Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Cisco IOS Firewall Stateful Failover
Prerequisites for Stateful Failover
Restrictions for Stateful Failover
Information About Stateful Failover
Supported Deployment Scenarios: Stateful Failover for the Cisco IOS Firewall
Stateful Failover Architecture
How to Configure Stateful Failover for Cisco IOS Firewalls
Enabling HSRP: IP Redundancy and a Virtual IP Address
Prerequisites for Spanning Tree Protocol and HSRP Stability
SSO: Interacting with by Cisco IOS Firewall Session
Enabling Stateful Failover for a Cisco IOS Firewall
Configuring the Cisco IOS Firewall HA Update Interval
Troubleshooting Stateful Failover
Maintaining Firewall Stateful Failover
Displaying Firewall Stateful Failover Information
Configuration Examples for Stateful Failover
Feature Information for Stateful Failover
Cisco IOS Firewall Stateful Failover
First Published: February 27, 2006Last Updated: February 27, 2006Stateful failover for the Cisco IOS firewall enables a router to continue processing and forwarding firewall session packets after a planned or unplanned outage occurs. You employ a backup (secondary) router that automatically takes over the tasks of the active (primary) router if the active router loses connectivity for any reason. This process is transparent and does not require adjustment or reconfiguration of any remote peer.
Stateful failover for the Cisco IOS firewall is designed to work in conjunction with stateful switchover (SSO) and Hot Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP). HSRP provides network redundancy for IP networks, ensuring that user traffic immediately and transparently recovers from failures in network edge devices or access circuits. That is, HSRP monitors both the inside and outside interfaces so that if either interface goes down, the whole router is deemed to be down and ownership of firewall sessions is passed to the standby router (which transitions to the HSRP active state). SSO allows the active and standby routers to share firewall session state information so that each router has enough information to become the active router at any time. To configure stateful failover for the Cisco IOS firewall, a network administrator should enable HSRP, assign a virtual IP address, and enable the SSO protocol.
Finding Feature Information in This Module
Your Cisco IOS software release may not support all of the features documented in this module. To reach links to specific feature documentation in this module and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, use the "Feature Information for Stateful Failover" section.
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for Stateful Failover
•
Restrictions for Stateful Failover
•
Information About Stateful Failover
•
How to Configure Stateful Failover for Cisco IOS Firewalls
•
Maintaining Firewall Stateful Failover
•
Feature Information for Stateful Failover
Prerequisites for Stateful Failover
Complete, Duplicate Cisco IOS Firewall Configuration on the Active and Standby Devices
This document assumes that you have a complete Cisco IOS firewall configuration.
The Cisco IOS firewall configuration that is set up on the active device must be duplicated on the standby device. That is, firewall protocols inspected, the interface ACL's, the global firewall settings and the interface firewall configuration.
Note
None of the configuration information between the active and standby device is automatically transferred; the user is responsible for ensuring that the Cisco IOS firewall configurations match on both devices. If the Cisco IOS firewall configurations on both devices do not match, failover from the active device to the standby device will not be successful.
Device Requirements
•
The active and standby Cisco IOS routers must be running the same Cisco IOS software,
Release 12.4(6)T or later.•
Stateful failover for the Cisco IOS firewall requires that your network contains two identical routers that are available to be either the primary or secondary device. Both routers should be the same type of device, have the same CPU and memory.
•
This feature is currently supported only on a limited number of platforms. To check the latest platform support, go to Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn.
Restrictions for Stateful Failover
When configuring redundancy for a Cisco IOS firewall, the following restrictions exist:
•
Both the active and standby devices must run the identical version of the Cisco IOS software, and both the active and standby devices must be connected via hub or switch.
•
HSRP requires the inside interface to be connected via LANs.
•
Load balancing is not supported; that is, no more than one device in a redundancy group can be active at any given time.
•
Any restrictions that exist for intradevice SSO will also exist for the firewall High Availability (HA). The behavior of intra-device active where the Active device re-boots when the SSO state changes from Active to anything will be the same with firewall HA.
•
No support for configuration synchronization and In-Service Software Upgrade (ISSU) which are not yet available for intra-box failover in Cisco IOS T releases.
•
Stateful failover of the Cisco IOS firewall is not supported with Zone-Based Policy firewall configuration.
•
This phase of the feature will not provide support for asymmetric routing and it is the responsibility of the user to configure the network to avoid this.
•
The stateful failover feature does not synchronize any statistics or mib firewall information between the active and standby devices.
•
The stateful failover feature does not support rate-limiting of firewall sessions on the standby router for the failed over sessions.
•
Currently only Layer 4 TCP and UDP protocol failover is supported. Therefore, all TCP only sessions, UDP only sessions, and single channel granular protocols sessions for which L7 inspection is not supported are failed over.
•
Layer 4 ICMP session will not be failed over to the standby
•
Any session configured for Layer 7 inspection will NOT be failed over.
•
CiscoIntrusion Prevention Services (IPS)/Intrusion Detection Services (IDS) feature will not be made HA aware in this release.
Information About Stateful Failover
Before configuring the Stateful Failover feature, you should understand the following concepts:
•
Supported Deployment Scenarios: Stateful Failover for the Cisco IOS Firewall
•
Stateful Failover Architecture
Supported Deployment Scenarios: Stateful Failover for the Cisco IOS Firewall
It is recommended that you implement stateful failover in one of the following recommended deployment scenarios:
•
Dual LAN Interface
•
LAN WAN Interface
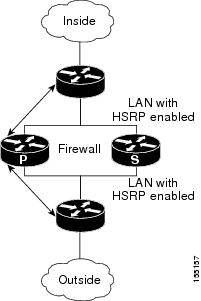
In a dual LAN interface scenario, the active and standby routers running the firewall are connected to each other via LAN interface on both the inside and the outside (see Figure 1). HSRP is configured on both the inside and outside interface. The next hop routers in this scenario talk to the HA pair via the virtual IP address. In this scenario there are two virtual IP address, one on the inside and the other on the outside. Virtual IP addresses cannot be advertised using routing protocols. You need to create static routes on the next hops to get to the virtual IP address.
You need to configue HSRP tracking in order to track multiple pairs of interfaces. If you run HSRP on only one pair of interfaces, or run on both without mutual tracking of the pairs, each pair functions independently of each other and are unaware of each other's state changes. For example, if HSRP is run on only the two outside interfaces (as shown in Figure 1), this could cause HSRP to failover on the outside interfaces, whilst the inside interfaces are unchanged. This causes the black holing of traffic, which continues to be directed to the primary from the inside. This introduces the possibility of problems arising from one interface on a primary router failing and triggering a move to the secondary, while the other interface on the ex-primary remains active. Mutual tracking means that if the outside interface does fail, the inside interface on the same router will also be deemed down allowing for complete router failover to the secondary.
Figure 1 Dual Interface Network Topology
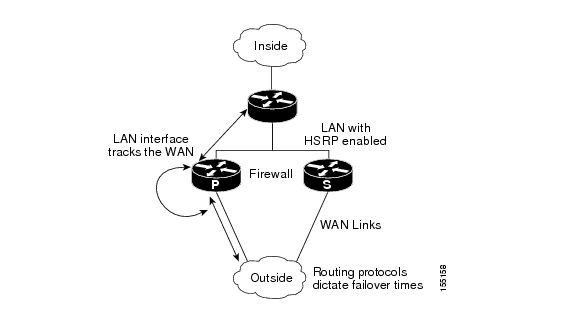
In a LAN WAN scenario, the inside interface of the Active Standby pair running the firewall are connected via LAN interface on the inside and WAN interface on the outside (see Figure 2). HSRP is configured on the inside interface. The inside network communicates with the HA pair using the inside virtual IP address.
HSRP tracking should be configured on the inside LAN interfaces to track the state of the outside WAN interface. If the outside WAN interface goes down on the active the LAN interface that is tracking it reduces the HSRP priority and initiates a failover to the standby. Traffic from the outside flowing into the HSRP pair should now be directed to the new active device.
In the scenario where the LAN interfaces track the WAN interfaces, the failover to the standby happens immediately. However, for traffic to start flowing on the new active router, routing convergence needs to happen. The net failover time is dictated by the routing protocol.
In this scenario the traffic flows from the inside to the outside through the Active due to the HSRP configuration on the inside LAN interfaces. The traffic from the outside to the inside should also flow through the active device. The configuration of the network so that the traffic always flows through the active is beyond the scope of this document. In this scenario, the network administrator is responsible to ensure that the traffic always flows through the active device.
Figure 2
LAN WAN Network Topology
Stateful Failover Architecture
Firewall stateful failover is a client of Cisco IOS SSO. SSO is a method of providing redundancy and synchronization for Cisco IOS applications and features.
State Synchronization
The synchronization manager will be responsible for checking firewall to determine the state of the active device, which must be check pointed to the redundant peers and update that state on the firewall on standby devices.
Periodic updates are sent from the active to the standby for all HA sessions. This information enables the standby to take over the sessions and process the sessions if there is a failover.
The stateful failover feature supports deterministic updates. This means that the updates for a session get sent every N seconds, where N is configurable. Default value for N is 10 sec.
Bulk Synchronization
Bulk synchronization happens at boot time or when you use the clear ip inspect ha sessions all command on the standby device. If the standby device is configured after the active device already has sessions, then only new ha sessions established on the active device are synchronized to the standby device through dynamic synchronization. If you want all the current sessions synchronized from the active to the standby, you must specifically issue the clear ip inspect ha sessions all command on the standby device. A single request message is sent from the standby device to the active device which result in add_session messages from active to standby for all sessions open on the active at that time.
How to Configure Stateful Failover for Cisco IOS Firewalls
The following sections describe how the two devices are configured for to enable stateful failover. Configuration tasks for stateful failover include:
•
Enabling HSRP: IP Redundancy and a Virtual IP Address
•
Enabling Stateful Failover for a Cisco IOS Firewall
•
Configuring the Cisco IOS Firewall HA Update Interval
•
Troubleshooting Stateful Failover
•
Maintaining Firewall Stateful Failover
•
Displaying Firewall Stateful Failover Information
Enabling HSRP: IP Redundancy and a Virtual IP Address
HSRP provides two services—IP redundancy and a Virtual IP (VIP) address. Each HSRP group may provide either or both of these services. Cisco IOS firewall stateful failover uses the IP redundancy services from only one HSRP standby group. It can use the VIP address from one or more HSRP groups. Use the following task to configure HSRP on the outside and inside interfaces of the router.
Note
Perform this task on both routers (active and standby) and on both interfaces of each router.
Prerequisites for Spanning Tree Protocol and HSRP Stability
If a switch connects the active and standby routers, you must perform one of the following steps to ensure that the correct settings are configured on that switch:
•
Enable the spanning-tree portfast command on every switch port that connects to a HSRP-enabled router interface.
•
Disable the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the switch only if your switch does not connect to other switches. Disabling spanning tree in a multi-switch environment may cause network instability.
•
Enable the standby delay minimum [min-delay] reload [reload-delay] command if you do not have access to the switch. The reload-delay argument should be set to a value of at least 120 seconds. This command must be applied to all HSRP interfaces on both routers.
For more information on HSRP instability, see the document Avoiding HSRP Instability in a Switching Environment with Various Router Platforms.
Note
You must perform at least one of these steps for correct HSRP operation.
Restrictions
•
Both the inside (private) interface and the outside (public) interface must belong to separate HSRP groups, but the HSRP group number can be the same.
•
The state of the inside interface and the outside interface must be the same—both interfaces must be in the active state or standby state; otherwise, the packets will not have a route out of the private network.
•
Standby priorities should be equal on both active and standby routers. If the priorities are not equal, the higher priority router will unnecessarily take over as the active router, negatively affecting uptime.
•
The IP addresses on the HSRP-tracked interfaces of the standby and active routers should both be either lower or higher on one router than the other. In the case of equal priorities (an HA requirement), HSRP will assign the active state on the basis of the IP address. If an addressing scheme exists so that the public IP address of Router A is lower than the public IP address of Router B, but the opposite is true for their private interfaces, an active/standby-standby/active split condition could exist which will break connectivity.
•
Interface ACL should allow HSRP traffic to flow through.
Note
Each time an active device relinquishes control to become the standby device, the active device will reload. This functionality ensures that the state of the new standby device synchronizes correctly with the new active device.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface type number
4.
standby standby-group-number name standby-group-name
5.
standby standby-group-number ip ip-address
6.
standby standby-group-number track interface-name
7.
standby [group-number] preempt
8.
standby [group-number] timers [msec] hellotime [msec] holdtime
9.
standby delay minimum [min-delay] reload [reload-delay]
10.
Repeat.
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting Tips
To help troubleshoot possible HSRP-related configuration problems, issue any of the following HSRP-related debug commands—debug standby errors, debug standby events, and debug standby packets [terse].
Examples
The following example shows how to configure HSRP on a router:
interface Ethernet0/0ip address 209.165.201.1 255.255.255.224standby 1 ip 209.165.201.3standby 1 preemptstandby 1 name HA-outstandby 1 track Ethernet1/0standby delay minimum 120 reload 120What to Do Next
After you have successfully configured HSRP on both the inside and outside interfaces, you should enable SSO as described in the section "Enabling SSO."
Enabling SSO
Use this task to enable SSO, which is used to transfer Cisco IOS firewall session state information between two routers.
SSO: Interacting with by Cisco IOS Firewall Session
SSO is a method of providing redundancy and synchronization for many Cisco IOS applications and features. SSO is necessary for the Cisco IOS firewall to learn about the redundancy state of the network and to synchronize their internal application state with their redundant peers.
Prerequisites
•
You should configure HSRP before enabling SSO.
•
To avoid losing SCTP communication between peers, be sure to include the following commands to the local address section of the SCTP section of the IPC configuration:
–
retransmit-timeout retran-min [msec] retra-max [msec]
–
path-retransmit max-path-retries
–
assoc-retransmit retries
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
redundancy inter-device
4.
scheme standby standby-group-name
5.
exit
6.
ipc zone default
7.
association 1
8.
protocol sctp
9.
local-port local-port-number
10.
local-ip device-real-ip-address [device-real-ip-address2]
11.
retransmit-timeout retran-min [msec] retran-max [msec]
12.
path-retransmit max-path-retries
13.
assoc-retransmit retries
14.
exit
15.
remote-port remote-port-number
16.
remote-ip peer-real-ip-address [peer-real-ip-address2]
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting Tips
To help troubleshoot possible SSO-related configuration problems, issue the debug redundancy command.
Examples
The following example shows how to enable SSO:
!redundancy inter-devicescheme standby HA-in!!ipc zone defaultassociation 1no shutdownprotocol sctplocal-port 5000local-ip 10.0.0.1retransmit-timeout 300 10000path-retransmit 10assoc-retransmit 10remote-port 5000remote-ip 10.0.0.2!What to Do Next
After you have enabled SSO, you should enable stateful failover for a firewall, as shown in the following section.
Enabling Stateful Failover for a Cisco IOS Firewall
Use this task to enabling Stateful Failover for the Cisco IOS firewall.
Prerequisites
Before performing this task, the Cisco IOS firewall inspect rule must be configured. Also, HSRP and SSO must be configured to enable box-to-box redundancy.
Restrictions
The inspect rules should not have ICMP or protocols for which Cisco IOS firewall supports Layer 7 inspection.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface [interface-name]
4.
ip inspect [rule] in |out redundancy stateful [hsrp-group-name]
5.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the Cisco IOS Firewall HA Update Interval
Use this task to change the amount of time between each update to the standby. The default interval of 10 seconds.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ip inspect redundancy update seconds [10-60]
4.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting Stateful Failover
The following commands may be used to display information about Stateful Failover messages or sessions. The debug commands may be used in any order or independent of the other debug commands.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
debug ip inspect ha [manager | update]
DETAILED STEPS
Maintaining Firewall Stateful Failover
The clear ip inspect ha command is used to clear all inspect ha sessions on the device. If the device is the standby device then it initiates a bulk sync of all session from the active. It is also used to clear the ha statistics on the device
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
clear ip inspect ha [sessions-all | statistics]
DETAILED STEPS
Displaying Firewall Stateful Failover Information
Use the show ip inspect ha {sessions [detail] | statistics} [vrf vrf-name]}command to display firewall stateful failover information.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
show ip inspect ha {sessions [detail] | statistics} [vrf vrf-name]}
DETAILED STEPS
The following tables provide examples of Stateful Failover error messages and alert message.
Table 1 contains the stateful failover HA error messages.
Table 1 Stateful Failover Error Messages
If audit trail is configured on the standby HA device the standard alerts that are shown when a session is added or deleted will be changed to reflect that the session is a standby session. Table 2 contains the stateful failover alert messages.
Table 2 Stateful Failover Alert Messages
Configuration Examples for Stateful Failover
This section includes the following example.
Stateful Failover: Example
The following output example shows stateful failover that has been configured on a Cisco IOS router:
Router 1)hostname ha-R1!boot-start-markerboot-end-marker!!redundancy inter-devicescheme standby HAin!!redundancylogging buffered 10000000 debugginglogging rate-limit console 10000!no aaa new-model!resource policy!!ipc zone defaultassociation 1no shutdownprotocol sctplocal-port 5000local-ip 10.0.0.1remote-port 5000remote-ip 10.0.0.2!!ip inspect tcp idle-time 180ip inspect name ha-protocols tcpip inspect name ha-protocols udpip inspect redundancy update seconds 60!!!inside interfaceinterface Ethernet0/0ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0standby delay minimum 120 reload 120standby 1 ip 10.0.0.3standby 1 timers 1 10standby 1 priority 60standby 1 preemptstandby 1 name HAinstandby 1 track Ethernet1/0!!outside interfaceinterface Ethernet1/0ip address 211.0.0.1 255.255.255.0ip access-group fw-ha-acl in!! The HSRP group used with the inspect config should be the inside HSRP groupip inspect ha-protocols out redundancy stateful HAinstandby delay minimum 120 reload 120standby 2 ip 211.0.0.3standby 2 timers 1 10standby 2 priority 60standby 2 preemptstandby 2 name HAoutstandby 2 track Ethernet0/0!!!! ACL on interface should permit HSRP, HA traffic from active to standby deviceip access-list extended fw-ha-aclpermit ip host 211.0.0.2 host 211.0.0.1permit ip host 211.0.0.1 host 211.0.0.2deny any any!!!!line con 0exec-timeout 0 0line aux 0##########################################################################Router 2)hostname ha-R2!boot-start-markerboot-end-marker!!redundancy inter-devicescheme standby HAin!!redundancylogging buffered 10000000 debugginglogging rate-limit console 10000!no aaa new-model!resource policy!!ipc zone defaultassociation 1no shutdownprotocol sctplocal-port 5000local-ip 10.0.0.2remote-port 5000remote-ip 10.0.0.1!!ip inspect tcp idle-time 180ip inspect name ha-protocols tcpip inspect name ha-protocols udpip inspect redundancy update seconds 60!!!inside interfaceinterface Ethernet0/0ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0standby delay minimum 120 reload 120standby 1 ip 10.0.0.3standby 1 priority 60standby 1 preemptstandby 1 name HAinstandby 1 track Ethernet1/0!!outside interfaceinterface Ethernet1/0ip address 211.0.0.2 255.255.255.0ip access-group fw-ha-acl in!! The HSRP group used with the inspect config should be the inside HSRP groupip inspect ha-protocols out redundancy stateful HAinstandby delay minimum 120 reload 120standby 2 ip 211.0.0.3standby 2 priority 60standby 2 preemptstandby 2 name HAoutstandby 2 track Ethernet0/0!!!! ACL on interface should permit HSRP, HA traffic from active to standby deviceip access-list extended fw-ha-aclpermit ip host 211.0.0.2 host 211.0.0.1permit ip host 211.0.0.1 host 211.0.0.2!!!!line con 0exec-timeout 0 0line aux 0Additional References
The following sections provide references related to Network Admission Control.
Related Documents
Configuring HSRP
"Configuring HSRP" chapter of the Cisco IOS IP Addressing Services Configuration Guide, Release 12.4.
Interfaces, configuring
Cisco IOS Interface and Hardware Component Configuration Guide, Release 12.4.
Stateful Failover for IPsec
"Stateful Failover for IPsec" chapter of the Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide, Release 12.3
Standards
MIBs
RFCs
Technical Assistance
Command Reference
This section documents new and modified commands only.
clear ip inspect ha
To delete the Firewall stateful failover sessions information from a router's memory, use the clear ip inspect ha command in privileged EXEC mode.
clear ip inspect ha [sessions all | statistics]
Syntax Description
sessions all
Clears all the firewall HA sessions.
statistics
Clears the HA statistics on the device.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
If the clear ip inspect ha sessions all command is used on the standby device, the standby HA sessions are cleared. This initiates re-synchronization of all HA sessions from the active device to the standby device.
Examples
The following example shows all sessions being deleted:
Router# clear ip inspect ha session allThe following example shows statitics being deledted.
Router# clear ip inspect ha statisticsdebug ip inspect ha
To display messages about Cisco IOS Stateful Failover High Availablity (HA) events, use the debug ip inspect ha command in privileged EXEC mode. To disable debugging output, use the no form of this command.
debug ip inspect ha [manager | packet | update]
no debug ip inspect ha [manager | packet | update]
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Examples
The following is sample output from the debug ip inspect ha command. This example shows an add session message and a delete session message received by the the active and standby devices:
Router# debug ip inspect haActive debugs -*Apr 13 17:15:20.795: FW-HA:Send add session msg for session 2C6B820*Apr 13 17:15:36.919: FW-HA:Send delete session msg for session 2C6B820Standby debugs -*Apr 13 17:19:00.471: FW-HA:Received add session message (10.0.0.10:56733:0)=>(11.0.0.10:23:0)*Apr 13 17:19:12.051: FW-HA:Received delete session message (10.0.0.10:56733:0)=>(11.0.0.10:23:0)The following is sample output from the debug ip inspect ha manager command. Using the manager keyword provides a more detailed debug analysis:
Router# debug ip inspect ha manager*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: HA Message 0:flags=0x01 len=727 FW_HA_MSG_INSERT_SESSION (1)*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: ID: grp1*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_INITIATOR_ADDR (1) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 0A 00 00 0A*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_RESPONDER_ADDR (2) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 0B 00 00 0A*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_INITIATOR_PORT (3) len 2*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: BF 1C*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_RESPONDER_PORT (4) len 2*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00 17*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_L4_PROTOCOL (5) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00 00 00 01*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_SRC_TABLEID (6) len 1*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_DST_TABLEID (7) len 1*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_R_RCVNXT (20) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 79 EA E2 9A*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_R_SNDNXT (21) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 6C 7D E4 04*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_R_RCVWND (22) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00 00 10 20*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_R_LAST_SEQ_TO_SND (23) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00 00 00 00*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_I_RCVNXT (24) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 6C 7D E4 04*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_I_SNDNXT (25) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 79 EA E2 9A*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_I_RCVWND (26) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00 00 10 20*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_I_LAST_SEQ_TO_SND (27) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00 00 00 00*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_TCP_STATE (28) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00 00 00 04*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_INITIATOR_ALT_ADDR (8) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 0A 00 00 0A*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_RESPONDER_ALT_ADDR (9) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 0B 00 00 0A*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_INITIATOR_ALT_PORT (10) len 2*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: BF 1C*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_RESPONDER_ALT_PORT (11) len 2*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00 00*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_L7_PROTOCOL (12) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00 00 00 05*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_INSP_DIR (13) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00 00 00 01*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_I_ISN (29) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 79 EA E2 99*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_R_ISN (30) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 6C 7D E4 03*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_APPL_INSP_FLAGS (15) len 2*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00 10*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_TERM_FLAGS (16) len 1*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_IS_LOCAL_TRAFFIC (17) len 1*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_DATA_DIR (18) len 4*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00 00 00 00*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_SESSION_LIMITING_DONE (19) len 1*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 00*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: attr FW_HA_ATT_INSPECT_RULE (14) len 256*Apr 13 17:23:28.995: 74 65 73 74 00 00 00 00ip inspect
To apply a set of inspection rules to an interface, use the ip inspect command in interface configuration mode. There are two different modes for this command, configuration mode and interface configuration mode. To remove the set of rules from the interface, use the no form of this command.
Global Configuation Mode
ip inspect {redundancy update seconds <10-60>}
no ip inspect {redundancy update seconds <10-60>}
Interface Configuration Mode
ip inspect {inspection-name {in | out} [redundancy stateful hsrp-group-name]}
no ip inspect {inspection-name {in | out} [redundancy stateful hsrp-group-name]}
Syntax Description
Defaults
If no set of inspection rules is applied to an interface, no traffic will be inspected by CBAC. If redundancy stateful <hsrp-grp-name> is not used, there will be no stateful firewall high-availability.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
11.2
This command was introduced.
12.4(6)T
Added support for redunancy, update, seconds, and stateful keywords.
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to apply a set of inspection rules to an interface.
Typically, if the interface connects to the external network, you apply the inspection rules to outbound traffic; alternately, if the interface connects to the internal network, you apply the inspection rules to inbound traffic.
In the Interface Configuration mode, use ip inspect<name> in/out redundancy stateful <hsrp-group> command. Use the redundancy stateful <hsrp-grp> option to turn on stateful high availability for all session that come up on this inspect rule.
In the Global Configuration mode, use ip inspect redundancy update seconds <10-60>. Use the redundancy update seconds option to configure the time interval between the synchronization of the active and standby firewall HA sessions.
Examples
The following example applies a set of inspection rules named "outboundrules" to an external interface's outbound traffic. This causes inbound IP traffic to be permitted only if the traffic is part of an existing session, and to be denied if the traffic is not part of an existing session.
interface serial0ip inspect MY-INSPECT_RULE out redundancy stateful B2B-HA-HSRP-GRPRelated Commands
show ip inspect
To display Context-Based Access Control (CBAC) configuration and session information, use the show ip inspect command in privileged EXEC mode.
show ip inspect {name inspection-name | config | interfaces | session [detail] | statistics | all} [vrf vrf-name]
Firewall MIB Statistics Syntax
show ip inspect mib connection-statistics {global | 14-protocol {all | icmp | tcp | udp} | 17-protocol {all | other | telnet | ftp} | policy policy-name target target name {14-protocol {all | icmp | tcp | udp} | 17-protocol {all | other | telnet | ftp}}
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to view the CBAC and HA configuration and session information.
ACL Bypass Functionality
ACL bypass allows a packet to avoid redundant ACL checks by allowing the firewall to permit the packet on the basis of existing inspection sessions instead of dynamic ACLs. Because input and output dynamic ACLs have been eliminated from the firewall configuration, the show ip inspect session detail command output no longer shows dynamic ACLs. Instead, the output displays the matching inspection session for each packet that is permitted through the firewall.
Firewall MIB Functionality
The Cisco Unified Firewall MIB monitors the following firewall performance statistics:
•
Connection statistics, which are a record of the firewall traffic streams that have attempted to flow through the firewall system. Connection statistics can be displayed on a global basis, a protocol-specific basis, or a firewall policy basis.
•
URL filtering statistics, which includes the status of distinct URL filtering servers that are configured on the firewall and the impact of the performance of the URL filtering servers on the latency and throughput of the firewall.
Examples
The following example shows sample output for the show ip inspect name myinspectionrule command, where the inspection rule "myinspectionrule" is configured. In this example, the output shows the protocols that should be inspected by CBAC and the corresponding idle timeouts for each protocol.
Router# show ip inspect name myinspectionruleInspection Rule ConfigurationInspection name myinspectionruletcp timeout 3600udp timeout 30ftp timeout 3600The following is sample output for the show ip inspect config command. In this example, the output shows CBAC configuration, including global timeouts, thresholds, and inspection rules.
Session audit trail is disabledone-minute (sampling period) thresholds are [400:500] connectionsmax-incomplete sessions thresholds are [400:500]max-incomplete tcp connections per host is 50. Block-time 0 minute.tcp synwait-time is 30 sec -- tcp finwait-time is 5 sectcp idle-time is 3600 sec -- udp idle-time is 30 secdns-timeout is 5 secInspection Rule ConfigurationInspection name myinspectionruletcp timeout 3600udp timeout 30ftp timeout 3600The following is sample output for the show ip inspect interfaces command:
Interface ConfigurationInterface Ethernet0Inbound inspection rule is myinspectionruletcp timeout 3600udp timeout 30ftp timeout 3600Outgoing inspection rule is not setInbound access list is not setOutgoing access list is not setThe following is sample output for the show ip inspect session command. In this example, the output shows the source and destination addresses and port numbers (separated by colons), and it indicates that the session is an FTP session.
Router# show ip inspect sessionEstablished SessionsSession 25A3318 (10.0.0.1:20)=>(10.1.0.1:46068) ftp-data SIS_OPENSession 25A6E1C (10.1.0.1:46065)=>(10.0.0.1:21) ftp SIS_OPENThe following is sample output for the show ip inspect all command:
Router# show ip inspect allSession audit trail is disabledone-minute (sampling period) thresholds are [400:500] connectionsmax-incomplete sessions thresholds are [400:500]max-incomplete tcp connections per host is 50. Block-time 0 minute.tcp synwait-time is 30 sec -- tcp finwait-time is 5 sectcp idle-time is 3600 sec -- udp idle-time is 30 secdns-timeout is 5 secInspection Rule ConfigurationInspection name alltcp timeout 3600udp timeout 30ftp timeout 3600Interface ConfigurationInterface Ethernet0Inbound inspection rule is alltcp timeout 3600udp timeout 30ftp timeout 3600Outgoing inspection rule is not setInbound access list is not setOutgoing access list is not setEstablished SessionsSession 25A6E1C (30.0.0.1:46065)=>(40.0.0.1:21) ftp SIS_OPENSession 25A34A0 (40.0.0.1:20)=>(30.0.0.1:46072) ftp-data SIS_OPENThe following is sample output from the show ip inspect session detail command, which shows that an outgoing ACL and an inbound ACL (dynamic ACLs) have been created to allow return traffic:
Router# show ip inspect session detailEstablished SessionsSession 80E87274 (192.168.1.116:32956)=>(192.168.101.115:23) tcp SIS_OPENCreated 00:00:08, Last heard 00:00:04Bytes sent (initiator:responder) [140:298] acl created 2Outgoing access-list 102 applied to interface FastEthernet0/0Inbound access-list 101 applied to interface FastEthernet0/1The following is sample output from the show ip inspect session detail command, which shows related ACL information (such as session identifiers [SIDs]), but does not show dynamic ACLs, which are no longer created:
Router# show ip inspect session detailEstablished SessionsSession 814063CC (192.168.1.116:32955)=>(192.168.101.115:23) tcp SIS_OPENCreated 00:00:10, Last heard 00:00:06Bytes sent (initiator:responder) [140:298]HA state: HA_STANDBYIn SID 192.168.101.115[23:23]=>192.168.1.117[32955:32955] on ACL 101 (15 matches)Out SID 192.168.101.115[23:23]=>192.168.1.116[32955:32955] on ACL 102The following is sample output from the show ip inspect statistics command:
Router# show ip inspect statisticsPacket inspection statistics [process switch:fast switch]tcp packets: [616668:0]http packets: [178912:0]Interfaces configured for inspection 1Session creations since subsystem startup or last reset 42940Current session counts (estab/half-open/terminating) [0:0:0]Maxever session counts (estab/half-open/terminating) [98:68:50]Last session created 5d21hLast statistic reset neverLast session creation rate 0Last half-open session total 0The following examples are sample outputs from the show ip inspect mib command with global or protocol-specific keywords.
Global MIB Statistics
Router# show ip inspect mib connection-statistics global -------------------------------------------------- Connections Attempted 7 Connections Setup Aborted 0 Connections Policy Declined 0 Connections Resource Declined 0 Connections Half Open 2 Connections Active 3 Connections Expired 2 Connections Aborted 0 Connections Embryonic 0 Connections 1-min Setup Rate 5 Connections 5-min Setup Rate 7Protocol-based MIB Statistics
Router# show ip inspect mib connection-statistics l4 tcp -------------------------------------------------- Protocol tcp Connections Attempted 3 Connections Setup Aborted 0 Connections Policy Declined 0 Connections Resource Declined 0 Connections Half Open 1 Connections Active 2 Connections Aborted 0 Connections 1-min Setup Rate 3 Connections 5-min Setup Rate 3Router# show ip inspect mib connection-statistics l7 http -------------------------------------------------- Protocol http Connections Attempted 3 Connections Setup Aborted 0 Connections Policy Declined 2 Connections Resource Declined 0 Connections Half Open 0 Connections Active 1 Connections Aborted 0 Connections 1-min Setup Rate 1 Connections 5-min Setup Rate 2Policy-target-based MIB Statistics
Router# show ip inspect mib connection-statistics policy ftp interface GigabitEthernet0/0 l4-Protocol tcp ! Policy Target Protocol Based Connection Summary Stats ------------------------------------------------------ Policy ftp-inspection Target GigabitEthernet0/0 Protocol tcp Connections Attempted 3 Connections Setup Aborted 0 Connections Policy Declined 0 Connections Resource Declined 0 Connections Half Open 1 Connections Active 2 Connections Aborted 0Router# show ip inspect mib connection-statistics policy ftp interface GigabitEthernet0/0 l7-Protocol ftp ! Policy Target Protocol Based Connection Summary Stats ------------------------------------------------------ Policy ftp-inspection Target GigabitEthernet0/0 Protocol ftp Connections Attempted 3 Connections Setup Aborted 0 Connections Policy Declined 0 Connections Resource Declined 0 Connections Half Open 1 Connections Active 2 Connections Aborted 0show ip inspect ha
To display Stateful Failover High Availability (HA) session information, use the show ip inspect ha command in privileged EXEC mode.
show ip inspect ha { session [detail] | statistics} [vrf vrf-name]
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use this command to view the Stateful Failover HA session information.
Examples
The following is sample output for the show ip inspect ha {session | detail} command. The following information is displayed for each session:
•
Session ID
•
Source address and port
•
Destination address and port
•
Protocol
•
Session State
•
HA State
Router# show ip inspect ha sessionsSess_ID (src_addr:port)=>(dst_addr:port) proto sess_state ha_stateEstablished Session2CA8958 (10.0.0.5:37690)=>(11.0.0.4:00023) tcp SIS_OPEN HA_ACTIVEThe following is sample output for the show ip inspect ha session detail command. This command displays additional information for each session.
Router #show ip inspect ha sessions detailSess_ID (src_addr:port)=>(dst_addr:port) proto sess_state ha_stateEstablished Session2CA8958 (10.0.0.5:37690)=>(10.0.0.4:00023) tcp SIS_OPEN HA_ACTIVECreated 00:01:52, Last heard 00:01:39Bytes sent (initiator:responder) [50:91]In SID 11.0.0.4[23:23]=>10.0.0.5[37690:37690] on ACL test (25 matches)The following is sample output for the show ip inspect ha statistics command. This command displays the following information for each session.
On the active router:
Router #show ip inspect ha statistics****************************************************FW HA ACTIVE STATS****************************************************FW HA active num add session sent 1FW HA active num delete session sent 0FW HA active num update session requests 0FW HA active num update session sent 17FW HA active bulk sync session 0FW HA active num error 0FW HA active RF error 0FW HA active CF error 0FW HA active manager error 0****************************************************On the standby router:
Router #show ip inspect ha statistics****************************************************FW HA STANDBY STATS****************************************************FW HA standby num add session received 1FW HA standby num delete session received 0FW HA standby num update session received 17FW HA standby num bulk sync request sent 0FW HA standby num error 0FW HA standby config error 0*****************************************************The following information displays on the active router:
•
Number of add session message sent
•
Number of delete session message sent
•
Number of update session message requests
•
Number of update session message sent
•
Number of bulk sync requests received and
•
Error statistics
The following information displays on the standby router:
•
Number of add session message received
•
Number of delete session message received
•
Number of update session message received
•
Number of bulk sync requests sent and
•
Error statistics
Glossary
HSRP - Hot Standby Routing Protocol. Provides Cisco IOS firewall box-to-box failover. However, this is not stateful failover
SSO - Stateful Switch-Over Protocol. This protocol provides redundancy and synchronization for Cisco IOS applications and features.
VIP - Virtual IP Address. Enables creation of logically separated switched IP workgroups.
FW HA- Firewall High Availability
Note
Refer to Internetworking Terms and Acronyms for terms not included in this glossary.
Feature Information for Stateful Failover
Table 3 lists the release history for this feature.
Not all commands may be available in your Cisco IOS software release. For release information about a specific command, see the command reference documentation.
Cisco IOS software images are specific to a Cisco IOS software release, a feature set, and a platform. Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Note
Table 3 lists only the Cisco IOS software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given Cisco IOS software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that Cisco IOS software release train also support that feature.
Table 3
Feature Information for Cisco IOS Firewall Stateful Failover
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.