-
Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Configuration Guide, Release 12.2
-
About Cisco IOS Software Documentation
-
Using Cisco IOS Software
-
Quality of Service Overview
- Part 1: Classification
- Part 2: Congestion Management
- Part 3: Congestion Avoidance
- Part 4: Policing and Shaping
- Part 5: Signalling
- Part 6: Link Efficiency Mechanisms
- Part 7: Quality of Service Solutions
- Part 8: Modular Quality of Service Command-Line Interface
- Part 9: Security Device Manager
-
Index
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring Class-Based Shaping
Class-Based Shaping Configuration Task List
Configuring Class-Based Shaping
Configuring CBWFQ Inside Generic Traffic Shaping
Verifying the Configuration of Policy Maps and Their Classes
Class-Based Shaping Configuration Examples
CBWFQ in Conjunction with GTS Example
Configuration Verification Example
Configuring Class-Based Shaping
This chapter describes the tasks for configuring the Class-Based Shaping feature.
For complete conceptual information, see the section "Class-Based Shaping" in the chapter "Policing and Shaping Overview" in this book.
For a complete description of the Class-Based Shaping commands mentioned in this chapter, refer to the Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Command Reference. To locate documentation of other commands that appear in this chapter, use the command reference master index or search online.
To identify the hardware platform or software image information associated with a feature, use the Feature Navigator on Cisco.com to search for information about the feature or refer to the software release notes for a specific release. For more information, see the "Identifying Supported Platforms" section in the "Using Cisco IOS Software" chapter in this book.
Class-Based Shaping Configuration Task List
To configure Class-Based Shaping, perform the tasks described in the following sections. The task in the first section is required; the tasks in the remaining sections are optional.
•
Configuring Class-Based Shaping (Required)
•
Configuring CBWFQ Inside Generic Traffic Shaping (Optional)
•
Verifying the Configuration of Policy Maps and Their Classes (Optional)
See the end of this chapter for the section "Class-Based Shaping Configuration Examples."
Configuring Class-Based Shaping
To configure Class-Based Shaping, use the first two commands in global configuration mode to specify the name of the policy map and the name of the class map. To specify average or peak rate, use the remaining commands in class-map configuration mode:
Configuring CBWFQ Inside Generic Traffic Shaping
To configure class-based weighted fair queueing (CBWFQ) inside GTS, use the first two commands in global configuration mode to specify the name of the policy map and the name of the class map. To specify average or peak rate and to attach the service policy to the class, use the remaining commands in class-map configuration mode:
Verifying the Configuration of Policy Maps and Their Classes
To display the contents of a specific policy map, a specific class from a specific policy map, or all policy maps configured on an interface, use the following commands in EXEC mode, as needed:
Class-Based Shaping Configuration Examples
The following sections provide Class-Based Shaping configuration examples:
•
CBWFQ in Conjunction with GTS Example
•
Configuration Verification Example
For information on how to configure Class-Based Shaping, see the section "Class-Based Shaping Configuration Task List" in this chapter.
Class-Based Shaping Example
The following example defines one class, c1. Class c1 is configured to shape traffic to 384 kbps, with a normal burst size of 15440 bits.
Router(config)# policy-map shapeRouter(config-pmap)# class c1Router(config-pmap-c)# shape average 384000 15440Router(config-pmap-c)# configure terminalRouter(config)# interface Serial 3/3Router(config-if)# service out shapeCBWFQ in Conjunction with GTS Example
The following example uses CBWFQ at the interface and shapes the traffic before it is queued to CBWFQ.
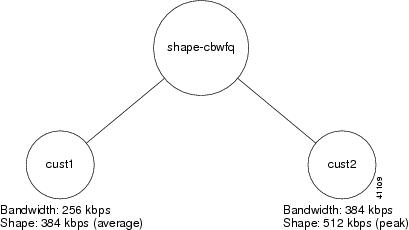
In this example, two classes are defined, cust1 and cust2. The class called cust1 is ensured a bandwidth of 256 kbps, and the output is shaped to 384 kbps. The class called cust2 is ensured a bandwidth of 384 kbps, but if enough bandwidth is available on the interface, the class can obtain throughput up to a peak of 512 kbps.
Figure 13 illustrates this example.
Figure 13 CBWFQ in Conjunction with GTS
The following commands are used to configure this example:
Router(config)# policy-map shape-cbwfqRouter(config-pmap)# class cust1Router(config-pmap-c)# shape average 384000Router(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth 256Router(config-pmap)# class cust2Router(config-pmap-c)# shape peak 512000Router(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth 384Router(config-pmap-c)# configure terminalRouter(config)# interface Serial 3/3Router(config-if)# service out shape-cbwfqCBWFQ Inside GTS Examples
This section provides two examples of configuring CBWFQ inside GTS.
The first example uses hierarchical policy maps and configures CBWFQ inside GTS.
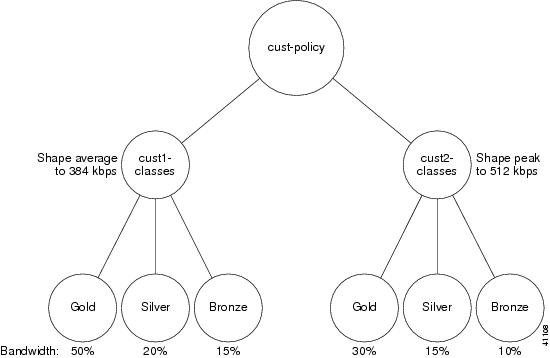
In the following example, three policy maps are defined—cust1-classes, cust2-classes, and cust-policy. The policy maps called cust1-classes and cust2-classes have three classes defined—gold, silver, and bronze.
For cust1-classes, gold is configured to use 50 percent of the bandwidth. Silver is configured to use 20 percent of the bandwidth, and bronze is configured to use 15 percent of the bandwidth.
For cust2-classes, gold is configured to use 30 percent of the bandwidth. Silver is configured to use 15 percent of the bandwidth, and bronze is configured to use 10 percent of the bandwidth.
The policy map cust-policy specifies average rate shaping of 384 kbps and assigns the service policy called cust1-classes to the class called cust1. The policy map cust-policy specifies peak rate shaping of 512 kbps and assigns the service policy cust2-classes to the class called cust2.
Figure 14 illustrates this example.
Figure 14 Hierarchical Policy Maps Using Class-Based Shaping
cust1-classes Configuration
Router(config)# policy-map cust1-classesRouter(config-pmap)# class goldRouter(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth percent 50Router(config-pmap)# class silverRouter(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth percent 20Router(config-pmap)# class bronzeRouter(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth percent 15cust2-classes Configuration
Router(config)# policy-map cust2-classesRouter(config-pmap)# class goldRouter(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth percent 30Router(config-pmap)# class silverRouter(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth percent 15Router(config-pmap)# class bronzeRouter(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth percent 10Customer Policy and QoS Features Configuration
Router(config)# policy-map cust-policyRouter(config-pmap)# class cust1Router(config-pmap-c)# shape average 384000Router(config-pmap-c)# service-policy cust1-classesRouter(config-pmap)# class cust2Router(config-pmap-c)# shape peak 512000Router(config-pmap-c)# service-policy cust2-classesRouter(config-pmap-c)# interface Serial 3/2Router(config-if)# service out cust-policyIn this second example, the Class-Based Shaping feature is configured for the class called shaped in the policy map called GTS_in_ModCLI. The class shaped is shaped to an average rate of 241,000 bits per second (bps). CBWFQ is also enabled on the class, which guarantees a bandwidth of 241 kbps during times of congestion at the interface.
The shaped class is a congestion point for all the subclasses that comprise that class. Therefore, the subclasses can be further differentiated in the shaped class. All these subclasses are part of the policy map, CBWFQ_in_GTS, that is attached to the shaped class.
Policy Map GTS_in_ModCLI Configuration
Router(config)# policy-map GTS_in_ModCLIRouter(config-pmap)# class shapedRouter(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth 241Router(config-pmap-c)# shape average 241000Router(config-pmap-c)# service-policy CBWFQ_in_GTSPolicy Map CBWFQ_in_GTS Configuration
The policy map called CBWFQ_in_GTS has four CBWFQ classes:
Router(config)# policy-map CBWFQ_in_GTSRouter(config-pmap)# class cust_ARouter(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth percent 25Router(config-pmap)# class cust_BRouter(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth percent 25Router(config-pmap)# class cust_CRouter(config-pmap-c)# bandwidth percent 25Router(config-pmap)# class class-defaultRouter(config-pmap-c)# fairConfiguration Verification Example
The following example is output of the show policy-map command for GTS_in_ModCLI displays an expanded configuration, including the subclasses:
Router# show policy-map GTS_in_ModCLIPolicy Map GTS_in_ModCLIClass shapedWeighted Fair QueueingBandwidth 241 (kbps) Max Threshold 64 (packets)Traffic ShapingAverage Rate Traffic ShapingCIR 241000 (bps) Max. Buffers Limit 1000 (Packets)Policy Map CBWFQ_in_GTSClass cust_AWeighted Fair QueueingBandwidth 25 (%) Max Threshold 64 (packets)Class cust_BWeighted Fair QueueingBandwidth 25 (%) Max Threshold 64 (packets)Class cust_CWeighted Fair QueueingBandwidth 25 (%) Max Threshold 64 (packets)Class class-defaultWeighted Fair QueueingFlow based Fair QueueingThe policy map called GTS_in_ModCLI can be attached to any logical interface that provides a congestion point. Run-time statistics after attaching to serial interface 3/0 are shown.
Router# show policy interface Serial 3/0Serial3/0output : GTS_in_ModCLIClass shapedWeighted Fair QueueingOutput Queue: Conversation 267Bandwidth 241 (kbps) Max Threshold 64 (packets)(pkts matched/bytes matched) 3852/947384(pkts discards/bytes discards/tail drops) 0/0/0Traffic ShapingTarget Byte Sustain Excess Interval Increment AdaptRate Limit bits/int bits/int (ms) (bytes) Active241000 1928 7712 7712 32 964 -Queue Packets Bytes Packets BytesDepth Delayed Delayed Active41 3980 978872 3967 975686 yesClass cust_AWeighted Fair QueueingOutput Queue: Conversation 41Bandwidth 25 (%) Max Threshold 64 (packets)(pkts matched/bytes matched) 0/0(pkts discards/bytes discards/tail drops) 0/0/0Class cust_BWeighted Fair QueueingOutput Queue: Conversation 42Bandwidth 25 (%) Max Threshold 64 (packets)(pkts matched/bytes matched) 0/0(pkts discards/bytes discards/tail drops) 0/0/0Class cust_CWeighted Fair QueueingOutput Queue: Conversation 43Bandwidth 25 (%) Max Threshold 64 (packets)(pkts matched/bytes matched) 0/0(pkts discards/bytes discards/tail drops) 0/0/0Class class-defaultWeighted Fair QueueingFlow Based Fair QueueingMaximum Number of Hashed Queues 32

 Feedback
Feedback