-
Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide, Release 12.2
-
About the Cisco IOS Software Documentation
-
Using Cisco IOS Software
-
Security Overview
- Part 1: Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA)
- Part 2: Security Server Protocols
- Part 3: Traffic Filtering and Firewalls
- Part 4: IP Security and Encryption
- Part 5: Other Security Features
- Part 6: RADIUS Attributes
- Part 7: Appendixes
-
Installation and Configuration for Common Criteria EAL4 Evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec
-
Table Of Contents
Installation and Configuration for Common Criteria EAL4 Evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec
Supported Hardware and Software
Supported Hardware Documentation
Organizational Security Policy
Security Implementation Considerations
Remote Administration and Management
Verification of Image and Hardware IPSec Module
Hardware Versions of Hardware IPSec VPN Modules
MD5 Hash Values for Cisco IOS Software Images
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Contacting TAC by Using the Cisco TAC Website
Installation and Configuration for Common Criteria EAL4 Evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec
July 2002 (version 1.0)
Contents
This document describes how to install and configure Cisco IOS routers in accordance with the Common Criteria Evaluation Assurance Level 4 (EAL4) evaluated Cisco IOS IP Security (IPSec).
Note
Any changes to the information provided in this document will result in noncompliance between the Cisco IOS router and the Cisco IOS IPSec evaluation and may make the router insecure.
This document includes the following sections:
•
Supported Hardware and Software
•
Hardware Versions of Hardware IPSec VPN Modules
•
MD5 Hash Values for Cisco IOS Software Images
•
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Introduction
This document is an addendum to the Cisco IOS Release 12.1 and Release 12.2 documentation sets, which should be read prior to configuring a Cisco IOS router in accordance with the Common Criteria EAL4 evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec.
The Cisco IOS Release 12.1 and Release 12.2 documentation sets include the following elements:
•
Configuration guides, which provide a descriptive overview of functions, the commands needed to enable specified functions, and the sequence of operations that should be followed to implement them.
•
Command references, which provide a complete description of all configuration commands and options, their effects, and examples and guidelines for the use of the commands. The command references should be used to confirm detailed syntax and functionality options.
•
System Error Messages, which describe all error messages issued by Cisco IOS routers.
This document references the following Cisco IOS Release 12.1 and Release 12.2 documentation:
•
Cisco IOS Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide
•
Cisco IOS Configuration Fundamentals Command Reference
•
Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide
•
Cisco IOS Security Command Reference
•
Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide
•
Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 1 of 3: Addressing and Services
•
Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols
•
Cisco IOS System Error Messages
•
Release Notes and Caveats for Cisco IOS Release 12.2
Cisco IOS documentation is available on CD-ROM, in printed paper form, and online (in HTML and PDF formats). This document should be used in conjunction with the October 2001 edition of the CD-ROM-based documentation.
Audience
This document is written for administrators who configure Cisco IOS routers in accordance with the Common Criteria evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec. This document assumes that you are familiar with networks and networking technology, are a trusted individual, and been trained to use the IPSec technology and its applications, such as site-to-site Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). There are no components of the Cisco IOS IPSec that are accessible to nonadministrative users (end users); therefore, there is not any user-level documentation.
Supported Hardware and Software
The hardware and software combinations that are complaint with Common Criteria evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec are outlined in Table 1. (The supporting hardware documentation is outlined in Table 2.)
Note
Only the hardware versions of the IPSec VPN hardware modules that are listed in Table 8 are compliant with Common Criteria evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec. To display the hardware version of an IPSec VPN hardware module, use the show diag command in privileged EXEC mode.
Table 1 Supported Hardware and Software for the Common Criteria Evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec
Cisco 1700 series
1720, 1750
MOD1700-VPN
Cisco IOS 12.2(6)
IPSec 56
IPSec 3DES1
Cisco 2600 series
2610, 2611, 2612, 2613, 2620, 2621, 2650, and 2651
AIM-VPN/BP
Cisco IOS 12.2(6)
IPSec 56
IPSec 3DES1
Cisco 3600 series3620, 3640
NM-VPN/MP
Cisco IOS 12.2(6)IPSec 56
IPSec 3DES1
3660
AIM-VPN/HP
Cisco IOS 12.2(6)IPSec 56
IPSec 3DES1
Cisco 7100 series2
7120, 7140
SA-ISA or SM-ISM
Cisco IOS 12.2(6)
IPSec 56
IPSec 3DES1
SM-VAM3 or SA-VAM3
Cisco IOS 12.1(10)E
IPSec 56
IPSec 3DES1
Cisco 7200 series
7204, 7206, 7204VXR, 7206VXRSA-ISA (max 2)
Cisco IOS 12.2(6)
IPSec 56
IPSec 3DES1
SA-VAM3
Cisco IOS 12.1(10)E
IPSec 56
IPSec 3DES1
1 The Cisco IOS software image must contain at least the IPSec 56 or IPSec 3DES feature, which can be in combination with other feature sets such as IP, Firewall, Plus, or Enterprise.
2 The Cisco 7100 series and Cisco 7200 series without optional IPSec hardware acceleration modules can be configured with Cisco IOS Release 12.2(6)T or Cisco IOS Release 12.1(10)E.
3 Cisco 7100 series and Cisco 7200 series that are equipped with an SA-VAM or SM-VAM do not support Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman (RSA) public or private key pairs for IKE authentication.
Security Information
This section contains the following sections:
•
Supported Hardware Documentation
•
Organizational Security Policy
•
Security Implementation Considerations
Supported Hardware Documentation
In addition to the regulatory compliance documentation for each hardware platform listed in Table 2, the sections that follow provide additional security information for use with a Common Criteria evaluation Cisco IOS IPSec router.
Organizational Security Policy
Ensure that your Cisco IOS router is delivered, installed, managed, and operated in a manner that maintains an organizational security policy for IPSec protected traffic. The organizational security policy must describe the following variables:
•
The networks that are to be considered trusted and untrusted
•
The traffic flows between trusted networks that must be protected using IPSec to provide confidentiality, authenticity, and integrity in terms of source and destination IP addresses or port number
•
The Cisco IOS routers that are associated with each trusted network that provide IPSec services to the identified traffic flows
The administrator must identify which interfaces on the Cisco IOS router are considered trusted and untrusted. An untrusted interface is one that is connected to an untrusted network over which the administrator wishes to send and receive trusted traffic that is protected by IPSec encryption.
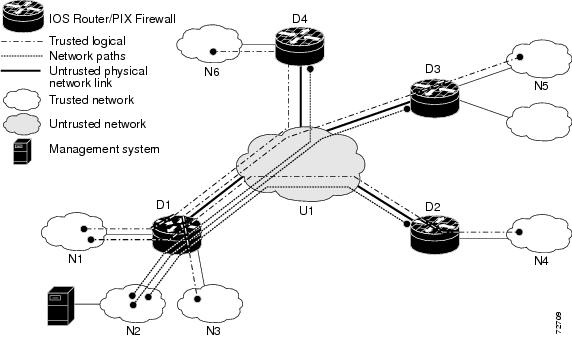
Figure 1 Organizational Security Policy Example
Figure 1 displays an organizational security policy with traffic flows that are identified solely by source and destination IP addresses. All Cisco IOS routers (D1, D2, D3, and D4) must be configured to implement a portion of the organizational security policy. For example, Router D1 has three trusted networks attached to it (N1, N2, and N3); this router implements a policy for the three trusted network-to-network flows and three secure management flows that cross the untrusted network (U1). (The policy that Router D1 implements is outlined in Table 3.)
Table 3 Policy for Cisco IPSec Crypto System Example
N1
N6
D4
N1
N5
D3
N3
N4
D2
N2
D2
D2
N2
D3
D3
N2
D4
D4
All other routers (D2, D3, D4) must have a matching configuration to implement the organizational security policy. Each of the rows in Table 3 is configured on the Cisco IOS router as an IPSec tunnel.
An organizational security policy may implement a site-to-site VPN between multiple locations (trusted networks) over the Internet (an untrusted network), or it may specify that all LAN traffic (trusted networks) be encrypted when transmitted over any WAN link (untrusted network).
Security Implementation Considerations
The following sections provide implementation considerations that need to be addressed to administer Cisco IOS routers in a secure manner that is consistent with Common Criteria evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec:
•
Remote Administration and Management
•
SNMP
Evaluated Configuration
Only the hardware and software version combinations that are described in Table 1 can be used to implement an evaluated configuration. You will invalidate the evaluated status of a particular hardware platform if you change the software to a different version.
The Common Criteria Target of Evaluation (TOE) for Cisco IOS IPSec defines only the following features:
•
IPSec Internet Key Exchange (IKE) using preshared keys, RSA keys, or digital certificates
Note
The Cisco 7100 series and Cisco 7200 series with an SM-VAM or SA-VAM do not support IKE with RSA keys.
•
IPSec encapsulating security payload (ESP) using tunnel mode with Data Encryption Standard (DES) or 3DES
•
Optional hardware acceleration of IPSec (as specified in Table 1)
•
Cryptographic key generation and management
•
Inbound access lists
•
Message logging
•
User authentication for access to the command-line interface (CLI) using locally configured passwords
Note
Although Cisco IOS supports authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) user authentication, it is not supported within the Cisco IOS-IPSec TOE.
•
Time management
All other hardware and software features and functions of a Cisco IOS router are outside the scope of this evaluated product configuration, and therefore can be used in conjunction with the TOE functions only if the TOE functions are configured, operated, and managed in accordance with this document.
To ensure that the Cisco IOS router configuration continues to meet the organizational security policy, you should review your router configurations for the following possible changes:
•
Changes in the Cisco IOS router configuration
•
Changes in the organizational security policy
•
Changes in the threats presented from untrusted networks
•
Changes in the administration and operation staff or of the physical environment of the Cisco IOS router
Physical Security
The Cisco IOS router must be located in a physically secure environment in which only a trusted administrator has access. The secure configuration of a Cisco IOS router can be compromised if an intruder gains physical access to the router.
Certificate Authority
If digital certificates are used to provide authentication between evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec routers, the certificate authority that issues the certificates must be trusted or evaluated to the same level as Cisco IOS IPSec (Common Criteria EAL4).
Time Sources
Routers configured in accordance with the Cisco IOS IPSec evaluation must time-stamp system log messages. For Cisco routers without internal, real-time hardware clocks (Cisco 1700, 2600, 3600 series), their software clock must be set from an external time source via the Network Time Protocol (NTP). To provide a trusted time source for the TOE, NTP servers must be connected to a trusted network in a secure location.
Access Control
The Cisco IOS router must be configured to authenticate privileged (enable mode) and unprivileged access to the CLI using a username or password. A good password has a combination of alphabetic and numeric characters, as well as punctuation characters. This password must be at least eight characters in length. We recommend that you tell the password to someone who is in a position of trust.
Remote Administration and Management
If you administer and manage the Cisco IOS router from a remote management system across an untrusted network, the following requirements apply:
•
The management station must be connected to a trusted network.
•
There must be another Cisco IOS router connected to the trusted and untrusted network.
•
There must be an IPSec tunnel between the trusted network and the Cisco IOS router that is managed.
A topology such as Figure 1, which displays these requirements, applies to any in-band administrative protocol including Telnet, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), and syslog.
SNMP
If SNMP read-write access is permitted, the TOE operation can be modified via SNMP. Therefore, SNMP must be configured explicitly in read-only mode if it is enabled on the TOE to support monitoring of the Cisco IOS router.
Logging and Messages
Monitoring activity in the log files is an important aspect of your network security and should be conducted regularly. Monitoring the log files allows you take appropriate and timely action when you detect breaches of security or events that are likely to lead to a potential security breach.
To view log file messages, use the show logging EXEC command. For configuration details, refer to the section "Message Logging" in Table 6.
Access Lists
The access-list command operates on a first match basis. Thus, the last rule added to the access list is the last rule checked. The administrator should make a note of the last rule during initial configuration because it may impact the remainder of the rule parsing.
To enable logging of access-list matches, use the log keyword with access-list definitions.
Monitoring and Maintenance
There are several ways (from logs to messages) in which you can monitor the operation of your Cisco IOS routers. However, ensure you know how you will monitor the router for performance and possible security issues. Also, plan your backups; if there should be hardware or software problems, you may need to restore the router configuration.
Installation Notes
Table 4 lists the documentation that should be used when installing a Cisco IOS IPSec evaluated router.
Table 4 Installation Documentation for Cisco IOS IPSec Hardware Platforms
Cisco 1700 series
Cisco 1720 Series Router Hardware Installation Guide
Cisco 1750 Series Router Hardware Installation Guide
Installing the Data Encryption AIM in Cisco 1700 Series Routers1
Cisco 2600 series
Cisco 2600 Series Hardware Installation Guide
Installing the Data Encryption AIM in Cisco 2600 Series and Cisco 3600 Series Routers1
Cisco 3600 series
Cisco 3600 Series Hardware Installation Guide
Installing the Data Encryption AIM in Cisco 2600 Series and Cisco 3600 Series Routers1
Cisco 7100 series
Cisco 7100 Series VPN Router Installation and Configuration Guide
Integrated Service Adapter and Integrated Service Module Installation and Configuration1
VPN Acceleration Module Installation and Configuration1
Cisco 7200 series
Cisco 7204 Installation and Configuration Guide
Cisco 7206 Installation and Configuration Guide
Cisco 7200 VXR Installation and Configuration Guide
Integrated Service Adapter and Integrated Service Module Installation and Configuration1
VPN Acceleration Module Installation and Configuration1
1 Hardware encryption acceleration modules are optional.
Verification of Image and Hardware IPSec Module
To verify that the Cisco IOS software and hardware IPSec VPN module (if used) has not been tampered with during delivery, perform the following steps.
Note
If a hardware IPSec VPN module is not being used, only steps 6 and 7 are necessary.
Note
Hardware IPSec VPN modules are delivered either as separate discrete items or preinstalled in a Cisco router platform.
Step 1
Inspect the physical packaging in which the equipment was delivered before unpacking the hardware IPSec VPN module.
•
Verify that the external cardboard packing is printed with the Cisco Systems logo and motifs. If the external packaging is not printed with Cisco branding, contact the equipment supplier (Cisco Systems or an authorized Cisco distributor or partner).
Step 2
Verify that the packaging has not been opened and resealed by examining the tape that seals the package. If the package appears to have been resealed, contact the equipment supplier.
Step 3
Verify that the box has a white tamper-resistant, tamper-evident Cisco Systems bar-coded label that is applied to the external cardboard box. (This label will include the Cisco product number, serial number, and other information regarding the contents of the box.) If this label is missing, contact the equipment supplier.
Step 4
Note the serial number of the hardware IPSec VPN module on the shipping documentation. If the hardware IPSec VPN module has been preinstalled, the white label on the outer box will show the serial number of the router platform inside; thus, the serial number of the hardware IPSec VPN module will appear on the shipping documents also attached to the outer box. Otherwise, if the VPN has not been preinstalled, the serial number of the hardware IPSec VPN module will be displayed on the white label.
Ensure that the serial number on the shipping documentation matches the serial number on the separately mailed invoice for the equipment. If the serial numbers do not match, contact the equipment supplier.Step 5
Verify that the box has been shipped from the expected equipment supplier by performing the following tasks:
•
Contact the supplier to verify that the box was shipped with the courier company that delivered the box and that the consignment note number for the shipment matches the number used for the delivery.
•
Verify that the serial numbers of the items shipped match the serial numbers of the items delivered. For equipment shipped directly from Cisco, you can verify the serial numbers online through Cisco's Networking Products Marketplace, Order Status Tool. For other suppliers, verify that the serial numbers match by using a mechanism that was not involved in the actual equipment delivery; for example, use the phone, fax, or another online tracking service.
Step 6
Inspect the module after the hardware IPSec VPN module has been unpacked. Verify that the serial number displayed on the module matches the serial number on the shipping documentation and the invoice. If the serial numbers do not match, contact the equipment supplier.
Step 7
Download a Common Criteria evaluated software image file from Cisco Connection Online (CCO) for your specific hardware platform onto a trusted computer system (as specified in Table 1). For all images, ensure that you have sufficient system and Flash memory to support the image on your router hardware by checking the release notes appropriate for the Cisco IOS release and by selecting the IPSec 56 or IPSec 3DES feature set.
Software images for Release 12.2(6) are available from CCO at the following URL:
http://cco.cisco.com/kobayashi/library/12.2/index.shtml
Software images for Release 12.1(10)E available from CCO at the following URL:
http://cco.cisco.com/kobayashi/library/12.1/index.shtmlAfter you have downloaded the file, verify that the file has not been tampered with by using a Message Digest 5 (MD5) utility to compute an MD5 hash for the file; compare this MD5 hash with the MD5 hash for the image, which is listed in Table 9. If the MD5 hashes do not match, contact Cisco Technical Support.
Step 8
Install the downloaded and verified software image onto your Cisco IOS router. For information on completing this task, refer to the chapter "Loading and Maintaining System Images" in the part "File Management" of the Cisco IOS Configuration Fundamentals Configuration Guide.
Step 9
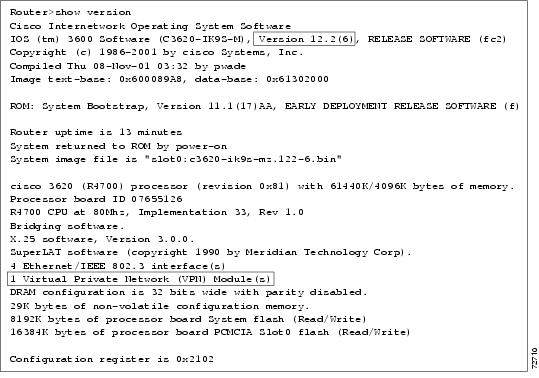
Start your router as described in the appropriate installation documentation that is outlined in Table 4. Confirm that your router loads the image correctly, completes internal self-checks, and displays the cryptographic export warning on the console. At the prompt, type the show version command. (See Figure 2.) Verify that the version matches one of the valid versions listed in Table 1. If the versions do not match or if the image fails to load, contact Cisco Technical Support.
Step 10
If the hardware IPSec VPN module has not been preinstalled, refer to one of the installation guides in Table 4.
Step 11
After the IPSec VPN module is installed, restart the router. At the prompt, enter the show version command. (See Figure 2.) To verify that a VPN module is installed, read the output display. If the output display does not report that the hardware IPSec VPN module is present, contact Cisco Technical Support.
Step 12
Enter the show diag command. Examine the output to ensure that the serial number reported by the hardware IPSec VPN module is the same as the serial number on the shipping documentation, invoice, and the hardware IPSec VPN module itself. Also, verify that the hardware version and revision of the module are listed in Table 8.
Figure 2 Sample show version Output That Shows the Cisco IOS Version and Presence of the Hardware IPSec VPN Module
Configuration Notes
The Common Criteria TOE for Cisco IOS IPSec defines the following two groups of features:
Note
Upon delivery, a Cisco IOS router is not configured to support any of these security enforcing or supporting functions. To ensure that your router is operating in accordance with Common Criteria evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec, these functions must be explicitly configured as described in this document and in the appropriate product documentation.
Security Enforcing
Security enforcing consists of the following functions:
•
IPSec IKE using preshared keys, RSA keys, or digital certificates
Note
Cisco 1700 series and Cisco 7200 series with an SM-VAM or SA-VAM do not support IKE with RSA keys.
•
IPSec ESP using tunnel mode with DES or 3DES
•
Optional hardware acceleration of IPSec (as specified in Table 1)
•
Cryptographic key generation and management
For information on configuring these security enforcing functions, refer to the chapters in the part "IP Security and Encryption" of the Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide. (If you are using the Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide, Release 12.1, use all chapters within the part "IP Security and Encryption" except the chapter "Configuring Cisco Encryption Technology.")
To ensure that your Cisco IOS router configuration is consistent with Common Criteria evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec, you must consider the IPSec options listed in Table 5.
Security Supporting
Security supporting consists of the following functions:
•
Inbound access lists
•
Message logging
•
User authentication for access to the CLI using locally configured passwords.
Note
Although Cisco IOS supports AAA user authentication, it is not supported within Common Criteria evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec.
•
Time management
Table 6 lists the documents that you should use to configure security supporting functions.
Saving Configurations
When making changes to the configuration of the router, use the write memory command frequently. If the router reboots and resumes operation when uncommitted changes have been made, these changes will be lost and the router will revert to the last configuration saved.
Enabling Time Stamps
By default, all audit records are not stamped with the time and date, which are generated from the system clock when an event occurs.
The Common Criteria evaluated Cisco IOS IPSec requires that the time-stamp feature be enabled on your Cisco IOS router. To enable the time stamp of audit events, use the service timestamps log datetime command.
To ensure that the timestamps option is meaningful, the system clock in your router must be set correctly. (See the following section, "Setting the System Clock," for more information.)
Setting the System Clock
To provide accurate time stamps for logging and to ensure that your router can process validity dates for digital certificates, the system clock must be set. Some models of Cisco IOS routers have real-time clocks that maintain real time when the router is powered down; these real-time clocks are used to initialize the system clock at startup. Other models of Cisco IOS routers do not have a real-time clock and must obtain the correct date and time from a reliable time source using the NTP. One example of a reliable time source is a Cisco IOS router with a real-time clock operating as an NTP Server. Table 7 lists router clock functions for use with Cisco IOS IPSec.
Hardware Versions of Hardware IPSec VPN Modules
Table 8 lists the hardware versions of IPSec VPN modules.
MD5 Hash Values for Cisco IOS Software Images
Table 9 lists the MD5 hash values for Cisco IOS software images.
For verification of MD5 hash values, contact Cisco Technical Support.
Related Documentation
Use this document in conjunction with the appropriate Cisco IOS software documentation, which can be found at the following location:
Documentation for Cisco IOS Release 12.1:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios121/index.htmDocumentation for Cisco IOS Release 12.2:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios122/index.htmObtaining Documentation
The following sections provide sources for obtaining documentation from Cisco Systems.
World Wide Web
The most current Cisco documentation is available on the World Wide Web at the following website:
http://www.cisco.com
Translated documentation is available at the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.html
Documentation CD-ROM
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM is updated monthly and may be more current than printed documentation. The CD-ROM package is available as a single unit or through an annual subscription.
Ordering Documentation
Cisco documentation can be ordered in the following ways:
•
Registered Cisco Direct Customers can order Cisco product documentation from the Networking Products MarketPlace:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/order/order_root.pl
•
Registered Cisco.com users can order the Documentation CD-ROM through the online Subscription Store:
http://www.cisco.com/go/subscription
•
Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local account representative by calling Cisco corporate headquarters (California, USA) at 408 526-7208 or, in North America, by calling 800 553-NETS(6387).
Documentation Feedback
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit technical comments electronically. Click Feedback in the toolbar and select Documentation. After you complete the form, click Submit to send it to Cisco.
You can e-mail your comments to bug-doc@cisco.com.
To submit your comments by mail, use the response card behind the front cover of your document, or write to the following address:
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Document Resource Connection
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883We appreciate your comments.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco provides Cisco.com as a starting point for all technical assistance. Customers and partners can obtain documentation, troubleshooting tips, and sample configurations from online tools. For Cisco.com registered users, additional troubleshooting tools are available from the TAC website.
Cisco.com
Cisco.com is the foundation of a suite of interactive, networked services that provides immediate, open access to Cisco information and resources at anytime, from anywhere in the world. This highly integrated Internet application is a powerful, easy-to-use tool for doing business with Cisco.
Cisco.com provides a broad range of features and services to help customers and partners streamline business processes and improve productivity. Through Cisco.com, you can find information about Cisco and our networking solutions, services, and programs. In addition, you can resolve technical issues with online technical support, download and test software packages, and order Cisco learning materials and merchandise. Valuable online skill assessment, training, and certification programs are also available.
Customers and partners can self-register on Cisco.com to obtain additional personalized information and services. Registered users can order products, check on the status of an order, access technical support, and view benefits specific to their relationships with Cisco.
To access Cisco.com, go to the following website:
http://www.cisco.com
Technical Assistance Center
The Cisco TAC website is available to all customers who need technical assistance with a Cisco product or technology that is under warranty or covered by a maintenance contract.
Contacting TAC by Using the Cisco TAC Website
If you have a priority level 3 (P3) or priority level 4 (P4) problem, contact TAC by going to the TAC website:
http://www.cisco.com/tac
P3 and P4 level problems are defined as follows:
•
P3—Your network performance is degraded. Network functionality is noticeably impaired, but most business operations continue.
•
P4—You need information or assistance on Cisco product capabilities, product installation, or basic product configuration.
In each of the above cases, use the Cisco TAC website to quickly find answers to your questions.
To register for Cisco.com, go to the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/register/
If you cannot resolve your technical issue by using the TAC online resources, Cisco.com registered users can open a case online by using the TAC Case Open tool at the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/tac/caseopen
Contacting TAC by Telephone
If you have a priority level 1 (P1) or priority level 2 (P2) problem, contact TAC by telephone and immediately open a case. To obtain a directory of toll-free numbers for your country, go to the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
P1 and P2 level problems are defined as follows:
•
P1—Your production network is down, causing a critical impact to business operations if service is not restored quickly. No workaround is available.
•
P2—Your production network is severely degraded, affecting significant aspects of your business operations. No workaround is available.

 Feedback
Feedback