Contents
Affected DISA Windows 2008 Member Server Version 6 Release 1.12 Policy Details
Overview
CiscoWorks LMS
United States Department of Defense: Defense Information Systems Agency Security Technical Implementation Guide
Affected Policies
Table 1. STIG Security Best Practices Affected in CiscoWorks LMS 3.2 and 4.0.x
Policy Implementation
Table 2. User Rights Requiring casuser or casusers Access
|
User Rights |
User Account |
User Group |
|
Access this computer from the network |
casusers |
|
|
Deny log on locally |
casuser |
|
|
Log on as a batch job |
casuser |
casusers |
Table 3. User Right "Deny access to this computer from the network"
Figure 1. User right "Deny access to this computer from the network."
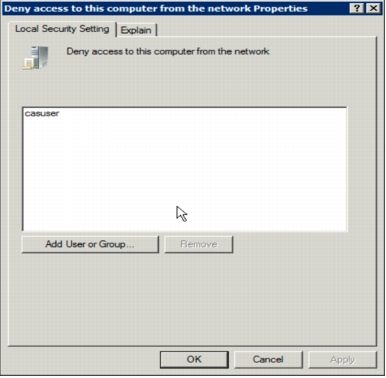
Table 4. CiscoWorks LMS Required Services
Windows Known Issues
Summary
Appendix
Affected DISA Windows 2008 Member Server Version 6 Release 1.12 Policy Details
Group Title: Shared User Accounts
Rule ID: SV-29623r1_rule
Severity: CAT II
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 1.008
Rule Title: Shared user accounts are permitted on the system.
Vulnerability Discussion: Shared accounts do not provide individual accountability for system access and resource usage.
Responsibility: System administrator
Information Assurance (IA) Controls: IAGA-1
Check Content:
Interview the system administrator to determine whether any shared accounts exist.
Any shared account must be documented with the information assurance officer (IAO). Documentation should include the reason for the account, who has access to this account, and how the risk of using a shared account (which provides no individual identification and accountability) is mitigated.
Note: As an example, a shared account may be permitted for a help desk or a site security personnel machine, if that machine is standalone and has no access to the network.
Fix Text: Remove any shared accounts that do not meet the exception requirements listed.
Group Title: Approved Service Packs
Rule ID: SV-29338r1_rule
Severity: CAT II
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 2.005
Rule Title: The current, approved service pack is not installed.
Vulnerability Discussion: Failure to install the most current Windows service pack leaves a system vulnerable to exploitation. Current service packs correct known security and system vulnerabilities. If a Windows OS is at an unsupported service pack this will be upgraded to a CAT I finding since new vulnerabilities may not be patched.
Documentable: Yes
Security Override Guidance: Unsupported service packs will be upgraded to a CAT I finding.
Responsibility: System administrator
IA Controls: VIVM-1
Check Content:
From the menu bar, click Start and then Run.
Type winver.exe in the dialog box and click OK.
If the "About Windows" box does not display the current approved service pack, then this is a finding.
Current Required Service Packs: Windows 2008 - Service Pack 2
Note: Application of new service packs should be thoroughly tested before deploying in a production environment.
Severity Override: Unsupported Service Packs will be upgraded to a CAT I finding. This includes the following: 2008 - N/A at this time
Documentable Explanation: Some managed systems such as DMS and GCSS receive service pack updates through system releases. In this case the current approved application release should be installed.
Fix Text: Install the current approved service pack.
Group Title: User Rights Assignments
Rule ID: SV-18393r2_rule
Severity: CAT II
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 4.010
Rule Title: User rights and advanced user rights settings do not meet minimum requirements.
Vulnerability Discussion: Inappropriate granting of user and advanced user rights can provide system, administrative, and other high-level capabilities not required by the normal user.
Documentable: Yes
Potential Impacts: Arbitrarily removing application accounts from certain user rights may cause the applications to cease functioning.
Responsibility: System administrator
IA Controls: ECLP-1
Check Content:
Windows 2008 Member Server
Analyze the system using the Security Configuration and Analysis snap-in. Expand the Security Configuration and Analysis tree view.
Navigate to Local Policies > User Rights Assignment.
Compare the User Rights chart to the following list. If any unauthorized accounts are given rights that they are not authorized in the chart, then this is a finding.
Access credential manager as a trusted caller - (None)
Access this computer from network - Administrators, Authenticated Users
Act as part of the operating system - See separate vulnerability 4.009/V-1102
Add workstations to domain - Not Defined
Adjust memory quotas for a process - Administrators, Local Service, Network Service
Allow log on locally - Administrators
Allow log on through Terminal Services - Administrators
Backup files and directories - Administrators
Bypass traverse checking - Administrators, Authenticated Users, Local Service, Network Service
Change the system time - Administrators, Local Service
Change the time zone - Administrators, Local Service
Create a pagefile - Administrators
Create a token object - (None)
Create global objects - Administrators, Service, Local Service, Network Service
Create permanent shared objects - (None)
Create symbolic link - Administrators
Debug programs - See separate vulnerability 4.005/V-18010
Deny access to this computer from the network - See separate vulnerability 4.025/V-1155
Deny logon as a batch job - Guests
Deny logon as a service - (None)
Deny logon locally - Guests
Deny log on through Terminal Services - Guests
Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation - Administrators
Force shutdown from a remote system - Administrators
Generate security audits - Local Service, Network Service
Impersonate a client after authentication - Administrators, Service, Local Service, Network Service
Increase a process working set - Administrators, Local Service
Increase scheduling priority - Administrators
Load and unload device drivers - Administrators
Lock pages in memory - (None)
Log on as a batch job - Administrators
Log on as a service - Not Defined
Manage auditing and security log - "Auditor's" Group; plus Exchange Enterprise Servers Group on Exchange Servers
Modify an object label - Administrators
Modify firmware environment values - Administrators
Perform volume maintenance tasks - Administrators
Profile single process - Administrators
Profile system performance - Administrators
Remove computer from docking station - Administrators
Replace a process level token - Local Service, Network Service
Restore files and directories - Administrators
Shut down the system - Administrators
Synchronize directory service data - Not Defined (Directory Services Checklist)
Take ownership of files or other objects - Administrators
Documentable Explanation: Some applications require one or more of these rights to function. Any exception needs to be documented with the IAO.
Fix Text: Configure the system to prevent accounts from having unauthorized user rights.
Group Title: Maximum Password Age
Rule ID: SV-29647r1_rule
Severity: CAT II
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 4.011
Rule Title: Maximum password age does not meet minimum requirements.
Vulnerability Discussion: The longer a password is in use, the greater the opportunity for someone to gain unauthorized knowledge of it. Further, scheduled changing of passwords hinders the ability of unauthorized system users to crack passwords and gain access to a system.
Responsibility: System administrator
IA Controls: IAIA-1, IAIA-2
Check Content:
Analyze the system using the Security Configuration and Analysis snap-in.
Expand the Security Configuration and Analysis tree view.
Navigate to Account Policies > Password Policy.
If the value for the Maximum Password Age is greater than 60 days, then this is a finding. If the value is set to 0 (never expires), then this is a finding.
Fix Text: Configure the Maximum Password Age so that it is not 0 and doesn't exceed 60 days.
Group Title: Dormant Accounts
Rule ID: SV-29482r1_rule
Severity: CAT III
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 4.019
Rule Title: User account is dormant.
Vulnerability Discussion: Outdated or unused accounts provide penetration points that may go undetected.
False Positives: The reviewer should review the list with the system administrator to determine the finding validity for each account reported.
Documentable: Yes
Responsibility: System administrator
IA Controls: IAAC-1
Check Content:
Using the DumpSec utility:
Select Dump Users as Table from the Report menu.
Select the available fields in the following sequence, and click the Add button for each entry:
UserName
SID
PswdRequired
PswdExpires
PswdLastSetTime
LastLogonTime
AcctDisabled
Groups
If any enabled accounts have not been logged into within the past 35 days, then this is a finding. This can be ascertained by examining the time in the "LastLogonTime" column. The following accounts are exempt from this check:
The built-in administrator account
The built-in guest account
Application accounts
The "IUSR"-guest account (used with IIS or Peer Web Services)
Accounts that are less than 35 days old
Disabled accounts
Note: The reviewer should review the list with the system administrator to determine the finding validity for each account reported.
Note: The following command can be used on Windows 2003/2008 Active Directory if DumpSec cannot be run:
Open a Command Prompt.
Enter Dsquery user -limit 0 -inactive 5 -o rdn (This command will work only if the domain is at least at a Windows Server 2003 functional level, not Windows 2000 Native).
A list of user accounts that have been inactive for 5 weeks will be displayed.
Disabled accounts can be determined by using the following:
Enter Dsquery user -limit 0 -disabled -o rdn.
Documentable Explanation: Dormant accounts that have been reviewed and deemed to be required should be documented with the IAO.
Fix Text: Regularly review accounts to determine if they are still active. Accounts that have not been used in the last 35 days should be either removed or disabled.
Group Title: Deny Access from the Network
Rule ID: SV-29599r1_rule
Severity: CAT I
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 4.025
Rule Title: User right to deny access to this computer from the network is not configured to include guests. (Anonymous Logon and Support_388945a0 in applicable Windows versions.)
Vulnerability Discussion: This is a CAT 1 finding because allowing network logins by the built-in guest accounts, which are members of the Everyone group and Guests group, with all the rights and permissions associated with those groups, could provide anonymous access to system resources to unauthorized users. Anonymous Logon and Support_388945a0 are also included in applicable Windows versions.
Documentable: Yes
Responsibility: System administrator
IA Controls: ECLP-1
Check Content:
Analyze the system using the Security Configuration and Analysis snap-in.
Expand the Security Configuration and Analysis tree view.
Navigate to Local Policies > User Rights Administration.
If the following groups/accounts are not listed under the right "Deny access to this computer from the network," then this is a finding.
Windows 2000 - Guests
Windows 2003 - Guests, Anonymous Logon, Support_388945a0
Windows XP - Guests, Support_388945a0
Vista - Guests
Windows 2008 - Guests
Note: If an account listed, such as the Support_388945a0 account, has been deleted from the system, the Gold Disk may incorrectly report the account as a finding. If the account does not exist on a system it would not be a finding.
Documentable Explanation: On Exchange Server 2003 supporting Outlook Web Access (OWA), the Guests group should be removed and replaced with "Anonymous Logon." Document with the IAO.
Fix Text: Configure the system to give the right "Deny access to this computer from the network" to the accounts/groups specified in the manual check.
Group Title: Unencrypted Remote Access
Rule ID: SV-29696r1_rule
Severity: CAT I
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 3.061
Rule Title: Unencrypted remote access is permitted to system services.
Vulnerability Discussion: This is a CAT 1 finding because when unencrypted access to system services is permitted, an intruder can intercept user identification and passwords that are being transmitted in clear text. This could give an intruder unlimited access to the network.
Responsibility: Information assurance officer
IA Controls: ECCT-1, ECCT-2
Check Content:
Interview the IAO to ensure that encryption of user ID and password information is required and that data is encrypted according to DoD policy.
If the user account used for unencrypted remote access within the enclave (premise router) has administrator privileges, then this is a finding.
If the user ID and password information used for remote access to system services from outside the enclave is not encrypted, then this is a finding.
Fix Text: Encryption of user ID and password information is required.
Encryption of the user data inside the network firewall is also highly recommended.
Encryption of user data coming from or going outside the network firewall is required.
Encryption for administrator data is always required.
Refer to the Enclave Security STIG section on "FTP and Telnet" for detailed information on its use.
Group Title: Intrusion Detection System
Rule ID: SV-29699r1_rule
Severity: CAT II
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 1.025
Rule Title: A server does not have a host-based intrusion detection system.
Vulnerability Discussion: A properly configured host-based intrusion detection system provides another level of defense against unauthorized access to critical servers. With proper configuration and logging enabled, such a system can stop and/or alert for many attempts to gain unauthorized access to resources.
Security Override Guidance: This finding can be downgraded to CAT III if there is an active JIDS or firewall protecting the network.
Responsibility: System administrator
IA Controls: ECID-1
Check Content:
Interview the system administrator to determine if there is a host-based intrusion detection system on each server.
Severity Override: This finding can be downgraded to CAT III if there is an active JIDS or firewall protecting the network.
Note: If the Host-Intrusion Prevention System (HIPS) component of the Host-Based Security System (HBSS) is installed and active on the host and the alerts of blocked activity are being logged and monitored, this will meet the requirement of this finding.
Note: A HID device is not required on a system that has the role as the network intrusion device (NID). However, this exception needs to be documented with the site IAO.
Group Title: FIPS Compliant Algorithms
Rule ID: SV-29533r1_rule
Severity: CAT II
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 3.077
Rule Title: The system is not configured to use FIPS-compliant algorithms for encryption, hashing, and signing.
Vulnerability Discussion: This setting ensures that the system uses algorithms that are FIPS compliant for encryption, hashing, and signing. FIPS-compliant algorithms meet specific standards established by the U.S. government and should be the algorithms used for all OS encryption functions.
Potential Impacts: Clients with this setting enabled will not be able to communicate through digitally encrypted or signed protocols with servers that do not support these algorithms. Both the browser and web server must be configured to use TLS or the browser will not be able to connect to a secure site.
Responsibility: System administrator
IA Controls: ECCT-1, ECCT-2
Check Content:
Analyze the system using the Security Configuration and Analysis snap-in.
Expand the Security Configuration and Analysis tree view.
Navigate to Local Policies > Security Options.
If the value for "System cryptography: Use FIPS compliant algorithms for encryption, hashing, and signing" is not set to Enabled, then this is a finding.
Warning: Clients with this setting enabled will not be able to communicate through digitally encrypted or signed protocols with servers that do not support these algorithms. Both the browser and web server must be configured to use TLS, or the browser will not be able to connect to a secure site.
Fix Text: Configure the system to require the use of FIPS-compliant algorithms.
Group Title: Unnecessary Services
Rule ID: SV-16965r2_rule
Severity: CAT II
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 5.068
Rule Title: Unnecessary services are not disabled.
Vulnerability Discussion: Unnecessary services increase the attack surface of a system. Some services may be run under the local system account, which generally has more permissions than required by the service. Compromising a service could allow an intruder to obtain system permissions and open the system to a variety of attacks.
Responsibility: System administrator
IA Controls: ECSC-1
Check Content:
Windows 2008 - Select Start.
Right-click the Computer icon on the Start menu.
Select Manage from the drop-down menu.
Expand the Services and Applications object in the tree window.
Select the Services object.
Alternately enter Services.msc in the run box.
Unnecessary services increase the attack surface of a system. This check verifies that unnecessary services are not enabled on a system.
Required services will vary among organizations, and will vary depending on the role of the individual system. Organizations will develop their own list of services, which will be documented and justified with the IAO. The site's list will be provided for any security review. Services that are common to multiple systems can be addressed in one document. Exceptions for individual systems should be identified separately by system.
If the site hasn't documented the services required for its system(s) this is a finding.
The following services have been specifically identified as required to be disabled. If any of these are installed and not disabled, this is a finding. (Only the IP Helper service is installed by default.)
Fax (fax)
IP Helper (iphlpsvc)
FTP Publishing Service (msftpsvc)
Peer Networking Identity Manager (p2pimsvc)
Simple TCP/IP Services (simptcp)
Telnet (tlntsvr)
Services for Windows Server 2008 roles are managed automatically, adding those necessary for a particular role. The following tables list the default services for a baseline installation and those for common roles as a reference.
Default Installation
Name Startup Type
Application Experience Automatic
Application Information Manual
Application Layer Gateway Service Manual
Application Management Manual
Background Intelligent Transfer Service Automatic (Delayed Start)
Base Filtering Engine Automatic
Certificate Propagation Manual
CNG Key Isolation Manual
COM+ Event System Automatic
COM+ System Application Manual
Computer Browser Disabled
Cryptographic Services Automatic
DCOM Server Process Launcher Automatic
Desktop Window Manager Session Manager Automatic
DHCP Client Automatic
Diagnostic Policy Service Automatic
Diagnostic Service Host Manual
Diagnostic System Host Manual
Distributed Link Tracking Client Automatic
Distributed Transaction Coordinator Automatic (Delayed Start)
DNS Client Automatic
Extensible Authentication Protocol Manual
Function Discovery Provider Host Manual
Function Discovery Resource Publication Manual
Group Policy Client Automatic
Health Key and Certificate Management Manual
Human Interface Device Access Manual
IKE and AuthIP IPsec Keying Modules Automatic
Interactive Services Detection Manual
Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) Disabled
IP Helper Disabled (Automatic is the default)
IPsec Policy Agent Automatic
KtmRm for Distributed Transaction Coordinator Automatic (Delayed Start)
Link-Layer Topology Discovery Mapper Manual
Microsoft .NET Framework NGEN v2.0.50727_X86 Manual
Microsoft Fibre Channel Platform Registration Service Manual
Microsoft iSCSI
Fix Text: Configure the system to disable any services that are not required.
Group Title: Password Expiration
Rule ID: SV-29396r2_rule
Severity: CAT II
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 4.026
Rule Title: To the extent system capabilities permit, system mechanisms are not implemented to enforce automatic expiration of passwords and to prevent reuse.
Vulnerability Discussion: Passwords that do not expire or are reused increase the exposure of a password with greater probability of being discovered or cracked.
False Positives: The following accounts are exempt from this check: Built-in Administrator Account Application accounts.
Documentable: Yes
Potential Impacts: Enforcing passwords to be changed at regular intervals may invite users to write down the passwords each time they are required to make a change. Ensure that all users store passwords in a secured location.
Responsibility: System administrator
IA Controls: IAIA-1, IAIA-2
Check Content:
Using the DumpSec utility:
Select Dump Users as Table from the Report menu.
Select the available fields in the following sequence, and click the Add button for each entry:
UserName
SID
PswdRequired
PswdExpires
PswdLastSetTime
LastLogonTime
AcctDisabled
Groups
If any accounts listed in the user report have a "No" in the "PswdExpires" column, then this is a finding.
Note: The following command can be used on Windows 2003/2008 Active Directory if DumpSec cannot be run:
Open a command prompt.
Enter Dsquery user -limit 0 | Dsget user -dn -pwdneverexpires.
This will return a list of user accounts with Yes/No for Pwdneverexpires.
If any accounts have "Yes", then this is a finding.
The results can be directed to a text file by adding > filename.txt at the end of the command.
The following are exempt from this requirement:
Built-in Administrator Account
Application Accounts
Documentable Explanation: Accounts that meet the requirements for allowable exceptions should be documented with the IAO.
Fix Text: Configure all information systems to expire passwords.
Group Title: Application Account Passwords
Rule ID: SV-29337r1_rule
Severity: CAT II
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 4.018
Rule Title: Application account passwords length and change requirement
Vulnerability Discussion: Setting application accounts to expire may cause applications to stop functioning. The site will have a policy that application account passwords manually generated and entered by a system administrator are changed at least annually or when a system administrator with knowledge of the password leaves the organization. Application/service account passwords will be at least 15 characters and follow complexity requirements for all passwords.
Responsibility: System administrator
IA Controls: IAIA-1
Check Content:
The site should have a local policy to ensure that passwords for application/service accounts are at least 15 characters in length and meet complexity requirements for all passwords. Application/service account passwords manually generated and entered by a system administrator must be changed at least annually or whenever a system administrator that has knowledge of the password leaves the organization.
Interview the system administrators on their policy for application/service accounts. If it does not meet the above requirements, this is a finding.
Using the DumpSec utility:
Select Dump Users as Table from the Report menu.
Select the available fields in the following sequence, and click the Add button for each entry:
UserName
SID
PswdRequired
PswdExpires
PswdLastSetTime
LastLogonTime
AcctDisabled
Groups
If any application accounts listed in the DumpSec user report have a date older than one year in the "PwsdLastSetTime" column, then this is a finding.
Note: The following command can be used on Windows 2003/2008 Active Directory if DumpSec cannot be run:
Open a command prompt.
Enter Dsquery user -limit 0 -o rdn -stalepwd 365.
This will return a list of user accounts with passwords older than one year.
Fix Text: Create application/service account passwords that are at least 15 characters in length and meet complexity requirements. Change application/service account passwords that are manually generated and entered by a system administrator at least annually or whenever an administrator with knowledge of the password leaves the organization.
Group Title: HBSS CMA Agent
Rule ID: SV-29560r1_rule
Severity: CAT II
Rule Version (STIG-ID): 5.140
Rule Title: The HBSS CMA Agent is not installed.
Responsibility: System administrator
IA Controls: ECSC-1
Check Content:
Search for the file FrameworkService.exe (by default in the \Program Files\McAfee\Common Framework\ directory) and check that the version is 3 or 4.
And verify that the service "McAfee Framework Service" is running.
If either of these conditions does not exist, then this is a finding.
Fix Text: Deploy the CMA agent as detailed in the CTO and in accordance with the DoD IA Enterprise Solutions STIG.