Feedback Feedback
|
Table Of Contents
NetFlow ToS-Based Router Aggregation
ToS-Based NetFlow Aggregation Schemes
Protocol-Port-ToS Aggregation Scheme
SourcePrefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme
DestinationPrefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme
Prefix-Port Aggregation Scheme
Content of NetFlow Aggregation Schemes
Contents of NetFlow ToS-Based Aggregation Schemes
Related Features and Technologies
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Configuring a ToS-Based NetFlow Aggregation Scheme
Verifying ToS-Based NetFlow Aggregation Schemes
AS-ToS Aggregation Scheme Example
Prefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme Example
show ip cache verbose flow aggregation
NetFlow ToS-Based Router Aggregation
Feature History
This feature module describes the NetFlow ToS-Based Router Aggregation feature and includes the following sections:
•
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Feature Overview
The NetFlow ToS-Based Router Aggregation feature provides the ability to enable limited router-based type of service (ToS) aggregation of NetFlow Export data, which results in summarized NetFlow Export data to be exported to a collection device. The result is lower bandwidth requirements for NetFlow Export data and reduced platform requirements for NetFlow data collection devices.
Benefits
Router-Based Aggregation
Aggregation of export data is typically performed by NetFlow collection tools on management workstations. Router-based aggregation allows limited aggregation of NetFlow export records to occur on the router for the following benefits:
•
Reduce the required bandwidth between the router and the workstations
•
Reduce the number of collection workstations required
•
Improve performance and scalability on high flow-per-second routers
NetFlow Aggregation Cache
Cisco IOS NetFlow aggregation maintains one or more extra flow caches with different combinations of fields that determine which traditional flows are grouped together. These extra flow caches are called aggregation caches. As flows expire from the main flow cache, they are added to each enabled aggregation cache.
Note
The normal flow ager process runs on each active aggregation cache the same way it runs on the main cache. On-demand aging is also supported.
ToS-Based NetFlow Aggregation Schemes
The NetFlow ToS-Based Router Aggregation feature introduces support for six aggregation schemes that include the ToS byte as a field. This support is described in the following sections:
•
Protocol-Port-ToS Aggregation Scheme
•
Prefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme
•
SourcePrefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme
•
DestinationPrefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme
•
Prefix-Port Aggregation Scheme
Export Formats for ToS-Based Aggregation Schemes
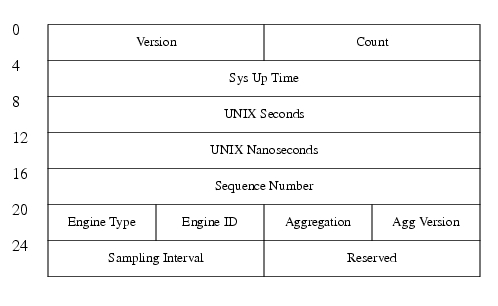
Six new aggregation export records are defined, one for each new aggregation scheme. The new aggregation export records also use the Version 8 datagram format (just like the current aggregation export records do). The Version 8 datagram consists of a header with the version number (which is 8) and time stamp information, followed by one or more records corresponding to individual entries in the flow cache. Figure 1 displays the Version 8 header format followed by the six new export formats.
Figure 1 Version 8 Header Format
Version: Flow export format version number. In this case 8.
Count: Number of export records contained in the datagram.
Sys Up Time: Current time in milliseconds since router booted.
UNIX Seconds: Current seconds since 0000 UTC 1970.
UNIX Nanoseconds: Residual nanoseconds since 0000 UTC 1970.
Sequence Number: Sequence counter of total flows sent for this export stream.
Engine Type: Type of flow switching engine. (RP, VIP, and so on.)
Engine ID: ID number of the flow switching engine.
Aggregation: Aggregation method being used.
Agg Version: Version of the aggregation export sub format.
Sampling Interval: Interval value used if Sampled NetFlow is configured.
Reserved: Zero field.
AS-ToS Aggregation Scheme
The AS-ToS aggregation scheme groups together flows that have the same source and destination BGP autonomous system, source and destination interfaces, and ToS byte. The aggregated NetFlow Export record reports the following:
•
Source BGP autonomous system
•
Destination BGP autonomous system
•
ToS byte
•
Number of flows summarized by the aggregated record
•
Number of bytes summarized by this aggregated record, number of packets summarized by this aggregation record
•
Source and destination interface
•
Starting and ending time stamps
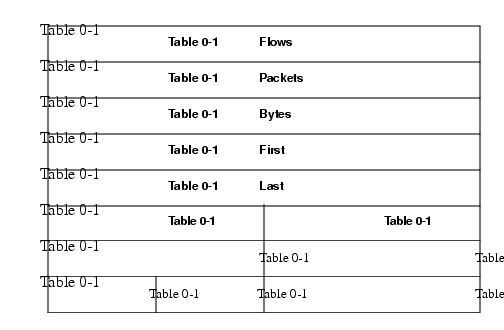
This aggregation scheme is particularly useful for generating autonomous system-to-autonomous system traffic flow data, and for providing substantial NetFlow Export data volume reduction. Figure 2 displays the AS-ToS aggregation export record format and a list follows describing the data.
Figure 2 AS-ToS Aggregation Export Record Format
Flows: Number of main cache flows that were aggregated.
Packets: Number of packets in the aggregated flows.
Bytes: Number of bytes in the aggregated flows.
First: Sys up time at which the first packet was switched.
Last: Sys up time at which the last packet was switched.
Source AS: autonomous system of the source IP address (peer or origin).
Destination AS: autonomous system of the destination IP address (peer or origin).
Source Interface: SNMP index of the interface the packets arrived on.
Destination Interface: SNMP index of the interface the packets went out.
ToS: Type of service byte.
Pad: Zero field.
Reserved: Zero field.
Protocol-Port-ToS Aggregation Scheme
The Protocol-Port-ToS aggregation scheme groups flows with common IP protocol, ToS byte, source and destination port numbers when applicable, and source and destination interfaces. The aggregated NetFlow Export record reports the following:
•
Source application port number
•
Destination port number
•
Source and destination interface
•
IP protocol
•
ToS byte
•
Number of flows summarized by the aggregated record
•
Number of bytes summarized by this aggregated record
•
Number of packets summarized by this aggregation record
•
Starting and ending time stamps
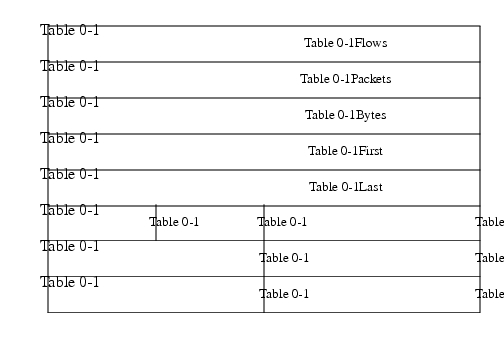
This aggregation scheme is particularly useful for generating data with which to examine network usage by type of traffic. Figure 3 displays the Protocol-Port-ToS aggregation export record format and a list follows describing the data.
Figure 3 Protocol-Port-ToS Aggregation Export Record Format
Flows: Number of main cache flows that were aggregated.
Packets: Number of packets in the aggregated flows.
Bytes: Number of bytes in the aggregated flows.
First: Sys up time at which the first packet was switched.
Last: Sys up time at which the last packet was switched.
Protocol: IP protocol byte.
ToS: Type of service byte.
Reserved: Zero field.
Source Port: Source UDP or TCP port number.
Destination Port: Destination UDP or TCP port number.
Source Interface: SNMP index of the interface the packets arrived on.
Destination Interface: SNMP index of the interface the packets went out.
Prefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme
The Prefix-ToS aggregation scheme groups together flows with common source prefix, source mask, destination prefix, destination mask, source BGP autonomous system, destination BGP autonomous system, input interface, output interface and ToS byte. The aggregated NetFlow Export record reports the following:
•
Source prefix
•
Source prefix mask
•
Destination prefix
•
Destination prefix mask
•
Source autonomous system
•
Destination autonomous system
•
Source interface
•
Destination interface
•
ToS byte
•
Number of flows summarized by the aggregated record
•
Number of bytes summarized by this aggregated record
•
Number of packets summarized by this aggregation record
•
Starting and ending time stamps
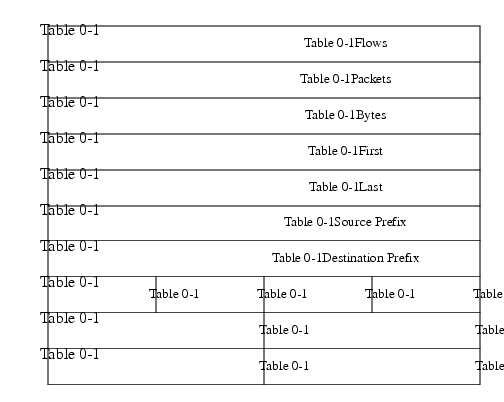
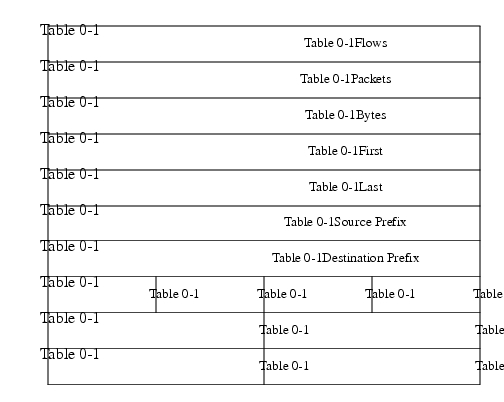
This aggregation scheme is particularly useful for generating data with which to examine the sources and destinations of network traffic passing through a NetFlow-enabled device. Figure 4 displays the Prefix-ToS aggregation export record format and a list follows describing the data.
Figure 4 Prefix-ToS Aggregation Export Record Format
Flows: Number of main cache flows that were aggregated together.
Packets: Number of packets in the aggregated flows.
Bytes: Number of bytes in the aggregated flows.
First: Sys up time at which the first packet was switched.
Last: Sys up time at which the last packet was switched.
Source Prefix: Prefix that the source IP address of the aggregated flows belonged to.
Destination Prefix: Prefix that the destination IP address of the aggregated flows belonged to.
Dest Mask Bits: Number of bits in the destination prefix.
Src Mask Bits: Number of bits in the source prefix.
ToS: Type of Service byte.
Pad: Zero field.
Source AS: autonomous system of the source IP address (peer or origin).
Destination AS: autonomous system of the destination IP address (peer or origin).
Source Interface: SNMP index of the interface the packets arrived on.
Destination Interface: SNMP index of the interface the packets went out.
SourcePrefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme
The SourcePrefix-ToS aggregation scheme groups flows with common source prefix, source prefix mask, source BGP autonomous system, ToS byte, and input interface. The aggregated NetFlow Export record reports the following:
•
Source prefix
•
Source prefix mask
•
Source autonomous system
•
ToS byte
•
Number of bytes summarized by this aggregated record
•
Number of packets summarized by this aggregation record
•
Input interface
•
Starting and ending time stamps
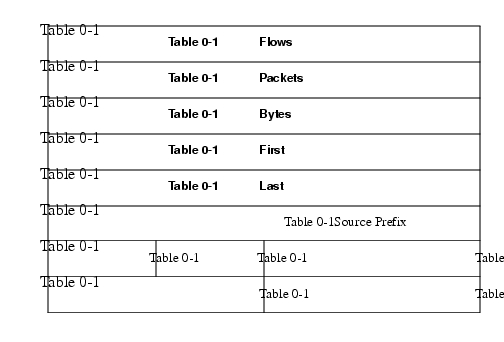
This aggregation scheme is particularly useful for generating data with which to examine the sources of network traffic passing through a NetFlow-enabled device. Figure 5 displays the Source Prefix-ToS aggregation export record format and a list follows describing the data.
Note
When a router does not have a prefix for the source IP address in the flow, 0.0.0.0 with 0 mask bits is used rather than making /32 entries to prevent DOS attacks with random source address from thrashing the aggregation caches. This is done for the destination in the DestinationPrefix-ToS, and the Prefix-ToS and Prefix-Port aggregation schemes.
Figure 5 Source Prefix ToS Aggregation Export Record Format
Flows: Number of main cache flows that were aggregated.
Packets: Number of packets in the aggregated flows.
Bytes: Number of bytes in the aggregated flows.
First: Sys up time at which the first packet was switched.
Last: Sys up time at which the last packet was switched.
Source Prefix: Prefix that the source IP address of the aggregated flows belonged to.
Src Mask Bits: Number of bits in the source prefix.
ToS: Type of Service byte.
Source AS: autonomous system of the source IP address (peer or origin).
Source Interface: SNMP index of the interface the packets arrived on.
Reserved: Zero field.
DestinationPrefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme
The DestinationPrefix-ToS aggregation scheme groups flows with common destination prefix, destination prefix mask, destination BGP autonomous system, ToS byte, and output interface. The aggregated NetFlow Export record reports the following:
•
Destination IP address
•
Destination prefix mask
•
Destination autonomous system
•
ToS byte
•
Number of flows summarized by the aggregated record
•
Number of bytes summarized by this aggregated record
•
Number of packets summarized by this aggregation record
•
Output interface
•
Starting and ending time stamps
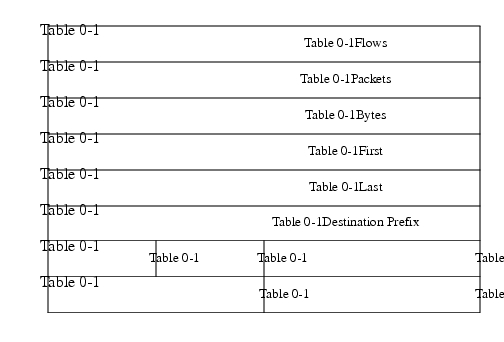
This aggregation scheme is particularly useful for generating data with which to examine the destinations of network traffic passing through a NetFlow-enabled device. Figure 6 displays the Destination Prefix aggregation export record format and a list follows describing the data.
Figure 6 Destination Prefix Aggregation Export Record Format
Flows: Number of main cache flows that were aggregated.
Packets: Number of packets in the aggregated flows.
Bytes: Number of bytes in the aggregated flows.
First: Sys up time at which the first packet was switched.
Last: Sys up time at which the last packet was switched.
Destination Prefix: Prefix that the destination IP address of the aggregated flows belonged to.
Dest Mask Bits: Number of bits in the destination prefix.
ToS: Type of service byte.
Destination AS: autonomous system of the destination IP address (peer or origin).
Destination Interface: SNMP index of the interface the packets went out.
Reserved: Zero field.
Prefix-Port Aggregation Scheme
The Prefix-Port aggregation scheme groups flows with common source prefix, source mask, destination prefix, destination mask, source port and destination port when applicable, input interface, output interface, Protocol and ToS byte. The aggregated NetFlow Export record reports the following:
•
Source prefix
•
Source prefix mask
•
Destination prefix
•
Destination prefix mask
•
Source port
•
Destination port
•
Source interface
•
Destination interface
•
Protocol
•
ToS byte
•
Number of flows summarized by the aggregated record
•
Number of bytes summarized by this aggregated record
•
Number of packets summarized by this aggregation record
•
Starting and ending time stamps
This aggregation scheme is particularly useful for generating data with which to examine the sources and destinations of network traffic passing through a NetFlow-enabled device. Figure 7 displays the Prefix-Port aggregation export record format and a list follows describing the data.
Figure 7 Prefix-Port Aggregation Export Record Format
Flows: Number of main cache flows that were aggregated.
Packets: Number of packets in the aggregated flows.
Bytes: Number of bytes in the aggregated flows.
First: Sys up time at which the first packet was switched.
Last: Sys up time at which the last packet was switched.
Source Prefix: Prefix that the source IP address of the aggregated flows belonged to.
Destination Prefix: Prefix that the destination IP address of the aggregated flows belonged to.
Dest Mask Bits: Number of bits in the destination prefix.
Src Mask Bits: Number of bits in the source prefix.
ToS: Type of service byte.
Protocol: IP protocol byte.
Source Port: Source UDP or TCP port number.
Destination Port: Destination UDP or TCP port number.
Source Interface: SNMP index of the interface the packets arrived on.
Destination Interface: SNMP index of the interface the packets went out.
Content of NetFlow Aggregation Schemes
Table 1 displays which fields are valid for the different aggregation schemes and in the different main cache schemes.
Note
Each aggregation cache has independent configuration for cache size, cache ager parameters, and export destination. The default size of an aggregation cache is 4096 entries.
The table lists the exported fields and the exported key fields. "X" indicates exported field, "*" indicates exported key fields. Fields in the key are what defines what makes a unique flow.
"X" indicates exported field, "*" indicates exported key fields.
Contents of NetFlow ToS-Based Aggregation Schemes
Table 2 displays the six new ToS-based aggregation schemes, the different main cache export schemes, and which fields are valid for the different aggregation schemes and which fields are part of the keys. "X" indicates exported field, "*" indicates exported key fields. Fields in the key define what makes a unique flow.
X indicates exported field, * indicates exported key fields
Related Features and Technologies
For more information on setting the minimum prefix mask for router-based aggregation, refer to the Cisco IOS Release 12.1(2)T feature module NetFlow Minimum Prefix Mask for Router-Based Aggregation.
Supported Platforms
This feature is supported on the following platforms:
•
Cisco 1720 router
•
Cisco 2600 series
•
Cisco 3600 series
•
Cisco 4500 series
•
Cisco 4700 series
•
Cisco 5800 series
•
Cisco Route Switch Processor (RSP) 7000 series
•
Cisco 7200 series
•
Cisco 7500 series
•
Cisco MGX (RSP) 8800 series
•
Cisco RSM (Catalyst5000)
This feature is supported on the following platforms for Cisco IOS Release 12.2(14)S:
•
Cisco 7200 series
•
Cisco 7400 series
•
Cisco 7500 series
Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs
Standards
None
MIBs
No new MIBs are supported by this feature.
To obtain lists of supported MIBs by platform and Cisco IOS release, and to download MIB modules, go to the Cisco MIB web site on Cisco Connection Online (CCO) at http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml.
RFCs
None
Prerequisites
Each NetFlow aggregation cache must be explicitly enabled by entering the enabled keyword from aggregation cache configuration mode.
Configuration Tasks
See the following section for the required configuration task for the NetFlow ToS-Based Router Aggregation feature.
•
Configuring a ToS-Based NetFlow Aggregation Scheme (Required)
Configuring a ToS-Based NetFlow Aggregation Scheme
To enable a ToS-based NetFlow aggregation scheme, use the following commands in aggregation cache configuration mode:
Verifying ToS-Based NetFlow Aggregation Schemes
To view the configured ToS-based NetFlow aggregation scheme, use the following show commands in EXEC mode as needed:
Configuration Examples
This section provides the following configuration examples:
•
AS-ToS Aggregation Scheme Example
•
Prefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme Example
AS-ToS Aggregation Scheme Example
!ip flow-aggregation cache as-toscache timeout active 20export destination 2.2.2.2 3000enabled!Prefix-ToS Aggregation Scheme Example
!ip flow-aggregation cache prefix-tosexport destination 4.4.4.4 4000enabled!Command Reference
This section documents modified commands. All other commands used with this feature are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 12.1 command reference publications.
•
ip flow-aggregation cache
•
show ip cache verbose flow aggregation
•
show ip flow export
ip flow-aggregation cache
To enable aggregation cache configuration mode, use the ip flow-aggregation cache global configuration mode. To disable aggregation cache configuration mode, use the no form of this command.
ip flow-aggregation cache {as | as-tos | destination-prefix | destination-prefix-tos | prefix | prefix-port | prefix-tos | protocol-port | protocol-port-tos | source-prefix | source-prefix-tos}
no ip flow-aggregation cache {as | as-tos | destination-prefix | destination-prefix-tos | prefix | prefix-port | prefix-tos | protocol-port | protocol-port-tos | source-prefix | source-prefix-tos}
Syntax Description
Defaults
This command is not enabled by default.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
Usage Guidelines
In source-prefix aggregation mode, only the source mask is configurable. In destination-prefix aggregation mode, only the destination mask is configurable.
Examples
The following example shows how to enable an autonomous system aggregation scheme:
ip flow-aggregation cache asenabledThe following example shows how to enable an autonomous system ToS aggregation scheme:
ip flow-aggregation cache as-tosenabledRelated Commands
mask destination
Specifies the destination mask.
mask source
Specifies the source mask.
show ip cache verbose flow aggregation
Displays the aggregation cache configuration.
show ip cache verbose flow aggregation
To display the aggregation cache configuration, use the show ip cache verbose flow aggregation command in EXEC mode.
show ip cache verbose flow aggregation {as | as-tos | destination-prefix | destination-prefix-tos | prefix | prefix-port | prefix-tos | protocol-port | protocol-port-tos | source-prefix | source-prefix-tos}
Syntax Description
Defaults
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
Examples
The following is an example display of an autonomous system aggregation cache using the show ip cache verbose flow aggregation as command:
Router# show ip cache verbose flow aggregation asIP Flow Switching Cache, 278544 bytes2 active, 4094 inactive, 13 added178 ager polls, 0 flow alloc failuresSrc If Src AS Dst If Dst AS Flows Pkts B/Pk ActiveFa1/0 0 Null 0 1 2 49 10.2Fa1/0 0 Se2/0 20 1 5 100 0.0The following is an example display of a main cache using the show ip cache verbose flow aggregation command:
Router# show ip cache verbose flowIP packet size distribution (230151 total packets):1-32 64 96 128 160 192 224 256 288 320 352 384 416 448 480.999 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000512 544 576 1024 1536 2048 2560 3072 3584 4096 4608.000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000 .000IP Flow Switching Cache, 6553988 bytes19 active, 65517 inactive, 19073 added48401 ager polls, 0 flow alloc failureslast clearing of statistics neverProtocol Total Flows Packets Bytes Packets Active(Sec) Idle(Sec)-------- Flows /Sec /Flow /Pkt /Sec /Flow /FlowTCP-BGP 71 0.0 1 49 0.0 2.5 15.8UDP-other 17 0.0 1 328 0.0 0.0 15.7ICMP 18966 6.7 10 28 72.9 0.1 22.9Total: 19054 6.7 10 28 72.9 0.1 22.9SrcIf SrcIPaddress DstIf DstIPaddress Pr TOS Flgs PktsPort Msk AS Port Msk AS NextHop B/Pk ActiveEt1/1 52.52.52.1 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 55 10 37480000 /8 50 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.8Et1/2 52.52.52.1 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 CC 10 35680000 /8 50 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.8Et1/2 10.1.3.2 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 C0 10 11240000 /0 0 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.8Et1/2 11.1.3.2 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 C0 10 11570000 /0 0 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.7Et1/2 14.1.3.2 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 C0 10 11490000 /0 0 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.8Et1/2 15.1.3.2 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 C0 10 11270000 /0 0 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.7Et1/2 12.1.3.2 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 C0 10 12040000 /0 0 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.8Et1/2 13.1.3.2 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 C0 10 11590000 /0 0 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.8Et1/2 18.1.3.2 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 C0 10 12230000 /0 0 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.8Et1/2 19.1.3.2 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 C0 10 12640000 /0 0 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.8Et1/2 16.1.3.2 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 C0 10 11700000 /0 0 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.8Et1/2 17.1.3.2 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 C0 10 11670000 /0 0 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.8Et1/2 22.1.3.2 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 C0 10 11930000 /0 0 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.8Et1/2 23.1.3.2 Fd4/0 42.42.42.1 01 C0 10 12120000 /0 0 0000 /8 40 202.120.130.2 28 17.7Et1/1 50.50.50.1 Local 31.31.31.1 06 C0 18 200B3 /32 0 2AF8 /32 0 0.0.0.0 49 10.1The following is an example display of an autonomous system ToS aggregation cache using the show ip cache verbose flow aggregation as-tos command:
Router# show ip cache verbose flow aggregation as-tosIP Flow Switching Cache, 278544 bytes4 active, 4092 inactive, 103 added1609 ager polls, 0 flow alloc failuresSrc If Src AS Dst If Dst AS TOS Flows Pkts B/Pk ActiveEt1/2 50 Fd4/0 40 CC 1 3568 28 17.8Et1/2 0 Fd4/0 40 C0 15 17K 28 17.8Et1/1 50 Fd4/0 40 55 1 3748 28 17.8Fd4/0 0 Null 0 C0 1 2 49 0.9The following is an example display of a protocol port ToS aggregation cache using the show ip cache verbose flow aggregation protocol-port-tos command:
Router# show ip cache verbose flow aggregation protocol-port-tosIP Flow Switching Cache, 278544 bytes4 active, 4092 inactive, 102 added1584 ager polls, 0 flow alloc failuresProt Src If SrcPort Dst If DstPort TOS Flows Pkts B/Pk Active0x01 Et1/2 0000 Fd4/0 0000 C0 15 17K 28 17.80x01 Et1/2 0000 Fd4/0 0000 CC 1 3568 28 17.80x01 Et1/1 0000 Fd4/0 0000 55 1 3748 28 17.80x06 Fd4/0 00B3 Null 2AF9 C0 1 2 49 0.9The following is an example display of a source prefix ToS aggregation cache using the show ip cache verbose flow aggregation source-prefix-tos command:
Router# show ip cache verbose flow aggregation source-prefix-tosIP Flow Switching Cache, 278544 bytes4 active, 4092 inactive, 105 added1683 ager polls, 0 flow alloc failuresSrc If Src Prefix Msk AS TOS Flows Pkts B/Pk ActiveEt1/1 52.0.0.0 /8 50 55 1 3748 28 17.8Et1/2 52.0.0.0 /8 50 CC 1 3568 28 17.8Et1/2 0.0.0.0 /0 0 C0 15 17K 28 17.8Fd4/0 20.20.20.1 /32 0 C0 1 2 49 0.9The following is an example display of a destination prefix ToS aggregation cache using the show ip cache verbose flow aggregation destination-prefix-tos command:
Router# show ip cache verbose flow aggregation destination-prefix-tosIP Flow Switching Cache, 278544 bytes4 active, 4092 inactive, 86 added1480 ager polls, 0 flow alloc failuresDst If Dst Prefix Msk AS TOS Flows Pkts B/Pk ActiveLocal 31.31.31.1 /32 0 C0 1 2 49 0.9Fd4/0 42.0.0.0 /8 40 55 1 3748 28 17.8Fd4/0 42.0.0.0 /8 40 CC 1 3568 28 17.8Fd4/0 42.0.0.0 /8 40 C0 15 17K 28 17.8The following is an example display of a prefix ToS aggregation cache using the show ip cache verbose flow aggregation prefix-tos command:
Router# show ip cache verbose flow aggregation prefix-tosIP Flow Switching Cache, 278544 bytes4 active, 4092 inactive, 4 added14 ager polls, 0 flow alloc failuresSrc If Src Prefix Dst If Dst Prefix TOS Flows PktsMsk AS Msk AS B/Pk ActiveEt1/2 0.0.0.0 Fd4/0 42.0.0.0 C0 15 3933/0 0 /8 40 28 3.9Et1/1 52.0.0.0 Fd4/0 42.0.0.0 55 1 826/8 50 /8 40 28 3.9Et1/2 52.0.0.0 Fd4/0 42.0.0.0 CC 1 787/8 50 /8 40 28 3.9The following is an example display of a prefix port aggregation cache using the show ip cache verbose flow aggregation prefix-port command:
Router# show ip cache verbose flow aggregation prefix-portIP Flow Switching Cache, 278544 bytes4 active, 4092 inactive, 105 added1679 ager polls, 0 flow alloc failuresSrc If Src Prefix Dst If Dst Prefix TOS Flows PktsPort Msk Port Msk Pr B/Pk ActiveFd4/0 20.20.20.1 Local 31.31.31.1 C0 1 200B3 /32 2AF9 /32 06 49 0.9Et1/2 0.0.0.0 Fd4/0 42.0.0.0 C0 15 17K0000 /0 0000 /8 01 28 17.8Et1/1 52.0.0.0 Fd4/0 42.0.0.0 55 1 37480000 /8 0000 /8 01 28 17.8Et1/2 52.0.0.0 Fd4/0 42.0.0.0 CC 1 35680000 /8 0000 /8 01 28 17.8Table 3 describes the significant fields shown in this example.
Related Commands
ip flow-aggregation cache
Enables aggregation cache configuration mode.
show ip flow export
Displays the statistics for the data export.
show ip flow export
To display the statistics for the data export, including the main cache and all other enabled caches, use the show ip flow export command in EXEC mode.
show ip flow export
Syntax Description
This command has no keywords and arguments.
Defaults
No default behavior or values.
Command Modes
EXEC
Command History
Examples
The following example displays the enabled aggregation caches using the show ip flow export command:
Router# show ip flow exportFlow export is enabledExporting flows to 2.2.2.2 (3000)Exporting using source IP address 181.1.1.1Version 5 flow records, peer-asCache for as aggregation:Exporting flows to 33.1.1.1 (6000)Exporting using source IP address 181.1.1.1Cache for as-tos aggregation:Exporting flows to 2.2.2.2 (3000)Exporting using source IP address 181.1.1.1Cache for source-prefix-tos aggregation:Exporting flows to 3.3.3.3 (3000)Exporting using source IP address 150.1.2.1Cache for destination-prefix-tos aggregation:Exporting flows to 6.6.6.6 (6000)Exporting using source IP address 181.1.1.1Cache for prefix-tos aggregation:Exporting flows to 4.4.4.4 (4000)Exporting using source IP address 181.1.1.1Cache for prefix-port aggregation:Exporting flows to 5.5.5.5 (5000)Exporting using source IP address 5.5.5.53 flows exported in 3 udp datagrams0 flows failed due to lack of export packet0 export packets were sent up to process level0 export packets were punted to the RP3 export packets were dropped due to no fib0 export packets were dropped due to adjacency issues0 export packets were dropped enqueuing for the RP0 export packets were dropped due to IPC rate limiting0 export packets were dropped due to output dropsRelated Commands
ip flow-aggregation cache
Enables aggregation cache configuration mode.
show ip cache verbose flow aggregation
Displays the aggregation cache configuration.