Table Of Contents
Medianet Branch Cisco ISR G2 QoS Design
Step 1: Configure WAN/VPN Edge QoS Model(s)
Step 2: LAN Edge QoS on Enhanced EtherSwitch E3 Service Modules (If Required)
Medianet Branch Cisco ISR G2 QoS Design
Role in Medianet WAN Network
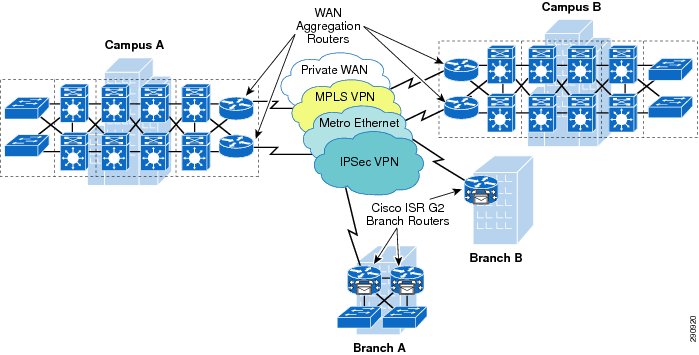
The Cisco ISR G2 routers are well suited to the role of branch routers in medianet WAN and VPN networks. As such, these routers may connect branch networks to private WANs, MPLS VPNs, Metro Ethernet circuits, and/or IPSec-based VPNs, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Cisco ISR G2 Routers in Medianet WAN/VPN Networks
QoS Design Steps
There are two main steps to configure QoS on Cisco ISR G2 series routers:
1.
Configure WAN/VPN edge QoS Model(s):
–
4-Class Model
–
8-Class Model
–
12-Class Model
2.
Configure LAN Edge QoS on Enhanced EtherSwitch (ES3) service modules (if required)
Step 1: Configure WAN/VPN Edge QoS Model(s)
The number of classes of service provisioned on the WAN/VPN edge is a function of the business priorities of the enterprise. Each class of business-critical applications that has unique service-level requirements (in terms of latency, jitter, and packet loss) needs a dedicated class of service.
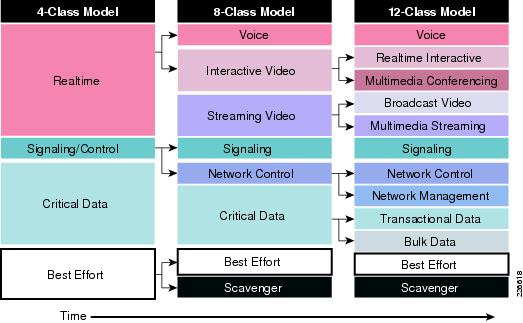
While RFC 4594 outlines a 12-class model, Cisco recognizes that not all enterprises are ready to implement such a complex QoS design. Therefore, Cisco recommends a phased approach to media application class expansion, as illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Medianet Application Class Expansion
Administrators can incrementally implement QoS policies across their medianet WAN/VPN networks in a progressive manner, utilizing such a phased approach to application class expansion to keep in step with their evolving business needs.
DSCP Marking codepoints should remain as consistent as possible as the number of application classes expand. Multiple application classes can be matched on a single codepoint or as a group of several codepoints, with the latter being the preferred option as it facilitates easier expansion.
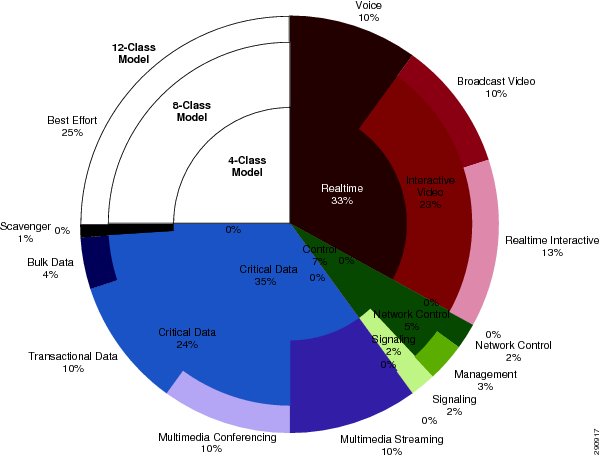
Not only should marking values remain consistent as the number of classes of service expand, but also relative bandwidth allocations, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Example Medianet Bandwidth Allocation Models
Additional WAN Edge QoS design recommendations include:
•
Limit LLQ(s) to 33%
•
Provision at least 25% for the Best Effort Queue
•
Limit the Scavenger Queue to 1%
•
Enable Fair-Queuing Pre-Sorters on all classes except control & scavenger classes
•
Expand queue limits as required
•
Enable DSCP-based WRED on all AF classes
•
Optional: Tune DSCP-based WRED:
–
Set min-thresholds to 60% for AFx3
–
Set min-thresholds to 70% for AFx2
–
Set min-thresholds to 80% for AFx1
–
Set all max-thresholds to 100%
Step 2: LAN Edge QoS on Enhanced EtherSwitch E3 Service Modules (If Required)
The Cisco Enhanced EtherSwitch E3 service modules offer full feature parity with Cisco Catalyst 3560-E switches. As such these service modules can perform LAN edge QoS functions such as classification and trust, marking and policing, and ingress and egress queuing in hardware. Additionally, these service modules support the AutoQoS for Medianet feature which can deploy complete recommended best practice QoS designs for various medianet endpoints with a single command.
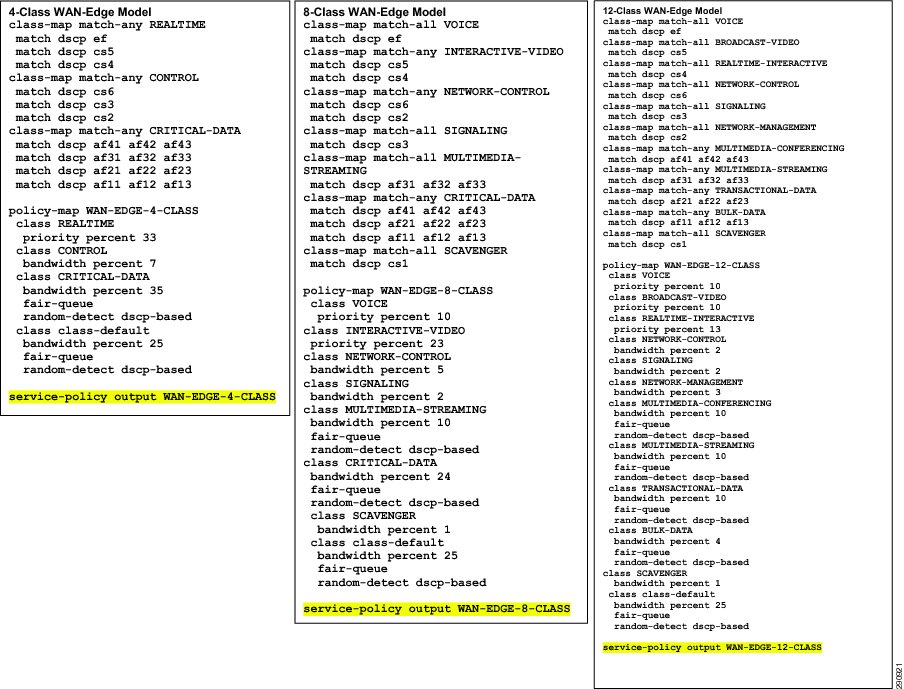
Cisco Validated Design (CVD)
Cisco Validated Designs for WAN Edge QoS Models for Cisco ISR G2 series routers in the role of a branch router in a medianet WAN network are presented on the reverse.
Note: Highlighted commands are interface specific; otherwise these are global.For LAN Edge QoS policies for the Enhanced EtherSwitch ES3 service modules, refer to the Cisco Catalyst 3560 section of the Medianet Campus QoS Design Guide at: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/WAN_and_MAN/QoS_SRND_40/QoSCampus_40.html.For more details, see Medianet WAN Aggregation QoS Design 4.0: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/WAN_and_MAN/QoS_SRND_40/QoSWAN_40.html.