://<host>
CautionIf you want to log in using HTTP, you will need to change the properties file. See the "Changing Configuration Property Values" section on page 16-1 for details. Remember, if you enable HTTP, you are making your connection to the ANM less secure.
•
To log in after an upgrade (which uses the previously non-default web ports of 10443 and 10080 and therefore it is necessary to explicitly enter them), enter: https://<host>:10443 or https://<host>:10080
Note
All browsers require that cookies, Javascript/scripting, and popup windows are enabled. If you reinstall a subsequent ANM release, delete the cookies and clear the browser cache.
For example, enter https://192.168.10.10. The login screen appears.
A new installation comes with predefined credentials; user name and password are both admin. Please use it for first time login.
Step 2
In the User Name field, type admin.
Note
If you are logging in using ACS authentication (TACACS or RADIUS), you must add '@<organization> to the username (initially admin as shown here) on the login page, or you will not be able to log in.
Once you are logged in using this account, you can create additional user accounts. For information on changing account passwords, see the "Modifying User Accounts" section on page 15-44.
Step 3
In the Password field, type admin.
This is the default password. We recommend you change the password after you install or upgrade. For information about changing the default password, see the "Changing Your Account Password" section.
Step 4
Press Enter or click Login.
When you log in, the default window that appears is the Config > Devices screen. You can change your default window by editing your user profile. For a description of the user interface, see Figure 1-1. The interface will not contain data until you add devices by one of the methods described in the "Adding Network Devices into ANM" section on page 2-7.
Related Topics
•
Changing Your Account Password
Changing Your Account Password
Use this procedure to change your account password.
Procedure
Step 1
Using a web browser, navigate to the ANM login screen by typing the IP address or hostname where ANM is installed. For example, enter https://192.168.10.10. The login screen appears.
Step 2
In the User Name field, enter your account user name.
Step 3
Click Change Password. The Change password configuration screen appears.
Step 4
In the User Name field, enter the user name of the account you want to modify.
Step 5
In the Old Password field, enter the current password for this account.
Step 6
In the New Password field, enter the new password for this account.
Password attributes such as minimum and maximum length or accepted characters are defined at the organizational level. For more information on configuring passwords, see the "Configuring User Authentication" section on page 15-33.
Step 7
In the Confirm New Password field, reenter the new password for this account.
Step 8
Click:
•
OK to save your entries and to return to the login screen.
•
Cancel to exit this procedure without saving your entries and to return to the login screen.
Related Topics
•
Logging Into the Cisco Application Networking Manager
Understanding ANM Licenses
In order for ANM to manage all your ACE devices, you must have the appropriate number of ANM licenses for your network devices. An ANM Server license comes with the software and must be uploaded to ANM after the installation in order for your software to work properly. ANM can manage up to two ACE devices with a default set of five virtual contexts each. You will need additional licenses for any devices you plan to manage beyond the standard configuration.
For detailed steps on adding new ANM licenses to expand the number of network devices you can manage, see the "Managing ANM Licenses" section on page 15-60. For details on how to install ACE licenses to increase the number of virtual contexts that you can create and manage on a device, see the "Managing ACE Licenses" section on page 3-27.
The ANM server also requires its own license (which you must install before ANM will work). For step-by-step instructions on uploading your ANM server license, see the Installation Guide for the Cisco Application Networking Manager 2.1.
Related Topics
•
Viewing ACE Licenses, page 3-28
•
Installing ACE Licenses, page 3-28
•
Understanding ANM License Information, page 15-61
•
Checking on License Compliance, page 15-64
•
Viewing Licenses in License Management, page 15-63
ANM Interface Overview
This section covers the following ANM interface components including:
•
Understanding ANM Screens and Menus
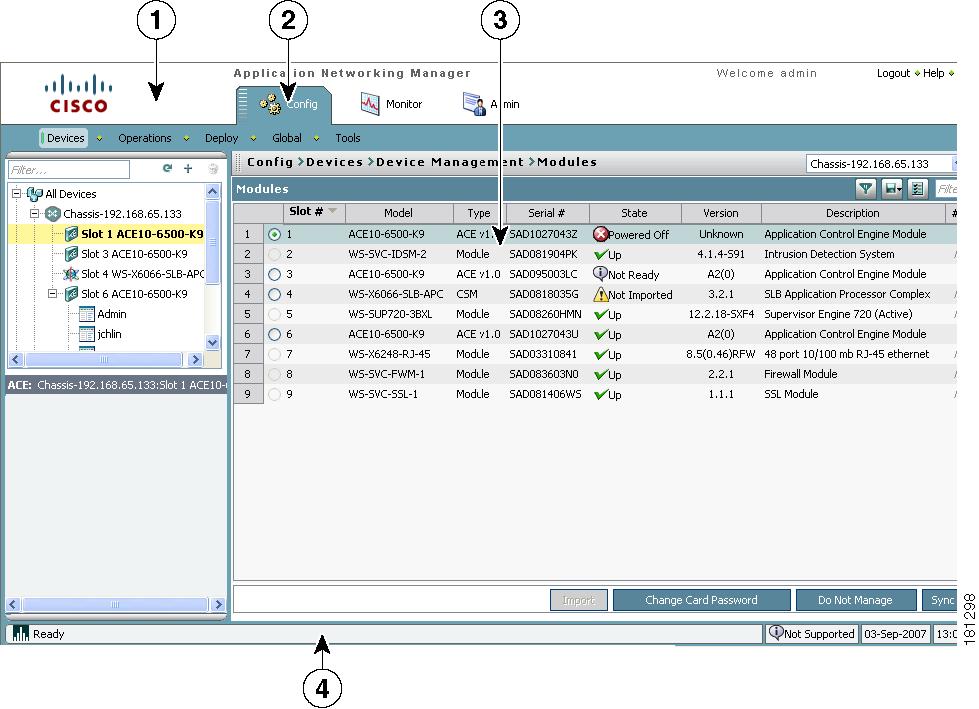
When you log into ANM, the default window that appears is the Config > Devices screen (similar to Figure 1-1 except that a new installation will have no devices or modules). You will need to import devices in order for your data to display in ANM. Table 1-1 describes the numbered fields.
Figure 1-1 ANM Interface Components
You can change the default window that appears when you log in by modifying user attributes under Admin > Role-Based Access Control > Users (see the "Modifying User Accounts" section on page 15-44).
Related Topics
•
Understanding ANM Screens and Menus
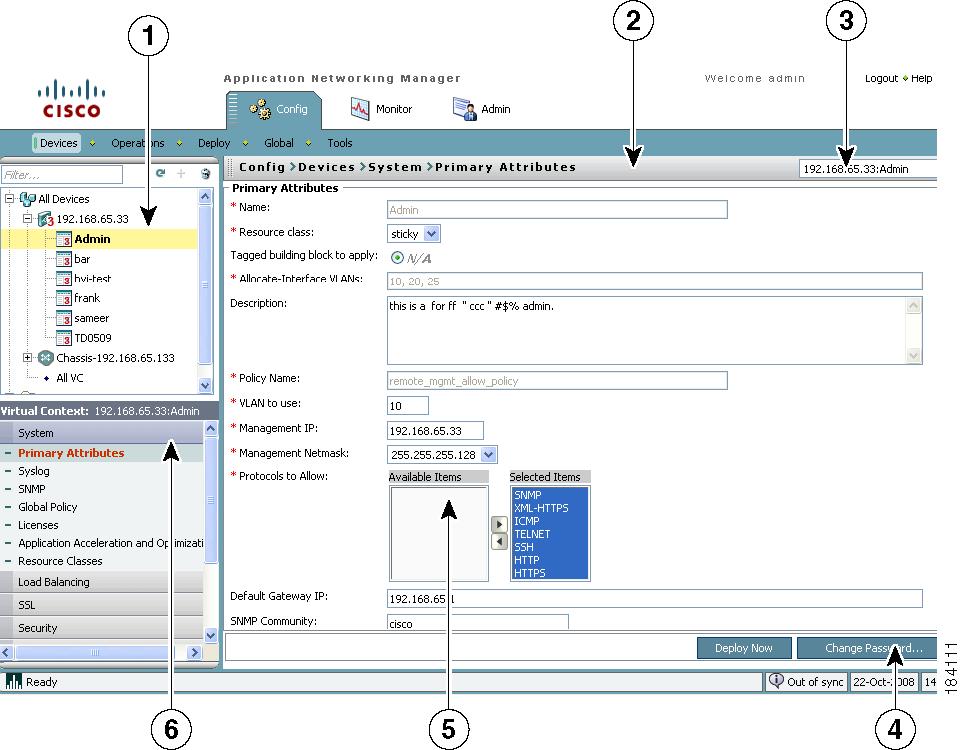
Understanding ANM Screens and Menus
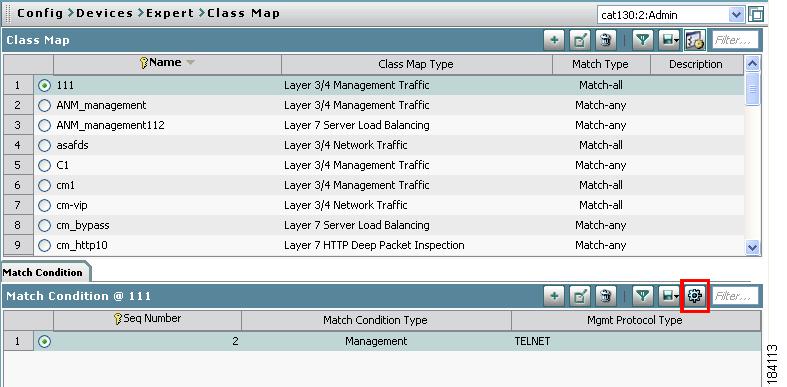
Figure 1-2 contains many common screen elements found in ANM and described in Table 1-2. Not all screens contain all buttons.
Figure 1-2 Example ANM Screen
Table 1-2 Example ANM Screen Descriptions
1
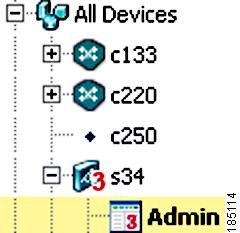
Device tree, which appears when you click Config or Monitor. The device tree includes All Devices and Groups:
•
The All Devices folder expands to show the names of imported Cisco devices and their associated modules or virtual contexts. When you click the plus sign (+) in front of a chassis icon, you can see a list of the modules in the chassis. When you expand an ACE appliance or ACE module, you can see the list of existing virtual contexts for that device. For more information about adding devices, see the "Adding Network Devices into ANM" section on page 2-7.
•
The Groups folder contains the list of user-defined groups. For more information about user-defined groups, see the "Configuring User-Defined Groups" section on page 2-57.
The Organization tree displays when you click Admin > Role-Based Access Control. The organization tree includes all organizations in ANM. Selecting an organization name displays its details.
To expand folders in the device tree, click the plus sign (+) to the right of an option. To collapse the structure, click the minus sign (-). Double-clicking on objects results in various actions; for example, displaying the object's configuration screen.
At the top of the tree are the following buttons:
•
Refresh—Refreshes the device tree after you have imported devices or made changes to the User Groups.
•
Plus sign (+) —Allows you to add an item to the selected option in the device tree.
•
Garbage can—Deletes the selected entry.
Note
Menus are based on device types. Although menu labels are the same for different device types, the actual menu definition is different. For this reason, it is not possible to preserve the menu state while traversing from a module to a virtual context and vice-versa in the device tree.
2
Option menus, which appear in Config screens. Click the icon on the bar to show or hide the options.
3
Object selector. Use this field to choose a device, context, building block, or other object that you want to view information on or configure. This filters what is displayed in the content area.
4
Command buttons. Use these buttons to perform the action identified by the button label.
5
Input fields. Use these fields to make selections and provide information. When there are more than three choices for any field, the field displays as a dropdown list. Otherwise, selections display with radio buttons.
6
Feature panel that contains functions that correspond to what is selected in the device or organization tree. Click on a command to expand the list of options that correspond to that command.
Related Topics
Understanding ANM Buttons
Table 1-3 describes the buttons that appear in some of the Config, Monitor, and Admin screens.
Note
ANM documentation, including online help, uses the names of buttons in all procedures. For example, "Click Next to deploy the current entry and add another entry."
Table 1-3 Button Descriptions
ACL table (Expand)
Click to expand all ACL table entries.
ACL table (Collapse)
Click to collapse all ACL table entries.
ACL table (Resequence)
Click to open the resequence popup window that allows you to reorder the ACL table entries.
Add
Lets you add an entry to the displayed table.
Add Another
Saves the current entries and refreshes the screen so you can add another entry.
Advanced Editing Mode
Lets you view or enter advanced arguments for the selected display.
Auto Refresh (Pause)
Allows you to interrupt the table data autorefresh process.
Auto Refresh (Resume)
Indicates that the table data autorefresh process is on pause and allows you to resume.
Customize
Lets you customize the table to suit your needs. (See the "Customizing Tables" section.)
Delete
Deletes the selected entry in the table.
Duplicate
Duplicates the selected entry in the table.
Edit
Opens the configuration screen of a selected entry in the table.
Filter
Filters the displayed list of items according to the criteria you specify. (See the "Filtering Entries" section.) Also displays a filter text box where strings can be entered.
Go
Appears when filtering is enabled; updates the table with the filtering criteria.
Key
Indicates that the associated field is a foreign key field; that is, one that takes its values from another table.
Plus
Displays a table with information related to the field where Plus appears. For example, if Plus appears next to the field label VLAN Group, clicking Plus displays a list of all VLAN groups in a separate window.
Refresh
Refreshes the content area.
Save
Displays the current information in a new window in either raw data or Excel format so you can save it to a file or print it.
Screen View (Full)
Allows you to adopt a larger (full) screen view for table.
Screen View (Normal)
Allows you to adopt a smaller (normal) screen view for table.
Sort
Sorts a column alphabetically up or down.
Stop
Stops the current process. If a process is only partially complete, it will finish its current operation and exit. For example, when stop is used during the import of two modules, it will complete only the first of two module imports.
Switch between Configure and Browse modes
Displays the subtables for those items that have additional sets of parameters that can be configured, such as Config > Devices > Network > VLAN Interfaces.
Note
This button is not available on single-row tables such as Config > Devices > System > Syslog or Config > Devices > System > SNMP. To switch between these modes, navigate to another screen where the button appears (for example, Config > Devices > Load Balancing > Server Farms), click the button to enter desired mode, then return to the screen on which the button was missing. You will remain in the mode you selected.
View Excel
View the raw data in Excel format in a separate browser window.
View Raw Data
View the raw data in table format.
Related Topics
•
Understanding ANM Screens and Menus
Conventions in Tables
Filtering Entries
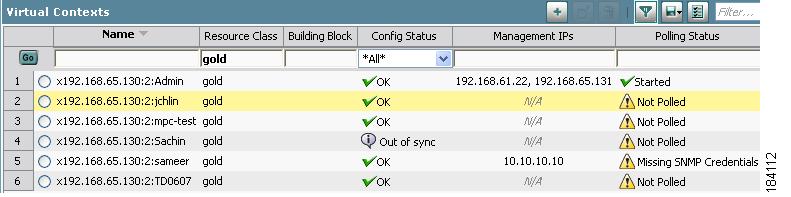
Click Filter to view table entries using criteria you select. When filtering is enabled, a filter row appears above the first table entry that allows you to filter entries in the following ways:
•
In fields with drop-down lists, choose one of the ANM-identified categories (see Figure 1-3). The table refreshes automatically with the entries that match the selected criterion.
•
In fields without drop-down lists, enter the string you want to match, and then click Go above the first table entry. The table refreshes with the entries that match your input.
•
Enter the string in the filter box. For example, by entering the string gold and clicking Go, only the gold Resource Class virtual contexts will be displayed (see Figure 1-3).
Figure 1-3 Example Table with Filtering Enabled
Related Topics
•
Using the Advanced Editing Option
Customizing Tables
Click Customize in a table to configure the table to suit your needs.
When you place the cursor over Customize, the following items appear:
•
Default—When selected with a check mark, this item indicates that the ANM default table format is being used by the current table.
•
Configure—When selected, this item opens a dialog box that allows you to create a new customized table format or to modify the table format currently in use.
Use this procedure to customize tables for your use.
Procedure
Step 1
When viewing a table, choose Customize > Configure. The List Configuration dialog box appears.
Step 2
In the List Configuration dialog box, enter the information in Table 1-4.
Note
Depending on the table you select, the available fields in the configuration table differ. Table 1-4 includes sample fields that might appear.
Note
You can be as inclusive or as restrictive as you like when setting table configuration options. The criteria are cumulative and greater specificity results in fewer results.
Step 3
Click:
•
Save to save your entries under a new name and to close the List Configuration dialog box. If a table using this format is displayed, the table is updated automatically.
•
Cancel to exit the procedure without saving your entries and to close the List Configuration dialog box.
•
Apply to apply your current entries to the table you are viewing, save your entries, and to close the List Configuration dialog box.
•
Delete to delete the currently selected customized table format. It no longer appears as an option when you click Customize.
Related Topics
•
Using the Advanced Editing Option
Using the Advanced Editing Option
By default, tables include columns that contain configured attributes, or a subset of columns related to a key field.
To view all configurable attributes in table format, click Advanced Editing Mode (the highlighted button in Figure 1-4). When advanced editing mode is enabled, all columns appear for your review (see Figure 1-4).
Figure 1-4 Advanced Editing Enabled Screen
Related Topics
ANM Screen Conventions
Table 1-5 describes other conventions used in ANM screens.
Related Topics
Understanding Cisco Application Networking Manager Terminology
It is useful to understand the following terms when using the ANM:
•
ACE
Cisco Application Control Engine, available as a module that resides in a Cisco Catalyst 6500 series chassis, Cisco 7600 series router, or as a standalone appliance. The ACE offers high-performance server load balancing (SLB), routing and bridging configuration, traffic policies, redundancy (high availability), virtualization for resource management, SSL, security features, and application acceleration and optimization.
•
Object
A physical entity, service, or resource that can be managed using the ANM
•
Organizations
An organization allows you to configure AAA server lookup for your users or set up users who work for a service provider customer. Organizations in the Cisco ANM system are defined by the system administrator.
•
Resource class
A resource class is a defined set of resources and allocations available for use by a virtual context. Using resource classes prevents a single context from using all available resources.
•
User contexts
There are two types of user contexts:
–
Admin context
The Admin context, which contains the basic settings for each virtual device or context, allows a user to configure and manage all contexts. When a user logs into the Admin context, he or she has full system administrator access to the entire ACE and all contexts and objects within it. The Admin context provides access to network-wide resources, for example, a syslog server or context configuration server. All global commands for ACE settings, contexts, resource classes, and so on, are available only in the Admin context.
–
User context
A user context has access to the resources in which the context was created. For example, a user context that was created by an administrator while in Admin context, by default, has access to all resources in an ACE device. Any user created by someone in a user-defined context, only has access to the resources within that context. In addition, roles are assigned to users, which determine the commands and resources that are available to that user.
•
Virtual context
A virtual context is a concept that allows users to partition an ACE into multiple virtual devices. Each virtual context contains its own set of policies, interfaces, and resources, allowing administrators to more efficiently manage system resources and services.
•
Virtual server
In a load-balancing environment, a virtual server is a construct that allows multiple physical servers to appear as one for load-balancing purposes. A virtual server is bound to physical services running on real servers in a server farm and uses IP address and port information to distribute incoming client requests to the servers in the server farm according to a specified load-balancing algorithm.
Related Topics

 Feedback
Feedback