Table Of Contents
Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
Prerequisites for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
Restrictions for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
Information About Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
NetFlow Aggregation of Output Flows on ISE Line Cards
Using a Maximum Mask with a Minimum Mask Configuration
Types of NetFlow Supported on Cisco 12000 Series ISE Line Cards
How to Configure Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
Monitoring and Maintaining Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
Configuration Examples for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
Displaying Cache Information for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow Example
hw-module slot ip flow output collect-from-slot
hw-module slot ip flow output destination
hw-module slot ip flow output source
Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
The Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature is an extension of NetFlow accounting that allows you to capture Internet Protocol (IP) flow information on Cisco 12000 series IP services engine (ISE) line cards by specifying a maximum source prefix or destination prefix mask that filters flows for the Prefix-Type of Service (ToS) aggregation scheme. NetFlow data is collected on output flows for packets that arrive on a provider edge (PE) router in either Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) or IP format and are transmitted on an egress ISE interface in IP format to a customer edge (CE) device.
Feature History for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Contents
•
Prerequisites for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
•
Restrictions for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
•
Information About Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
•
How to Configure Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
•
Monitoring and Maintaining Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
•
Configuration Examples for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
Prerequisites for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
In IOS Release 12.0(30)S, the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature is supported only on the following ISE line cards:
•
Packet-over-SONET line cards
–
4-Port OC-3 POS ISE
–
8-Port OC-3 POS ISE
–
16-Port OC-3 POS ISE
–
4-Port OC-12 POS ISE
–
1-Port OC-48 POS ISE
–
4-Port OC-3 POS ISE
•
Channelized edge line cards
–
4-Port CHOC-12 ISE
–
1-Port CHOC-48 ISE
•
Ethernet line cards
–
4-Port Gigabit Ethernet
The Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature requires a NetFlow collector and analyzer that supports NetFlow data exported in Version 8 and 9 formats.
Restrictions for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
The following restrictions apply to the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature:
•
Aggregation scheme
The Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature supports only the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme for summarizing output flows on a Cisco 12000 series Internet router, before the data is exported to a NetFlow collection system.
•
ISE subinterfaces
The configuration of the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature on an individual ISE subinterface is not supported. However, if you configure Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow on an ISE interface, NetFlow data is also collected from output flows on the associated subinterfaces and reported in the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme.
•
Multicast traffic
The Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature does not support NetFlow accounting for multicast traffic.
•
IPv6 packets
The Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature does not support NetFlow accounting for IPv6 traffic.
•
SNMP
The Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature does not support the configuration of Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) or MIBs on the Cisco 12000 series Internet router.
•
NetFlow Version 9 Export Format
The export format used in NetFlow Version 9 does not distinguish flows collected from input NetFlow and flows collected from output NetFlow.
•
Control packets on the local router
Control packets, Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo packets that originate from the route processor (RP), and ICMP response packets that originate from the line card CPU are not accounted by Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow on the router on which they are generated.
Control packets and ICMP echo and response packets are accounted by Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow on all other routers, except the one on which they are generated.
Information About Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
To configure the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature, you should understand the following concepts:
•
NetFlow Aggregation of Output Flows on ISE Line Cards
•
Prefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme
•
Types of NetFlow Supported on Cisco 12000 Series ISE Line Cards
NetFlow Aggregation of Output Flows on ISE Line Cards
On a Cisco 12000 series Internet router, the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature allows you to specify the ISE output interfaces for which you want to aggregate data about flows. An output flow for which NetFlow data is collected is a unidirectional set of packets that:
•
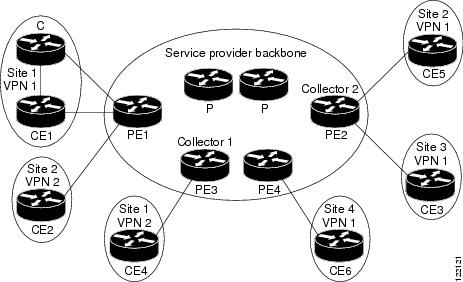
Arrives at the provider edge (PE) router in IP or MPLS format (MPLS backbone) or at a provider (P) router in IP format (IP backbone) and is transmitted in IP format (if necessary, after MPLS label disposition) on an output interface on any ISE line card to a customer edge (CE) router. See Figure 1 for an example.
•
Has the same source prefix, destination prefix, source mask, destination mask, source autonomous system (AS), destination autonomous system, input interface, output interface, and ToS byte in the IP header. This is known as the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme.
Figure 1 shows a sample topology. To capture the flow of traffic going to customer sites 2 and 3 of VPN 1 from the remote Site 1, you enable Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow accounting on one or more ISE line cards on the provider edge router PE2 that are configured for the PE2-CE3 and PE2-CE5 links. The flows are stored in a global flow cache maintained by the router. You can use the show ip cache flow or show ip cache flow aggregation prefix-tos commands to view the active output flow data.
The PE2 router exports the captured ISE output flows to configured collector devices in the provider network, such as NetFlow FlowCollector or NetFlow Analyzer, for further processing and analysis.
Figure 1 Provider and Customer Networks with Maximum Mask Aggregated Output NetFlow
Prefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme
Although there are other ToS-based NetFlow aggregation schemes, the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature supports only the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme. This aggregation scheme groups together output flows on ISE egress interfaces that are defined by having the same key fields: source prefix, source mask, destination prefix, destination mask, source autonomous system, destination autonomous system, input interface, output interface, and ToS byte.
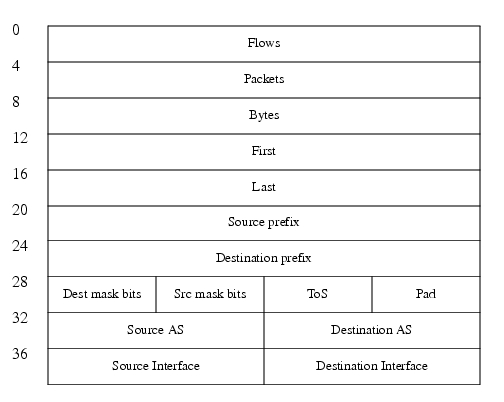
As shown in Figure 2, the aggregated NetFlow export record reports the following data:
•
Source prefix
•
Source prefix mask
•
Destination prefix
•
Destination prefix mask
•
Source autonomous system
•
Destination autonomous system
•
Source interface
•
Destination interface
•
ToS byte
•
Number of flows summarized by the aggregated record
•
Number of bytes summarized by this aggregated record
•
Number of packets summarized by this aggregation record
•
Starting and ending time stamps
The Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme is particularly useful for generating data to review the sources and destinations of network traffic passing through a NetFlow-enabled Cisco 12000 series Internet router, used as a PE router in an IP or MPLS backbone, to a CE device.
Figure 2 Prefix-ToS Aggregation Export Record Format
Note
Figure 2 shows an example of a NetFlow Version 8 export record.
Table 1 describes the fields in the Prefix-ToS aggregation export record.
Maximum Mask Configuration
The Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature was developed to provide NetFlow accounting for output flows on ISE interfaces in PE-CE connections by sharing NetFlow processing between the egress ASIC and the line card CPU.
For input NetFlow accounting, the ingress ASIC populates the ternary content addressable memory (TCAM) used by NetFlow with flows that have source and destination IP addresses because the forwarding information is available in the ingress ASIC. However, for output NetFlow accounting, forwarding information is not available in the egress ASIC and must be looked up in the Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) Forwarding Information Base (FIB).
If the entire source and destination IP address is used as a key field in NetFlow records, many more flows are generated than flows to which packets would have been assigned based on actual source and destination routing prefixes. To filter and reduce the number of flows reported in TCAM, you can configure a maximum prefix mask that is applied to all source and destination IP addresses before they are reported to TCAM.
When the line card CPU retrieves the NetFlow flow records from TCAM, it performs a lookup in the CEF FIB to find the routing prefix lengths of the source and destination IP prefixes reported by the egress ASIC based on the maximum mask value, and populates software flows with the source and destination prefixes and AS number from the corresponding FIB entry. The Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature collects data on flows based on routing prefixes whose lengths are equal to or less than the configured maximum mask value.
The Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature allows you to configure a separate maximum mask length for source and destination IP addresses. You can specify a unique maximum mask length for source and destination addresses on each ISE line card, and then select the output interfaces that you want to enable for the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature. Also, the hw-module slot ip flow output collect-from-slot command allows you to aggregate output flows from a selected subset of source line cards in the router using the same maximum mask filter.
Recommendations
When configuring the maximum mask lengths, you need to balance your needs for accurate NetFlow statistics and optimal line card performance. To increase the accuracy and granularity of NetFlow statistics, it is recommended that you configure a longer maximum mask. To achieve the most accuracy and desired level of granularity of NetFlow data, configure the maximum mask length to be the length of the longest routing prefix used by the packets in the flows that you want NetFlow to collect.
To reduce the peak rate of new flows and optimize ISE hardware performance, configure a shorter maximum mask. In general, if the maximum mask length is shorter, fewer flows are created. For example, in the extreme case that you configure a maximum mask of /0, only one flow is created for all packets. In the other extreme case, if you configure a maximum mask of /32, a new flow is created for each individual TCP or User Datagram Protocol (UDP) session.
Note
If the aggregated flow rate on an ISE line card exceeds 100 K per second in either direction or 150 K per second in both directions combined, NetFlow accounting may not be performed on some packets. Although ISE line cards do not provide a counter for unaccounted packets, an error message is displayed to indicate that some packet flows are not being recorded by NetFlow. This message allows you to configure a shorter maximum mask value to reduce the number of flows that are created.
Using a Maximum Mask with a Minimum Mask Configuration
To achieve the desired level of granularity of NetFlow information in the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme, you can configure the NetFlow Minimum Prefix Mask for Router-Based Aggregation feature along with the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature on a router.
The NetFlow Minimum Prefix Mask feature allows you to configure a minimum mask size (from 1 to 32 bits) that also determines the granularity of the NetFlow data that is collected:
•
For coarse NetFlow collection granularity, select a low minimum mask value.
•
For fine NetFlow collection granularity, select a high minimum mask value.
For more information about using minimum mask values to customize your NetFlow collection scheme, refer to NetFlow Minimum Prefix Mask for Router-Based Aggregation.
Example
The following example shows how using a minimum mask and a maximum mask configuration can increase the level of granularity in the NetFlow information reported, as compared to using only a maximum mask configuration. The strategy is that if the source or destination prefix of a packet does not match a specific entry in the routing table, a prefix can match a less specific entry used as the minimum mask value and be included in a traffic flow collected by NetFlow.
For example, if you set a minimum mask size of /24 and a maximum mask of /28, packet addresses that match a covering prefix /16, but do not match a more specific prefix /24, are reported as separate flows in the NetFlow data as in the following conditions:
•
10.3.0.0/16 and 10.3.3.0/24 are the routing prefixes.
•
The source or destination prefix in packets is 10.3.4.1.
To increase the granularity of NetFlow data, you can configure the minimum mask value at increasingly longer lengths for a given maximum mask length:
•
If no minimum mask is configured, only information on packets that match the 10.3.0.0/16 prefix is collected by NetFlow and reported in show commands.
•
If you configure a minimum mask of /20, information on packets that match the 10.3.0.0/20 prefix is reported (although no packet has this routing prefix).
•
In a similar way, if you configure a minimum mask of /24, information on packets that match the 10.3.4.0/24 prefix is reported (although there is no such routing prefix).
In this example, using a minimum mask value of /24 reports more traffic information than if you did not use a minimum mask configuration, and allows packets with a source or destination prefix of 10.3.4.1 to be reported as a separate flow.
A second example that shows how to increase the accuracy of NetFlow data by using a minimum mask and a maximum mask configuration is as follows:
•
The maximum mask is set at /28.
•
The minimum mask is set at /26.
•
The routing table entry is 10.3.3.208/32.
•
The source or destination address of a packet is 10.3.3.208.
In this case, you can configure minimum mask and maximum mask values to include the shortest covering prefix length (for example, /16), so that the corresponding traffic flow data is reported as follows:
•
If the minimum mask (/26) and maximum mask (/28) values are not configured, NetFlow data is reported with prefix 10.3.3.208/32.
•
If the minimum mask, but no maximum mask, is configured, NetFlow data is reported with prefix 10.3.3.208/32.
•
If the maximum mask, but no minimum mask, is configured, NetFlow data is reported with prefix 0.0.0.0/32.
In this case, if the routing table has an address entry 10.3.3.208/32 and a covering prefix of 10.3.3.0/24, and if a packet has a source or destination address 10.3.3.208, NetFlow data is reported with prefix 10.3.3.0/24.
•
If the minimum mask and maximum mask values are configured, NetFlow data is reported with 10.3.3.192/26.
Note
If you configure a minimum mask for a NetFlow aggregation scheme and enable input NetFlow and output NetFlow at the same time on a router, the minimum mask is applied to both input and output NetFlow.
Types of NetFlow Supported on Cisco 12000 Series ISE Line Cards
In addition to the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature, the following types of NetFlow accounting are also supported on Cisco 12000 series ISE line cards:
•
Sampled NetFlow on input and output interfaces
•
MPLS-aware NetFlow (sampled)
•
NetFlow Aggregation (non-sampled) on input interfaces
•
NetFlow Minimum Prefix Mask for Router-Based Aggregation on input and output interfaces
How to Configure Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
This section describes the procedure for configuring the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
ip flow-export destination ip-address
4.
ip flow-aggregation cache prefix-tos
5.
enable
6.
exit
7.
(Optional) hw-module slot number ip flow output {source | destination} max-mask-length length
8.
(Optional) hw-module slot number ip flow output collect-from-slot number
9.
Repeat Step 9 for each additional ISE line card from which you want to collect output flows in the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme using the maximum mask lengths configured in Step 7 and Step 8.
10.
hw-module slot number tcam carve region percentage
11.
microcode reload slot-number
Note
After you enter the microcode reload command, the line card is reset. As a result, traffic forwarding is interrupted. The control protocols and interfaces are down until the line card reset is complete.
12.
interface type slot/port
13.
ip route-cache flow output
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
enable
Example:Router> enable
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
•
Enter your password if prompted.
Step 2
configure terminal
Example:Router# configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode.
Step 3
ip flow-export destination ip-address
Example:Router(config)# ip flow-export destination 10.3.1.1 3000
Enables the exporting of information in NetFlow cache entries to the collection device at the specified IP address.
For detailed information on the command syntax, refer to NetFlow Multiple Export Destinations.
Step 4
ip flow-aggregation cache prefix-tos
Example:Router(config)# ip flow-aggregation cache prefix-tos
Enters NetFlow cache command mode to configure the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme.
For detailed information on the command syntax, refer to NetFlow ToS-Based Router Aggregation.
Step 5
enable
Example:Router(config-flow-cache)# enable
Enables the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme.
For detailed information on the command syntax, refer to NetFlow ToS-Based Router Aggregation.
Step 6
exit
Example:Router(config-flow-cache)# exit
Exits NetFlow cache command mode and returns to global configuration mode.
For detailed information on the command syntax, refer to NetFlow ToS-Based Router Aggregation.
Step 7
hw-module slot number ip flow output {source | destination} max-mask-length length
Example:Router(config)# hw-module slot 3 ip flow output source max-mask-length 24
(Optional) Configures the length of the maximum mask used to mask the source and/or destination prefix in output flows collected for the NetFlow Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme on a customer-facing ISE line card.
For detailed information on the command syntax, refer to hw-module slot ip flow output source, and hw-module slot ip flow output destination.
Step 8
hw-module slot number ip flow output collect-from-slot number
Example:Router(config)# hw-module slot 3 ip flow output collect-from slot 2
Router(config)# hw-module slot 3 ip flow output collect-from slot 4
(Optional) Configures a subset of source slots in the router to collect output flows for the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme using the maximum mask length configured in Step 5.
To include a line card into the subset of source slots used to collect output flows for the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature, enter the command once for each additional line card, as shown in the example.
To collect output flows from all ISE line cards in the router (default setting), do not enter the command.
For detailed information on the command syntax, refer to hw-module slot ip flow output collect-from-slot.
Step 9
Repeat Step 9 for each additional ISE line card from which you want to collect output flows in the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme using the maximum mask lengths configured in Step 7 and Step 8.
—
Step 10
hw-module slot number tcam carve region percentage
Example:Router(config)# hw-module slot 3 tcam carve tx_top_nf 35
Router(config)# hw-module slot 3 tcam carve tx_144b 30
Router(config)# hw-module slot 3 tcam carve tx_288b 20
Reconfigures the percentage of TCAM hardware used in source and destination address lookups for Netflow-related processing.
To increase the TCAM capacity for handling an increased amount of output flows created for NetFlow accounting and decrease the percentage allocated to other software features on a NetFlow-enabled line card, enter the command more than once, as shown in the example.
For detailed information on the command syntax, refer to hw-module slot tcam carve.
Step 11
microcode reload slot-number
Example:Router(config)# microcode reload 3
Reloads the software and microcode on the specified line card so that the new TCAM region sizes take effect.
The microcode reload command is necessary only if you reconfigure TCAM regions on a line card. For example, when you enable output NetFlow on an additional interface on the same line card, you do not have to reload the microcode a second time.
Note
After you enter the microcode reload command, the line card is reset. As a result, traffic forwarding is interrupted. The control protocols and interfaces are down until the line card reset is complete.
Step 12
interface type slot/port
Example:Router(config)# interface pos 3/0
Specifies an interface and enters interface configuration mode.
•
The type argument is the type of interface to be configured.
•
The slot/port argument specifies the slot and port numbers of the interface
Step 13
ip route-cache flow output
Example:Router(config-if)# ip route-cache flow output
Enables the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature to collect data for outgoing traffic on the egress interface.
Monitoring and Maintaining Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
To display information about the NetFlow data collected in the Prefix-ToS aggregation cache using the configured maximum mask lengths, use the following show commands in privileged EXEC mode:
Router# show ip cache [verbose] flow aggregation prefix-tos
Displays statistics and the configuration of the Prefix-ToS aggregation cache.
For more information, refer to NetFlow ToS-Based Router Aggregation.
Router# show ip cache verbose flow
Displays statistics about input and output flows in IP format that were recorded in the global NetFlow aggregation cache.
Router# show ip flow export
Displays statistics about the NetFlow data to be exported, including output flows collected in the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow.
For more information, refer to NetFlow ToS-Based Router Aggregation.
Configuration Examples for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow
This section contains the following configuration examples for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow:
•
Displaying Cache Information for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow Example
Configuring NetFlow Prefix-ToS Aggregation with Maximum Mask Lengths for Output Flows on ISE Line Cards Example
The following example shows how to configure the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature (including the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme and maximum mask lengths for source and destination prefixes) on an ISE line card in a Cisco 12000 series Internet router, and how to enable Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow on the POS interface 3/1:
Router# configure terminalRouter(config)# ip cache flow aggregation prefix-tosRouter(config)# hw-module slot 3 ip flow output source max-mask-length 24
Router(config)# hw-module slot 3 ip flow output destination max-mask-length 16Router(config)# hw-module slot 3 ip flow output collect-from slot 5Router(config)# interface pos 3/1Router(config-if)# ip route-cache flow outputDisplaying Cache Information for Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow Example
The following example shows how to display detailed statistical and configuration information from the Prefix-ToS aggregation cache used to collect NetFlow data for the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature:
Router# exec slot 3 show ip cache verbose flow aggregation prefix-tos========= Line Card (Slot 3) =========IP Flow Switching Cache, 278544 bytes2 active, 4094 inactive, 3 added70 ager polls, 0 flow alloc failuresActive flows timeout in 1 minutesInactive flows timeout in 10 secondsSrc If Src Prefix Dst If Dst Prefix TOS Flows PktsMsk AS Msk AS B/Pk ActivePO1/0 10.4.1.0 PO3/1* 10.7.0.0 E0 7105 37M/24 0 /16 0 40 18.5PO1/0 10.4.1.0 PO3/0* 10.5.1.1 E0 7104 37M/24 0 /32 0 40 18.5Table 2 describes the significant fields shown in this example.
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature.
Related Documents
NetFlow switching description and configuration tasks
NetFlow Switching chapter in the
Cisco IOS Switching Services Configuration Guide, Release 12.2NetFlow configuration commands
Cisco IOS NetFlow Commands
Cisco IOS Switching Services Command Reference, Release 12.2NetFlow concepts and features, guidelines for exporting NetFlow accounting statistics to a NetFlow FlowCollector (NFC) and to the Network Data Analyzer (NDA), high-level examples showing how to deploy these features in different network environments
NetFlow statistics in ToS-based aggregation schemes
Netflow statistics for output IP flows of IPv4 traffic using deterministic sampling
Netflow statistics for output IP flows of packets undergoing MPLS label disposition (packets that arrive on a router as MPLS and are transmitted as IP)
NetFlow statistics for MPLS traffic in MPLS-enabled networks
NetFlow statistics collected in Prefix, Destination-Prefix, and Source-Prefix aggregation schemes using a specified minimum mask value.
Procedures to configure the export of NetFlow data to multiple destinations
Cisco Network Data Analyzer functions, features, and uses
Network Data Analyzer Installation and User Guide, Release 3.6
Standards
MIBs
RFCs
Technical Assistance
Command Reference
This section documents new and modified commands. All other commands used with this feature are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 12.0S command reference publications.
•
hw-module slot ip flow output collect-from-slot
•
hw-module slot ip flow output destination
•
hw-module slot ip flow output source
hw-module slot ip flow output collect-from-slot
To collect output flows from a subset of source slots on the router using an existing Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow configuration, use the hw-module slot ip flow output collect-from-slot command in global configuration mode. To remove a source slot from the subset of source slots configured for the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature, use the no form of this command.
hw-module slot number ip flow output collect-from-slot number
no hw-module slot number ip flow output collect-from-slot number
Syntax Description
Defaults
By default, the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature collects data on output flows from all source slots in a Cisco 12000 series Internet router.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use the hw-module slot ip flow output collect-from-slot number command to specify a subset of source line cards in the Cisco 12000 series Internet router from which output flows are to be collected using the maximum mask lengths configured for the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature on the ISE line card in the slot specified by hw-module slot number.
Note
If you enter the hw-module slot ip flow output collect-from-slot number command to specify a subset of source slots, output flows for which the ingress and egress line card is the same are not collected by default, unless you enter the hw-module slot number ip flow output collect-from-slot number command with the slot number of the line card in collect-from-slot number.
The hw-module slot ip flow output collect-from-slot number command is optional. If you want to collect output flows from all source line cards in the router using an existing maximum mask configuration, do not enter the command.
Note that, because the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature collects output flows for packets that are received on the router in IP or MPLS format, you can customize the collection of output flows (based on the source slots of the flows) for IP packets transmitted to different CE devices through different customer-facing ISE line cards. For example, you can use the feature to collect NetFlow statistics on Virtual Private Network (VPN) traffic, such as the VPN 1 traffic in Figure 1 that is transmitted over PE2 between CE3 and CE5 in two different customer sites.
If you have a line card configured for redundancy that you want to include in a subset of source slots, you must enter the hw-module slot ip flow output collect-from-slot number command twice, once to include the primary line card and a second time to include the secondary line card.
Examples
The following example shows how to specify a subset of source slots (slots 1 and 2) that use the maximum mask lengths configured on the line card in slot 4.
Router(config)# hw-module slot 4 ip flow output source collect-from-slot 1
Router(config)# hw-module slot 4 ip flow output source collect-from-slot 2
The next example shows how to specify a subset of source slots (slots 1, 2, and 4) that use the maximum mask lengths configured on the line card in slot 4.
Router(config)# hw-module slot 4 ip flow output source collect-from-slot 1
Router(config)# hw-module slot 4 ip flow output source collect-from-slot 2
Router(config)# hw-module slot 4 ip flow output source collect-from-slot 4
Related Commands
hw-module slot ip flow output destination
To configure the maximum mask length used to filter destination prefixes in output flows collected for the NetFlow Prefix-ToS aggregation on an ISE line card, use the hw-module slot ip flow output command in global configuration mode. To disable a maximum mask length configuration, use the no form of this command.
hw-module slot number ip flow output destination max-mask-length length
no hw-module slot number ip flow output destination max-mask-length length
Syntax Description
Defaults
The hw-module slot ip flow output destination command is disabled by default.
The default value of the maximum mask length for the destination prefix is 32 bits.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use the hw-module slot ip flow output destination command to configure the maximum length of the destination mask used to collect output flows in the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme on an ISE line card connected to a CE device.
You can configure different maximum mask lengths for the source and destination prefix by entering a different value with the hw-module slot ip flow output source command.
Also, you can configure different maximum lengths on different ISE line cards for the source and destination masks used to filter traffic in Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow.
If you need to reduce the peak rate of new output flows and reduce line card CPU utilization, reconfigure a shorter maximum mask length. If you want to increase the granularity and improve the accuracy of NetFlow statistics, configure a longer maximum mask length.
For information about how to use a minimum mask configuration with a maximum mask configuration of the source and destination prefix masks used by NetFlow to collect data on output flows, see Using a Maximum Mask with a Minimum Mask Configuration.
After you configure the maximum length of the source and destination masks on an ISE line card, enable the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature on an ISE interface by using the ip route-cache flow output command. See ip route-cache flow output for more information.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure maximum mask lengths for source and destination prefixes in output flows collected for the NetFlow Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme on a customer-facing ISE interface in slot 4.
Router(config)# hw-module slot 4 ip flow output source max-mask-length 15
Router(config)# hw-module slot 4 ip flow output destination max-mask-length 20Related Commands
hw-module slot ip flow output source
To configure the maximum mask length used to filter source prefixes in output flows collected for the NetFlow Prefix-ToS aggregation on an ISE line card, use the hw-module slot ip flow output source command in global configuration mode. To disable a maximum mask length configuration, use the no form of this command.
hw-module slot number ip flow output source max-mask-length length
no hw-module slot number ip flow output source max-mask-length length
Syntax Description
Defaults
The hw-module slot ip flow output source command is disabled by default.
The default value of the maximum mask length for the source prefix is 32 bits.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use the hw-module slot ip flow output source command to configure the maximum length of the source prefix mask used to collect output flows in the Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme.
You can configure different maximum mask lengths for the source and destination prefix by entering a different value with the hw-module slot ip flow output destination command.
Also, you can configure different values on different ISE line cards for the maximum mask lengths used to filter traffic in the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature.
If you need to reduce the peak rate of new output flows and reduce line card CPU utilization, reconfigure a shorter maximum mask length. If you want to increase the granularity and improve the accuracy of NetFlow statistics, configure a longer maximum mask length.
For information about how to use a minimum mask configuration with a maximum mask configuration of the source and destination prefix masks used by NetFlow to collect data on output flows, see Using a Maximum Mask with a Minimum Mask Configuration.
After you configure the maximum length of the source and destination masks on an ISE line card, enable Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow on an ISE interface by using the ip route-cache flow output command. See ip route-cache flow output for more information.
Examples
The following example shows how to configure maximum mask lengths for source and destination prefixes in output flows collected for the NetFlow Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme on a customer-facing ISE interface in slot:
Router(config)# hw-module slot 4 ip flow output source max-mask-length 16
Router(config)# hw-module slot 4 ip flow output destination max-mask-length 20Related Commands
hw-module slot tcam carve
To reconfigure the percentage of ternary content addressable memory (TCAM) capacity used in source and destination address lookups for Netflow-related processing, use the hw-module slot tcam carve command in global configuration mode. The no form of this command has no effect.
hw-module slot number tcam carve region percentage
Syntax Description
number
Slot number of a line card.
region
Region in TCAM reserved for a software feature.
percentage
Percentage of TCAM reserved for the specified software region.
Defaults
This command has no default behavior or values.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
12.0(23)S
This command was introduced.
12.0(30)S
Support for the TX_TOP_NF region was added.
Usage Guidelines
Use the hw-module slot tcam carve command to reconfigure the percentage of TCAM hardware used in source and destination address lookups for Netflow-related processing.
To increase the TCAM capacity for handling an increased number of output flows created for NetFlow accounting and decrease the percentage allocated to other software features on a NetFlow-enabled line card, enter the command once to configure the TCAM percentage reserved for each software region.
For the new TCAM region sizes to take effect, you must enter the microcode reload slot-number command. This command reloads the software and microcode on the specified line card.
The microcode reload command is necessary only if you reconfigure TCAM regions on a line card. For example, when you enable output NetFlow on an additional interface on the same line card, you do not have to reload the microcode a second time.
Note
After you enter the microcode reload command, the line card is reset. As a result, traffic forwarding is interrupted. The control protocols and interfaces are down until the line card reset is complete.
Examples
The following example shows to increase the percentage of TCAM used for the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature to 30 percent and decrease the amounts used in two regions in the default configuration:
Router(config)# hw-module slot 3 tcam carve tx_top_nf 35
Router(config)# hw-module slot 3 tcam carve tx_144b 30
Router(config)# hw-module slot 3 tcam carve tx_288b 20
Router(config)# microcode reload 3
Related Commands
ip route-cache flow output
To enable a maximum mask configuration for the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature on an interface, use the ip route-cache flow output command. To disable the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature, use the no form of this command.
ip route-cache flow [output | sampled [input | output]]
no ip route-cache flow [output | sampled [input | output]]
Syntax Description
Defaults
This command is not enabled by default.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Use the ip route-cache flow output command to enable a maximum mask configuration to collect output flows for the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature on an ISE interface.
Note
By using the ip route-cache flow [output | sampled [input | output]] command, you can enable sampled or aggregate input NetFlow for incoming IP traffic flows on an ISE interface that is configured for the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature on output flows.
You cannot enable the Output Sampled NetFlow feature and the Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow feature at the same time on an ISE egress interface.
For more information about how to use the ip route-cache flow command, refer to Output Sampled NetFlow.To export NetFlow data (traffic statistics) to a remote workstation for further processing, use the ip flow-export command in global configuration mode.
Examples
The following example enables Maximum Mask Aggregate Output NetFlow on an interface:
interface pos 3/0ip address 17.252.245.2 255.255.255.0ip route-cache flow outputRelated Commands
Copyright © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.