Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
Prerequisites for SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
Information About SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
SIP: Caller ID Removable to Improve Privacy
SIP: Calling Number Substitution for the Display Name When the Display Name is Unavailable
SIP: Calling Number Passing as Network-Provided or User-Provided
How to Configure SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
Configuring SIP: Blocking Caller ID Information Globally When Privacy Exists
Configuring Dial-Peer Level SIP: Blocking of Caller ID Information When Privacy Exists
Configuring Globally the SIP: Pass-Through of the Passing Calling Number as Network-Provided
Configuring Globally the SIP: Pass-Through of the Passing Calling Number as User-Provided
Configuration Examples for SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
The SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature adds three command-line interface (CLI) options that make the handling of caller ID information more flexible. Specifically, the SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature addresses the following situations:
•
Passing along caller ID information when privacy exists
•
Handling the Display Name field when no display name exists
•
Allowing caller ID information to be passed to ISDN as network-provided
History for the SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists Feature
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
•
Information About SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
•
How to Configure SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
•
Configuration Examples for SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
Prerequisites for SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
•
Establish a working IP network.
•
Configure VoIP.
•
Ensure that the gateway has voice functionality configured for SIP.
Note
For information about configuring voice functionality, see the Cisco IOS Voice Configuration Library.
Information About SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
The SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature is comprised of three main components, as follows:
•
SIP: Caller ID Removable to Improve Privacy
•
SIP: Calling Number Substitution for the Display Name When the Display Name is Unavailable
•
SIP: Calling Number Passing as Network-Provided or User-Provided
SIP: Caller ID Removable to Improve Privacy
The caller ID information is passed through from the ISDN-to-SIP by copying the number in the Calling Party Number information element (IE) in an ISDN Setup message into the Calling Number field of the SIP Remote-Party-ID and From headers.
The Calling Name from the ISDN Display IE is copied into the SIP Display Name field in the SIP Remote-Party-ID and From headers. The Calling Party Number IE contains a Presentation Indicator field that is set to presentation allowed, presentation restricted, number not available due to interworking, or reserved. Presentation allowed and presentation restricted are translated into privacy set to off or privacy set to null, respectively, in the SIP Remote-Party-ID header field.
However, for added privacy, the SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature introduces CLI to completely remove the Calling Number and Display Name from an outgoing message's From header if presentation is prohibited. This prohibits sending the SIP Remote Party ID header, because the Cisco gateway does not send SIP Remote-Party ID headers without both a Display Name and Calling Number.
Note
The SIP: Caller ID Removable to Improve Privacy option is available both globally and at the dial-peer level.
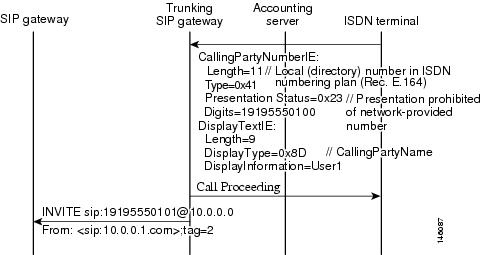
See Figure 1 for call flows and Table 1 and Table 2 for additional presentation mapping.
Figure 1 Call Flow for Blocking Caller ID Information When Privacy Exists
SIP: Calling Number Substitution for the Display Name When the Display Name is Unavailable
When the Display information element (IE) in a PSTN-to-SIP call is not available with a Setup message, the Cisco gateway leaves the Display Name field in the SIP Remote-Party-ID and From headers blank.
When presentation is allowed, the SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature enables the substitution of the Calling Number for the missing Display Name in the SIP Remote-Party-ID and From headers. Upon receipt of a Setup message where a name to follow is indicated, the Calling Number is not copied into the Display Name.
Also, the SIP Extensions for Caller Identity and Privacy on SIP gateway feature added the ability to hardcode calling name and number in the SIP Remote-Party-ID and From headers. The SIP Extensions for Caller Identify and Privacy feature settings take precedence over the SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature settings.
Note
The SIP: Calling Number Substitutions for the Display Name When the Display Name is Unavailable option is available both globally and at the dial-peer level.
See Figure 2 for the call flow where the Calling Number is substituted for the Display Number.
Figure 2 Call Flow for Substituting the Calling Number for the Display Name When the Display Name is Unavailable
SIP: Calling Number Passing as Network-Provided or User-Provided
ISDN numbers can be passed along as network-provided or user-provided in an ISDN Calling Party information element (IE) Screening Indicator field. The Cisco gateway automatically sets the Screening Indicator to user-provided in SIP-to-ISDN calls.
The SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature allows toggling between user-provided and network-provided ISDN numbers for the screening indicator. Therefore, after bits 1 and 2 are set to reflect network-provided, any existing screening information is lost. However, presentation information in bits 6 and 7 is preserved.
Note
The SIP: Calling Number Passing as Network-Provided or User-Provided option is available both globally and at the dial-peer level.
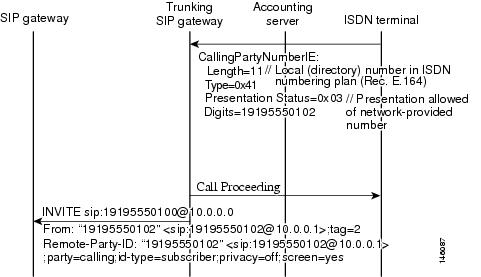
See Figure 3 for the call flow when the calling number is passed along as network-provided.
Figure 3 Call Flow for Passing Through the Calling Number as Network-Provided
How to Configure SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
This section contains the following procedures:
•
Configuring SIP: Blocking Caller ID Information Globally When Privacy Exists (optional)
•
Configuring Dial-Peer Level SIP: Blocking of Caller ID Information When Privacy Exists (optional)
•
Configuring Globally the SIP: Calling Number for Display Name Substitution When Display Name Is Unavailable (optional)
•
Configuring Globally the SIP: Pass-Through of the Passing Calling Number as Network-Provided (optional)
•
Configuring at the Dial-Peer Level the SIP: Pass-Through of Passing the Calling Number as Network-Provided (optional)
•
Configuring Globally the SIP: Pass-Through of the Passing Calling Number as User-Provided (optional)
•
Configuring at the Dial-Peer Level the SIP: Pass-Through of Passing the Calling Number as User-Provided (optional)
Configuring SIP: Blocking Caller ID Information Globally When Privacy Exists
The Call-ID information is private information. In ISDN there is a private setting that can be set to protect this information. However, whenever SIP gets the Call-ID information, it does not hide the private information, rather, it just sets a field to reflect that it is private and not to display it on a Call-ID display. But, the data is still viewable in the SIP message requests. This option allows the Cisco gateway to delete the Call-ID information from the SIP message requests so it cannot be read on the network.
The global commands to strip the Calling Name and Calling Number from the Remote-Party-ID and From headers are as follows:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
voice service voip
4.
clid strip pi-restrict all
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Dial-Peer Level SIP: Blocking of Caller ID Information When Privacy Exists
The dial-peer specific command to strip the Calling Number from the Remote-Party-ID and From headers is as follows:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
dial-peer voice dial-peer-number voip
4.
clid strip pi-restrict all
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Globally the SIP: Calling Number for Display Name Substitution When Display Name Is Unavailable
When this is enabled, if there is no Display Name field but there is a number, it copies the number into the Display Name field, so the number is displayed on the recipient's Call-ID display.
The steps for substituting the Calling Number for the Display Name when it is unavailable in the Remote-Party-ID and From headers are as follows:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
voice service voip
4.
clid substitute name
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Dial-Peer-Level SIP: Substitution of the Calling Number for Display Name When the Display Name Is Unavailable
The dial-peer-specific steps for substituting the Calling Number for the Display Name when it is unavailable in the Remote-Party-ID and From headers are as follows:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
dial-peer voice dial-peer-number voip
4.
clid substitute name
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Globally the SIP: Pass-Through of the Passing Calling Number as Network-Provided
This field shows whether the Call-ID information was supplied by the network or not. This is for screening purposes.
The steps for globally setting set the Screening Indicator to network-provided are as follows:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
voice service voip
4.
clid network-provided
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring at the Dial-Peer Level the SIP: Pass-Through of Passing the Calling Number as Network-Provided
The dial-peer specific command to set the Screening Indicator to network-provided is as follows:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
dial-peer voice dial-peer-number voip
4.
clid network-provided
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Globally the SIP: Pass-Through of the Passing Calling Number as User-Provided
The steps for globally setting set the Screening Indicator to user-provided are as follows:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
voice service voip
4.
no clid network-provided
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring at the Dial-Peer Level the SIP: Pass-Through of Passing the Calling Number as User-Provided
The dial-peer specific command to set the Screening Indicator to user-provided is as follows:
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
dial-peer voice dial-peer-number voip
4.
no clid network-provided
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists
The following shows an example of the SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature when enabled globally and disabled on the dial-peer level:
Router# show running-configBuilding configuration...Current configuration: 1234 bytes!version 12.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime service timestamps log datetime msec localtime no service password-encryption ! hostname pip ! boot-start-marker boot system tftp user1/c3660-is-mz 172.18.207.15 boot-end-marker ! logging buffered 1000000 debugging enable secret 5 $1$li0u$IkIqPXzKq4uKme.LhzGut0 enable password lab ! no aaa new-model ! resource policy ! clock timezone GMT 0 clock summer-time EDT recurring ip subnet-zero ip tcp path-mtu-discovery ! ip cef ip domain name sip.com ip host sip-server1 172.18.193.100 ip host CALLGEN-SECURITY-V2 10.76.47.38 10.30.0.0 ip name-server 172.18.192.48 no ip dhcp use vrf connected ! ip vrf btknet rd 8262:2000 ! voice call send-alert ! voice service voip <- SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature enabled globally clid substitute name clid strip pi-restrict all clid network-provided sip ! voice class codec 1 codec preference 1 g729r8 codec preference 2 g711alaw codec preference 3 g711ulaw codec preference 4 g729br8 codec preference 5 g726r32 codec preference 6 g726r24 codec preference 7 g726r16 codec preference 8 g723ar53 codec preference 9 g723r53 codec preference 10 g723ar63 codec preference 11 gsmefr codec preference 12 gsmfr codec preference 13 g728 ! voice class codec 2 codec preference 1 g729r8 codec preference 2 g711ulaw codec preference 3 g711alaw ! voice class codec 99 codec preference 1 g729r8 codec preference 2 g711ulaw codec preference 3 g711alaw ! fax interface-type fax-mail ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 172.18.195.49 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto no cdp enable ip rsvp bandwidth 96 96 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 172.18.193.190 255.255.255.0 shutdown duplex auto speed auto no cdp enable ! no ip http server ! ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 FastEthernet0/0 ip route 172.16.0.0 255.0.0.0 172.18.195.1 ! snmp-server community public RO ! control-plane ! voice-port 1/0/0 ! voice-port 1/0/1 ! mgcp behavior rsip-range tgcp-only ! dial-peer cor custom ! dial-peer voice 100 pots destination-pattern 9001 ! dial-peer voice 3301 voip destination-pattern 9002 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.87 incoming called-number 9001 codec g711ulaw no vad ! dial-peer voice 3303 voip destination-pattern 777 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.199.94 ! dial-peer voice 36601 voip destination-pattern 36601 no modem passthrough session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.98 ! dial-peer voice 5 voip destination-pattern 5550100 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.197.182 codec g711ulaw ! dial-peer voice 36602 voip destination-pattern 36602 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.120 incoming called-number 9001 dtmf-relay rtp-nte codec g711ulaw ! dial-peer voice 111 voip destination-pattern 111 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.251 ! dial-peer voice 5550199 voip <- SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature disabled on dial-peer destination-pattern 3100801 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:10.102.17.208 codec g711ulaw ! dial-peer voice 333 voip preference 2 destination-pattern 333 modem passthrough nse codec g711ulaw voice-class codec 99 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.250 dtmf-relay rtp-nte no vad ! dial-peer voice 9003 pots preference 2 destination-pattern 9003 ! dial-peer voice 90032 voip preference 1 destination-pattern 9003 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.97 ! dial-peer voice 1 pots ! num-exp 5550100 5550199 num-exp 5550199 5550100 gateway timer receive-rtp 1200 ! sip-ua srv version 1 retry response 1 ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 password cisco login ! no process cpu extended no process cpu autoprofile hog ntp clock-period 17180176 ntp server 172.68.10.150 prefer ! endThe following shows an example of the SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature when disabled globally and disabled on the dial-peer level:
Router# show running-configBuilding configuration...Current configuration: 1234 bytes!service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime service timestamps log datetime msec localtime no service password-encryption ! hostname pip ! boot-start-marker boot system tftp user1/c3660-is-mz 172.18.207.15 boot-end-marker ! logging buffered 1000000 debugging enable secret 5 $1$li0u$IkIqPXzKq4uKme.LhzGut0 enable password lab ! no aaa new-model ! resource policy ! clock timezone GMT 0 clock summer-time EDT recurring ip subnet-zero ip tcp path-mtu-discovery ! ip cef ip domain name sip.com ip host sip-server1 172.18.193.100 ip host CALLGEN-SECURITY-V2 10.76.47.38 10.30.0.0 ip name-server 172.18.192.48 no ip dhcp use vrf connected ! ip vrf btknet rd 8262:2000 ! voice call send-alert ! voice service voip <- SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature disabled globally sip ! voice class codec 1 codec preference 1 g729r8 codec preference 2 g711alaw codec preference 3 g711ulaw codec preference 4 g729br8 codec preference 5 g726r32 codec preference 6 g726r24 codec preference 7 g726r16 codec preference 8 g723ar53 codec preference 9 g723r53 codec preference 10 g723ar63 codec preference 11 gsmefr codec preference 12 gsmfr codec preference 13 g728 ! voice class codec 2 codec preference 1 g729r8 codec preference 2 g711ulaw codec preference 3 g711alaw ! voice class codec 99 codec preference 1 g729r8 codec preference 2 g711ulaw codec preference 3 g711alaw ! fax interface-type fax-mail ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 172.18.195.49 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto no cdp enable ip rsvp bandwidth 96 96 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 172.18.193.190 255.255.255.0 shutdown duplex auto speed auto no cdp enable ! no ip http server ! ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 FastEthernet0/0 ip route 172.16.0.0 255.0.0.0 172.18.195.1 ! snmp-server community public RO ! control-plane ! voice-port 1/0/0 ! voice-port 1/0/1 ! mgcp behavior rsip-range tgcp-only ! dial-peer cor custom ! dial-peer voice 100 pots destination-pattern 9001 ! dial-peer voice 3301 voip destination-pattern 9002 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.87 incoming called-number 9001 codec g711ulaw no vad ! dial-peer voice 3303 voip destination-pattern 777 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.199.94 ! dial-peer voice 36601 voip destination-pattern 36601 no modem passthrough session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.98 ! dial-peer voice 5 voip destination-pattern 5550100 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.197.182 codec g711ulaw ! dial-peer voice 36602 voip destination-pattern 36602 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.120 incoming called-number 9001 dtmf-relay rtp-nte codec g711ulaw ! dial-peer voice 111 voip destination-pattern 111 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.251 ! dial-peer voice 5550199 voip <- SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature disabled on dial-peer destination-pattern 5550199 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:10.102.17.208 codec g711ulaw ! dial-peer voice 333 voip preference 2 destination-pattern 333 modem passthrough nse codec g711ulaw voice-class codec 99 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.250 dtmf-relay rtp-nte no vad ! dial-peer voice 9003 pots preference 2 destination-pattern 9003 ! dial-peer voice 90032 voip preference 1 destination-pattern 9003 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.97 ! dial-peer voice 1 pots ! num-exp 5550100 5550199 num-exp 5550101 5550198 gateway timer receive-rtp 1200 ! sip-ua srv version 1 retry response 1 ! ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 password cisco login ! no process cpu extended no process cpu autoprofile hog ntp clock-period 17180176 ntp server 171.68.10.150 prefer ! endThe following shows an example of the SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature when disabled globally and enabled on the dial-peer level:
Router# show running-configBuilding configuration...Current configuration: 1234 bytes!version 12.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime service timestamps log datetime msec localtime no service password-encryption ! hostname pip ! boot-start-marker boot system tftp judyg/c3660-is-mz 172.18.207.15 boot-end-marker ! logging buffered 1000000 debugging enable secret 5 $1$li0u$IkIqPXzKq4uKme.LhzGut0 enable password lab ! no aaa new-model ! resource policy ! clock timezone GMT 0 clock summer-time EDT recurring ip subnet-zero ip tcp path-mtu-discovery ! ip cef ip domain name sip.com ip host sip-server1 172.18.193.100 ip host CALLGEN-SECURITY-V2 10.76.47.38 10.30.0.0 ip name-server 172.18.192.48 no ip dhcp use vrf connected ! ip vrf btknet rd 8262:2000 ! voice call send-alert ! voice service voip <- SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature disabled globally sip ! voice class codec 1 codec preference 1 g729r8 codec preference 2 g711alaw codec preference 3 g711ulaw codec preference 4 g729br8 codec preference 5 g726r32 codec preference 6 g726r24 codec preference 7 g726r16 codec preference 8 g723ar53 codec preference 9 g723r53 codec preference 10 g723ar63 codec preference 11 gsmefr codec preference 12 gsmfr codec preference 13 g728 ! voice class codec 2 codec preference 1 g729r8 codec preference 2 g711ulaw codec preference 3 g711alaw ! voice class codec 99 codec preference 1 g729r8 codec preference 2 g711ulaw codec preference 3 g711alaw ! fax interface-type fax-mail ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 172.18.195.49 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto no cdp enable ip rsvp bandwidth 96 96 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 172.18.193.190 255.255.255.0 shutdown duplex auto speed auto no cdp enable ! no ip http server ! ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 FastEthernet0/0 ip route 172.16.0.0 255.0.0.0 172.18.195.1 ! snmp-server community public RO ! control-plane ! voice-port 1/0/0 ! voice-port 1/0/1 ! mgcp behavior rsip-range tgcp-only ! dial-peer cor custom ! dial-peer voice 100 pots destination-pattern 9001 ! dial-peer voice 3301 voip destination-pattern 9002 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.87 incoming called-number 9001 codec g711ulaw no vad ! dial-peer voice 3303 voip destination-pattern 777 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.199.94 ! dial-peer voice 36601 voip destination-pattern 36601 no modem passthrough session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.98 ! dial-peer voice 5 voip destination-pattern 5550102 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.197.182 codec g711ulaw ! dial-peer voice 36602 voip destination-pattern 36602 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.120 incoming called-number 9001 dtmf-relay rtp-nte codec g711ulaw ! dial-peer voice 111 voip destination-pattern 111 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.251 ! dial-peer voice 5550100 voip <- SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature enabled on dial-peer destination-pattern 5550100 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:10.102.17.208 codec g711ulaw clid strip pi-restrict all clid network-provided clid substitute name ! dial-peer voice 333 voip preference 2 destination-pattern 333 modem passthrough nse codec g711ulaw voice-class codec 99 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.250 dtmf-relay rtp-nte no vad ! dial-peer voice 9003 pots preference 2 destination-pattern 9003 ! dial-peer voice 90032 voip preference 1 destination-pattern 9003 session protocol sipv2 session target ipv4:172.18.193.97 ! dial-peer voice 1 pots ! num-exp 5550100 5550199 num-exp 5550101 5550198 gateway timer receive-rtp 1200 ! sip-ua srv version 1 retry response 1 ! ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 password cisco login ! no process cpu extended no process cpu autoprofile hog ntp clock-period 17180176 ntp server 172.31.10.150 prefer ! endAdditional References
The following sections provide references related to the SIP: CLI for Caller ID When Privacy Exists feature.
Related Documents
Standards
MIBs
RFCs
Technical Assistance
Command Reference
This section documents the following new and modified commands:
clid (dial-peer)
To control the presentation and use of calling-line ID (CLID) information, use the clid command in dial-peer configuration mode. To remove CLID controls, use the no form of this command.
clid {network-number number [second-number strip] | network-provided | overrider dnis | restrict | strip [name | pi-restrict [all]] | substitute name}
no clid {network-number number [second-number strip] | network-provided | overrider dnis | restrict | strip [name | pi-restrict [all]] | substitute name}
Syntax Description
Command Default
No default behavior or values
Command Modes
Dial-peer configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
The override rdnis keywords are supported only for POTS dial peers.
CLID is the collection of information about the billing telephone number from which a call originated. The CLID value might be the entire phone number, the area code, or the area code plus the local exchange. It is also known as caller ID. The various keywords to this command manage the presentation, restriction, or stripping of the various CLID elements.
The clid network-number command sets the presentation indicator to "y" and the screening indicator to "network-provided." The second-number strip keyword strips from the H.225 source-address field the original calling-party number, and is valid only if a network number was previously configured.
The clid override rdnis command overrides the CLID with the RDNIS if it is available.
The clid restrict command causes the calling-party number to be present in the information element, but the presentation indicator is set to "n" to prevent its presentation to the called party.
The clid strip command causes the calling-party number to be null in the information element, and the presentation indicator is set to "n" to prevent its presentation to the called party.
Examples
The following example sets the calling-party network number to 98765 for POTS dial peer 4321:
Router(config)# dial-peer voice 4321 potsRouter(config-dial-peer)# clid network-number 98765An alternative method of accomplishing this result is to enter the second-number strip keywords as part of the clid network-number command. The following example sets the calling-party network number to 56789 for VoIP dial peer 1234 and also prevents the second network number from being sent:
Router(config)# dial-peer voice 1234 voipRouter(config-dial-peer)# clid network-number 56789 second-number stripThe following example overrides the calling-party number with RDNIS if available:
Router(config-dial-peer)# clid override rdnisThe following example prevents the calling-party number from being presented:
Router(config-dial-peer)# clid restrictThe following example removes the calling-party number from the CLID information and prevents the calling-party number from being presented:
Router(config-dial-peer)# clid stripThe following example strips the name from the CLID information and prevents the name from being presented:
Router(config-dial-peer)# clid strip nameThe following example strips the calling party number when PI is set to restrict clid strip from the CLID information and prevents the calling party number from being presented:
Router(config-dial-peer)# clid strip pi-restrictThe following example strips calling party name and number when the PI is set to the restrict all clid strip from the CLID information and prevents the calling party name and number from being presented:
Router(config-dial-peer)# clid strip pi-restrict allThe following example substitutes the calling party number into the display name:
Router(config-dial-peer)# clid substitute nameThe following example allows you to set the screening indicator to reflect that the number was provided by the network:
Router(config-dial-peer)# clid network-providedRelated Commands
clid (voice-service-voip)
Passes the network-provided ISDN numbers in an ISDN calling party information element screening indicator field, removes the calling party name and number from the calling-line identifier in voice service voip configuration mode, or allows a presentation of the calling number by substituting for the missing Display Name field in the Remote-Party-ID and From headers.
clid {network-provided | strip pi-restrict all | substitute name}
no {clid network-provided | strip pi-restrict all | substitute name}
Syntax Description
Command Default
The clid (voice-service-voip) command passes along user-provided ISDN numbers in an ISDN calling party information element screening indicator field.
Command Modes
Voice-service-VoIP configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use the clid network-provided command to pass along network-provided ISDN numbers in an ISDN calling party information element screening indicator field.
Use the clid strip pi-restrict all command to remove the Calling Party Name and Calling Party Number from the CLID.
Use the clid substitute name command to allow a presentation of the Display Name field in the Remote-Party-ID and From headers. The Calling Number is substituted for the Display Name field.
Examples
The following passes along network-provided ISDN numbers in an ISDN calling party information element screening indicator field:
Router(config)# clid network-providedThe following passes along user-provided ISDN numbers in an ISDN calling party information element screening indicator field:
Router(config)# no clid network-providedThe following removes the calling party name and number from the calling-line identifier (CLID):
Router(config)# clid strip pi-restrict allThe following does not remove the calling party name and number from the CLID:
Router(config)# no clid strip pi-restrict allThe following allows the presentation of the calling number to be substituted for the missing Display Name field in the Remote-Party-ID and From headers:
Router(config)# clid substitute nameThe following disallows the presentation of the calling number to be substituted for the missing Display Name field in the Remote-Party-ID and From headers:
Router(config)# no clid substitute nameRelated Commands
clid (dial-peer)
Controls the presentation and use of CLID information in dial-peer configuration mode.
Copyright © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.