Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
Prerequisites for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
Restrictions for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
Information About the Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones Feature
How to Configure Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
Configuring Cisco Text Relay Globally
Configuring Cisco Text Relay for a Specific Dial Peer (H.323 and SIP Only)
Verifying and Troubleshooting Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
Configuration Examples for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
Global Settings for Cisco Text Relay: Example
Dial-Peer Settings for Cisco Text Relay: Example
Feature Information for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
First Published: February 27, 2006Last Updated: December 13, 2006The Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones (Cisco Text Relay) feature implements a mechanism for reliable transport of teletype text phone (TTY) signals over VoIP calls. TTY text phones, also known as telecommunication devices for the deaf (TDD), are specialized phones that enable people who are deaf, hard of hearing, or speech-impaired to communicate over time-division multiplex (TDM) or IP networks by allowing them to type messages to one another instead of, or in addition to, talking and listening.
Cisco Text Relay is based on the proposed ITU V.151 (V.ToIP) standard. Cisco Text Relay leverages Audio/T.140, which means text characters are carried over the same Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) stream as voice (similar to the way dual tone multifrequency (DTMF) characters are carried in the RTP stream [RFC 2833]). Cisco Text Relay has minimal impact on bandwidth because the text characters are transported efficiently in the RTP stream. There is also a configurable redundancy option enabling TTY to run reliably in demanding network conditions.
Finding Feature Information in This Module
Your Cisco IOS software release may not support all of the features documented in this module. To reach links to specific feature documentation in this module and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, use the "Feature Information for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones" section.
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
•
Restrictions for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
•
Information About the Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones Feature
•
How to Configure Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
•
Configuration Examples for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
•
Feature Information for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text PhonesFeature Information for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
Prerequisites for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
To enable the Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones feature, you must do the following:
•
Establish a working H.323, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP), or Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) network for voice calls.
•
Ensure that you have a Cisco IOS image that supports Cisco Text Relay.
•
Use text phones that support TIA-825-A, A Frequency Shift Keyed Modem for Use on the Public Switched Telephone Network, the basic standard defining the Baudot TTY.
Restrictions for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
Restrictions for Cisco Text Relay are as follows:
•
The Cisco Text Relay option must be configured on both the terminating and originating gateways.
•
The text relay RTP payload type configuration must match on the terminating and originating gateways in order for TTY characters to be transmitted across the VoIP network.
•
Cisco Text Relay supports Baudot 45.45 and Baudot 50 TTY modulations only. Any other TTY modulation is treated as a normal voice signal.
•
Cisco Text Relay does not support third-party gateways.
•
The voice interface cards and platforms supported by the Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones feature in Cisco IOS releases 12.4(6)T and 12.4(4)XC are listed in Table 1.
Information About the Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones Feature
To configure the Cisco Text Relay feature, you should understand the following concepts:
TTY Text Phones
A TTY text phone is a text communication device that allows people with hearing or speech disabilities to use the telephone. TTY text phones have neither a handshake procedure at the beginning of a call nor a carrier tone during the call. This limits the transmission speed but permits TTY tones, DTMF signals (touch tones), and voice to be intermixed on the same call. This also allows TTY calls to be put on hold and to be transferred, like voice calls.
Each TTY text character consists of a sequence of seven individual tones:
•
The start tone at 1800 Hz.
•
A series of five tones (at either 1400 Hz or 1800 Hz) that specifies the character.
•
A stop tone at 1400 Hz. The stop tone separates one character from the next.
The first six tones are each 22 ms in duration for Baudot 45.45, 20 ms for Baudot 50, and the stop tone is 33 to 44 ms in duration. This equates to 165 ms per TTY text character, or six characters per second.
TTY text phones operate in half duplex. Users must take turns transmitting and cannot interrupt each other. The TTY text phones have a special key called go ahead, which tells the other user to type.
Text over IP
Text over IP (ToIP) is the transport of analog-modulated signals generated by TTY text phones over an IP network. In a voice network, ToIP is the transport of text characters from a legacy text phone (TTY device) connected to a public switched telephone network (PSTN) gateway through the Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) port or through an acoustic coupler.
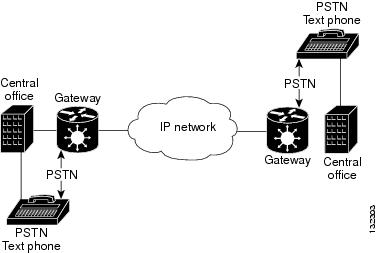
Figure 1 shows a typical ToIP network.
Figure 1 Typical Text over IP Network
Real-time text over IP networks can transmit one character at a time bidirectionally, providing real-time communication, like voice or video systems that transport streaming media over IP.
Cisco Text Relay
Text relay is part of the voice call and is configured as an additional capability during the voice call setup. Because there is no handshake procedure when TTY text phones are used, text relay does not require a call agent or Cisco CallManager to operate in a voice network. During the call setup, Cisco IOS software instructs the DSP with the text relay parameters and modulations.
The difference between text relay and the text over G.711 audio codec is that with text relay, the tones are translated into characters. In text over G.711, the text is transported as tones. Text relay also has a better packet loss recovery rate.
Cisco Text Relay allows you to configure the text relay parameters on the gateway. Both the originating and terminating gateways must have text relay enabled for this feature to operate, and the payload types must match. Text relay calls are treated like DTMF relay, encapsulated into an RTP packet with a configured static or dynamic payload type, and sent to the other gateway. The configured text relay commands hold for the duration of the call.
Cisco Text Relay supports:
•
PSTN-to-IP-to-PSTN networks, with connections from a PSTN text phone to a PSTN text phone.
•
Baudot 45.45 and Baudot 50 TTY modulations.
•
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) RFC 4351. Cisco Text Relay is partially compliant with the ITU V.151 recommendation.
•
High-complexity, medium-complexity, and flex-complexity voice card configurations.
The support of all voice codecs saves bandwidth, and the redundancy level option repeats the data for redundancy and lowers the risk of packet loss, which improves the quality of the text messages.
How to Configure Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
This section contains the following procedures:
•
Configuring Cisco Text Relay Globally
•
Configuring Cisco Text Relay for a Specific Dial Peer (H.323 and SIP Only)
Configuring Cisco Text Relay Globally
For MGCP configurations, Cisco Text Relay is configured globally. For H.323 and SIP configurations, Cisco Text Relay can be configured at two levels:
•
Under voice service configuration mode—This configuration is the global, or system-wide, configuration that is applied to any VoIP call on the gateway. The default for voice service configuration mode is no text relay.
•
Under dial peer voice configuration mode for VoIP dial peers—This configuration applies only to calls that match a specific dial peer. The default dial peer voice configuration is no text relay. See the "Configuring Cisco Text Relay for a Specific Dial Peer (H.323 and SIP Only)" section.
The two configuration tasks can be used separately or together. If both are configured, the dial peer voice configuration overrides the global configuration.
To configure Cisco Text Relay parameters globally for H.323, SIP, SCCP, and MGCP, perform the following task.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
voice service voip
4.
text relay protocol cisco
5.
text relay rtp {[payload-type {value | default}] [redundancy level] | redundancy level}
6.
text relay modulation {baudot45.45 | baudot50} {autobaud-on | autobaud-off}
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Cisco Text Relay for a Specific Dial Peer (H.323 and SIP Only)
To configure Cisco Text Relay for a specific dial peer for H.323 and SIP, complete the following task.
Note
When Cisco Text Relay is configured for a specific dial peer, the dial peer voice configuration takes precedence over the global configuration.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
dial-peer voice tag voip
4.
text relay protocol [cisco | system]
5.
text relay rtp {[payload-type {value | default}] [redundancy level] | redundancy level}
6.
text relay modulation {baudot45.45 | baudot50} {autobaud-on | autobaud-off}
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying and Troubleshooting Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
Before using debug or show commands to troubleshoot Cisco Text Relay, be sure of the following:
•
You can complete a voice call.
•
Cisco Text Relay is configured on both the originating and terminating gateways.
•
Both the originating and terminating gateways have the same payload type number and codec parameters.
Tip
Try configuring a different text relay RTP payload type. Another application might be using the configured payload-type.
For troubleshooting, steps 1 and 2 can be used to troubleshoot the Cisco Text Relay configuration. To obtain information about the performance of the configuration, steps 3 through 8 can be used to display information about the history, status, and statistics for the Cisco Text Relay configuration.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
debug voip rtp session text-relay
2.
debug voip vtsp session
3.
show call active voice brief id called-number
4.
show call history voice
5.
show dial peer voice
6.
show mgcp
7.
show port operational status
8.
show voice call status
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
debug voip rtp session text-relay
This command displays specific session debug information for text relay.
Step 2
debug voip vtsp session
This command displays information that traces how the router interacts with the digital signal processor (DSP) based on the signaling indications from the signaling stack and requests from the application.
Step 3
show call active voice brief id called-number
This command displays a truncated version of information for the call with the specified identifier.
Step 4
show call history voice
This command displays the call history table for voice calls.
Step 5
show dial-peer voice
This command displays information for voice dial peers.
Step 6
show mgcp
This command provides high-level administrative information about the values configured for MGCP parameters on the router.
Step 7
show port operational status
This command displays the statistics for the operational status of a specific port or port range. The port should have an associated active session when the command is executed.
Step 8
show voice call status
This command displays the call status for active calls on the voice ports of the router.
Configuration Examples for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
This section provides the following configuration examples:
•
Global Settings for Cisco Text Relay: Example
•
Dial-Peer Settings for Cisco Text Relay: Example
Global Settings for Cisco Text Relay: Example
In the following example, the global configuration shows that the text relay cisco protocol is enabled and that the RTP redundancy level is changed from the default to level 3. The configuration for dial-peer 2000 shows that the redundancy level setting of 1 is different from, and takes precedence over, the global setting of 3.
version 12.3service timestamps debug datetime msecservice timestamps log datetime msecno service password-encryption!hostname 2691!boot-start-markerboot system flash:c2691-ipvoice-mz.0404boot-end-marker!logging buffered 100000 debuggingenable password lab!no aaa new-model!resource manager!memory-size iomem 25clock timezone PST -8clock summer-time PDT recurringno network-clock-participate slot 1voice-card 1codec complexity highdspfarm!ip subnet-zeroip cef!!no ip dhcp use vrf connected!!no ip domain lookupno ftp-server write-enableisdn switch-type primary-qsig!voice service voiptext relay protocol ciscotext relay rtp redundancy 3text relay modulation baudot50 autobaud-offfax protocol pass-through g711ulawsip!controller T1 1/0framing sflinecode ami!controller T1 1/1framing sflinecode ami!interface FastEthernet0/0ip address 10.0.0.4 255.255.0.0duplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet0/1no ip addressshutdownduplex autospeed auto!ip default-gateway 10.2.0.1ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.2.0.8!no ip http server!control-plane!dial-peer voice 2000 voipmodem relay nse codec g711ulaw redundancy gw-controlledtext relay protocol ciscotext relay rtp redundancy 1fax rate disablefax protocol pass-through g711alaw!!line con 0exec-timeout 0 0line aux 0line vty 0 1exec-timeout 0 0password labloginline vty 2 4login!ntp clock-period 17180770ntp server 192.168.254.253 prefer!endDial-Peer Settings for Cisco Text Relay: Example
The following examples shows the text relay configuration on dial-peer 2000:
Router# show dial-peer voice 2000VoiceOverIpPeer2000peer type = voice, information type = voice,description = `',tag = 2000, destination-pattern = `',answer-address = `', preference=0,CLID Restriction = NoneCLID Network Number = `'CLID Second Number sentCLID Override RDNIS = disabled,source carrier-id = `', target carrier-id = `',source trunk-group-label = `', target trunk-group-label = `',numbering Type = `unknown'group = 2000, Admin state is up, Operation state is down,incoming called-number = `', connections/maximum = 0/unlimited,DTMF Relay = disabled,modem transport = relay, nse, payload-type = 100, codec = g711ulaw, redundancy, gateway-controlled,URI classes:Incoming (Called) =Incoming (Calling) =Destination =huntstop = disabled,in bound application associated: 'DEFAULT'out bound application associated: ''dnis-map =permission :bothincoming COR list:maximum capabilityoutgoing COR list:minimum requirementTranslation profile (Incoming):Translation profile (Outgoing):incoming call blocking:translation-profile = `'disconnect-cause = `no-service'advertise 0x40 capacity_update_timer 25 addrFamily 4 oldAddrFamily 4type = voip, session-target = `',technology prefix:settle-call = disabledip media DSCP = ef, ip signaling DSCP = af31,ip video rsvp-none DSCP = af41,ip video rsvp-pass DSCP = af41ip video rsvp-fail DSCP = af41,UDP checksum = disabled,session-protocol = cisco, session-transport = system,req-qos = best-effort, acc-qos = best-effort,req-qos video = best-effort, acc-qos video = best-effort,req-qos audio def bandwidth = 64, req-qos audio max bandwidth = 0,req-qos video def bandwidth = 384, req-qos video max bandwidth = 0,RTP dynamic payload-type values: NTE = 101Cisco: NSE=100, fax=96, fax-ack=97, dtmf=121, fax-relay=122CAS=123, TTY=119, ClearChan=125, PCM switch over u-law=0,A-law=8RTP comfort noise payload-type = 19fax rate = disable, payload size = 20 bytesfax protocol = pass-throughfax-relay ecm enableFax Relay SG3-to-G3 Enabled (by system configuration)fax NSF = 0xAD0051 (default)codec = g729r8, payload size = 20 bytes,text relay = enabledtty protocol = ciscotty rtp payload-type = 119 redundancy = 1tty mod = baudot50 autobaud-offMedia Setting = flow-through (global)Expect factor = 10, Icpif = 20,Playout Mode is set to adaptive,Initial 60 ms, Max 250 msPlayout-delay Minimum mode is set to default, value 40 msFax nominal 300 msMax Redirects = 1, signaling-type = cas,VAD = enabled, Poor QOV Trap = disabled,Source Interface = NONEvoice class sip url = system,voice class sip rel1xx = system,redirect ip2ip = disabledprobe disabled,voice class perm tag = `'Time elapsed since last clearing of voice call statistics neverConnect Time = 0, Charged Units = 0,Successful Calls = 0, Failed Calls = 0, Incomplete Calls = 0Accepted Calls = 0, Refused Calls = 0,Last Disconnect Cause is "",Last Disconnect Text is "",Last Setup Time = 0.Additional References
The following sections provide references related to the Cisco Text Relay feature.
Related Documents
Secure TTY (Secure RTP)
Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS MGCP Gateways
Cisco IOS command references
•
Cisco IOS Debug Command Reference
Cisco MGCP functionality
•
MGCP 1.0 Including NCS 1.0 and TGCP 1.0 Profiles
Cisco SIP functionality
•
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for VoIP
•
Session Initiation Protocol Gateway Call Flows
Standards
MIB
RFCs
RFC 2198
RTP Payload for Redundant Audio Data
RFC 2793bis
RTP Payload for Text Conversation
RFC 4351
RTP Payload for Text Conversation Interleaved in an Audio Stream
Technical Assistance
Command Reference
This section documents modified commands only.
debug voip rtp
To enable debugging for Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) named event packets, use the debug voip rtp command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging output, use the no form of this command.
debug voip rtp {error | session [conference | dtmf-relay | event | multicast | named-event [payload-type] | nse | text-relay] | packet [callid id-number packet-number | remote-ip ip-address remote-port port-number packet-number]}
no debug voip rtp
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
This command severely impacts performance and should be used only for single-call debug capture.
Examples
The following example shows debugging output for the debug voip rtp session named-event command. The example is for a gateway that sends digits 1, 2, 3, then receives digits 9,8,7. The payload type, event ID, and additional packet payload are shown in each log.
The first three packets indicate the start of the tone (initial packet and two redundant). The last three packets indicate the end of the tone (initial packet and two redundant). The packets in between are refresh packets that are sent every 50 milliseconds (without redundancy).
Router# debug voip rtp session named-event00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:1 Pkt:03 00 00 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:1 Pkt:03 00 00 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:1 Pkt:03 00 00 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:1 Pkt:03 01 90 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:1 Pkt:03 03 20 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:1 Pkt:03 04 B0 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:1 Pkt:83 04 C8 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:1 Pkt:83 04 C8 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:1 Pkt:83 04 C8 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:2 Pkt:03 00 00 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:2 Pkt:03 00 00 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:2 Pkt:03 00 00 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:2 Pkt:03 01 90 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:2 Pkt:03 03 20 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:2 Pkt:03 04 B0 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:2 Pkt:83 05 18 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:2 Pkt:83 05 18 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:2 Pkt:83 05 18 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:3 Pkt:03 00 00 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:3 Pkt:03 00 00 <<<Rcv>00:09:29: Pt:99 Evt:3 Pkt:03 00 00 <<<Rcv>00:09:30: Pt:99 Evt:3 Pkt:03 01 90 <<<Rcv>00:09:30: Pt:99 Evt:3 Pkt:03 03 20 <<<Rcv>00:09:30: Pt:99 Evt:3 Pkt:03 04 B0 <<<Rcv>00:09:30: Pt:99 Evt:3 Pkt:03 06 40 <<<Rcv>00:09:30: Pt:99 Evt:3 Pkt:83 06 80 <<<Rcv>00:09:30: Pt:99 Evt:3 Pkt:83 06 80 <<<Rcv>00:09:30: Pt:99 Evt:3 Pkt:83 06 80 <<<Rcv>00:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:9 Pkt:02 00 0000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:9 Pkt:02 00 0000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:9 Pkt:02 00 0000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:9 Pkt:02 01 9000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:9 Pkt:02 03 2000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:9 Pkt:02 04 B000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:9 Pkt:02 06 4000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:9 Pkt:82 06 5800:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:9 Pkt:82 06 5800:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:9 Pkt:82 06 5800:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:8 Pkt:02 00 0000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:8 Pkt:02 00 0000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:8 Pkt:02 00 0000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:8 Pkt:02 01 9000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:8 Pkt:02 03 2000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:8 Pkt:02 04 B000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:8 Pkt:02 06 4000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:8 Pkt:82 06 9000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:8 Pkt:82 06 9000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:8 Pkt:82 06 9000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:7 Pkt:02 00 0000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:7 Pkt:02 00 0000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:7 Pkt:02 00 0000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:7 Pkt:02 01 9000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:7 Pkt:02 03 2000:09:31: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:7 Pkt:02 04 B000:09:32: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:7 Pkt:02 06 4000:09:32: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:7 Pkt:82 06 5800:09:32: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:7 Pkt:82 06 5800:09:32: <Snd>>> Pt:99 Evt:7 Pkt:82 06 58The following example shows debugging output for the debug voip rtp session text-relay command:
Router# debug voip rtp session text-relayPt:119 Evt:0 4 247 37 128 Cnt:F7 4B <Snd>>>Related Commands
text relay protocol
Configures the system-wide protocol type for text packets transmitted between gateways.
text relay rtp
Configures the RTP payload type and redundancy level.
text relay modulation
To configure the teletype text phone (TTY) modulation used on the gateway for Cisco text relay for Baudot text phones, use the text relay modulation command in dial peer voice configuration mode or voice service configuration mode. To disable text relay modulation, use the no form of this command.
text relay modulation {baudot45.45 | baudot50} {autobaud-on | autobaud-off}
no text relay modulation
Syntax Description
Command Default
The TTY modulation is baudot45.45 autobaud-on.
Command Modes
Dial peer voice configuration
Voice service configurationCommand History
Usage Guidelines
You must select a baud rate and enable or disable the autobaud functionality on the DSP.
Use this command in voice service configuration mode to set the TTY modulation globally. A global configuration is the system-wide configuration that is applied to any VoIP call on the gateway.
Use this command in dial peer voice configuration mode to set the TTY modulation for calls that match a specific dial peer. The dial peer voice configuration takes precedence over the global configuration.
Examples
The following example shows how to globally set the text relay TTY modulation to Baudot 50:
Router(config)# voice service voip
Router(config-voi-serv)# text relay modulation baudot50 autobaud-off
The following example shows how to set the text relay TTY modulation to Baudot 50 for calls that match a specific dial peer:
Router(config)# dial-peer voice 2000 voip
Router(config-dial-peer)# text relay modulation baudot50 autobaud-off
Related Commands
text relay protocol
Configures the system-wide protocol type for text packets transmitted between gateways.
text relay rtp
Configures the RTP payload type and redundancy level.
text relay protocol
To enable Cisco text relay for Baudot text phones, use the text relay protocol command in dial peer voice configuration mode or voice service configuration mode. To disable text relay capabilities, use the no form of this command.
text relay protocol [cisco | system]
no text relay protocol
Syntax Description
cisco
(Optional) Uses the Cisco proprietary text relay protocol.
system
(Optional; dial peer voice configuration only) Uses the global configuration settings.
Command Default
The text relay protocol is disabled.
Command Modes
Dial-peer configuration
Voice-service configurationCommand History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command in voice-service configuration mode to enable text relay globally for H.323, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP), and Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP). A global configuration is the system-wide configuration that is applied to any VoIP call on the gateway.
Use this command in dial peer voice configuration mode to enable text relay for calls that match a specific dial peer. The dial peer voice configuration takes precedence over the global configuration.
Examples
The following example shows how to enable text relay for all VoIP calls on the gateway:
Router(config)# voice service voip
Router(config-voi-serv)# text relay protocol ciscoThe following example shows how to enable text relay for calls that match a specific dial peer:
Router(config)# dial-peer voice 2000 voip
Router(config-dial-peer)# text relay protocol cisco
Related Commands
text relay modulation
Configures the TTY modulation on the gateway.
text relay rtp
Configures the RTP payload type and redundancy level.
text relay rtp
To configure the Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) payload type and redundancy level for Cisco text relay for Baudot text phones, use the text relay rtp command in dial peer voice configuration mode or voice service configuration mode. To disable the text relay RTP payload type and redundancy level, use the no form of this command.
text relay rtp {[payload-type {value | default}] [redundancy level] | redundancy level}
no text relay rtp
Syntax Description
Command Default
Text relay RTP is disabled.
Command Modes
Dial peer voice configuration
Voice service configurationCommand History
Usage Guidelines
When using the text relay rtp command, you can either configure the payload-type, or the redundancy level, or both.
•
Use this command in voice service configuration mode to set the RTP payload type and redundancy level globally for H.323, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP), and Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP). A global configuration is the system-wide configuration that is applied to any VoIP call on the gateway.
•
Use this command in dial-peer configuration mode to set the RTP payload type and redundancy level for calls that match a specific dial peer. The dial peer voice configuration takes precedence over the global configuration.
Examples
The following example shows how to globally configure text relay RTP payload type 117 and redundancy level 2:
Router(config)# voice service voip
Router(config-voi-serv)# text relay rtp payload-type 117 redundancy 2
The following example shows how to configure the default text relay RTP payload type and redundancy level 1 for calls that match a specific dial peer:
Router(config)# dial-peer voice 2000 voip
Router(config-dial-peer)# text relay rtp payload-type default redundancy 1
Related Commands
text relay modulation
Configures the TTY modulation on the gateway.
text relay protocol
Configures the system-wide protocol type for text packets transmitted between gateways.
Feature Information for Cisco Text Relay for Baudot Text Phones
Table 2 lists the release history for this feature.
Cisco IOS software images are specific to a Cisco IOS software release, a feature set, and a platform. Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Note
Table 2 lists only the Cisco IOS software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given Cisco IOS software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that Cisco IOS software release train also support that feature.
Glossary
ANS tone—answer tone. Also called CED tone. A 2100-Hz tone used to disable echo suppression for data transmission.
ANSam—A modified answer tone sent by V.8-capable equipment.
CM—call menu signal. A V.8 signal transmitted from the call DCE to indicate modulation modes available in the call DCE. CM consists of a repeating sequence of bits, modulated using V.21 low-band channel. See joint menu signal (JM).
DSMP—distributed stream media processor. The software component that controls the DSP on behalf of the media service provider that handles conference calls. The DSMP also manages packet transmission and reception in fast switching.
HPI—host port interface. The interface used to communicate with TI DSPs.
JM—joint menu signal. A V.8 signal transmitted from the answer DCE to indicate modulation modes available jointly in the call and answer DCEs. JM consists of a repeating sequence of bits, modulated using V.21 high-band channel. See call menu signal (CM).
TDD—telecommunication device for the deaf. Phones that enable those who are deaf, hard of hearing, or speech-impaired to communicate over TDM. See TTY.
text relay—Text payload that is encapsulated into RTP packets with a negotiated payload type and sent over an IP network as part of a voice call. Text relay is controlled by the voice gateways.
ToIP—Text over IP. The transport of analog modulated signals generated by PSTN text telephones over an IP Network.
TTY—text telephones or teletype phones. Phones that enable those who are deaf, hard of hearing, or speech-impaired to communicate over TDM. See TDD.
Note
Refer to Internetworking Terms and Acronyms for terms not included in this glossary.
Copyright © 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.