Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways
Benefits of Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways
Cisco IOS H.323 Gateway Behavior
Cisco IOS IP-to-IP Gateway Behavior
Configuring Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption for Secure Voice Calls Globally
Configuring Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption for Secure Dial-Peer Calls
Configuration Examples for Secure Global and Dial Peer Calls
Global and Dial Peer SRTP Calls: Example
Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways
First Published: 2006
Last Updated: June 11, 2009The Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways feature provides authentication, integrity, and encryption of voice media and call control signaling for H.323 protocol-based voice gateways.
Finding Feature Information in This Module
Your Cisco IOS software release may not support all of the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To reach links to specific feature documentation in this module and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, use the "Feature Information for Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways" section.
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Contents
•
Configuration Examples for Secure Global and Dial Peer Calls
Prerequisites for Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways
Make sure that the following tasks have been completed before configuring the Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways feature:
•
Cisco IOS H.323 protocol is configured.
•
Cisco IOS gateways have the prerequisite Cisco IOS images installed. Voice security features are delivered on Advanced IP Services or Advanced Enterprise Services images.
•
IP security (IPSec) is configured on the Cisco IOS gateway. For more information on configuring Cisco IOS-based (software) IPSec, refer to the following:
–
IPSec Considerations and Recommendations
–
Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide, Release 12.4
–
Cisco IOS Security Command Reference, Release 12.4
•
Cisco CallManager 5.0 or a later release is running if the Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways feature is deployed in a Cisco CallManager network. For more information on configuring Cisco CallManager, refer to the document Cisco CallManager Security Guide, Release 5.0.
Restrictions for Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways
The following secure encrypted services are not supported in Cisco IOS Release 12.4(6)T1:
•
Voice security during conferencing, transcoding, and music-on-hold.
•
Secure Cisco IOS SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) gateways and call flows.
•
H.323 endpoints other than those listed in Table 1.
•
Interworking scenarios on the Cisco IOS IP-to-IP gateway, including:
–
Fast start to slow start signaling
–
Slow start to fast start signaling
•
The call failure retry (rotary) feature on the Cisco IOS IP-to-IP gateway.
•
Voice security for IVR applications, such as automated attendant, where, even though the endpoint is Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP) capable, voice is streamed to the gateway without using a digital signal processor (DSP).
Table 1 lists supported gateways, network modules, and codecs for voice security features.
Information About Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways
To configure the Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways feature, you should understand the following concepts:
•
Benefits of Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways
Benefits of Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways
•
Provides privacy and confidentiality for voice calls
•
Protects against voice security violations
•
Facilitates the replacement of traditional time-division multiplexing (TDM) telephony systems with IP systems
Feature Design of Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways
In a typical communications network, there is a risk of security breaches affecting voice communications over the IP network. The Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS MGCP Gateways feature provided voice security features to address requirements for privacy, integrity, and confidentiality of voice conversations for Cisco IOS Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) gateways. With the new Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways feature, Cisco extends voice security features to Cisco IOS H.323 protocol-based gateways, and expands the number of network modules that support media authentication and encryption.
The Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways feature supports the following capabilities between gateways:
•
Gateway to gateway call control authentication and encryption using IPSec.
•
Media encryption and authentication of voice streams using SRTP.
•
Exchange of RTP Control Protocol (RTCP) information using Secure RTCP.
•
SRTP to RTP fallback for calls between secure and nonsecure endpoints. You can configure secure call fallback either globally or by dial peer.
•
Cisco IOS IP-to-IP gateway interoperation with secure Cisco IOS H.323 gateways.
Security Technologies
The Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways feature provides secure IP telephony signaling and media to achieve secure voice calls. Cisco implements voice security over the IP telephony network by establishing and maintaining authenticated communications using the following security technologies:
•
Signaling authentication validates that no tampering has occurred with signaling packets during transmission.
•
Encryption, the process of converting clear-text data into enciphered data, provides data integrity and authentication.
•
IPSec, a standards-based set of security protocols and algorithms, ensures that signaling information such as DTMF digits, passwords, personal identification numbers (PINs), and encryption keys that is sent between voice gateways and gatekeepers is encrypted.
•
Media encryption using standards-based SRTP ensures that media streams between supported devices are secure.
•
Cisco IOS H.323 supports the AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_32 cryptographic suite, which includes the AES-128-countermode encryption algorithm and the Hashed Message Authentication Codes (HMAC) Secure Hash Algorithm1 (SHA1) authentication algorithm.
•
Cisco IOS H.323 supports H.235.8 compliant procedures for the signalling, negotiation and transport of the SRTP cryptographic keys, authentication and encryption algorithm identifiers and other session parameters between H.323 endpoints.
Note
Although you may enable media authentication and encryption without signaling encryption, Cisco discourages this practice. If the connection between gateways is not secure, media keys will be sent in clear text and your voice call will not be considered secure.
The following behaviors must be present for a voice call to be secure in the Cisco IOS H.323 IP telephony network:
•
The network modules, as listed in Table 1, and digital signal processor (DSP) associated with the TDM/analog call leg must be secure capable.
•
VoIP call leg security is enabled either globally or on a per-dial peer basis.
•
H.323 call setup generates encryption keys are carried to the remote end.
•
The terminating gateway (TGW) checks for secure capabilities of the DSP and indicates its capabilities to the originating gateway (OGW).
•
Once the OGW receives remote end capabilities indicating the TGW is secure capable, the call is secure.
If the previous behaviors do not occur, the call is not secure, and depending on the fallback policy configured, the call is disconnected.
Both IPSec and SRTP must be enabled for voice call security. Possible interactions of IPSec and SRTP and the resulting outcomes are listed in Table 2.
Note
We strongly recommend that you first establish an IPSec connection between gateways before you configure security using SRTP. Otherwise, media keys will be sent in clear text and your voice call will not be considered secure.
Cisco IOS H.323 Gateway Behavior
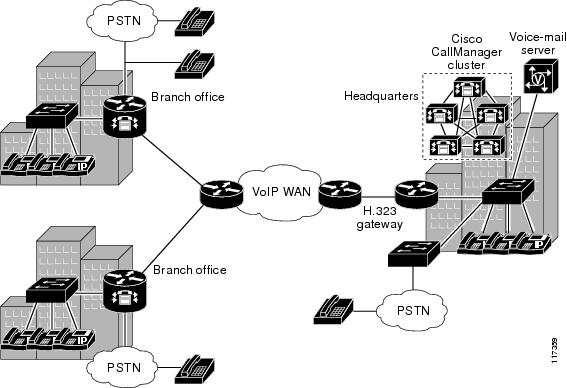
In order to secure voice call control and signaling, IPSec is configured on both gateways and gatekeeper (GK), if any, with a preshared key. Upon bootup, the gateway and GK, if any, authenticate each other by preshared key. After successful authentication, IPSec starts secured traffic in tunnel mode. After IPSec is started, the gateway sends Registration, Admission, and Status (RAS) messages to the GK through secured IPSec tunnel. H.225 call control messages between gateways flow through the secured IPSec channel established between them. IPSec configuration on both gateways, OGW and TGW, is required before voice calls can be placed. Cisco recommends hardware Virtual Private Network (VPN) on the gateway for improved performance. After the IPSec tunnel is established, all call control signaling H.225 and H.245 packets between gateways go through the secured IPSec tunnel. OGW and TGW then determine if an endpoint is SRTP and SRTCP capable and send this information to the other end.
Figure 1 shows a typical topology where voice security features are deployed.
Figure 1 Voice Security Features in the IP Telephony Network
Cisco IOS IP-to-IP Gateway Behavior
The Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways feature interoperates with the Cisco IOS IP-to-IP gateway to provide voice security features. An IP-to-IP gateway (IPIPGW), also known as a border element or session border controller, facilitates connectivity between independent VoIP networks by enabling H.323 VoIP and video conferencing calls from one IP network to another. The IPIPGW performs many of the same functions as a public switched telephone network (PSTN)-to-IP gateway, but typically joins two IP call legs, rather than a PSTN and an IP call leg. The Cisco Multiservice IP-to-IP Gateway feature is a special Cisco IOS software image that runs on Cisco multiservice gateway platforms. It provides a network-to-network interface point for billing, security, call admission control, quality of service, and signaling interworking.
When used in a secure H.323 deployment with Cisco IOS H.323 gateways, the IPIPGW supports secure calls in flow through and flow around mode. In flow through mode, SRTP packets are terminated and reorganized, and passed through the IPIPGW. Because only the User Datagram Protocol (UDP ) header is changed, and RTP packet contents are not decrypted and encrypted, no DSP resource is required. In flow around mode, RTP packets flow around and do not enter the IPIPGW. Signaling is fully terminated and reorganized in either mode.
The following IPIPGW features are not supported:
•
Secure transcoding and conferencing support on the IPIPGW using SRTP to RTP and vice versa
•
Fast start to slow start signaling and vice versa
•
H.323 to SIP network interconnection
For more information on the Cisco IOS IP-to-IP gateway, refer to the Cisco Multiservice IP-to-IP Gateway document.
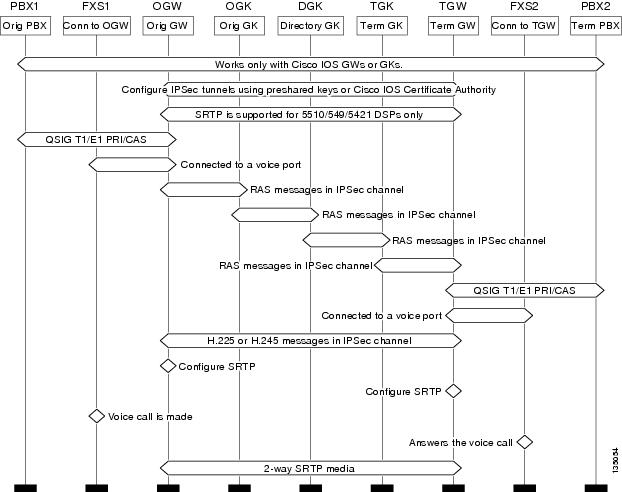
Figure 2 shows a toll bypass topology diagram for secure voice call setup in an IPIPGW scenario. The following points summarize this configuration:
•
Configure IPSec tunnels between GW-GK and GW-GW, a prerequisite to protect the signaling channels. IPSec tunnels are terminated and reorganized hop by hop.
•
Configure SRTP at the OGW and TGW to protect the media. SRTP media is end to end.
•
When voice calls are made, calls will be secure per the configuration.
•
SRTP is supported on secure-capable DSPs and the associated network modules listed in Table 1.
Figure 2 Toll Bypass Topology Diagram
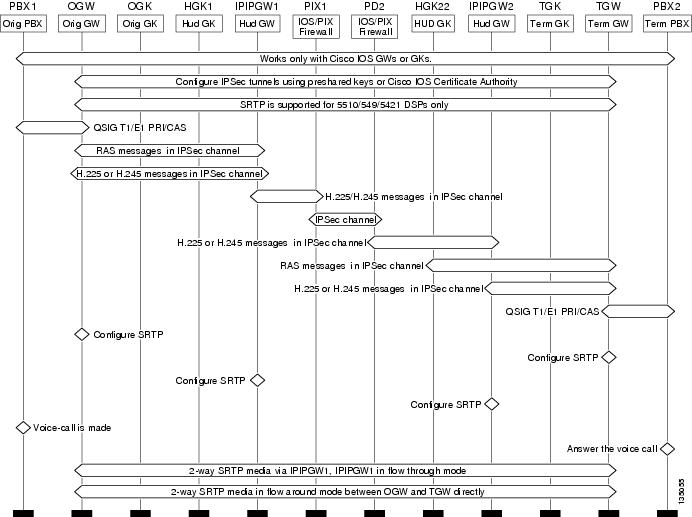
Figure 3 shows a topology diagram for secure voice call setup in an IPIPGW and Network Address Translation (NAT)/firewall scenario. The following points summarize this configuration:
•
Configure IPSec tunnels between GW-GK and GW-GW, IPIPGW-PIX, a prerequisite to protect the signaling channels. IPSec tunnels are terminated and reorganized hop by hop.
•
Configure SRTP at the OGW and TGW to protect the media. SRTP media is end to end.
•
When voice calls are made, calls will be secure per the configuration.
•
SRTP is supported on secure-capable DSPs and the associated network modules listed in Table 1.
Figure 3 IPIPGW and PIX Topology Diagram
How to Configure Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways
This section contains the following procedures:
•
Configuring Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption for Secure Voice Calls Globally, (required)
•
Configuring Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption for Secure Dial-Peer Calls, (required)
•
Verifying and Troubleshooting Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Secure Call Configuration, (optional)
Configuring Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption for Secure Voice Calls Globally
This task configures secure media authentication and encryption on the H.323 gateway. You can configure SRTP capability either globally or at the dial peer level; configuration in only one mode is necessary.
Prerequisites
We strongly recommend that you first establish an IPSec connection between gateways before you configure security using SRTP. Otherwise, media keys will be sent in clear text and your voice call will not be considered secure.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
voice service voip
4.
srtp [fallback]
5.
allow-connections from-type to to-type
6.
exitvoice-card slot
7.
codec complexity secure
8.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption for Secure Dial-Peer Calls
This task configures all calls for a given dial peer to go through in either secure or nonsecure mode. You can configure SRTP capability either at the dial peer level or globally; configuration in only one mode is necessary.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
dial-peer voice tag voip
4.
srtp [fallback | system]
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying and Troubleshooting Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Secure Call Configuration
This task verifies and troubleshoots secure call configuration.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
show running-config
2.
debug h245 srtp
3.
show voice call status
4.
show dial-peer voice number
Step 1
To verify the configuration, use the show running-config command. Sample output is located in the "Global and Dial Peer SRTP Calls: Example" section.
Step 2
Use the debug h245 srtp command to display SRTP information exchanged during H.225 and H.245 signaling.
Step 3
Use the show voice call status command to verify the status of encrypted and decrypted packets:
a.
Use the show voice call status command to display all voice ports and obtain the CallID of a specific call.
b.
Use the show voice call status call-id command to display encrypted and decrypted packets for the specified call.
Step 4
Use the show dial-peer voice number command to display SRTP and fallback configuration status for a specific VoIP dial peer.
Configuration Examples for Secure Global and Dial Peer Calls
This section provides the following configuration example:
•
Global and Dial Peer SRTP Calls: Example
Global and Dial Peer SRTP Calls: Example
The following ia a sample configuration of the Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways feature showing secure calls enabled globally on the originating gateway, without the capability to fall back to nonsecure mode:
Router# show running-config
Note
The following sample configuration does not allow a call to fall back to nonsecure mode, that is, a user cannot make nonsecure calls.
Building configuration...Current configuration : 2826 bytes!! Last configuration change at 15:23:32 UTC Sat Apr 20 2002!version 12.3service timestamps debug datetime msecservice timestamps log datetime msecno service password-encryptionservice internalservice sequence-numbers!hostname router_1!boot-start-markerboot-end-marker!logging buffered 6000000 debuggingenable password cisco!no network-clock-participate slot 1no network-clock-participate slot 2no network-clock-participate aim 0no network-clock-participate aim 1voice-card 1codec complexity securedspfarm!voice-card 2no dspfarm!no aaa new-modelip subnet-zeroip cef!no ip domain lookupip host dirt 10.1.1.129ip ips po max-events 100no ftp-server write-enableisdn switch-type primary-5essThe following lines show SRTP enabled and fallback to nonsecure mode is disabled at the global level:
voice service voipsrtpfax protocol pass-through g711ulawh323call start slow!!voice class codec 1codec preference 1 g711ulaw!voice class codec 2codec preference 1 g711ulawcontroller T1 1/0framing esfclock source internallinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-24!controller T1 1/1framing esflinecode b8zs!no crypto isakmp enable!interface Loopback0ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255!interface FastEthernet0/0no ip addressduplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet0/1ip address 10.4.127.2 255.255.0.0duplex autospeed auto!interface Serial1/0:23no ip addressisdn switch-type primary-5essisdn protocol-emulate networkisdn incoming-voice voiceno cdp enable!ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.4.0.1!ip http serverno ip http secure-servercontrol-plane!!!voice-port 1/0:23!voice-port 2/1/0connection plar 5550102!voice-port 2/1/1!voice-port 2/1/2!voice-port 2/1/3!!!!dial-peer cor custom!dial-peer voice 100 potsdestination-pattern 5550101incoming called-number 5550191direct-inward-dialport 1/0:23forward-digits all!dial-peer voice 101 voipdestination-pattern 5550191modem passthrough nse codec g711ulawvoice-class codec 1session target ipv4:10.4.127.4dtmf-relay rtp-nteno vad!dial-peer voice 102 voipdestination-pattern 5550102voice-class codec 1session target ipv4:10.4.127.4dtmf-relay rtp-nteno vaddial-peer voice 200 potsdestination-pattern 5550110incoming called-number 5550100port 2/1/1!dial-peer voice 201 voipdestination-pattern 5550010voice-class codec 1session target ipv4:10.4.127.4no vad!dial-peer voice 300 potsdestination-pattern 5550120incoming called-number 5550150port 2/1/2!dial-peer voice 301 voipdestination-pattern 5550150voice-class codec 1session target ipv4:10.4.127.4no vad!gatewaytimer receive-rtp 1200!!!!line con 0exec-timeout 0 0line aux 0line vty 0 4exec-timeout 30 0password ciscologin!ntp masterendThe following ia a sample configuration of the Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways feature showing SRTP enabled on an individual dial peer on the terminating gateway with no fallback to nonsecure calls:
Note
The following sample configuration does not allow a call to fall back to nonsecure mode; that is, a user cannot make nonsecure calls.
Router# show running-configBuilding configuration...config_dialpeer_srtp:52:voipPeerCfgSrtp: 0 srtpCurrent configuration : 1932 bytes!! Last configuration change at 04:20:50 UTC Mon Mar 25 2002!version 12.3service timestamps debug datetime msecservice timestamps log datetime msecno service password-encryptionservice sequence-numbers!hostname router_2!boot-start-markerboot-end-marker!logging buffered 6000000 debuggingenable password cisco!no network-clock-participate slot 1no network-clock-participate aim 0no network-clock-participate aim 1voice-card 1codec complexity securedspfarm!no aaa new-modelno ip subnet-zeroip cef!no ip domain lookupip ips po max-events 100no ftp-server write-enableisdn switch-type primary-5ess!voice service voiph323!!voice class codec 1codec preference 1 g711alaw!voice class codec 2codec preference 1 g711alaw!controller T1 1/0framing esfclock source line primarylinecode b8zspri-group timeslots 1-20,24!controller T1 1/1framing esfclock source internallinecode b8zs!no crypto isakmp enable!interface FastEthernet0/0no ip addressshutdownduplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet0/1ip address 10.4.127.3 255.255.0.0duplex autospeed auto!interface Serial1/0:23no ip addressno logging event link-statusisdn switch-type primary-5essisdn protocol-emulate networkisdn incoming-voice voiceno cdp enable!ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.4.0.1!ip http serverno ip http secure-server!!!control-plane!voice-port 1/0:23!dial-peer cor custom!dial-peer voice 100 potsdestination-pattern 5550101incoming called-number 5550191port 1/0:23prefix 5550101The following lines show SRTP is enabled with no fallback to nonsecure mode on dial peer 101:
dial-peer voice 101 voipdestination-pattern 5550101voice-class codec 1session target ipv4:10.4.127.4srtpno vad!gatewaytimer receive-rtp 1200!line con 0line aux 0line vty 0 4exec-timeout 30 0password ciscologin!ntp clock-period 17179218ntp server 10.4.127.2endThe following is a sample configuration of the Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways feature showing secure calls disabled on a Cisco IOS IP-to-IP gateway:
Note
The following sample configuration does not allow secure calls on dial peer 101; that is, a user cannot make secure calls.
Router# show running-configBuilding configuration...Current configuration : 2130 bytes!! Last configuration change at 04:20:47 UTC Mon Mar 25 2002!version 12.3service timestamps debug uptimeservice timestamps log uptimeno service password-encryptionservice sequence-numbers!hostname router_2!boot-start-markerboot system flash:c3745-ipvoice-mzboot-end-marker!logging buffered 6000000 debuggingenable password cisco!no network-clock-participate slot 2network-clock-participate slot 3no network-clock-participate aim 0network-clock-participate aim 1no aaa new-modelip subnet-zerono ip cef!ip ips po max-events 100no ftp-server write-enablevoice-card 2no dspfarm!The following lines show H.323 connections are enabled on a Cisco IOS IP-to-IP gateway:
voice service voipallow-connections h323 to h323h323!voice class codec 1codec preference 1 g711alaw!voice class codec 2codec preference 1 g711alaw!controller E1 3/0!controller E1 3/1!no crypto isakmp enable!interface FastEthernet0/0ip address 10.4.127.4 255.255.0.0no ip mroute-cacheload-interval 30duplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet0/1no ip addressshutdownduplex autospeed auto!interface FastEthernet3/0no ip addressshutdownduplex autospeed auto!ip default-gateway 10.4.0.1ip classlessip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.4.0.1!no ip http serverno ip http secure-server!control-plane!dial-peer cor custom!dial-peer voice 1 voipdescription OGW->TGW [H.323->H.323]voice-class codec 2incoming called-number 408....no vad!dial-peer voice 10 voipdescription OGW->TGW [H.323->H.323]destination-pattern 408....voice-class codec 2session target ipv4:10.4.127.3no vad!dial-peer voice 2 voipdescription TGW->OGW [H.323->H.323]voice-class codec 1incoming called-number 919....no vad!dial-peer voice 20 voipdescription TGW->OGW [H.323->H.323]destination-pattern 919....voice-class codec 1session target ipv4:10.4.127.2no vadThe following lines show that secure calls are not enabled on the individual dial peer, and there is no fallback to nonsecure mode:
dial-peer voice 101 voipno srtp!gatewaytimer receive-rtcp 30timer receive-rtp 1200!line con 0line aux 0line vty 0 4exec-timeout 30 0password ciscologin!ntp clock-period 17173803ntp server 10.4.127.2endAdditional References
The following sections provide references related to the Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways feature.
Related Documents
Cisco CallManager security configuration
Cisco CallManager Security Guide, Release 5.0
Cisco IOS H.323 configuration
Cisco IOS voice configuration
Cisco IOS voice command reference
Cisco IOS Voice Command Reference, Release 12.4T
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) feature
IPSec configuration
Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide, Release 12.4
IPSec commands
Cisco IOS Security Command Reference, Release 12.4T
Standards
IETF draft draft-ietf-mmusic-sdescriptions-02.txt
Security Descriptions for Media Streams
IETF draft draft-ietf-avt-srtp-09.txt
Secure Real-time Transport Protocol
MIBs
RFCs
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature.
—
Technical Assistance
Command Reference
The following commands are introduced or modified in the feature or features documented in this module. For information about these commands, see the Cisco IOS Voice Command Reference at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/voice/command/reference/vr_book.html and the Cisco IOS Debug Command Reference at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/debug/command/reference/db_book.html. For information about all Cisco IOS commands, use the Command Lookup Tool at http://tools.cisco.com/Support/CLILookup or the Cisco IOS Master Command List, All Releases, at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html.
•
debug h245 srtp
•
show dial-peer voice
•
srtp (dial-peer)
•
srtp (voice)
Feature Information for Media and Signaling Authentication and Encryption Feature for Cisco IOS H.323 Gateways
Table 3 lists the release history for this feature.
Not all commands may be available in your Cisco IOS software release. For release information about a specific command, see the command reference documentation.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Note
Table 3 lists only the Cisco IOS software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given Cisco IOS software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that Cisco IOS software release train also support that feature.
Glossary
CLI—command-line interface.
HMAC—Hashed Message Authentication Codes.
IETF—Internet Engineering Task Force. Standards body for Internet Standards.
IPSec—IP security.
PIN—personal identification number.
RTCP—Real-Time Transport Protocol Control Protocol.
RTP—Real-Time Transport Protocol
SHA1—Secure Hash Algorithm1.
SRTP—Secure RTP.
SRTCP—Secure RTCP.
VoIP—Voice over IP.
CCDE, CCENT, CCSI, Cisco Eos, Cisco HealthPresence, Cisco IronPort, the Cisco logo, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco Nurse Connect, Cisco Pulse, Cisco StackPower, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, Cisco Unified Computing System, Cisco WebEx, DCE, Flip Channels, Flip for Good, Flip Mino, Flipshare (Design), Flip Ultra, Flip Video, Flip Video (Design), Instant Broadband, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Cisco Capital, Cisco Capital (Design), Cisco:Financed (Stylized), Cisco Store, and Flip Gift Card are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AllTouch, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, Continuum, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Explorer, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GainMaker, GigaDrive, HomeLink, iLYNX, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, Laser Link, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerKEY, PowerPanels, PowerTV, PowerTV (Design), PowerVu, Prisma, ProConnect, ROSA, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0908R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2006, 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.