Table Of Contents
Medianet Campus Cisco Catalyst 4500 Supervisor 6-E/7-E QoS Design
Role in Medianet Campus Network
Step 1: Configure Ingress QoS Model(s)
Step 2: Configure Egress Queuing
Medianet Campus Cisco Catalyst 4500 Supervisor 6-E/7-E QoS Design
Role in Medianet Campus Network
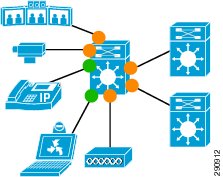
The Cisco Catalyst 4500 series switches with Supervisor 6-E/7-E are well-suited to the role of access- or distribution-layer switches in medianet campus networks. As such, these switches may connect directly to a variety of endpoints, as well as to distribution-layer and/or core-layer switches, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switch with Supervisor 6-E/7-E in a Medianet Campus Network
QoS Design Steps
There are only two main steps to configure QoS on a Cisco Catalyst 4500 series switch with Supervisor 6-E/7-E:
1.
Configure Ingress QoS Model(s):
–
Trust DSCP Model
–
Conditional Trust Model
–
Service Policy Models
2.
Configure Egress Queuing
Step 1: Configure Ingress QoS Model(s)
The three most utilized ingress QoS models for medianet campus networks are:
•
Trust DSCP Model
•
Conditional Trust Model
•
Service Policy Models
Combinations of these ingress QoS models may be used at the same time.
Trust DSCP Model
By default all interfaces trust DSCP; as such, no explicit configuration is required to enable this model.
In the default trust DSCP state, the interface statically accepts and preserves the Layer 3 DSCP markings of all incoming packets. This model is suitable for interfaces connecting to endpoints that can mark DSCP values and are administratively controlled (such as WLAN controllers) as well as for any uplinks to distribution layer switches. Switch ports that should trust DSCP are shown as yellow circles in Figure 1.
Conditional Trust Model
This model is configured with the mls qos trust device cisco-phone interface-configuration command along with some additional MQC configuration to perform CoS-to-DSCP mapping.
The Conditional Trust model configures the interface to dynamically accept markings from endpoints that have met a specific condition (currently based on a successful Cisco Discovery Protocol identification). This model is suitable for switch ports connecting to Cisco IP phones, as well as for ports connecting to PCs and untrusted devices (since the ports connecting to such devices will remain in an untrusted state). Switch ports that can be set to conditional trust are shown as green circles in Figure 1.
Service Policy Models
There may be cases where administrators require more detailed or granular policies on their ingress edges and as such they may construct MQC policies to implement classification, marking, and/or policing policies. These policies are constructed with:
•
class-maps which identify the flows using packet markings or by access-lists or other criteria
•
policy-maps which specify policy actions to be taken on a class-by-class basis
•
service-policy statements which apply a specific policy-map to an interface(s) and specify direction
Step 2: Configure Egress Queuing
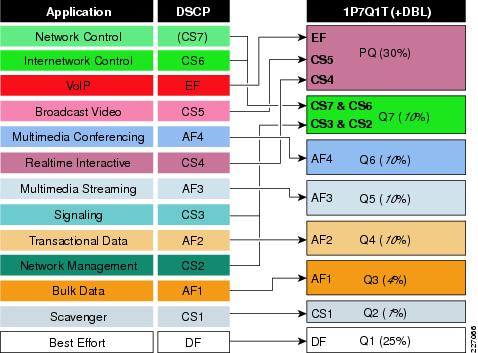
The medianet egress queuing model for the Catalyst 4500 with Supervisor 6-E/7-E is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Cisco Catalyst 4500 Supervisor 6-E/7-E Egress Queuing Model
EtherChannel QoS
Ingress QoS policies on the Cisco Catalyst 4500 Supervisor 6-E/7-E are configured on the logical Port-Channel interface (but typically these are simply to enable DSCP trust—which requires no explicit configuration), while egress QoS policies (such as the service-policy-statement to enable egress queuing) are configured on the physical port-member interfaces.
Cisco Validated Design (CVD)
The Cisco Validated Design for Cisco Catalyst 4500 with Supervisor 6-E/7-E in the role of an access switch in a medianet campus network is presented on the reverse.
Note: Highlighted commands are interface specific; otherwise these are global.For more details, see Medianet Campus QoS Design 4.0: :http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/WAN_and_MAN/QoS_SRND_40/QoSCampus_40.html.