Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing
Prerequisites for the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
Information About the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
Differences Between ATM- and Ethernet-Based Broadband Access Networks
Approach for a Circuit-Id Tag in Ethernet-Based Broadband Access Networks
Benefits of the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
How to Configure the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
Configuring the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
Removing the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag
Viewing the Session Activity Log
Configuration Examples for the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
Configuring PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing: Example
Removing the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag: Example
PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing
In an Ethernet access network, there is no unique mapping between the subscriber line identifier and the interface such as there is on a virtual circuit (VC) in an ATM-based network. The PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing feature provides a way to extract a Circuit-Id tag from the digital subscriber line (DSL) as an identifier for the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) access request on an Ethernet interface, thereby simulating ATM-based broadband access, but using cost-effective Ethernet instead. The tag is useful for troubleshooting the network, and is also used in RADIUS authentication and accounting processes.
History for the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
•
Information About the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
•
How to Configure the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
•
Configuration Examples for the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
Prerequisites for the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
It is recommended that you be familiar with RFC 2516 before configuring this feature. See the "RFCs" section for a pointer to this standard.
Information About the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
To configure the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing feature, you should understand the following concepts:
•
Differences Between ATM- and Ethernet-Based Broadband Access Networks
•
Approach for a Circuit-Id Tag in Ethernet-Based Broadband Access Networks
•
Benefits of the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
Differences Between ATM- and Ethernet-Based Broadband Access Networks
Broadband Digital Subscriber Line Multiplexer (DSLAM) and Broadband Remote Access Server (BRAS) vendors see a need to provide Ethernet-based networks as an alternative to an ATM access network, with a DSLAM bridging the ATM-DSL local loop to the Ethernet-based access network and allowing Ethernet-based connectivity to the BRAS. But in an Ethernet access network, there is no unique mapping between the subscriber Line-Id and the interface, as is found in an ATM-based network. In an ATM-based network, the ATM VC is associated to a subscriber line. During the authentication phase that initiates the PPP access and AAA accounting requests, the BRAS includes a NAS-Port-Id attribute in RADIUS authentication packets that identify the DSL line for the subscriber.
DSL Forum 2004-71 Solution
To apply the same subscriber mapping capability to Ethernet interfaces that is possible on ATM interfaces, DSL Forum 2004-71 proposes a solution whereby the DSLAM sends the DSL Line-Id in the PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) discovery phase. This method provides a way for a PPPoE server acting as a BRAS to extract the Line-Id tag and use the Circuit-Id field of that tag as a NAS-Port-Id attribute in AAA access and accounting requests. The PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing feature makes use of the proposed DSL Forum 2004-71 method and allows the BRAS to detect the presence of the subscriber Circuit-Id tag inserted by the DSLAM during the PPPoE discovery phase. The BRAS will send this tag as a NAS-Port-Id attribute in PPP authentication and AAA accounting requests. The tag is useful in troubleshooting the Ethernet network, and it is also used in RADIUS authentication and accounting processes.
Approach for a Circuit-Id Tag in Ethernet-Based Broadband Access Networks
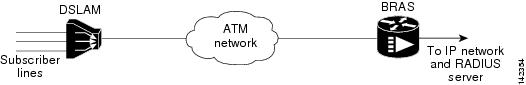
Traditional ATM-based DSL broadband access networks have the topology shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 ATM-Based DSL Broadband Access Network
In terms of logical connectivity, there is a one-to-one mapping of the DSL subscriber line to the end user and the ATM VC used to carry the PPP session through the DSLAM and to the BRAS, where this VC information is converted into a NAS-Port-Id for use in RADIUS packets.
The simple mapping available from an ATM-based network between the physical line in the DSL local loop to the end user and a virtual circuit (from DSLAM to BRAS) is not available for an Ethernet-based network. To solve this problem, the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing feature uses a PPPoE intermediate agent function on the DSLAM to attach a tag to the PPPoE discovery packets. The BRAS then receives the tagged packet, decodes the tag, and inserts the line identifier into RADIUS packets destined for the RADIUS server.
DSLAM intercepts PPPoE discovery frames from the client and inserts a unique line identifier using the PPPoE Vendor-Specific tag (0x0105) to PADI and PADR (PPPoE Active Discovery Initiation and Request) packets; see Figure 2. The DSLAM forwards these packets to the BRAS after the insertion. The tag contains the Line-Id of the DSL line on which the PADI or PADR packet was received, in the access node where the intermediate agent resides.
Figure 2 PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Solution
When the vendor-tag circuit-id service command is configured in BBA (broadband access) group configuration mode, the BRAS processes the received PPPoE Vendor-Specific tag in the PADR packet and extracts the Circuit-Id field, which is sent to the remote AAA server as the NAS-Port-Id attribute (RADIUS attribute 87) in RADIUS access and accounting requests. When the radius-server attribute nas-port format d global configuration command is also configured on the BRAS, the Acct-Session-Id attribute will contain the information about the incoming access interface, where discovery frames are received, and about the session being established.
Outgoing PADO and PADS (PAD Offer and Session-confirmation) packets from the BRAS will have the DSLAM-inserted Circuit-Id tag. DSLAM should strip the tag out of PADO and PADS packets. If the DSLAM cannot strip off the tag, the BRAS should remove it before sending the packets out, and this is accomplished using the vendor-tag circuit-id strip BBA group configuration mode command.
Benefits of the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
The shift towards Ethernet-based DSLAMs offers the following benefits:
•
Ability to use simpler and lower cost provisioning options for DSL subscribers over an Ethernet-based backhaul network rather than on an ATM-based network.
•
Ability to use higher bandwidth connectivity options available from Ethernet not possible on ATM.
•
Ability to upgrade to next-generation DSLAMs with quality of service (QoS), and support for higher bandwidth, asymmetric dual latency modems such as the ADSL2.
•
Ability to inject high-bandwidth content such as video in an Ethernet network.
How to Configure the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
This section contains the following procedures:
•
Configuring the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
•
Removing the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag
•
Viewing the Session Activity Log
Configuring the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
This section describes how to configure an Ethernet-based access network on a Cisco BRAS. The extracted Circuit-Id tag (see "Information About the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature" section) is sent in the following RADIUS syntax, as recommended by the DSL Forum:
"Access-Node-Identifier eth slot/port[:vlan-tag]"
The Access-Node-Identifier is a unique subscriber identifier or telephone number text string entered without spaces. Per DSL-Forum 2004-71, the maximum length supported for the tag is 48 bytes. The BRAS copies the entire tag into the NAS-Port-Id and sends it to the AAA server.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
radius-server attribute nas-port format d
4.
bba-group pppoe group-name
5.
vendor-tag circuit-id service
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
enable
Example:Router> enable
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
•
Enter your password if prompted.
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:Router# configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode.
Step 3
radius-server attribute nas-port format d
Example:Router(config)# radius-server attribute nas-port format d
(Optional) Selects the PPPoE extended NAS-Port format used for RADIUS access and accounting.
•
Configure this command so that the Acct-Session-Id attribute, as displayed in the debug radius command, will contain the information about the incoming access interface, where discovery frames are received, and about the session being established. See the "Viewing the Session Activity Log" and "Configuring PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing: Example" sections for more information.
Step 4
bba-group pppoe group-name
Example:Router(config-bba-group)# bba-group pppoe pppoe-group
Defines a PPPoE profile and enters BBA group configuration mode.
Step 5
vendor-tag circuit-id service
Example:Router(config-bba-group)# vendor-tag circuit-id service
Enables processing of the received PPPoE Vendor-Specific tag in the PADR packet, which extracts the Circuit-Id part of the tag and sends it to the AAA server as the NAS-Port-Id attribute in RADIUS access and accounting requests.
Removing the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag
Outgoing PADO and PADS packets will have the DSLAM-inserted Vendor-Specific Line-Id tag, and DSLAM must strip the Circuit-Id tag from the packets. If the DSLAM cannot strip the tag, the BRAS must remove it before sending out the packets. This task is accomplished through configuration of the vendor-tag circuit-id strip command under BBA group configuration mode.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
bba-group pppoe group-name
4.
vendor-tag circuit-id strip
DETAILED STEPS
Viewing the Session Activity Log
When the radius-server attribute nas-port format d global configuration command is added to the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing feature configuration on the BRAS (see the "Configuring PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing: Example" section for an example), the report from the debug radius privileged EXEC command will include information about the incoming access interface, where discovery frames are received, and about the session being established in PPPoE extended NAS-Port format (format d).
Step 1
Enable the debug radius command to display a report of session activity. In the example shown in this section:
•
The acct_session_id is 79 or 4F in hexadecimal format.
•
In the message "Acct-session-id pre-pended with Nas Port = 0/0/0/200," the interface on which the PPPoE discovery frames arrived is FastEthernet0/0.200. The 0/0/0 is Cisco format for slot/sub-slot/port.
•
The Acct-Session-Id vendor-specific attribute 44 contains the string "0/0/0/200_0000004F," which is a combination of the ingress interface and the session identifier.
Note
Strings of interest in the debug radius output log are presented in bold text for purpose of example only.
Router# debug radius02:10:49: RADIUS(0000003F): Config NAS IP: 0.0.0.002:10:49: RADIUS/ENCODE(0000003F): acct_session_id: 7902:10:49: RADIUS(0000003F): sending02:10:49: RADIUS/ENCODE: Best Local IP-Address 10.0.58.141 for Radius-Server 172.20.164.14302:10:49: RADIUS(0000003F): Send Access-Request to 172.20.164.143:1645 id 1645/65, len 9802:10:49: RADIUS: authenticator 1C 9E B0 A2 82 51 C1 79 - FE 24 F4 D1 2F 84 F5 7902:10:49: RADIUS: Framed-Protocol [7] 6 PPP [1]02:10:49: RADIUS: User-Name [1] 7 "peer1"02:10:49: RADIUS: CHAP-Password [3] 19 *02:10:49: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 Ethernet [15]02:10:49: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 6 20002:10:49: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 22 "FastEthernet6/0.200:"02:10:49: RADIUS: Service-Type [6] 6 Framed [2]02:10:49: RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 10.0.58.14102:10:49: RADIUS: Received from id 1645/65 172.20.164.143:1645, Access-Accept, len 32 02:10:49: RADIUS: authenticator 06 45 84 1B 27 1F A5 C3 - C3 C9 69 6E B9 C0 6F 9402:10:49: RADIUS: Service-Type [6] 6 Framed [2]02:10:49: RADIUS: Framed-Protocol [7] 6 PPP [1]02:10:49: RADIUS(0000003F): Received from id 1645/6502:10:49: [62]PPPoE 65: State LCP_NEGOTIATION Event PPP_LOCAL02:10:49: PPPoE 65/SB: Sent vtemplate request on base Vi202:10:49: [62]PPPoE 65: State VACCESS_REQUESTED Event VA_RESP02:10:49: [62]PPPoE 65: Vi2.1 interface obtained02:10:49: [62]PPPoE 65: State PTA_BINDING Event STAT_BIND02:10:49: [62]PPPoE 65: data path set to Virtual Acess02:10:49: [62]PPPoE 65: Connected PTA02:10:49: [62]PPPoE 65: AAA get dynamic attrs02:10:49: [62]PPPoE 65: AAA get dynamic attrs02:10:49: RADIUS/ENCODE(0000003F):Orig. component type = PPoE02:10:49: RADIUS/ENCODE(0000003F): Acct-session-id pre-pended with Nas Port = 0/0/0/20002:10:49: RADIUS(0000003F): Config NAS IP: 0.0.0.002:10:49: RADIUS(0000003F): sending02:10:49: RADIUS/ENCODE: Best Local IP-Address 10.0.58.141 for Radius-Server 172.20.164.14302:10:49: RADIUS(0000003F): Send Accounting-Request to 172.20.164.143:1646 id 1 646/42, len 11702:10:49: RADIUS: authenticator 57 24 38 1A A3 09 62 42 - 55 2F 41 71 38 E1 CC 2402:10:49: RADIUS: Acct-Session-Id [44] 20 "0/0/0/200_0000004F"02:10:49: RADIUS: Framed-Protocol [7] 6 PPP [1]02:10:49: RADIUS: User-Name [1] 7 "peer1"02:10:49: RADIUS: Acct-Authentic [45] 6 RADIUS [1]02:10:49: RADIUS: Acct-Status-Type [40] 6 Start [1]02:10:49: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Type [61] 6 Ethernet [15]02:10:49: RADIUS: NAS-Port [5] 6 20002:10:49: RADIUS: NAS-Port-Id [87] 22 "FastEthernet6/0.200:"02:10:49: RADIUS: Service-Type [6] 6 Framed [2]02:10:49: RADIUS: NAS-IP-Address [4] 6 10.0.58.14102:10:49: RADIUS: Acct-Delay-Time [41] 6 002:10:49: RADIUS: Received from id 1646/42 172.20.164.143:1646, Accounting-resp onse, len 2002:10:49: RADIUS: authenticator 34 84 7E B2 F4 40 B2 7C - C5 B2 4E 98 78 03 8B C0
Configuration Examples for the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing Feature
This section contains the following examples:
•
Configuring PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing: Example
•
Removing the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag: Example
Configuring PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing: Example
In the following example, outgoing PADO and PADS packets will retain the incoming Vendor-Specific Circuit-Id tag:
radius-server attribute nas-port format d!bba-group pppoe pppoe-groupsessions per-mac limit 50vendor-tag circuit-id service!interface FastEthernet0/0.1encapsulation dot1Q 120pppoe enable group pppoe-groupRemoving the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag: Example
In the following example, the BRAS will strip off incoming Vendor-Specific Circuit-Id tags from outgoing PADO and PADS packets:
bba-group pppoe pppoe-rm-tagsessions per-mac limit 50vendor-tag circuit-id servicevendor-tag circuit-id stripinterface FastEthernet0/0.1encapsulation dot1Q 120pppoe enable group pppoe-groupAdditional References
The following sections provide references related to the PPPoE Circuit-Id Tag Processing feature.
Related Documents
Configuring broadband and DSL
Cisco IOS Broadband and DSL Configuration Guide, Release 12.4
RADIUS attributes
Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide, Release 12.4
DSL Forum 2004-71
Standards
MIBs
None
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL:
RFCs
Technical Assistance
Command Reference
This section documents the following new commands:
•
vendor-tag circuit-id service
vendor-tag circuit-id service
To enable processing of the PPPoE Vendor-Specific tag in a PPPoE Active Discovery Request (PADR) packet, which extracts the Circuit-Id part of the tag and sends it to a authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) server as the NAS-Port-Id attribute in RADIUS access and accounting requests, use the vendor-tag circuit-id service command in BBA group configuration mode. To disable the command function (default), use the no form of this command.
vendor-tag circuit-id service
no vendor-tag circuit-id service
Syntax Description
This command has no argument or keywords.
Command Default
Command function is disabled.
Command Modes
BBA group configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
When this command is not enabled and the Broadband Remote Access Server (BRAS) receives a packet with the Vendor-Specific tag attached, the tag is ignored and the session is allowed to come up. The Vendor-Specific tag is extracted and processed for its Circuit-Id part when the vendor-tag circuit-id service command is enabled under BBA group configuration mode. Once configured, the BRAS processes incoming PADR packets and sends the Circuit-Id tag to the AAA server as a NAS-Port-Id RADIUS attribute.
Examples
In the following example, outgoing PADO and PADS packets will retain the incoming Vendor-Specific Circuit-Id tag:
bba-group pppoe pppoe-groupsessions per-mac limit 50vendor-tag circuit-id serviceinterface FastEthernet0/0.1encapsulation dot1Q 120pppoe enable group pppoe-groupRelated Commands
vendor-tag circuit-id strip
Removes an incoming Vendor-Specific Circuit-Id tag from outgoing PADO and PADR packets.
vendor-tag circuit-id strip
To remove the incoming Vendor-Specific Circuit-Id tag from outgoing PADO and PADR (PPPoE Active Discovery Offer and Request) packets, use the vendor-tag circuit-id strip command in BBA group configuration mode. To disable the command function (default), use the no form of this command.
vendor-tag circuit-id strip
no vendor-tag circuit-id strip
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Command function is disabled.
Command Modes
BBA group configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Outgoing packets from a Broadband Remote Access Server (BRAS) will have a DSLAM-inserted Circuit-Id tag when the vendor-tag circuit-id service command is configured. DSLAM should strip the tag from the PAD outgoing packets. If the DSLAM cannot strip the tag, the BRAS must remove it before sending out the packets. When the vendor-tag circuit-id strip command is configured, the BRAS removes the incoming Vendor-Specific Circuit-Id tag from the outgoing packets.
Outgoing PADO and PADS packets from the BRAS will have the DSLAM-inserted Circuit-Id tag. DSLAM should strip the tag out of PADO and PADS packets. If the DSLAM cannot strip off the tag, the BRAS should remove it before sending the packets out, and this is accomplished using the vendor-tag circuit-id strip command.
Examples
In the following example, the BRAS will strip off incoming Vendor-Specific Circuit-Id tags from outgoing PADO and PADS packets:
bba-group pppoe pppoe-rm-tagsessions per-mac limit 50vendor-tag circuit-id servicevendor-tag circuit-id stripinterface FastEthernet0/0.1encapsulation dot1Q 120pppoe enable group pppoe-groupRelated Commands
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.