As customers and regulators increasingly demand products that minimize energy costs and greenhouse gas emissions, energy efficiency is a growing consideration in our product design.
Cisco engages with regulators and industry peers to support the development of clear standards that enable effective measurement and comparison of product energy efficiency. In FY10, we signed the EU Code of Conduct on Energy Consumption of Broadband Equipment and continued to support the Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Standards (ATIS) in the development of standards for networking equipment.
We created a methodology with industry peers to measure product power consumption at typical networking loads to determine energy efficiency and understand energy use in the network, targeting improvements across product generations.
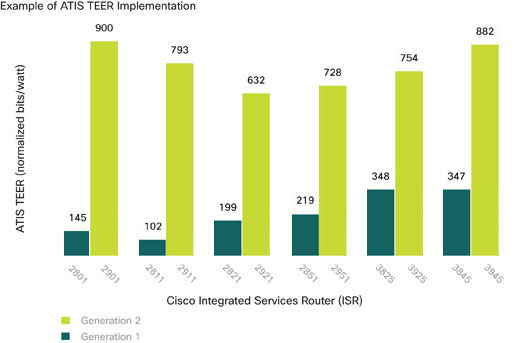
Targeting efficiency gains
Standby and power-down modes reduce power use. Significant power savings are possible for peripheral devices, including those that receive power over network cables (Power over Ethernet, or PoE devices) such as IP phones. Using the network to automatically darken the display units of IP phones out of business hours can cut each phone's energy use by up to 25 percent.
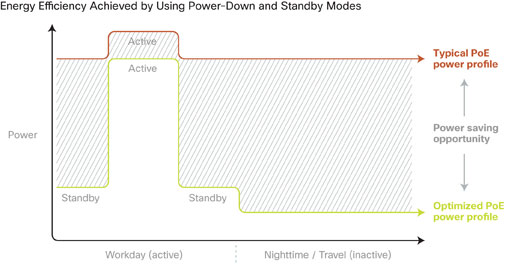
However, powering down critical equipment like routers is not always an option as they must operate on demand at all times. We can reduce their energy use in other ways.
Our Product Requirement Documents mandate that all power supplies must be at least 85 percent efficient. By improving the efficiency of the power supply for our Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switch from 80 to 90 percent, we enabled annual savings of more than 3500 kWh (if it is on 12 hours a day). See more details on how we cut power use from the Catalyst 6500 Series.
Making each component of our products more efficient also reduces overall energy use. We have introduced a range of measures to cut power used by Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), chips used in most Cisco products. These include voltage scaling to regulate the power needed to perform a particular task, and "clock gating" to power down portions of the chip circuitry that are not in active use.
Another way to achieve significant energy savings is to reduce the overall number of devices needed by designing equipment that integrates multiple services. The Cisco ASR 1000 Series Router, for example, provides the equivalent functionality of four separate networking devices using half the power requirement of those four prior devices.