Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Ethernet Local Management Interface
Prerequisites for Ethernet Local Management Interface
Restrictions for Ethernet Local Management Interface
Information About Ethernet Local Management Interface
How to Set Up Ethernet Local Management Interface
Enabling Ethernet LMI on All Supported Interfaces
Enabling Ethernet LMI on a Single Supported Interface
Configuration Examples for Ethernet Local Management Interface
Enabling Ethernet LMI on All Supported Interfaces: Example
Enabling Ethernet LMI on a Single Supported Interface: Example
Feature Information for Ethernet Local Management Interface
Ethernet Local Management Interface
First Published: June 19, 2006Last Updated: February 27, 2007Ethernet Local Management Interface (LMI) is an Ethernet layer operation, administration, and management (OAM) protocol. It provides information that enables autoconfiguration of customer edge (CE) devices and provides the status of Ethernet virtual connections (EVCs) for large Ethernet metropolitan-area networks (MANs) and WANs. Specifically, Ethernet LMI notifies a CE device of the operating state of an EVC and the time when an EVC is added or deleted. Ethernet LMI also communicates the attributes of an EVC and a user-network interface (UNI) to a CE device.
The advent of Ethernet as a MAN and WAN technology imposes a new set of OAM requirements on Ethernet's traditional operations, which were centered on enterprise networks only. The expansion of Ethernet technology into the domain of service providers, where networks are substantially larger and more complex than enterprise networks and the user-base is wider, makes operational management of link uptime crucial. More importantly, the timeliness in isolating and responding to a failure becomes mandatory for normal day-to-day operations, and OAM translates directly to the competitiveness of the service provider.
Finding Feature Information in This Module
Your Cisco IOS software release may not support all of the features documented in this module. To reach links to specific feature documentation in this module and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, use the "Feature Information for Ethernet Local Management Interface" section.
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for Ethernet Local Management Interface
•
Restrictions for Ethernet Local Management Interface
•
Information About Ethernet Local Management Interface
•
How to Set Up Ethernet Local Management Interface
•
Configuration Examples for Ethernet Local Management Interface
•
Feature Information for Ethernet Local Management Interface
Prerequisites for Ethernet Local Management Interface
Business Requirements
•
Ethernet OAM such as connectivity fault management (CFM) must be implemented and operational on the service provider's network.
Restrictions for Ethernet Local Management Interface
•
Ethernet LMI relies on Ethernet CFM for the status of an EVC, the remote UNI identifier associated with an EVC, and remote UNI status.
•
Ethernet LMI CE is available only on routing ports on routing platforms. For information about Ethernet LMI PE functionality on switching platforms, see the "Configuring Ethernet OAM, CFM and E-LMI" chapter of the Cisco ME 3400 Switch Software Configuration Guide, Release 12.2(46)SE.
•
Ethernet LMI in the Cisco IOS Software Release 12.4(9)T does not support autoconfiguration of CE devices.
Information About Ethernet Local Management Interface
Before you set up Ethernet LMI, you should understand the following concepts:
•
EVC
EVC
An EVC as defined by the Metro Ethernet Forum could be a port level point-to-point or multipoint-to-multipoint Layer 2 circuit. EVC status can be used by the CE device to find an alternative path in to the service provider network or in some cases, fall back to a backup path over Ethernet or another alternative service such as Frame Relay or ATM.
Ethernet LMI
Ethernet LMI is an Ethernet layer OAM protocol between a CE device and the PE in large Ethernet MANs and WANs. It provides information that enables service providers to autoconfigure CE devices with service parameters and parameter changes from a user provider edge (UPE) device.
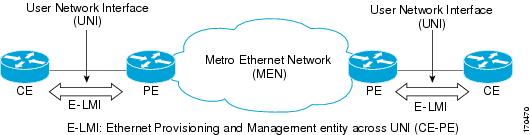
Figure 1 shows where in a network Etheret LMI functions.
Figure 1
Position in the Network Where Ethernet LMI Functions
LMI also provides the status of Ethernet EVCs in large Ethernet MANs and WANs to the CE. Specifically, Ethernet LMI notifies a CE device of the operating state of an EVC and the time when an EVC is added or deleted. Ethernet LMI also communicates EVC and UNI attributes to a CE device.
The Ethernet LMI protocol includes the following procedures, as defined by the MEF 16 Technical Specification:
•
Notifying the CE when an EVC is added
•
Notifying the CE when an EVC is deleted
•
Notifying the CE of the availability state of a configured EVC (Active, Not Active, or Partially Active)
•
Communicating UNI and EVC attributes to the CE
Benefits of Ethernet LMI
Ethernet LMI provides the following benefits:
•
Communication of end-to-end status of the EVC to the CE device
•
Communication of EVC and UNI attributes to a CE device
•
Competitive advantage for service providers
How to Set Up Ethernet Local Management Interface
To set up Ethernet LMI, perform the following tasks:
•
Enabling Ethernet LMI on All Supported Interfaces
•
Enabling Ethernet LMI on a Single Supported Interface
Enabling Ethernet LMI on All Supported Interfaces
Perform this task to enable Ethernet LMI on all supported interfaces on a device.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ethernet lmi global
4.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Enabling Ethernet LMI on a Single Supported Interface
Perform the steps in this task to enable Ethernet LMI on a specific supported interface.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface type number
4.
ethernet lmi interface
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Ethernet Local Management Interface
The examples in this section show the configurations that enable Ethernet LMI on all interfaces on a CE device (globally) and on a specific interface on a CE device.
•
Enabling Ethernet LMI on All Supported Interfaces: Example
•
Enabling Ethernet LMI on a Single Supported Interface: Example
Enabling Ethernet LMI on All Supported Interfaces: Example
The following example shows how to enable Ethernet LMI on all supported interfaces on a device:
enableconfigure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.ethernet lmi globalend00:06:33: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Ethernet0/0, changed pEnabling Ethernet LMI on a Single Supported Interface: Example
The following example shows how to enable Ethernet LMI on a single interface:
enableconfigure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.interface ethernet 0/0ethernet lmi interfaceend00:05:51: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by consoleAdditional References
The following sections provide references related to Ethernet Local Management Interface.
Related Documents
Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management
Ethernet Connectivity Fault Management, Release 12.2(33)SRA
Configuring CFM and E-LMI in a service provider network
Cisco ME 3400 Switch Software Configuration Guide, Rel. 12.2(46)SE
Commands used for configuring Ethernet LMI in a service provider network
Standards
MIBs
RFCs
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature.
—
Technical Assistance
Command Reference
This section documents only commands that are new or modified.
•
clear ethernet lmi statistics
clear ethernet lmi statistics
To clear Ethernet local management interface (LMI) statistics counters for all interfaces or for a specific interface, use the clear ethernet lmi statistics command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear ethernet lmi statistics [interface type number]
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
12.4(9)T
This command was introduced.
12.2(33)SRB
Support for this command on the Cisco 7600 router was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB.
Usage Guidelines
This command resets counters and is useful when you want to monitor Ethernet LMI errors for a period of time. For example, to monitor errors for 1 hour, you would issue the clear ethernet lmi statistics command to reset the counter. At the end of the hour, you would issue the show ethernet lmi statistics command to display errors that occurred during that one-hour time period.
Examples
The following example shows how to clear Ethernet LMI statistics counters on all interfaces:
Router# clear ethernet lmi statisticsClear "show ethernet lmi" statistics counters on all interfaces [confirm]Router#The following example shows how to clear Ethernet LMI statistics counters on the Gigabit Ethernet 1/0 interface:
Router# clear ethernet lmi statistics interface gigabitethernet 1/0Clear "show ethernet lmi" statistics counters on this interface [confirm]Router#Related Commands
show ethernet lmi
Displays Ethernet LMI Ethernet virtual connections (EVCs) configured on a device.
show interface
Displays statistics for all interfaces configured on a device.
debug ethernet lmi
To enable debugging of Ethernet local management interface (LMI) messages on all interfaces or on a specified interface, use the debug ethernet lmi command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging, use the no form of this command.
debug ethernet lmi {all | errors | events | packets} [interface type number]
no debug ethernet lmi {all | errors | events | packets} [interface type number]
Syntax Description
Command Default
Debugging is disabled.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
12.4(9)T
This command was introduced.
12.2(33)SRB
Support for this command on the Cisco 7600 router was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB.
Usage Guidelines
When you use the all keyword, keep in mind how many interfaces support Ethernet LMI. Some messages may be lost if many interfaces are supported.
Use of the errors keyword enables debugging of Ethernet LMI errors such as invalid messages; for example, unexpected information element (IE) and mandatory IE missing.
Use of the events keyword enables debugging of Ethernet LMI events such as status changes, timeouts, and messages received.
Use of the packets keyword enables debugging of decoded Ethernet LMI packets.
The output from this command is a log of activity. Use this command to troubleshoot Ethernet LMI in your network.
Examples
The following example output from the debug ethernet lmi all command shows event and packet messages:
Router# debug ethernet lmi allEthernet LMI errors debugging is onEthernet LMI packets debugging is onEthernet LMI events debugging is onEthernet LMI packets hex debugging is on00:29:32: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: ce_event: State 0x0, Event 0x400:29:32: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: Old State=0x0, Event=0x4, New State=0x200:29:32: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: Updated Stat Type: ETHER_LMI_ST_LMSG_SENT00:29:32: ELMI Et0/0 PKT HEX: TX->:0x01750101010202B4B3030500000000040000000000000:29:32: ELMI Et0/0 PACKET: OutgoingProtocol Version : 0x1Message : STATUS ENQ (0x75)Report Type : CheckSequence Number : Snd(0xB4), Rcv(0xB3)Data Instance : Value(0x4)00:29:32: ELMI Et0/0 PKT HEX: RX<-:0x017D0101010202B4B4030500000000040000000000000:29:32: ELMI Et0/0 PACKET: IncomingProtocol Version : 0x1Message : STATUS (0x7D)Report Type : CheckSequence Number : Snd(0xB4), Rcv(0xB4)Data Instance : Value(0x4)00:29:32: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: ce_event: State 0x2, Event 0x100:29:32: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: Update seq: current send 0xB4 rcv 0xB300:29:32: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: Updated Stat Type: ETHER_LMI_ST_LMSG_RCVD00:29:32: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: Old State=0x2, Event=0x1, New State=0x0The following example output from the debug ethernet lmi all command shows detailed information about the user-network interfaces (UNIs) and Ethernet virtual connections (EVCs) for packet messages.
Router# debug ethernet lmi allEthernet LMI errors debugging is onEthernet LMI packets debugging is onEthernet LMI events debugging is onEthernet LMI packets hex debugging is onJun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 PKT HEX: RX<-:0x017D0101000202D30103050000000004Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 PACKET: IncomingProtocol Version : 0x1Message : STATUS (0x7D)Report Type : FullSequence Number : Snd(0xD3), Rcv(0x1)Data Instance : Value(0x4)UNI : BundleUNI Id : 'uni_sandiego'EVC Status : Evc Ref(0x1), New, ActiveEVC Parameters : Point-to-PointEVC Id : 'EVC_P2P_110'Remote UNI Sum : Cfgd(1), Up(1)EVC Status : Evc Ref(0x2), New, ActiveEVC Parameters : MultiPoint-to-MultiPointEVC Id : 'EVC_MP2MP_101'Remote UNI Sum : Cfgd(2), Up(2)CEVLAN EVC Map : Evc Ref(0x1), Seq(0x1)EVC Map : Num Vlans(1), 110CEVLAN EVC Map : Evc Ref(0x2), Seq(0x1)EVC Map : Num Vlans(1), 101Remote UNI Status : Evc Ref(0x1), Uni Ref(0x26), UpUNI Id o deb al : 'cisco_newyork'Remote UNI Status : Evc Ref(0x2), Uni Ref(0x1D), UpUNI Id : 'uni_newyork'Remote UNI Status : Evc Ref(0x2), Uni Ref(0x96), UpUNI Id : 'miami-detroit'Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: ce_event: State 0x1, Event 0x0Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update seq: current send 0x1 rcv 0x0Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update uni:Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update evc_sts: ref_id: 0x1Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update evc_param: type 0x0Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update evc_idJun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update remote_uni_sum cfgd 1 up 1Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update evc_sts: ref_id: 0x2Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update evc_param: type 0x1Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update evc_idJun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update remote_uni_sum cfgd 2 up 2Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update cevlan_evc_map: ref_id: 0x1 seq#1Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update evc_map: num_vlans 1Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update cevlan_evc_map: ref_id: 0x2 seq# 1Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update evc_map: num_vlans 1Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update remote_uni_det: evc ref_id: 0x1 u6Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update remote_uni_det: evc ref_id: 0x2 uDJun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update remote_uni_det: evc ref_id: 0x2 u6Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: upd_lmi_db: new uni_evc ref 0x1Jun 16 18:59:49.372: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: upd_lmi_db: new uni_evc ref 0x2Jun 16 18:59:49.372: %ETHER_LMI-6-MISMATCHED_VLAN_NOT_CONFIGURED: VLAN 101,110 1Jun 16 18:59:49.372: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthnJun 16 18:59:49.376: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Update di: current 0x0 rcvd 0x4Jun 16 18:59:49.376: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Old State=0x1, Event=0x0, New State=0x0Jun 16 18:59:49.376: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Updated Stat Type: ETHER_LMI_ST_LFULL_MSDJun 16 18:59:50.100: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by consoleJun 16 18:59:59.376: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: ce_event: State 0x0, Event 0x4Jun 16 18:59:59.376: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Old State=0x0, Event=0x4, New State=0x2Jun 16 18:59:59.376: ELMI Gi0/1 EVENT: Updated Stat Type: ETHER_LMI_ST_LMSG_SENTThe following example shows output of the debug ethernet lmi all interface command for interface Ethernet 0/0.Router# debug ethernet lmi all interface ethernet 0/0Ethernet LMI errors debugging is on for Ethernet0/0Ethernet LMI packets debugging is on for Ethernet0/0Ethernet LMI events debugging is on for Ethernet0/0Ethernet LMI packets hex debugging is on for Ethernet0/000:45:14: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: ce_event: State 0x0, Event 0x400:45:14: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: Old State=0x0, Event=0x4, New State=0x200:45:14: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: Updated Stat Type: ETHER_LMI_ST_LMSG_SENT00:45:14: ELMI Et0/0 PKT HEX: TX->:0x017501010102021312030500000000040000000000000:45:14: ELMI Et0/0 PACKET: OutgoingProtocol Version : 0x1Message : STATUS ENQ (0x75)Report Type : CheckSequence Number : Snd(0x13), Rcv(0x12)Data Instance : Value(0x4)00:45:14: ELMI Et0/0 PKT HEX: RX<-:0x017D01010102021313030500000000040000000000000:45:14: ELMI Et0/0 PACKET: IncomingProtocol Version : 0x1Message : STATUS (0x7D)Report Type : CheckSequence Number : Snd(0x13), Rcv(0x13)Data Instance : Value(0x4)00:45:14: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: ce_event: State 0x2, Event 0x100:45:14: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: Update seq: current send 0x13 rcv 0x1200:45:14: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: Updated Stat Type: ETHER_LMI_ST_LMSG_RCVD00:45:14: ELMI Et0/0 EVENT: Old State=0x2, Event=0x1, New State=0x0ethernet lmi
To set Ethernet local management interface (LMI) parameters for a user-network interface (UNI), use the ethernet lmi command in interface configuration mode. To remove Ethernet LMI parameters on a UNI, use the no form of this command.
ethernet lmi {n391 | n393 | t391 | t392} value
no ethernet lmi {n391 | n393 | t391 | t392}
Syntax Description
Command Default
Ethernet LMI parameters are not set on any UNIs.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.4(9)T
This command was introduced.
12.2(33)SRB
Support for this command on the Cisco 7600 router was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB.
Usage Guidelines
The value for the polling verification timer (t392) should be greater than the value for the polling timer (t391).
The polling verification timer (t392) can be disabled.
A very high value for the polling timer (t391) means more time spent detecting Ethernet LMI link-down errors.
Examples
The following example shows how to set a polling counter for 30 seconds on interface Ethernet 1/0:
Router# configure terminalRouter(config)# interface ethernet 1/0Router(config-if)# ethernet lmi t391 30ethernet lmi global
To enable Ethernet local management interface (LMI) functionality globally on a device, use the ethernet lmi global command in global configuration mode. To disable Ethernet LMI globally on a device, use the no form of this command.
ethernet lmi global
no ethernet lmi global
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Ethernet LMI is disabled.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
12.4(9)T
This command was introduced.
12.2(33)SRB
Support for this command on the Cisco 7600 router was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB.
Usage Guidelines
Ethernet LMI is disabled by default on an interface and must be explicitly enabled. The ethernet lmi global command enables Ethernet LMI on all interfaces for an entire device. The benefit of this command is that you can enable Ethernet LMI on all interfaces with one command compared to enabling Ethernet LMI separately on each interface.
To disable Ethernet LMI on a specific interface after the ethernet lmi global command has been issued, the no ethernet lmi interface command must be issued on that interface.
The sequence in which the ethernet lmi interface and ethernet lmi global commands are issued is significant. The latest command issued overrides the prior command issued.
Examples
The following example shows how to enable Ethernet LMI globally on a device:
Router(config)# ethernet lmi globalRelated Commands
ethernet lmi interface
To enable Ethernet local management interface (LMI) on a user-network interface (UNI), use the ethernet lmi interface command in interface configuration mode. To remove Ethernet LMI on a UNI, use the no form of this command.
ethernet lmi interface
no ethernet lmi interface
Syntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Command Default
Ethernet LMI parameters are not set on any UNIs.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
12.4(9)T
This command was introduced.
12.2(33)SRB
Support for this command on the Cisco 7600 router was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB.
Usage Guidelines
This command enables Ethernet LMI processing on an interface if the ethernet lmi global command has not been issued. When the ethernet lmi global command has been issued, Ethernet LMI is enabled on all interfaces. In this case, the no ethernet lmi interface command overrides the ethernet lmi global command and disables Ethernet LMI processing on the interface.
The sequence in which the commands are issued is significant. The latest command issued overrides the prior command issued.
Examples
The following example shows how to enable Ethernet LMI on interface Ethernet 1/0:
Router# configure terminalRouter(config)# interface ethernet 1/0Router(config-if)# ethernet lmi interfaceRelated Commands
show ethernet lmi
To display Ethernet local management interface (LMI) Ethernet virtual connections (EVCs) configured on a device, use the show ethernet lmi command in privileged EXEC mode.
show ethernet lmi {{evc [detail evc-id [interface type number] | map interface type number]} | {parameters | statistics} interface type number | uni map [interface type number]}
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
12.4(9)T
This command was introduced.
12.2(33)SRB
Support for this command on the Cisco 7600 router was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRB.
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to check the operational statuses of EVCs.
Examples
The following examples show output from a show ethernet lmi command for interface Ethernet 0/0 using different keywords and arguments.
The following sample output is generated from the show ethernet lmi command using the evc keyword:
Router# show ethernet lmi evcSt EVC Id Port--- ------------------------------------------------------------ --------------A EVC_MP2MP_101 Gi0/1A EVC_P2P_110 Gi0/1Key: St=Status, A=Active, P=Partially Active, I=Inactive, ?=Link DownThe following sample output is generated from the show ethernet lmi command using the evc and optional detail keywords:
Router# show ethernet lmi evc detail EVC_MP2MP_101EVC Id: EVC_MP2MP_101interface Ethernet0/0Time since Last Full Report: 00:25:25Ether LMI Link Status: UpUNI Status: UpUNI Id: router3-e0/0+router-e0/0CE-VLAN/EVC Map Type: BundlingVLAN: 101EVC Status: ActiveEVC Type: Multipoint-to-MultipointRemote UNI Count: Configured = 2, Active = 2UNI Id UNI Status Port------ ---------- ----router4-e0/0+router1-e0/0 Up Remoterouter5-e0/0+router6-e0/0 Up RemoteTable 1 describes the significant fields shown in output of the show ethernet lmi command using the evc and detail keywords.
The following sample output is generated from the show ethernet lmi command using the map interface keyword:
Router# show ethernet lmi evc map interface Ethernet0/0UNI Id: router3-e0/0+router-e0/0St Evc Id CE-VLAN--- ---------------------------------------- ----------------------------------A EVC_MP2MP_101 101A EVC_P2P_110 110Key: St=Status, A=Active, P=Partially Active, I=Inactive, *=Default EVC,?=Link DownTable 2 describes the significant fields shown in output of the show ethernet lmi command using the evc and map keywords.
The following sample output is generated from the show ethernet lmi command using the parameters and interface keywords:
Router# show ethernet lmi parameters interface Ethernet0/0E-LMI Parameters for interface Ethernet0/0Version : MEF.16-0106Mode : CET391 : 10T392 : NAN391 : 360N393 : 4Table 3 describes the significant fields shown in output of the show ethernet lmi command using the parameters keyword.
The following sample output is generated from the show ethernet lmi command using the statistics and interface keywords:
Router# show ethernet lmi statistics interface Ethernet0/0E-LMI Statistics for interface Ethernet0/0Ether LMI Link Status: UpUNI Status: UpUNI Id: router3-e0/0+router-e0/0Reliability Errors:Status Timeouts 0 Invalid Sequence Number 0Invalid Status Response 0 Unsolicited Status Received 0Protocol Errors:Invalid Protocol Version 0 Invalid EVC Reference Id 0Invalid Message Type 0 Out of Sequence IE 0Duplicated IE 0 Mandatory IE Missing 0Invalid Mandatory IE 0 Invalid non-Mandatory IE 0Unrecognized IE 0 Unexpected IE 0Short Message 0Last Full Status Enq Sent 00:50:35 Last Full Status Rcvd 00:50:35Last Status Check Sent 00:00:06 Last Status Check Rcvd 00:00:06Last clearing of counters 00:09:57
Note
The UNI Id field displays only when it is available from the provider edge router.
Table 4 describes the significant fields shown in output of the show ethernet lmi command using the statistics keyword.
The following sample output is generated from the show ethernet lmi command using the uni map keyword:
Router# show ethernet lmi uni mapUNI Id EVC Id Port--------------------------------- --------------------------------- ------------uni_sandiego EVC_MP2MP_101 Gi0/1uni_sandiego EVC_P2P_110 Gi0/1Router#The following sample output is generated from the show ethernet lmi command using the uni map and optional interface keywords:
Router# show ethernet lmi uni map interface gigabitethernet 0/1UNI Id EVC Id Port--------------------------------- --------------------------------- ------------uni_sandiego EVC_MP2MP_101 Gi0/1uni_sandiego EVC_P2P_110 Gi0/1Router#Table 5 describes the significant fields shown in output of the show ethernet lmi command using the uni map keyword and uni map and interface keyword pair.
Table 5 show ethernet lmi uni map and uni map interface Field Descriptions
UNI Id
Identifier of the UNI.
EVC Id
Identifier of the EVC.
Port
Interface on the CE device.
Glossary
CE—customer edge. Edge equipment on the customer side of a user-network interface (UNI).
CE-VLAN ID—Identifier of a CE-VLAN.
E-LMI—Ethernet Local Management Interface. An Ethernet layer OAM protocol. It provides information that enables autoconfiguration of CE devices and provides the status of Ethernet virtual connections (EVCs) for large Ethernet MANs and WANs.
EVC—Ethernet virtual connection. An association of two or more user-network interfaces.
OAM—operations, administration, and maintenance. A term used by several standards bodies to describe protocols and procedures for operating, administrating, and maintaining networks. Examples are ATM OAM and IEEE Std. 802.3ah OAM.
PE—provider edge. Edge equipment on the service provider side of a user-network interface (UNI).
UNI—user-network interface. A common term for a bridge portion an operator's bridge that is connected to customer equipment. A UNI often includes a C-VLAN-aware bridge component. The term UNI is used broadly in the IEEE P802.1ag/D5.2 standard when the purpose for various features of LMI are explained.
Note
See Internetworking Terms and Acronyms for terms not included in this glossary.
Feature Information for Ethernet Local Management Interface
Table 6 lists the feature release history for this feature.
Not all commands may be available in your Cisco IOS software release. For release information about a specific command, see the command reference documentation.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Note
Table 6 lists only the Cisco IOS software release train that introduced support for a given feature in a given Cisco IOS software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that Cisco IOS software release also support that feature.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2006, 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.