Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
Lawful Intercept on Cisco 12000 Series Router ISE Line Cards
SNMPv3 Lawful Intercept Provisioning Interface
Implementation of Lawful Intercept
Lawful Intercept for Dial-up Calls
Related Features and Technologies
SNMP v3 Access for Lawful Intercept
Router Access Function Configuration
Call Agent Access Function Configuration
Surveillance Function Provisioning
Collection Function Provisioning
Lawful Intercept on Cisco 12000 Series Router ISE Line Cards
Part Number OL-8679-01 (Rev. A0) April 1, 2008
Feature History
See the following main sections for information about the Lawful Intercept feature:
Feature Overview
This feature module describes the Lawful Intercept functionality as it is implemented on the Cisco 12000 series routers.
The Feature Overview section contains the following sections:
•
Implementation of Lawful Intercept
•
Lawful Intercept for Dial-up Calls
•
Related Features and Technologies
Lawful Intercept Description
Lawful Intercept is the process by which law enforcement agencies conduct electronic surveillance of circuit and packet-mode communications as authorized by judicial or administrative order.
Service providers worldwide are already legally required to allow government agencies to conduct electronic surveillance on traditional telephone equipment. Lawful Intercept enables government agencies to conduct electronic surveillance on packet networks as well.
Note
Network management is the same as without Lawful Intercept. No difference is observable by management stations in the network. This ensures that unauthorized users cannot tell which nodes have Lawful Intercept enabled.
Cisco Lawful Intercept is based on Service Independent Intercept (SII) architecture and Simple Network Management Protocol Version 3 (SNMP V3) provisioning architecture.
Cisco SII architecture supports Lawful Intercept with the following features:
•
Standard architecture for all IP networks.
•
Intercept control is performed by the mediation device instead of by call control equipment.
•
Lawful Intercept control is separated from call control.
•
Common interfaces are defined for the mediation device and for call control partners.
The Cisco 12000 series routers support Lawful Intercept under SII architecture with the following features:
•
Legal Voice over IP (VoIP) and dial-up intercept provisioning from the mediation device using SNMPv3
•
Deliver intercepted voice data and dial-up data to the mediation device
•
SNMPv3 Lawful Intercept provisioning interface
•
Lawful Intercept MIB: CISCO-TAP-MIB, Version 1
•
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) encapsulation to Mediation Device
•
Voice over IP (VoIP) call intercept based on media gateway local IP address and UDP port number
•
Voice over IP (VoIP) intercept with Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP)
•
Dial-up call intercept based on account session ID
•
Dial-up intercept for PPP, multi-link PPP, and Exec/TCP-clear sessions
SNMPv3 Lawful Intercept Provisioning Interface
SNMPv3 is the provisioning interface for Cisco 12000 series router implementation of Lawful Intercept. SNMPv3 provides data origin authentication and secure connections. The law requires authentication and security so that unauthorized parties cannot observe or forge an intercept target.
Implementation of Lawful Intercept
There are two types of Cisco Lawful Intercepts on the Cisco 12000 series routers:
•
Lawful Intercept for Voice over IP (VoIP) calls
•
Lawful Intercept for dial-up calls
Lawful Intercept for VoIP
On Cisco 12000 series routers, Lawful Intercept for Voice over IP (VoIP) is done using SII architecture and SNMPv3 provisioning architecture. The mediation device provisions the intercept on the router using SNMPv3. The router intercepts the target Voice over IP (VoIP) calls and sends the intercepted data to the mediation device.
Before provisioning Lawful Intercept for Voice over IP (VoIP) can be done, the Lawful Intercept administrator must perform the following tasks.
1.
Provision the target number to be intercepted
2.
Register the routers used in the target number's calls
3.
Provision DNS on the SS8 mediation device
Lawful Intercept provisioning for Voice over IP (VoIP) on a Cisco 12000 series router is done as follows:
1.
The mediation device provisions Lawful Intercept information using SNMPv3.
2.
Security and authentication is done as defined by SNMPv3.
3.
Network management is done using the CISCO-TAP-MIB.
4.
Midcall Lawful Intercept provisioning allows an intercept to be provisioned and enabled or disabled while the call is active.
Voice over IP (VoIP) calls are intercepted as follows:
1.
The mediation device uses configuration commands to configure the intercept on the call control entity.
2.
The call control entity sends intercept-related information about the target to the mediation device.
3.
The mediation device initiates call content intercept requests to the edge router or trunk gateway using SNMPv3.
4.
The edge router or trunk gateway intercepts the call content, replicates it, and sends it to the mediation device in UDP format.
Content of intercepted Voice over IP (VoIP) is transmitted using UDP transport.
Lawful Intercept for Dial-up Calls
Cisco implements Lawful Intercept for dial-up calls using SII architecture and SNMP V3 provisioning architecture.
Before provisioning Lawful Intercept for dial-up calls can be done, the Lawful Intercept administrator must perform the following tasks.
•
Provision the target number to be intercepted
•
Register the routers used in the target number's calls
•
Provision DNS on the SS8 mediation device
On Cisco 12000 series routers, Lawful Intercept provisioning for dial-up calls is done as follows:
•
The mediation device provisions the Lawful Intercept information using SNMPv3.
•
Security and authentication is done as defined by SNMPv3.
•
Network Management is done using the CISCO-TAP-MIB.
•
Midcall Lawful Intercept provisioning allows an intercept to be provisioned, enabled, or disabled while the call is active.
Dial-up calls are intercepted as follows:
1.
A sniffer device is used to sniff all RADIUS messages between the router and the RADIUS server.
Note
Cisco provides TopLayer sniffer from SS8.
2.
The mediation device uses configuration commands to configure the intercept on the sniffer.
3.
The sniffer device sends intercept-related information about the target to the mediation device.
4.
The mediation device initiates communication content intercept requests to the edge router using SNMPv3.
5.
The edge router intercepts the communication content, replicates it, and sends it to the mediation device in UDP format.
Content of intercepted dial-up calls is transmitted using UDP transport.
Lawful Intercept Topology
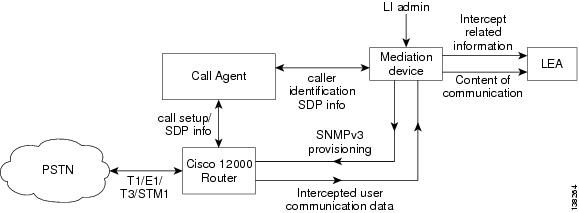
Figure 1 shows a Cisco 12000 series router in a Voice over IP (VoIP) network.
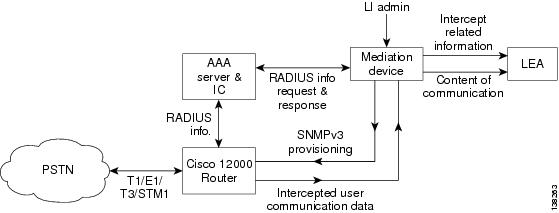
Figure 2 shows a Cisco 12000 series router in a dial-up access network.
Figure 1 Cisco 12000 series router in a VoIP Network
Figure 2 Cisco 12000 Series Router in a Dial-up Access Network
The following components are used in the network topology for a Voice over IP (VoIP) Lawful Intercept solution:
•
Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) call agent
•
Mediation device, such as SS8 or Verint
•
Cisco 12000 series router
When an Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) call agent must support the interface with the mediation device to provide the SDP signaling information. The router must support the mediation device extracts the intercept target's local IP/UDP address from the SDP signaling information to do the SNMPv3 Lawful Intercept provisioning. As long as the mediation device can use CISCO-TAP-MIB to provision an intercept, the router will be able to intercept the call.
Note
Currently, PGW and BTS are the only two Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) call agents that are supported.
The following components are used in the network topology for a dial-up access Lawful Intercept solution:
•
AAA radius server
•
TopLayer sniffer device
•
Mediation device (Cisco recommends SS8)
•
Cisco 12000 series router
For the dial-up Lawful Intercept solution, the sniffer device software caches the RADIUS server information. The mediation device obtains the Lawful Intercept provisioning information (such as the account session ID) from the sniffer. The mediation device provisions the intercept through the SNMPv3 interface using the CISCO-TAP-MIB.
Benefits
The Lawful Intercept feature provides service provides with the ability to meet law enforcement requirements and gives law enforcement agencies the ability to intercept Voice over IP (VoIP) and data traffic as it passes through edge routers.
Restrictions
When Lawful Intercept is enabled, forwarding performance of non-intercepted packets is degraded by 7 to 8 percent.
Network administrators are not able to observe Lawful Intercept is enabled. No Lawful Intercept program messages or error messages are ever displayed on the console.
Lawful Intercept on Cisco 12000 series routers does not provide the following features for Cisco IOS Release 12.0(32)S:
•
Support of RTP-NOR encapsulation
•
MAC based interception (requires support of MAC-based ACL on Tetra line cards)
•
VPN/VRF aware traffic (on tag imposition and tag disposition only)
•
Other line cards support
•
TAP MIBs version 2
•
MPLS traffic
•
Multicast traffic
•
IPv6 traffic
•
Per interface Lawful Intercept configuration
Related Features and Technologies
Lawful Intercept supports the following technologies on the Cisco 12000 series routers:
•
IPv4 traffic
•
Global Lawful Intercept configuration
•
UDP encapsulation
•
CISCO-TAP-MIB, Version 1
•
Cisco 12000 Series IP Services Engine (ISE)
Related Documents
For general configuration information on the Cisco 12000 series routers, refer to the following documentation:
•
Software Configuration Guide for the Cisco 12000 Series Internet Router
For information on how to configure a Cisco Media Gateway Controller (MGC), go to:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/sc/rel9/swinstl/3ins_cfg.htm#wp1464984
Supported Platforms
Lawful Intercept for Cisco 12000 series routers is supported on Cisco IOS Release 12.0(32)S and is supported on all Cisco 12000 Series IP Services Engine (ISE) line cards.
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions.
Supported Standards and MIBs
Lawful Intercept on the Cisco 12000 series router conforms to the following standards and MIBs.
Standards
•
Service Independent Intercept (SII) architecture
•
Simple Network Management Protocol Version 3 (SNMP V3)
MIBs
•
CISCO-TAP-MIB, Version 1
VoIP Lawful Intercept Provisioning TAP-MIB
Voice over IP (VoIP) Lawful Intercept provisioning is based on the local media gateway IP address and the UDP port. The mediation device uses the CISCO-TAP-MIB to provision Voice over IP (VoIP) intercepts. In Voice over IP (VoIP) Lawful Intercept provisioning, an intercept can be enabled or disabled during a voice call.
Dial-up Lawful Intercept Provisioning TAP-MIB
Dial-up Lawful Intercept provisioning does not have fixed IP addresses. The IP addresses are assigned dynamically. The mediation device uses the CISCO-TAP-MIB to provision dial-up intercepts.
Prerequisites
Before you can provision Lawful Intercept on a Cisco 12000 series router, you must have the following components already set up:
•
SNMP server with VACM views
•
Mediation device
Configuration Tasks
See the following sections for configuration tasks for the Lawful Intercept feature:
•
SNMP v3 Access for Lawful Intercept
•
Mediation Device Provisioning
•
Surveillance Function Provisioning
•
Collection Function Provisioning
SNMP v3 Access for Lawful Intercept
SNMP v3 Access for Lawful Intercept is configured on the router. The configuration commands to setup the configuration for SNMP v3 access are as follows:
Note
The following configuration commands can be saved into NVRAM and do not need to be entered every time the system boots up.
router(config)#snmp-server group group3 v3 auth read view3 write view3 notify view3router(config)#snmp-server view view3 snmp-server view view3 cTapMIB includedrouter(config)#snmp-server view view3 ciscoUserConnectionTapMIB includedrouter(config)#snmp-server enable traps ttyThe following configuration command is not saved in NVRAM and must be entered every time the router boots up:
router(config)#snmp-server user SS8user group3 v3 auth md5 ciscoIn the above example, group3 is an SNMP v3 group, which can access the three MIBS specified in read/write mode. SS8user is a user that belongs to group3 and can provision the specified MIBS securely. You can change the names, SS8user and group3, to any value.
Mediation Device Provisioning
Cisco 12000 series router provisioning is done on the mediation device by the mediation device vendor. In this case, the SS8 mediation device is used as an example.
The mediation device
•
activates the intercept at the authorized time and remove it when the authorized time period has elapsed.
•
periodically audits the elements in the network to ensure that all authorized intercepts are in place and that only authorized intercepts are in place.
The SS8 mediation device vendor must provision the following three functions to complete Lawful Intercept provisioning on the SS8 mediation device for a Cisco 12000 series router:
•
Access Function Provisioning
•
Surveillance Function Provisioning
•
Collection Function Provisioning
Access Function Provisioning
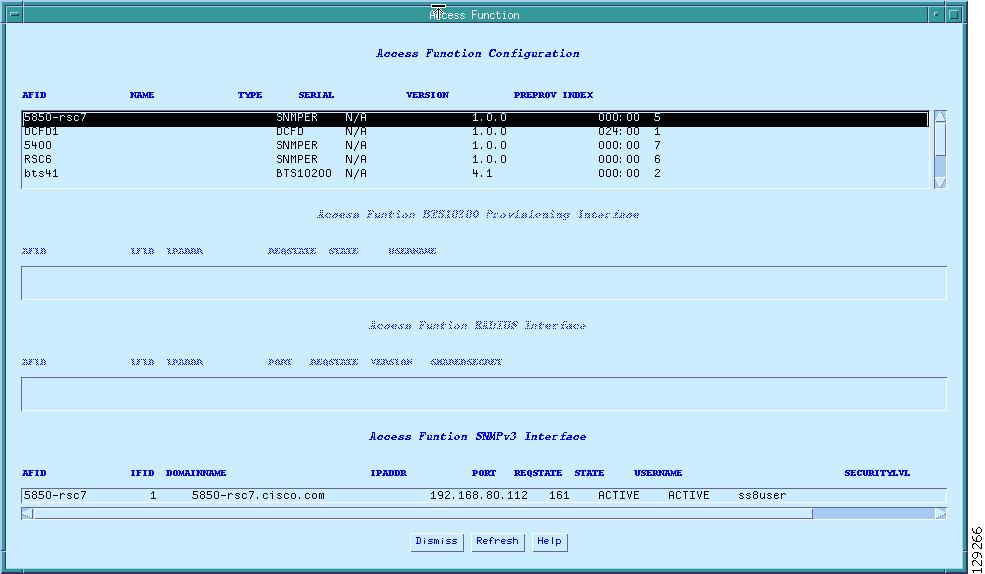
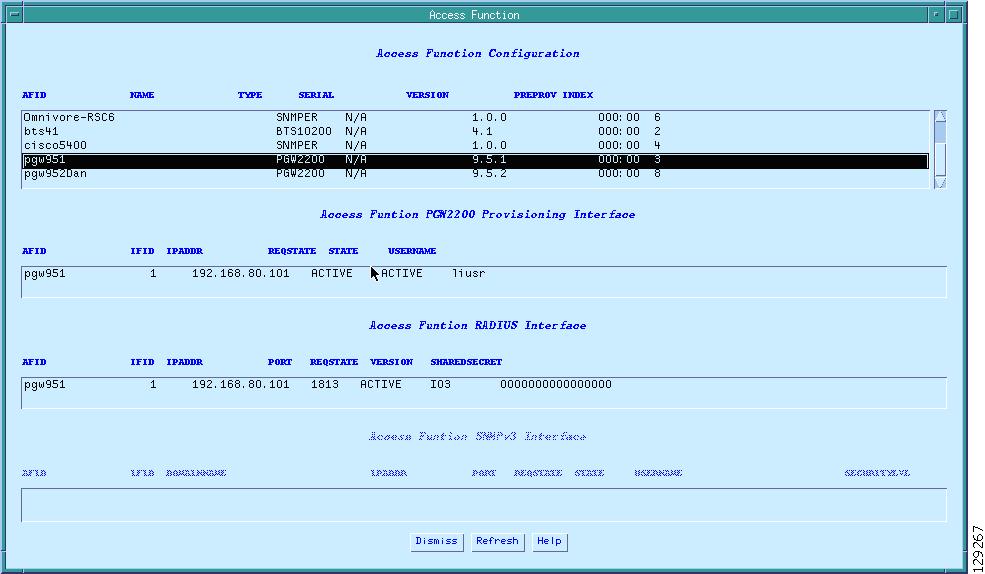
The SS8 mediation device vendor must verify that the SS8 Access Function Table for Broadband Telephony Softswitch (BTS) is populated with the correct data as shown in the examples in Figure 3:
•
Access Function Configuration
•
Access Function Provisioning Interface
•
Access Function RADIUS Interface
•
Access Function BTS10200 Provisioning Interface
•
Access Function SNMPv3 Interface
In the SS8 mediation device main window, select the Access button as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 SS8 Main Window with Access Selected
When you select the Access button, the Access Function Configuration table appears as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4 Access Function Configuration Table
Router Access Function Configuration
In the Access Function Configuration table, manually set the following fields for each router in the surveillance path as shown in the example in Figure 4:
•
Router name (AFID)
•
IP Address
•
Port (always 161 for routers)
•
Req State
•
State
•
Username (same as SNMP username)
•
Security Value
Call Agent Access Function Configuration
In the Access Function Configuration table, manually set the following fields for the call agent as show in the example in Figure 5:
•
Domain Name
•
IP Address
•
Port
•
Req State
•
State
•
Username (set username to the PGW name, for example pgw951)
•
Security Value
Figure 5 Access Function Configuration Table—PGW Example
Surveillance Function Provisioning
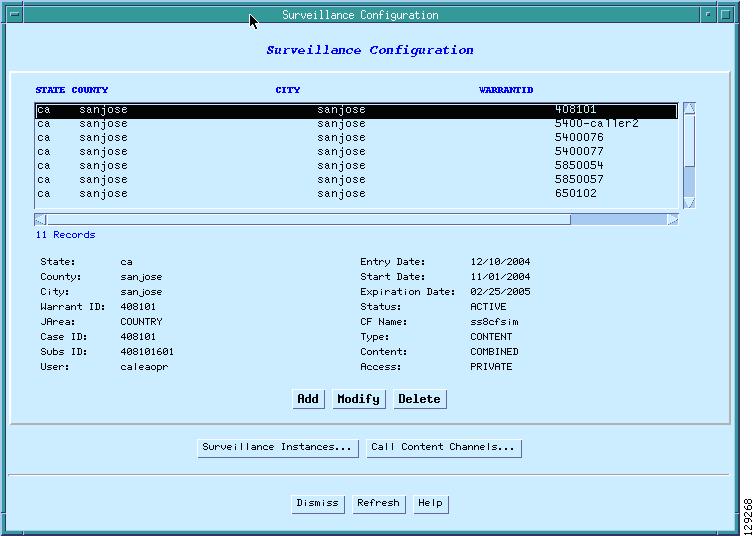
On the SS8 mediation device main window, select the Surveillance button as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6 SS8 Main Window with Surveillance Selected
\
When you select the Surveillance button, the Surveillance Configuration Window appears as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7 Surveillance Configuration Window
From the Surveillance Configuration window, perform the following steps:
Step 1
Select the Modify button to set the Subscriber ID and User fields.
Step 2
Set the Subscriber ID as follows:
•
For dial-up calls, click the Add button to set the subscriber ID to the username to be intercepted.
•
For Voice over IP (VoIP), click the Add button to set the subscriber ID to the phone number to be intercepted.
Step 3
Set the user field to caleaopr as shown in Figure 7 to grant the user caleaopr privileges.
Step 4
Go back to the the Surveillance Configuration window.
Step 5
Select the Call Content Channels button.
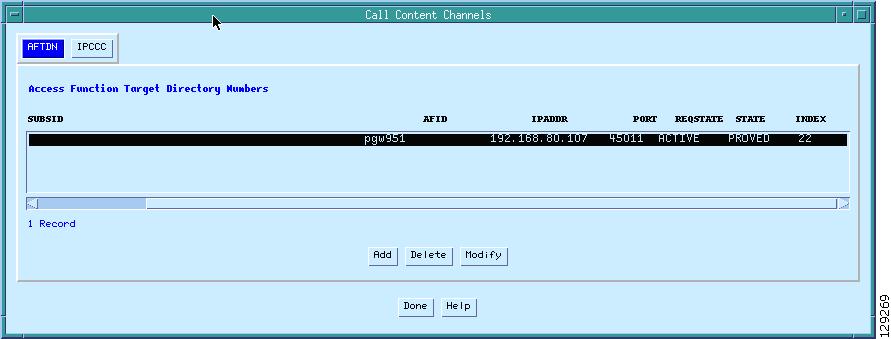
Step 6
Select the AFTDN tab and set the target phone number to be intercepted as shown in the example in Figure 8.
Figure 8 Call Content Channels—AFTDN Tab
Step 7
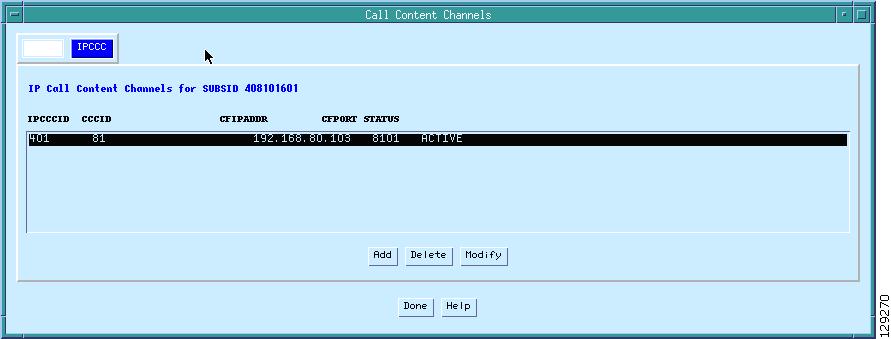
Select the IPCCC tab and set the IP address and port number of the collection function as shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9 Call Content Channels—IPCCC Tab
Collection Function Provisioning
On the SS8 mediation device main window, select the Collection button as shown in Figure 10.
Figure 10 SS8 Main Window with Collection Selected
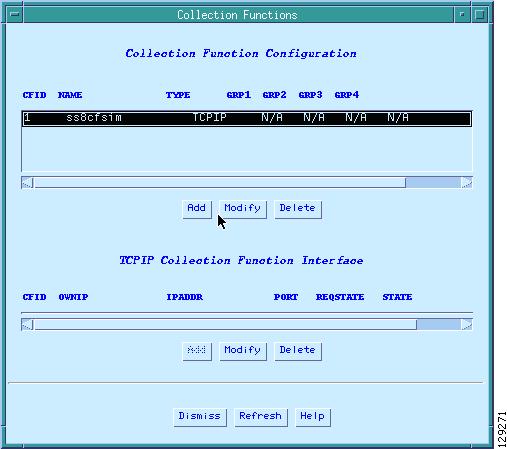
When you select the Collection button, the Collection Functions window appears as shown in Figure 11.
In the Collection Functions window, define the collection type.
Figure 11 show TCP/IP as the collection type.
Figure 11 Collection Functions Window
Call Agent Provisioning
In the CLI, register the call agent with the mediation device by entering the following code:
Note
In this example, PGW is the call agent.
mml>add-af:afid=pgw952Dan,type=PGW2200,version=9.5.2,preprov=000:00;mml>add-afgi:afid=pgw952Dan,ifid=1,ipaddr=192.168.80.129,username=liusr,passwd=test123;mml>add-fri:afid=pgw952Dan,ifid=1,ipaddr=192.168.80.129,port=1813,version=I03,sharedsecret =0000000000000000;Glossary
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.